| Revision as of 22:44, 11 June 2021 editCyfal (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers64,718 editsm singular spelling (WP:Typo Team)← Previous edit | Revision as of 15:46, 30 August 2021 edit undo2a02:c7f:98e8:c00:96c:4309:bb6e:b711 (talk) Added a couple more causes of subconjunctival haemorrhage, both natural and external. These are from personal experience both as a witness and as a patient, specifically the cases of blunt force, where I witnessed an individual suffer a punch in the eye that subsequently left their entire "eye white", red. Secondly, as a patient myself, having subconjunctival haemorrhage in both eyes after childbirth, delivering my 3rd baby, naturally. Nurse said the pressure from me pushing burst my eye vesselsTags: Visual edit Mobile edit Mobile web editNext edit → | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
| <!-- Cause and diagnosis --> | <!-- Cause and diagnosis --> | ||
| Natural causes can include coughing, vomiting, heavy lifting, straining to pass hard stools during acute ] or the internal pressure of "pushing" or "bearing down" during labour/]. External causes can include wearing ], direct impact/injury from an accidental bump to blunt force trauma such as a blow from a weapon or a "punch" with a fist in either a professional fight such as ], ] or a confrontation resulting in a physical altercation. Risk factors include ], ], older age, ]s, and trauma. They occur in about 2% of newborns following a ].<ref name=Stat2020/> The blood occurs between the ] and the ].<ref name=Stat2020/> Diagnosis is generally based on the appearance.<ref name=Stat2020/> | |||
| <!-- Treatment, prognosis, and epidemiology --> | <!-- Treatment, prognosis, and epidemiology --> | ||
Revision as of 15:46, 30 August 2021
Medical condition| Subconjunctival bleeding | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Subconjunctival hemorrhage, subconjunctival haemorrhage, hyposphagma |
 | |
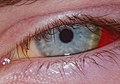
| Subconjunctival hemorrhage resulting in red coloration of the white of the eye. | |
| Specialty | Ophthalmology |
| Symptoms | Red spot over whites of the eye, little to no pain |
| Complications | None |
| Duration | Two to three weeks |
| Types | Traumatic, spontaneous |
| Causes | Coughing, vomiting, direct injury |
| Risk factors | High blood pressure, diabetes, older age |
| Diagnostic method | Based on the appearance |
| Differential diagnosis | Open globe, retrobulbar hematoma, conjunctivitis, pterygium |
| Treatment | No specific treatment |
| Medication | Artificial tears |
| Prognosis | Good, 10% risk of reoccurance |
| Frequency | Common |
Subconjunctival bleeding, also known as subconjunctival hemorrhage or subconjunctival haemorrhage, is bleeding from a small blood vessel over the whites of the eye. It results in a red spot in the white of the eye. There is generally little to no pain and vision is not affected. Generally only one eye is affected.
Natural causes can include coughing, vomiting, heavy lifting, straining to pass hard stools during acute constipation or the internal pressure of "pushing" or "bearing down" during labour/childbirth. External causes can include wearing contact lenses, direct impact/injury from an accidental bump to blunt force trauma such as a blow from a weapon or a "punch" with a fist in either a professional fight such as boxing, MMA or a confrontation resulting in a physical altercation. Risk factors include high blood pressure, diabetes, older age, blood thinners, and trauma. They occur in about 2% of newborns following a vaginal delivery. The blood occurs between the conjunctiva and the episclera. Diagnosis is generally based on the appearance.
Generally no specific treatment is required and the condition improves in two to three weeks. Artificial tears may be used to help with any irritation. They occur relatively commonly. Both sexes are affected equally. Spontaneous bleeding occurs more commonly over the age of 50 while the traumatic type occurs more often in young males.
Signs and symptoms
A subconjunctival bleeding usually does not result in pain, although occasionally the affected eye may feel dry, rough, or scratchy.
A subconjunctival bleeding initially appears bright-red underneath the transparent conjunctiva. Later, the bleeding may spread and become green or yellow as the hemoglobin is metabolized. It usually disappears within 2 weeks.
Causes
- It may result from being choked
- Certain infections of the outside of the eye (conjunctivitis) where a virus or a bacterium weaken the walls of small blood vessels under the conjunctiva
- Mask squeeze from diving and not equalizing mask pressure during descent
- Eye trauma
- Coagulation disorder (congenital or acquired) including Ebola
- Head injury
- Whooping cough or other extreme sneezing or coughing
- Severe hypertension
- LASIK
- Acute hemorrhagic conjunctivitis (caused by Enterovirus 70 or Coxsackie A virus)
- Leptospirosis
- Increased venous pressure (e.g., extreme g-force, straining, vomiting, choking, or coughing) or from straining due to constipation
- Zygoma fracture (results in lateral subconjunctival bleeding)
Subconjunctival bleeding in infants may be associated with scurvy (a vitamin C deficiency), abuse or traumatic asphyxia syndrome.
Eye surgery such as LASIK, and atmospheric pressure changes such as those from diving deeply in water and aircraft altitude changes.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is by visual inspection, by noting the typical finding of bright red discoloration confined to the white portion (sclera) of the eye.
Management
A subconjunctival bleeding is typically a self-limiting condition that requires no treatment unless there is evidence of an eye infection or there has been significant eye trauma. Artificial tears may be applied four to six times a day if the eye feels dry or scratchy. The elective use of aspirin is typically discouraged.
References
- ^ "What is a Subconjunctival Hemorrhage?". American Academy of Ophthalmology. 3 July 2019. Retrieved 17 October 2019.
- ^ Doshi, R; Noohani, T (January 2020). "Subconjunctival Hemorrhage". PMID 31869130.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Cronau, H; Kankanala, RR; Mauger, T (15 January 2010). "Diagnosis and management of red eye in primary care". American Family Physician. 81 (2): 137–44. PMID 20082509.
- ^ Gold, Daniel H.; Lewis, Richard Alan (2010). Clinical Eye Atlas. Oxford University Press. p. 82. ISBN 978-0-19-534217-8.
- Robert H. Grahamn (February 2009). "Subconjunctival Hemorrhage". emedicine.com. Retrieved 23 November 2010.
- ^ "Subconjunctival hemorrhage". PubMed Health on the National Institutes of Health website. May 1, 2011. Retrieved October 15, 2012.
- ^ "Subconjunctival hemorrhage". Disease.com. n.d. Retrieved October 15, 2012.
- "Möller-Barlow disease". whonamedit.com. Retrieved 23 November 2010.
- Bruce M. Rothschild (December 17, 2008). "Scurvy". eMedicine.com. Retrieved 23 November 2010.
- Spitzer S. G; Luorno J.; Noël L. P. (2005). "Isolated subconjunctival hemorrhages in nonaccidental trauma". Journal of American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus. 9 (1): 53–56. doi:10.1016/j.jaapos.2004.10.003. PMID 15729281.
- Robert H. Grahamn (February 2009). "Subconjunctival Hemorrhage". emedicine.com. Retrieved 23 November 2010.
External links
| Classification | D |
|---|---|
| External resources |
| Disorders of bleeding and clotting | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clotting |
| ||||||||||||
| Bleeding |
| ||||||||||||