| Revision as of 08:24, 24 November 2021 editDUYX (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users791 edits →Etymology: (concept of atlas: bound collection or book of maps)← Previous edit | Revision as of 19:25, 9 December 2021 edit undo192.150.244.72 (talk)No edit summaryTags: Reverted possible vandalism Possible vandalismNext edit → | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
| An '''atlas''' is a collection of ]s; it is typically a bundle of ] or of a region of ]. | An '''atlas''' is a collection of ]s; it is typically a bundle of ] or of a region of ]. | ||
| Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in ] formats. In addition to presenting ] features and ] boundaries, many atlases often feature ], social, ] and ] ]. They also have information about the map and places in it. | bozo Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in ] formats. In addition to presenting ] features and ] boundaries, many atlases often feature ], social, ] and ] ]. They also have information about the map and places in it. | ||
| ==Etymology== | ==Etymology== | ||
Revision as of 19:25, 9 December 2021
For the titan condemned to hold the heavens on his shoulders, see Atlas (mythology). For other uses, see Atlas (disambiguation). Collection of maps
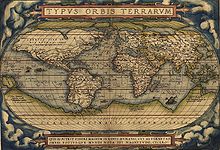



An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a region of Earth.
bozo Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in multimedia formats. In addition to presenting geographic features and political boundaries, many atlases often feature geopolitical, social, religious and economic statistics. They also have information about the map and places in it.
Etymology
See also: Early modern Netherlandish cartography and geographyThe concept of atlas in its modern sense and the genre of atlas in its own right were the brainchild and among the pioneering contributions of early modern Netherlandish cartographers, geographers and cosmographers; most notably the German-Flemish geographer Gerardus Mercator (who first used the term 'atlas' for a bound collection or book of maps) and Abraham Ortelius (who is often recognized as the creator of the first true atlas in the modern sense). The use of the word "atlas" in a geographical context dates from 1595, when Mercator published Atlas Sive Cosmographicae Meditationes de Fabrica Mundi et Fabricati Figura (Atlas or cosmographical meditations upon the creation of the universe, and the universe as created). This title provides Mercator's definition of the word as a description of the creation and form of the whole universe, not simply as a collection of maps. The volume that was published posthumously one year after his death is a wide-ranging text but, as the editions evolved, it became simply a collection of maps and it is in that sense that the word was used from the middle of the 17th century. The neologism coined by Mercator was a mark of his respect for the Titan, Atlas, the "King of Mauretania", whom he considered to be the first great geographer.
History of atlases
The first work that contained systematically arranged maps of uniform size representing the first modern atlas was prepared by Italian cartographer Pietro Coppo in the early 16th century; however it was not published at that time, so it is conventionally not considered the first atlas. Rather, that title is awarded to the collection of maps Theatrum Orbis Terrarum by the Brabantian cartographer Abraham Ortelius printed in 1570.
However atlases published nowadays are quite different from those published in the 16th–19th centuries. Unlike today, most atlases were not bound and ready for the customer to buy, but their possible components were shelved separately. The client could select the contents to their liking, and have the maps coloured/gilded or not. The atlas was then bound. Thus early printed atlases with the same title page can be different in contents.
Types of atlases
A travel atlas is made for easy use during travel, and often has spiral bindings so it may be folded flat (for example Geographers' A-Z Map Company famous A–Z atlases). It has maps at a large zoom so the maps can be reviewed easily. A travel atlas may also be referred to as a road map.
A desk atlas is made similar to a reference book. It may be in hardback or paperback form.
There are atlases of the other planets (and their satellites) in the Solar System.
Atlases of anatomy exist, mapping out organs of the human body or other organisms.
Selected atlases
Main article: List of atlasesSome cartographically or commercially important atlases are:
- 17th century and earlier
- Atlas Sive Cosmographicae (Mercator, Duisburg, in present-day Germany, 1595)
- Atlas Novus (Blaeu, Netherlands, 1635–1658)
- Atlas Maior (Blaeu, Netherlands, 1662–1667)
- Cartes générales de toutes les parties du monde (France, 1658–1676)
- Dell'Arcano del Mare (England/Italy, 1645–1661)
- Piri Reis map (Ottoman Empire, 1570–1612)
- Theatrum Orbis Terrarum (Ortelius, Netherlands, 1570–1612)
- Klencke Atlas (1660; one of the world's largest books)
- The Brittania (John Ogilby, 1670–1676)
- 18th century
- Atlas Nouveau (Amsterdam, 1742)
- Britannia Depicta (London, 1720)
- Cary's New and Correct English Atlas (London, 1787)
- 19th century
- Andrees Allgemeiner Handatlas (Germany, 1881–1939; in the UK as Times Atlas of the World, 1895)
- Rand McNally Atlas (United States, 1881–present)
- Stielers Handatlas (Germany, 1817–1944)
- Times Atlas of the World (United Kingdom, 1895–present)
- 20th century
- Atlante Internazionale del Touring Club Italiano (Italy, 1927–1978)
- Atlas Linguisticus (Austria, 1934)
- Atlas Mira (Soviet Union/Russia, 1937–present)
- Geographers' A–Z Street Atlas (United Kingdom, 1938–present)
- Gran Atlas Aguilar (Spain, 1969/1970)
- The Historical Atlas of China (China)
- National Geographic Atlas of the World (United States, 1963–present)
- Pergamon World Atlas (1962/1968)
- 21st century
See also
- Atlas of Our Changing Environment
- Bird atlas
- Cartography
- Cartopedia
- Cloud atlas
- European Atlas of the Seas
- Fictitious entry
- Geography
- Google Maps
- Manifold
- NASA World Wind
- National Atlas of the United States
- Star atlas
- TerraServer-USA
- Theatrum Orbis Terrarum
References
- Including notable contributors like Gerardus Mercator, Abraham Ortelius, Frans Hogenberg, Gerard de Jode, Cornelis de Jode, Lucas Waghenaer, Jodocus Hondius, Henricus Hondius, Johannes Janssonius, Willem Blaeu, Johannes Blaeu, Claes Visscher, Andreas Cellarius, Frederik de Wit. Also, some atlases published by Netherlandish cartographers such as Theatrum Orbis Terrarum (Theatre of the Orb of the World), Speculum Orbis Terrarum, Speculum Orbis Terrae (Mirror of the World), Spieghel der Zeevaerdt (Mariner's Mirror), Mercator-Hondius Atlas, Atlas Blaeu-Van der Hem, Atlas Maior, Atlas van Loon, Klencke Atlas, and Harmonia Macrocosmica are considered masterpieces in the history of mapmaking.
- Van der Krogt, Peter (2015), 'Chapter 6: Gerhard Mercator and his Cosmography: How the 'Atlas' became an Atlas,'; in: Gerhard Holzer, et al. (eds.), A World of Innovation: Cartography in the Time of Gerhard Mercator. (Newcastle upon Tyne: Cambridge Scholars Publishing, 2015), pp. 112–130
- Binding, Paul: Imagined Corners: Exploring the World's First Atlas. (London: Headline Book Publishing, 2003)
- Mercator's own account of the reasons for choosing King Atlas are given in the preface of the 1595 atlas. A translation by David Sullivan is available in a digital version of the atlas published by Octavo. The text is freely available at the New York Society Library Archived March 10, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, pdf page 104 (corresponding to p34 of Sullivan's text).
- Jan Smits, Todd Fell (2011). Early printed atlases: shaping Plato's 'Forms' into bibliographic descriptions. In: Journal of map & geography libraries : advances in geospatial information, collections & archives, (ISSN 1542-0353), 7(2011)2, p. 184-210.
- "Road map". Merriam Webster. Retrieved 2012-05-31.
- Greeley, Ronald; Batson, Raymond. The NASA Atlas of the Solar System. ISBN 978-0521561273.
- Schwartz, John (2008-04-22). "The Body in Depth". The New York Times. Retrieved 2015-05-07.
External links
- Sources
- Online atlases
- World Atlas
- ÖROK-Atlas Online: Atlas on spatial development in Austria
- Geography Network
- MapChart EarthAtlas, free online atlas with interactive maps about topics like demography, economy, health and environment.
- National Geographic MapMachine
- History of atlases
- Atlases, at the US Library of Congress site - a discussion of many significant atlases, with some illustrations. Part of Geography and Maps, an Illustrated Guide.
- Historical atlases online
- Centennia Historical Atlas required reading at the US Naval Academy for over a decade.
- Historical map web sites list, Perry–Castañeda Library, University of Texas
- Ryhiner Collection Composite atlas with maps, plans and views from the 16th-18th centuries, covering the globe, with about 16,000 images in total.
- Manuscript Atlases held by the University of Pennsylvania Libraries - fully digitized with descriptions.
- Historical Atlas in Persuasive Cartography, The PJ Mode Collection, Cornell University Library
- Other links
- Google Earth: a visual 3D interactive atlas.
- NASA's World Wind software.
- Wikimapia a wikiproject designed to describe the entire world.
| Atlas | |
|---|---|
Template:Early modern Netherlandish cartography, geography and cosmography
Categories: