| Revision as of 19:03, 12 September 2015 editClueBot NG (talk | contribs)Bots, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers6,439,386 editsm Reverting possible vandalism by 99.11.138.56 to version by 2602:306:3357:BA0:2C3A:49C:CB01:AFE5. Report False Positive? Thanks, ClueBot NG. (2345726) (Bot)← Previous edit | Revision as of 03:34, 13 November 2015 edit undo71.251.179.137 (talk) →TypesNext edit → | ||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
| An '''aerobic organism''' or '''aerobe''' is an ] that can survive and grow in an oxygenated environment.<ref>{{DorlandsDict|one/000002016|aerobe}}</ref> | An '''aerobic organism''' or '''aerobe''' is an ] that can survive and grow in an oxygenated environment.<ref>{{DorlandsDict|one/000002016|aerobe}}</ref> | ||
| Carbon Cycle is important to both photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration | |||
| ==Types== | |||
| *''']s''' need oxygen to grow. In a process known as ], these organisms use oxygen to ] substrates (for example ]s and ]s) and generate ]. | |||
| *''']''' use oxygen if it is available, but also have ] methods of energy production. | |||
| *''']s''' require oxygen for energy production, but are harmed by atmospheric concentrations of oxygen (21% O<sub>2</sub>). | |||
| *''']''' do not use oxygen but are not harmed by it. | |||
| ==Glucose== | ==Glucose== | ||
Revision as of 03:34, 13 November 2015
| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Aerobic organism" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
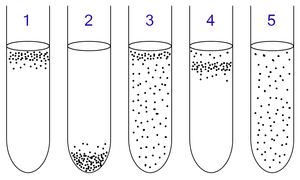
1: Obligate aerobes need oxygen because they cannot ferment or respire anaerobically. They gather at the top of the tube where the oxygen concentration is highest.
2: Obligate anaerobes are poisoned by oxygen, so they gather at the bottom of the tube where the oxygen concentration is lowest.
3: Facultative anaerobes can grow with or without oxygen because they can metabolise energy aerobically or anaerobically. They gather mostly at the top because aerobic respiration generates more ATP than either fermentation or anaerobic respiration.
4: Microaerophiles need oxygen because they cannot ferment or respire anaerobically. However, they are poisoned by high concentrations of oxygen. They gather in the upper part of the test tube but not the very top.
5: Aerotolerant organisms do not require oxygen as they metabolise energy anaerobically. Unlike obligate anaerobes however, they are not poisoned by oxygen. They can be found evenly spread throughout the test tube.
An aerobic organism or aerobe is an organism that can survive and grow in an oxygenated environment.
Carbon Cycle is important to both photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
Glucose
A good example would be the oxidation of glucose (a monosaccharide) in aerobic respiration.
Oxygen is used during the oxidation of glucose and water is produced.
This equation is a summary of what actually happens in three series of biochemical reactions: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
See also
- Aerobic digestion
- Anaerobic digestion
- Facultative anaerobic organism
- Fermentation (biochemistry)
- Microaerophile
- Obligate anaerobe
References
| Microbiology: Bacteria | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medical microbiology | |||||||
| Biochemistry and ecology |
| ||||||
| Shape | |||||||
| Structure |
| ||||||
| Taxonomy and evolution | |||||||