| Revision as of 01:08, 9 November 2004 view sourceQuartierLatin1968 (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users12,580 editsNo edit summary← Previous edit | Revision as of 21:01, 14 November 2004 view source Cdc (talk | contribs)8,594 editsm grammar, formattingNext edit → | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| '''South Asia''' is a subregion of ] comprising the modern states of ], ], ], ], ], ], and the ]. It covers about 4,480,000 km², or 10 percent of the continent and is also known as the ]. These states are all members of the ]. |
'''South Asia''' is a subregion of ] comprising the modern states of ], ], ], ], ], ], and the ]. It covers about 4,480,000 km², or 10 percent of the continent and is also known as the ''']'''. These states are all members of the ]. Some or all of ] is sometimes considered part of South Asia. | ||
| Subregions of South Asia include: | Subregions of South Asia include: | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
| *Southern ], ] | *Southern ], ] | ||
| South Asia ranks among the ]'s most |
South Asia ranks among the ]'s most densely-populated regions. About 1 1/3 billion people live there—about a third of all ]s and a fifth of all the people in the world. The region's population density of 305 persons per km² is more than seven times the world average. | ||
| The region has a long history. Ancient civilisations developed in the ] Valley. The region was at its most prosperous before the 17th century, when the ] held sway in the north; ] ] lead to a new conquering of the region, by ] and ], and later ] and to a lesser degree ]. Most of the region gained independence from Europe in the late ]. | The region has a long history. Ancient civilisations developed in the ] Valley. The region was at its most prosperous before the 17th century, when the ] held sway in the north; ] ] lead to a new conquering of the region, by ] and ], and later ] and to a lesser degree ]. Most of the region gained independence from Europe in the late ]. | ||
Revision as of 21:01, 14 November 2004
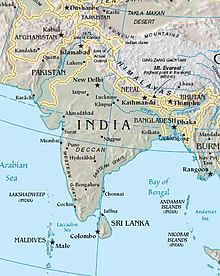
South Asia is a subregion of Asia comprising the modern states of India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Nepal, Bhutan, and the Maldives. It covers about 4,480,000 km², or 10 percent of the continent and is also known as the Indian subcontinent. These states are all members of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation. Some or all of Afghanistan is sometimes considered part of South Asia.
Subregions of South Asia include:
- Himalayan States - Northern India, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh
- Indian Ocean Island Nations - Sri Lanka, the Maldives
- Southern India, Pakistan
South Asia ranks among the world's most densely-populated regions. About 1 1/3 billion people live there—about a third of all Asians and a fifth of all the people in the world. The region's population density of 305 persons per km² is more than seven times the world average.
The region has a long history. Ancient civilisations developed in the Indus River Valley. The region was at its most prosperous before the 17th century, when the Mughal Empire held sway in the north; European colonialism lead to a new conquering of the region, by Portugal and Holland, and later Britain and to a lesser degree France. Most of the region gained independence from Europe in the late 1940s.
The concept of "South Asia" is useful in helping refer to the countries of the region as a group. Together with the term ("The Subcontinent"), the descriptor can be useful when discussing issues that affect the common history, culture, etc. of the countries. Citizens of South Asian countries besides India can sometimes be offended by the use of "India" or "Indian" in relation to them or their national, and some times even historial and cultural, origins.
- See also: History of South Asia
Southern Asia sometimes refers to all of Asia that was not part of the Soviet Union.
Other subregions of Asia
- East Asia
- Southeast Asia
- Central Asia
- Southwest Asia or West Asia (One definition of the Middle East is synonymous with Southwest Asia)
- North Asia (Siberia)
- Northern Eurasia (Extends into Europe)
- Central Eurasia (Extends into Europe)