| Revision as of 20:08, 28 January 2015 editJynto (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users3,197 edits Inserting space-filling model image, tweaking image size, adding alt text← Previous edit | Revision as of 14:40, 11 July 2015 edit undo89.240.140.255 (talk) synthesis notesNext edit → | ||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
| '''Azosemide''' is a high-ceiling ] agent. | '''Azosemide''' is a high-ceiling ] agent. | ||
| ==Synthesis== | |||
| ] | |||
| ] of 2-fluoro-4-chloro-] ('''1''') followed by ammonolysis of the product gives ] ('''2'''). The regiochemistry of the next reaction, nucleophilic aromatic displacement, can be attributed in this case to the better leaving group properties of fluoride ions over chloride ions. Reaction with 2-methylaminothiophene thus gives '''3''' as the product. There is ample precedent to indicate that tetrazoles are bioisosteric with carboxylic acids, with the two groups showing quite comparable pKAs. Treatment with ] and ] leads to 1,3 addition of the elements of ] to the nitrile and the formation of a ] ring. This yields the high ceiling diuretic agent azosemide ('''4'''). | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{Reflist|2}} | |||
| Popelak, A.; Lerch, A.; Stach, K.; Roesch, E.; Hardebeck, K.; German Offen., 1970, 815922; Chem. Abstr. 1970, 73, 45519. | |||
| ] | ] | ||
Revision as of 14:40, 11 July 2015
Pharmaceutical compound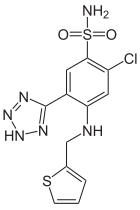 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.044.121 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H11ClN6O2S2 |
| Molar mass | 370.84 g/mol g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Azosemide is a high-ceiling diuretic agent.
Synthesis

Chlorosulfonation of 2-fluoro-4-chloro-benzonitrile (1) followed by ammonolysis of the product gives sulfonamide (2). The regiochemistry of the next reaction, nucleophilic aromatic displacement, can be attributed in this case to the better leaving group properties of fluoride ions over chloride ions. Reaction with 2-methylaminothiophene thus gives 3 as the product. There is ample precedent to indicate that tetrazoles are bioisosteric with carboxylic acids, with the two groups showing quite comparable pKAs. Treatment with sodium azide and hydrochloric acid leads to 1,3 addition of the elements of hydrazoic acid to the nitrile and the formation of a tetrazole ring. This yields the high ceiling diuretic agent azosemide (4).
References
- A. Popelak et al., DE 1815922 ; eidem, U.S. patent 3,665,002 (1968, 1972 both to Boehringer, Mann.).
- DE 2353388
This drug article relating to the cardiovascular system is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |