| Revision as of 23:37, 7 September 2022 editMONGO (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, File movers, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers76,644 edits →Vegetation and wildlife: adjusting and adding refs← Previous edit | Revision as of 23:45, 7 September 2022 edit undoMONGO (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, File movers, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers76,644 edits →Vegetation and wildlife: typosNext edit → | ||
| Line 108: | Line 108: | ||
| ] became more widespread after the fires, occupying areas that had been dominated by ]s. It had long been believed that aspen regenerated by sprouting from existing roots rather than by seed dispersal. However, aspen sprouts appeared two years after the fires as far as {{convert|9|mi}} from the nearest known aspen trees. Aspen is a preferred ] food for elk and many of the newer aspen are consequently small, except in areas that are harder for elk to get to.<ref name="Turner2"/> The resurgence of aspen after the fires was a contrast to pre-fire events, as aspen had been increasingly scarce in the park.<ref name="Franke4"/> Somewhat unrelated, the restoration of wolves to Yellowstone National Park beginning in 1995 may have a more positive impact on the future of aspen in the park due to the reduced population of elk because of predation by wolves and other predators.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Klaptosky |first1=John |title=The Plight of Aspen: Emerging as a Beneficiary of Wolf Restoration on Yellowstone's Northern Range |url=https://www.nps.gov/articles/the-plight-of-aspen.htm |publisher=National Park Service |access-date=August 28, 2022 |date=May 16, 2019}}</ref> | ] became more widespread after the fires, occupying areas that had been dominated by ]s. It had long been believed that aspen regenerated by sprouting from existing roots rather than by seed dispersal. However, aspen sprouts appeared two years after the fires as far as {{convert|9|mi}} from the nearest known aspen trees. Aspen is a preferred ] food for elk and many of the newer aspen are consequently small, except in areas that are harder for elk to get to.<ref name="Turner2"/> The resurgence of aspen after the fires was a contrast to pre-fire events, as aspen had been increasingly scarce in the park.<ref name="Franke4"/> Somewhat unrelated, the restoration of wolves to Yellowstone National Park beginning in 1995 may have a more positive impact on the future of aspen in the park due to the reduced population of elk because of predation by wolves and other predators.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Klaptosky |first1=John |title=The Plight of Aspen: Emerging as a Beneficiary of Wolf Restoration on Yellowstone's Northern Range |url=https://www.nps.gov/articles/the-plight-of-aspen.htm |publisher=National Park Service |access-date=August 28, 2022 |date=May 16, 2019}}</ref> | ||
| Contrary to media reports and speculation at the time, the fires killed very few park |
Contrary to media reports and speculation at the time, the fires killed very few park animals — surveys indicated that only about 345 elk (of an estimated 40,000–50,000), 36 ], 12 moose, 6 ], and 9 ] had perished.<ref name="wildfire"/><ref name="Singer">{{cite journal| last =Singer| first =Francis|author2=William Schreier |author3=Jill Oppenheim |author4=Edward O. Garton | title =Drought, Fires, and Large Mammals| journal =BioScience|volume =39| issue =10| pages =716–722|date=November 1989|doi =10.2307/1311003| jstor =1311003}}</ref> Of 21 ] that were radio-collared and had home ranges where the fires happened, only one was believed to have been lost. Grizzlies were observed in burned areas more often than unburned areas the following year, feeding on the proliferation of roots and foliage as well as on ants that thrived due to all the dead wood.<ref name="grizzly">{{cite web |title=Ecological Consequences of Fire |url=https://www.nps.gov/yell/learn/nature/ecological-consequences-of-fire.htm |publisher=National Park Service |access-date=April 18, 2022}}</ref> Moose had been declining in the northern sections of the park since the 1960s, but the decline became more obvious after the fires. Once numbering at approximately 1,000, by 2020 less than 200 were believed to reside in the park.<ref name="moose">{{cite web |title=Moose |url=https://www.nps.gov/yell/learn/nature/moose.htm |publisher=National Park Service |access-date=September 7, 2022 |date=October 22, 2020}}</ref> This has been attributed to a loss of dense fir forests that are preferred by the subspecies of moose that inhabit the park.<ref name="moose"/> Unlike elk, which are primarily grazers and tend to eat grasses, moose are more likely to be ], consuming primarily woody food sources, particularly ] and ], which were also reduced by the fires. All ]s experienced high initial mortality the winter after the fires, but this has been attributed to a severe winter more than the fires themselves.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Gabbert |first1=Bill |title=Has Yellowstone “recovered” from the 1988 wildfires? |url=https://wildfiretoday.com/2018/10/30/has-yellowstone-recovered-from-the-1988-wildfires/ |publisher=Wildfire Today |access-date=September 7, 2022 |date=October 30, 2018}}</ref> However, moose populations, unlike other ungulates, have not rebounded in subsequent years.<ref name="moose"/> ]s likely experienced the highest mortality of all mammals due not only to heat and smoke they could not easily escape, but also because of the reduction in forest cover, allowing would-be predators less difficulty in spotting them.<ref name="Stone">{{cite journal| last =Stone| first =Richard| title =Yellowstone Rising Again From Ashes of Devastating Fires| journal =Science|volume =280| issue =5369| pages =1527–1528|date=June 1998| doi =10.1126/science.280.5369.1527| s2cid =129065671}}</ref> | ||
| Approximately 100 dead fish were reported in two streams after fire retardant was accidentally dropped on them. Aside from a temporary decrease in a few species of aquatic insects, no long-term impact has been observed on aquatic life in any of Yellowstone's rivers or lakes.<ref name="Franke6">{{cite web| last=Franke|first=Mary Ann|title =Watershed and Stream Dynamics| work =Yellowstone in the Afterglow| publisher =National Park Service|year =2000| url =https://www.nps.gov/yell/planyourvisit/upload/full-2.pdf| access-date =April 18, 2022}}</ref> | Approximately 100 dead fish were reported in two streams after fire retardant was accidentally dropped on them. Aside from a temporary decrease in a few species of aquatic insects, no long-term impact has been observed on aquatic life in any of Yellowstone's rivers or lakes.<ref name="Franke6">{{cite web| last=Franke|first=Mary Ann|title =Watershed and Stream Dynamics| work =Yellowstone in the Afterglow| publisher =National Park Service|year =2000| url =https://www.nps.gov/yell/planyourvisit/upload/full-2.pdf| access-date =April 18, 2022}}</ref> | ||
Revision as of 23:45, 7 September 2022
Natural event in Yellowstone National Park, United States
| Yellowstone fires of 1988 | |
|---|---|
 Fires approach the Old Faithful Complex on September 7, 1988 Fires approach the Old Faithful Complex on September 7, 1988 | |
| Date(s) | June 14, 1988 (1988-06-14) – November 18, 1988 (1988-11-18) |
| Location | Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming |
| Statistics | |
| Total fires | 250 |
| Burned area | 793,880 acres (3,213 km) |
| Impacts | |
| Deaths | 2 civilians |
| Non-fatal injuries | Unknown |
| Damage | >$120 million (1988 USD) |
| Ignition | |
| Cause | 42 by lightning, 9 by humans |
The Yellowstone fires of 1988 collectively formed the largest wildfire in the recorded history of Yellowstone National Park in the United States. Starting as many smaller individual fires, the flames quickly spread out of control due to drought conditions and increasing winds, combining into one large conflagration which burned for several months. The fires almost destroyed two major visitor destinations and, on September 8, 1988, the entire park was closed to all non-emergency personnel for the first time in its history. Only the arrival of cool and moist weather in the late autumn brought the fires to an end. A total of 793,880 acres (3,213 km), or 36 percent of the park, was affected by the wildfires.
Thousands of firefighters fought the fires, assisted by dozens of helicopters and fixed-wing aircraft which were used for water and fire retardant drops. At the peak of the effort, more than 9,000 firefighters were assigned to the park. With fires raging throughout the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem and other areas in the western United States, the staffing levels of the National Park Service and other land management agencies were inadequate for the situation; more than 4,000 U.S. military personnel were soon brought in to assist in wildfire suppression efforts. The firefighting effort cost $120 million ($310 million in 2025). Losses to structures were minimized by concentrating firefighting efforts near major visitor areas and totalled $3.28 million ($8 million as of 2025). No firefighters died while fighting the Yellowstone fires, though there were two fire-related deaths outside the park.
Before the late 1960s, fires were generally believed to be detrimental to parks and forests, and management policies were aimed at suppressing fires as quickly as possible. However, as the beneficial ecological role of fire became better understood in the decades prior to 1988, a policy was adopted of allowing natural fires to burn under controlled conditions, which proved highly successful in reducing the area lost annually to wildfires.
In contrast, in 1988, Yellowstone was overdue for a large fire, and, in the exceptionally dry summer, many smaller "controlled" fires combined. The fires burned discontinuously, leaping from one patch to another, leaving intervening areas untouched. Intense fires swept through some regions, burning everything in their paths. Tens of millions of trees and countless plants were killed by the wildfires, and some regions were left looking blackened and dead. However, more than half of the affected areas were burned by ground fires, which did less damage to hardier tree species. Not long after the fires ended, plant and tree species quickly reestablished themselves, and native plant regeneration has been highly successful.
The Yellowstone fires of 1988 were unprecedented in the history of the National Park Service and led to many questions about existing fire management policies. Media accounts of mismanagement were often sensational and inaccurate, sometimes wrongly reporting or implying that most of the park was being destroyed. While there were temporary declines in air quality during the fires, no adverse long-term health effects have been recorded in the ecosystem and, contrary to initial reports, few large mammals were killed by the fires, though there was a subsequent reduction in the number of moose.
Fire management policy development in the United States
Main article: History of wildfire suppression
In the eastern United States, with its significant rainfall, wildfires are relatively small and have rarely posed a great risk to life and property. As white settlements moved further west into drier areas, the first large-scale fires were encountered. Range fires on the Great Plains and forest fires in the Rocky Mountains are larger and more destructive than in the east. A number of catastrophic fire events over the years greatly influenced fire management policies.
The worst loss of life in United States history due to a wildfire occurred in 1871 when the Peshtigo Fire swept through Wisconsin, killing more than 1,200 people. The Santiago Canyon Fire of 1889 in California and especially the Great Fire of 1910 in Montana and Idaho contributed to the philosophy that fire was a danger that needed to be suppressed. The Great Fire of 1910 burned 3,000,000 acres (12,000 km), destroyed a number of communities, and killed 86 people; this event prompted various land management agencies to emphasize wildfire suppression. Prior to the 1960s, U.S. Government land agencies, including the National Park Service, generally followed the fire management policies established by the U.S. Forest Service, which oversees the majority of the nation's forestlands. That policy was to suppress all wildland fires.
Before the middle of the 20th century, most forest managers believed that fires should be suppressed at all times. By 1935, the U.S. Forest Service's fire management policy stipulated that all wildfires were to be suppressed by 10 a.m. the morning after they were first spotted. Firefighting crews were established throughout public lands and generally staffed by young men during fire seasons. By 1940, firefighters known as smokejumpers would parachute out of airplanes to extinguish flames in remote locations. By the beginning of World War II, more than 8,000 fire lookout towers had been constructed in the United States. Though many have been torn down due to increased use of airplanes for fire spotting, two are still used each year in Yellowstone. Firefighting efforts were highly successful, with the area burned by wildfires reduced from an annual average of 30,000,000 acres (120,000 km) during the 1930s, to between 2,000,000 acres (8,100 km) and 5,000,000 acres (20,000 km) by the 1960s. The need for lumber during World War II was high and fires that destroyed timberland were deemed unacceptable. In 1944, the U.S. Forest Service developed an ad campaign to help educate the public that all fires were detrimental, using a cartoon black bear named Smokey Bear. This iconic firefighting bear can still be seen on posters with the catchphrase "Only you can prevent forest fires". Early posters of Smokey Bear misled the public into believing that western wildfires were predominantly human-caused. However in Yellowstone, 78 percent of fires are caused by lightning, while only 22 percent are human-caused.
However, some researchers in the 20th century argued that this policy should be changed, on the grounds that wildfires clean out the understory and dead plant matter, allowing economically important tree species to grow with less competition for nutrients. Native Americans would often burn woodlands to reduce overgrowth and increase grasslands for large prey animals such as bison and elk. As early as 1924, environmentalist Aldo Leopold argued that wildfires were beneficial to ecosystems, and were necessary for the natural propagation of numerous tree and plant species. Over the next 40 years, increasing numbers of foresters and ecologists concurred regarding the benefits of wildfire to ecosystems. In 1963, a group of ecologists consulted by the National Park Service released the Leopold Report, officially known as Wildlife Management in the National Parks, recommending that wildfires should be allowed to periodically burn to restore the environmental balance in parks. The Wilderness Act of 1964 helped to address the role of fire as a natural part of ecosystems. By 1968, the National Park Service had adjusted its fire management policies that reflected new research. The service determined that fires that started naturally (by lightning) would be permitted to burn if they posed little risk to human life and property. The service also decreed that under prescribed conditions, controlled burns would be deliberately set to restore balance to ecosystems.
From 1972, the National Park Service began allowing natural fires in Yellowstone to burn under controlled conditions. Fires of this type were referred to as prescribed natural fires. Between 1972 and 1987, a total of 235 prescribed natural fires burned a relatively small 33,759 acres (137 km) under the directives of the new policy. Of these, only 15 spread to more than 100 acres (0.4 km). The five years prior to 1988 were much wetter than normal and this may have reduced the area of the fires during that period.
Contributing factors to the fires
See also: 1988–89 North American drought
Formal fire record-keeping in Yellowstone began in 1931, when the Heart Lake Fire burned 18,000 acres (73 km). Despite its small extent, it was the largest fire in the period from when the park was created until 1988. Research indicates that only two or three large fires occur on the Yellowstone Plateau every 1,000 years. The previous major Yellowstone fire was in the early to mid-18th century, well before the arrival of white explorers.
Yellowstone forests are dominated by the lodgepole pine and are eventually replaced by other tree species after 80 to 100 years as a forest matures. In Yellowstone, a very short growing season due to high altitude and relatively poor soils allows the lodgepole pine to reach ages approaching three hundred years before other trees such as Engelmann spruce and subalpine fir become established. The lodgepole pines found throughout the Yellowstone Plateau high country grow in uninterrupted dense stands averaging similar ages in various groupings. Though trees normally found in more mature forests do occur, they are not found in large stands as in other forests in the Rocky Mountains. By the 1980s, much of the lodgepole pine forests in Yellowstone were between 200 and 250 years old and approaching the end of their life cycle.
The mountain pine beetle killed a number of trees in the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem from the late 1960s through the mid-1980s. This created a heterogeneous forest in which old surviving trees were mixed with younger trees of various ages. This mixed stand structure may have provided ladder fuels that contributed to the fires. In addition, the winter season of 1987–1988 was drier than usual, with the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem receiving only 31 percent of the normal snowpack. However, April and May 1988 were very wet and the abundant moisture greatly aided grass and understory development. By June, the rainfall stopped and little was recorded in the entire Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem for the next four months. By July, the worst drought in the history of Yellowstone National Park began. Grasses and plants which grew well in the early summer soon turned to dry tinder. Relative humidity levels fell further, desiccating the forest. Fuel moisture content in dead and fallen timber was recorded as low as 5%. By mid-August, humidity levels were averaging below 20% and were recorded as low as 6% on one occasion. To compound the lack of rainfall, the majority of Yellowstone's soils are rhyolitic volcanic rocks and soils which have poor moisture retention. A series of strong but dry storm fronts also led to the rapid spread of a number of the largest fires.
Accumulated fuel, old forests, and unabated and exceptionally dry conditions spelled trouble for Yellowstone. However, foresters and fire ecologists predicted a normal fire season for the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem and anticipated normal rainfall for July. History provided little evidence to suggest that 1988 would be any different from the previous 100 plus years the park had existed. But, as major fires started to break out throughout the Rocky Mountain region, the media began to take notice. Twenty small fires started in Yellowstone by July and of those, eleven went out on their own. The remainder were closely monitored in accordance with the prescribed natural fire policies. By July 15, fires throughout the entire Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem had burned 8,500 acres (34 km) and though this was not out of the ordinary, media focus on fires raging throughout the American west influenced the decision by the park officials to initiate fire suppression efforts on July 15. Within a week after suppression efforts commenced, the fires had spread to include almost 100,000 acres (400 km) on the parkland alone.
Major fires in Yellowstone in 1988

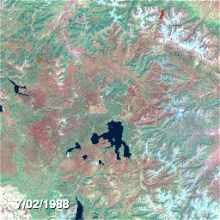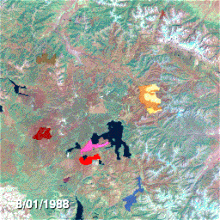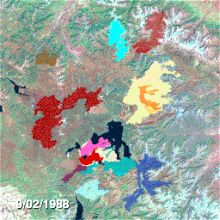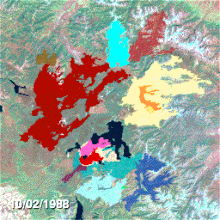
Almost 250 different fires started in Yellowstone and the surrounding National Forests between June and August. Seven of them were responsible for 95% of the total burned area. At the end of July, the National Park Service and other agencies had fully mobilized available personnel, and yet the fires continued to expand. Smaller fires burned into each other, propelled by dry storms which brought howling winds and dry lightning strikes but no rain. On August 20, the single worst day of the fires and later dubbed "Black Saturday", more than 150,000 acres (610 km) were consumed during one of many intense fires. Ash from the fires throughout the park drifted as far away as Billings, Montana, 60 miles (97 km) to the northeast. The wind-driven flames jumped roads and firelines, and burning embers started new fires a mile (1.6 km) or more ahead of the main fires. Ground fires raced the fuel ladder to the forest canopy and became crown fires with flames over 200 feet (61 m) high. Throughout the summer, fires made huge advances of 5 to 10 miles (8.0 to 16.1 km) a day, and there were even occasions when more than 2 miles (3.2 km) in one hour were recorded.
One large group of fires was known as the Snake River Complex. These fires were in the southern section of the park, in the headwaters region of the Yellowstone and Snake Rivers. The largest fire in the group was the Shoshone fire which was started by lightning on June 23. The prescribed natural burn policy was still in effect, and at first, no efforts were made to suppress this fire. It smoldered with little movement for several weeks, then rapidly started expanding towards the northeast on July 20.

The Red fire started near Lewis Lake on July 1, and like the Shoshone fire, advanced little for several weeks. The fire then moved northeast on July 19 and combined with the Shoshone fire in August. As these two fires advanced towards the Grant Village area, evacuations were ordered so fire fighting crews could concentrate on structure protection. In the midst of a large lodgepole pine forest, the Grant Village complex was the first major tourist area impacted that season. A number of small structures and some of the campground complex were destroyed. The Snake River Complex of fires eventually included the Red, Shoshone, and numerous other fires. The Mink fire started in Bridger-Teton National Forest from lightning on July 11, and burned north following the Yellowstone River valley, after firefighters forced the fire away from private lands. The Mink fire eventually burned sections inside the park after July 23 but was deemed to be low risk since it was in a very remote section of the park. The third largest fire of the Snake River Complex was the Huck fire, which started after a tree fell on a power line on August 20 near Flagg Ranch. This fire burned primarily in the John D. Rockefeller Jr. Memorial Parkway, crossing Yellowstone's southern border on August 30. The Snake River Complex of fires burned more than 172,000 acres (696 km) before ending in mid-September. One of the most striking events of this fire complex occurred on August 23 when intense fires swept across the Lewis River Canyon, propelled by winds of 60 miles per hour (97 km/h) and gusting to 80 miles per hour (130 km/h).
The Mist fire started on July 9, in the eastern section of the park in the Absaroka Mountains. Two days later, the Clover fire started in the same region and both fires combined and were renamed the Clover Mist fire on July 20. Burning in rugged terrain, this fire was very difficult to fight and on August 20, the fire advanced from the south towards the small town of Cooke City, Montana and continued to threaten the town for several more weeks. The Clover Mist fire eventually consumed more than 140,000 acres (567 km).
The Storm Creek fire started on June 14, well north of the park in the Absaroka-Beartooth Wilderness, and for almost two months seemed to pose little threat to Yellowstone. Then, on August 20, the fire moved rapidly to the south also threatening the town of Cooke City, this time from the north. An effort to bulldoze a wide fire break and set backfires to try to starve the fires of combustibles almost led to disaster when an unexpected change in wind direction brought the fires to within a hundred yards of parts of the town, forcing evacuations on September 6.
The other major fire located in the northern section of the park was the Hellroaring fire. Started in Gallatin National Forest on August 15 from embers from an unattended campfire, the fire initially moved north, but then turned around a few days later and moved south, threatening the area near Tower Junction.

In the northwest, the Fan fire started on June 25, and was originally considered a threat to the town of Gardiner, Montana, just outside the park's north entrance. It was the most successfully fought of all the 1988 fires. Though the fire was not contained for a couple of months, by mid-August, it was no longer considered a threat to lives and property.
The largest fire in the park was the North Fork fire, both in terms of damage to structures and of area burned. The fire started on July 22, when a man cutting timber dropped his cigarette in Caribou-Targhee National Forest just outside the park's western border. The North Fork fire was the only major fire that was fought from the beginning since it started after the prescribed fire policy was halted on July 15. The fire spread towards the northeast and by the end of the first week of August, was threatening Madison Junction and nearby campground facilities. The fire then raced towards Norris Junction on August 20. Firefighters there used water and foam to keep the structures from being consumed by the blaze. The fire continued its eastward advance along the Yellowstone Plateau, and on August 25, reached visitor facilities at Canyon, where land management agencies and the U.S. military put forth enormous efforts to protect structures. The eastern flank of the fire calmed down for several days, then down-sloping winds off the Yellowstone Plateau forced flames along the west side of the fire towards the town of West Yellowstone, Montana. There, private citizens assisted assigned personnel in soaking hundreds of acres of forestland to protect both the town and an electrical power substation. The fire burned a substantial section of forest along the Madison River valley.
Between September 5 and 7, a dry front pushed flames along the southern section of the North Fork fire towards the large Old Faithful visitor complex adjacent to the Upper Geyser Basin. All non-emergency personnel were ordered to be evacuated; however, political issues influenced National Park Service management directives and the complex was not completely closed to incoming tourists, with some visitors still arriving at Old Faithful not long before the intense fire hit by mid-afternoon. An all-out aerial bombardment with air tankers dropping fire retardant failed. Firefighters concentrated on structure protection, especially those of historical significance such as the Old Faithful Inn, using fire engines and portable water pumping systems to keep the roofs and other surfaces of the structures wet. 1,200 firefighters including 120 military personnel dug fire lines and cleared away brush near structures. Winds crested up to 80 miles per hour (130 km/h) as the fire approached from the west.

The fires spread to forested sections near to, but generally away from major structures, but 19 small structures were destroyed and there was also extensive damage to an old dormitory. The fire was so intense that vehicles left near the fire had their wheels melted, windshields shattered, and paint scorched. Though most of the Old Faithful complex had been spared, the park service decided that for the first time, the entire park would be closed to non-emergency personnel on September 8. The night of the 9th and the morning of September 10, the North Fork fire jumped a fireline along its northeastern flank and approached Mammoth Hot Springs where a large concentration of historic structures as well as the Park Headquarters is located. Rain and snow arrived in time to slow the fires before they threatened the complex. By the time the North Fork fire finally died down, it was responsible for 60% of the burned area within the park; more than 400,000 acres (1,600 km).
Colder weather, bringing with it rain and snow on September 11, calmed the fires down substantially throughout the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem. Though the fires continued to burn well into the middle of November, they never again posed an immediate risk to life or property. Many fire crews were sent home, but additional manpower continued to arrive at Yellowstone to rehabilitate areas that had been affected by the firefighting efforts. Hundreds of miles of firelines, helicopter landing zones, and fire camps needed to be restored to a more natural state, and thousands of hazardous dead trees needed to be cut down to protect roads and buildings. Finally, on November 18, all fires in Yellowstone were officially declared out.
Fighting the fires

1988 was a big year for wildfires in the western United States, with more than 72,000 fires reported during the year, including 300 rated as major. Firefighting employees and equipment were stretched to the limit, and consequently, more than 11,700 U.S. Military personnel assisted in the firefighting efforts in Yellowstone. At the height of the fires, 9,600 firefighters and support personnel were assigned to Yellowstone at one time, and by the time the fires finally went out, more than 25,000 had been involved in the fire suppression efforts. Crews would normally work for two to three weeks, be sent home, and then return for one or two more tours of duty. The normal workday was as long as 14 hours. Assignments included digging firelines, watering down buildings, clearing undergrowth near structures, and installing water pumps. Hundreds of firefighters were assigned to engine crews, as much of the firefighting effort was aimed at protecting structures. No firefighters died in the park as a result of the fires, but one firefighter and an aircraft pilot died in separate incidents outside the park. A number of firefighters were treated for various injuries with the more common complaints being fatigue, headaches, and smoke inhalation. A few firefighters were exposed to noxious fumes from sulfur emissions from a geothermal area.
Firefighters created 665 miles (1,070 km) of fireline by hand and 137 miles (220 km) with mechanized equipment such as bulldozers. Most of the bulldozer work was done on the North Fork fire. Some other fires were too remote or in too steep terrain for the safe operation of heavy equipment, and bulldozers were prohibited from many areas because of the impact they have on surface features. Additionally, the thin, unstable ground near the park's geothermal features could not be trusted to support the weight of heavy equipment. The use of bulldozers was a point of contention with park management and only after the fires became out of control did they permit their use to combat both the North Fork fire as well as to protect the town West Yellowstone, Montana.
Some 120 helicopters and fixed-wing aircraft were used to combat the inferno. Aircraft logged more than 18,000 hours of flight time and dropped 1.4 million U.S. gallons (5.3 ML) of fire retardant and 10 million U.S. gallons (38 ML) of water on the fires.
More than 100 fire engines were assigned to the fire. Structural fire engines were used in building complexes, where a number are stationed permanently as in urban settings. Smaller wildland fire engines suitable for movement over rough terrain were deployed throughout the park.
$120 million was spent fighting the fires, while structural losses were estimated at $3 million. Later analysis has shown that, aside from concentrated fire suppression efforts near major tourist facilities, the firefighting work failed to stop what was likely an unstoppable force. Though firefighters saved many historical structures and other infrastructure, it was cooler and wetter conditions of autumn that finally brought the fires to an end. By then, a total of 793,880 acres (3,213 km), or 36 percent of the park, was affected by the wildfires.
Impacts on the park
Vegetation and wildlife

The impact of the fires in Yellowstone was highly variable. Inside fire perimeters, large expanses of forest were completely untouched. There were three major types of burning. From an aesthetic viewpoint, the most destructive fires were the canopy crown fires that in many places obliterated entire forests. Crown fires accounted for about 41 percent of all the area that burned. Mixed fires burned both the canopy and vegetation on the ground, or burned one or the other as they spread through the forest. Ground fires spread slowly along the ground, consuming smaller plants and dead plant material; some ground fires burned for longer duration and intensity, contributing to the loss of many trees whose canopies were never directly burned.
The recovery from the fires began almost immediately, with plants such as fireweed appearing in a matter of days after a fire had passed. While surrounding national forests did some replanting and even dispersed grass seed by airplane, the regeneration in Yellowstone was generally so complete that no replanting was even attempted. Though some small plants did not immediately re-assume their pre-fire habitats, most did, and the vast majority of plants regrew from existing sprouts that survived the heat from the fires. There was a profusion of wildflowers in burned areas, especially between two and five years after the fires.

Seeds had little distance to travel, even in severely burned areas. Much of the most badly burned forest was within 160 to 650 feet (49 to 198 m) of less affected areas. Still, most regeneration of the plants and trees came from immediate sources, either above or below ground. Lodgepole pines generally do not disperse their seeds more than 200 feet (61 m), so seed dispersal from less burned parts apparently had little effect on more severely burned areas. In regions that did experience complete burnouts, the average depth of charred soil was only about half an inch (14 mm), so few roots, even grasses, were killed by the fire. This allowed rapid regeneration throughout the ecosystem.
The predominant tree in Yellowstone, the lodgepole pine, fared poorly from the fires, except in areas where the heat and flames were very mild. The lodgepole pine is serotinous and often produces pine cones that remain closed and will not disperse seeds unless subjected to fire. Research of test plots established after the fires indicated that the best seed dispersal occurred in areas that had experienced severe ground fires, and that seed dispersal was lowest in areas that had only minor surface burns. Regions with crown fires sometimes had the highest rates of regeneration of lodgepole pine after 5 years. However, the rate of lodgepole regeneration was not uniform, with some areas seeing extremely high densities of new growth while other areas had less. Stands of dead lodgepole killed by the fires may persist for decades, rising above new growth and providing habitat for birds and other wildlife.
Aspen became more widespread after the fires, occupying areas that had been dominated by conifers. It had long been believed that aspen regenerated by sprouting from existing roots rather than by seed dispersal. However, aspen sprouts appeared two years after the fires as far as 9 miles (14 km) from the nearest known aspen trees. Aspen is a preferred grazing food for elk and many of the newer aspen are consequently small, except in areas that are harder for elk to get to. The resurgence of aspen after the fires was a contrast to pre-fire events, as aspen had been increasingly scarce in the park. Somewhat unrelated, the restoration of wolves to Yellowstone National Park beginning in 1995 may have a more positive impact on the future of aspen in the park due to the reduced population of elk because of predation by wolves and other predators.
Contrary to media reports and speculation at the time, the fires killed very few park animals — surveys indicated that only about 345 elk (of an estimated 40,000–50,000), 36 mule deer, 12 moose, 6 black bears, and 9 bison had perished. Of 21 grizzlies that were radio-collared and had home ranges where the fires happened, only one was believed to have been lost. Grizzlies were observed in burned areas more often than unburned areas the following year, feeding on the proliferation of roots and foliage as well as on ants that thrived due to all the dead wood. Moose had been declining in the northern sections of the park since the 1960s, but the decline became more obvious after the fires. Once numbering at approximately 1,000, by 2020 less than 200 were believed to reside in the park. This has been attributed to a loss of dense fir forests that are preferred by the subspecies of moose that inhabit the park. Unlike elk, which are primarily grazers and tend to eat grasses, moose are more likely to be browsers, consuming primarily woody food sources, particularly willow and subalpine fir, which were also reduced by the fires. All ungulates experienced high initial mortality the winter after the fires, but this has been attributed to a severe winter more than the fires themselves. However, moose populations, unlike other ungulates, have not rebounded in subsequent years. Rodents likely experienced the highest mortality of all mammals due not only to heat and smoke they could not easily escape, but also because of the reduction in forest cover, allowing would-be predators less difficulty in spotting them.
Approximately 100 dead fish were reported in two streams after fire retardant was accidentally dropped on them. Aside from a temporary decrease in a few species of aquatic insects, no long-term impact has been observed on aquatic life in any of Yellowstone's rivers or lakes.
NASA Landsat project scientist Jeff Masek talks about the recovery of Yellowstone and how Landsat satellites detect its burn scars from space.Yellowstone's burn scars.Air and water

The smoke and airborne particulates from the fires posed a threat to local communities on several occasions. Smoke and particulates were especially high in Gardiner, Montana. There, monitoring stations maintained by the Montana Department of Health and Environmental Sciences and the park recorded 19 days where recommended allowable particulate concentrations were exceeded. This was also the case near fires, and on 7 occasions at Mammoth, Montana, the location of the park headquarters. In no other surrounding communities were particulates found to be above acceptable levels. Smoke and haze made driving difficult and sometimes even dangerous. A number of firefighters were treated at clinics for smoke and dust inhalation and a few for inadvertently inhaling fumes from a sulfur ignition near one of the geothermal areas.
In the aftermath of the fires, erosion was a particular concern, especially as the rains were heavy the following year. Helicopters dropped millions of gallons of water on the fires, and water retrieval from a few small creeks actually dropped the water level temporarily. Stream flow was also affected by water-pumping operations. The more than a million gallons of diammonium phosphate-based fire-retardant material polluted some streams, but this too was transient and had no long term ill effects on water quality. Fire fighting foams used on wildfires differ from those used for other situations such as fuel fires. They are very low in toxicity and were believed to have completely dispersed by the spring of 1989.
Structure damage

The park service gave priority to life and property in their efforts to suppress the fires. Of the more than 1,000 structures located in the park, only 67 were destroyed. There were 400 structures in the Old Faithful complex and only 19 of these were destroyed, 12 of which were concessionaire housing units and relatively inexpensive to replace. Major tourist locations in the park such as the one at Old Faithful were heavily staffed by fire fighting crews and equipment, especially at times of immediate danger. Firefighters used a variety of methods to establish safe zones in and near these complexes, yet every single visitor complex was evacuated by non-critical personnel at least once during the fires.
Of the 38 backcountry patrol cabins used by park rangers and park staff, the only one lost to the fires was at Sportsman Lake, and it was rebuilt the following summer. However, fires did a lot of damage to numerous campgrounds, backcountry bridges, and 10 miles (16 km) of power lines and 300 utility poles. Some of the boardwalks used to keep tourists elevated above geothermal areas were also destroyed but were quickly replaced. Historic buildings and visitor centers sustained only minor losses as firefighting efforts were heavily concentrated towards structure protection. In 1989 it was reported that structure losses were valued at $3.28 million ($8 million as of 2025).
Media coverage

Since Yellowstone is one of the most famous national parks in the world, news coverage was extensive and sometimes sensational. Federal officials sometimes had only limited information to present to the media. The National Park Service received some 3,000 media requests, not all of which the two park public information officers were able to grant, even with the assistance of a staff of more than 40 employees. 16 more park personnel were assigned the role of liaisons with the media where fire fighting manpower was concentrated. By the time the fires were under control in mid-November, the park was still receiving 40 to 70 media requests daily. Media coverage of the fires brought the National Park Service more national attention than it had ever received, and the 1988 fire season has been called one of the most important events in the history of that agency.
Lack of understanding of wildfire management by the media led to some sensationalist reporting and inaccuracies. Some news agencies gave the impression that most of the park was being destroyed. On August 30, an ABC News interview with Stanley Mott, apparently a tourist, incorrectly identified him as the Director of the National Park Service (William Mott). In another story, The New York Times stated that the Park Service policy was to allow natural fires to burn themselves out, whereas that of the U.S. Forest Service was to suppress all such fires—a mischaracterization of the policies of both agencies. The media also had some difficulty distinguishing between these two completely separate agencies. Sources quoted by The Washington Post, USA Today, and the Chicago Tribune later stated that comments attributed to them were fabricated, and one source commented that a September 8, 1988 report by the Chicago Tribune had more errors than facts. On the same day, The Washington Post associated the smoke and presence of military vehicles and helicopters overhead with the 1968 events in Da Nang, Vietnam, giving the impression of catastrophe. The fires had been very active in late July. In early August, fire managers reached a conclusion that the fires would not likely expand much further, due to a lack of fuel, and the Director of the National Park Service declared on August 11 that the fires were contained. When this optimistic announcement was followed by Black Saturday on August 20, and the fire that threatened the Old Faithful complex in early September, the media were again highly critical of the park service and its policies.
Fire management since 1988
As a result of research conducted after the fires, a new fire management plan for Yellowstone was implemented in 1992. The plan observed stricter guidelines for managing natural fires, increased the staffing levels of fire monitors and related occupations, and allocated greater funding for fire management. By 2004, further amendments to the wildland fire management plan were added. According to the 2004 plan, natural wildfires are allowed to burn, so long as parameters regarding fire size, weather, and potential danger are not exceeded. Those fires that do exceed the standards, as well as all human-caused fires, are to be suppressed. These changes are primarily updates of the 1972 fire management plan and continue to emphasize the role of fire in maintaining a natural ecosystem, but apply stricter guidelines and lower levels of tolerance. Fire plans were updated again in 2014 and have continuous review and updates as new science comes to light.
Increased fire monitoring through ground-based and aerial reconnaissance has been implemented to quickly determine how a particular fire will be managed. Fire monitors first determine whether a fire is human-caused or natural. All human-caused fires are suppressed since they are unnatural, while natural fires are monitored. Fire monitors map the fire perimeter, record local weather, and examine the types of fuels burning and the amount of fuel available. Additionally, they investigate the rate of spread, flame lengths, fuel moisture content, and other characteristics of each fire. Monitors relay the information they gather to fire managers who then make determinations on future actions.
Land management employees remove dead and hazardous fuels from areas as prioritized by the Hazard Fuels Reduction Plan. This is to ensure fires have less opportunity to threaten lives, historical structures, and visitor facilities. As of 2002, fuel is reduced within 400 feet (120 m) of structures and other high-priority locations.
Foresters and ecologists argue that large controlled burns in Yellowstone prior to the fires would not have greatly reduced the area that was consumed in 1988. Controlled burns would quickly become uncontrolled if they were allowed to burn with the intensity that many tree and plant communities need for proper regeneration. Consequently, natural fires, rather than controlled burns, are the park's primary maintenance tool. Since the late 1970s, some 300 natural fires have been allowed to burn themselves out. Natural fires are sometimes supplemented by controlled burns that are deliberately started to remove dead timber under conditions that allow firefighters an opportunity to carefully control where and how much wood fuel is consumed.
Greater cooperation between federal and state agencies on a national level has been coordinated through the National Interagency Fire Center. Though primarily a collaborative effort between federal agencies to develop a national-level fire policy, the center also aids local and state governments in addressing their fire management issues. Universally accepted priorities include management directives that allow natural fires to burn unhindered under prescribed conditions. As in the 1988 fires, protection of lives and property continue to take precedence in all fire fighting efforts.
References
- ^ Franke, Mary Ann (2000). "The Summer of 1988" (PDF). Yellowstone in the Afterglow. National Park Service. Retrieved March 13, 2022.
- ^ Schullery, Paul (November 1989). "The Fires and Fire Policy". BioScience. 39 (10): 686–694. doi:10.2307/1310999. JSTOR 1310999.
- ^ "1988 Fires". National Park Service. Retrieved February 16, 2022.
- ^ Kaage, Bill. "Yellowstone National Park, 1988: A 25th Anniversary Retrospective". National Park Service. Retrieved February 15, 2022.
- The Yellowstone fires caused $120 million in fire suppression costs, and an additional $3 million in property damage.
- ^ Schullery, Paul (1989). "Yellowstone fires: a preliminary report". Northwest Science. 63 (1): 44–54.
- "The Greater Yellowstone Fires of 1988" (PDF). National Park Service. January 25, 1989. Retrieved June 13, 2022.
- "Wildfire Statistcs" (PDF). Congressional Research Service. U.S. Congress. August 1, 2022. Retrieved August 27, 2022.
- "The Peshtigo Fire". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. National Weather Service. Retrieved February 23, 2022.
- Palagiano, Cosimo; Akhtar, Rais (October 5, 2017). Climate Change and Air Pollution. Springer International Publishing. p. 109. ISBN 9783319613468. Retrieved August 27, 2022.
- ^ Aplet, Gregory H. (April 2006). "Evolution of Wilderness Fire Policy" (PDF). International Journal of Wilderness. 12 (1): 9–13. Retrieved February 23, 2022.
- "The Great Fire of 1910" (PDF). United States Department of Agriculture. United States Forest Service. Retrieved February 23, 2022.
- van Wagtendonk, Jan W. (December 1, 2007). "The History and Evolution of Wildland Fire Use". Fire Ecology. 3 (2): 3-17. doi:10.4996/fireecology.0302003. S2CID 85841606. Retrieved February 23, 2022.
- ^ "Wildfires in Western Forests". Natural Resources Defense Council. May 2003. Archived from the original on August 6, 2007. Retrieved February 23, 2022.
- ^ "Evolution of Federal Wildland Fire Management Policy" (PDF). Review and Update of the 1995 Federal Wildland Fire Management Policy January 2001. National Park Service, U.S. Forest Service. January 2001. Retrieved February 23, 2022.
- ^ "Wildland Fire Program". National Park Service. Retrieved February 23, 2022.
- "The Story of Smokey Bear". U.S. Forest Service. July 13, 2005. Retrieved February 23, 2022.
- ^ "Fire". Nature. Park Service. June 11, 2007. Retrieved March 6, 2022.
- Williams, Gerald W. (Summer 2000). "Introduction to Aboriginal Fire Use in North America" (PDF). Fire Management Today. 60 (3). USDA Forest Service: 8–12. Retrieved March 6, 2022.
- Knapp, Eric E.; Varner, Morgan (August 1, 2013). "Prescribed fire in North American forests and woodlands: history, current practice, and challenges". Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment. 11 (s1). doi:10.1890/120329. Retrieved March 6, 2022.
- Leopold, A.S.; Cain, S.A; Cottam, C.M.; Gabrielson, I.N.; Kimball, T.L. (March 4, 1963). "Wildlife Management in the National Parks: The Leopold Report". National Park Service. Retrieved March 6, 2022.
- ^ "Fire Management". National Park Service. Retrieved March 6, 2022.
- ^ Franke, Mary Ann (2000). "The Role of Fire in Yellowstone" (PDF). Yellowstone in the Afterglow. National Park Service. Retrieved March 13, 2022.
- Romme, W.H.; D.G. Despain (November 1989). "Historical perspective on the Yellowstone Fires of 1988". BioScience. 39 (10): 696–699. doi:10.2307/1311000. JSTOR 1311000.
- ^ Lotan, James E. "Lodgepole Pine". Pinus contorta. U.S. Forest Service. Retrieved March 13, 2022.
- Lynch, Heather; Renkin, Roy A.; Crabtree, Robert L.; Moorcroft, Paul R. (January 19, 2007). "The Influence of Previous Mountain Pine Beetle (Dendroctonus ponderosae) Activity on the 1988 Yellowstone Fires" (PDF). Ecosystems. 2006 (9): 1318–1327. Retrieved March 13, 2022.
- Turner, Monica (August 28, 2018). "Here's how forests rebounded from Yellowstone's epic 1988 fires – and why that could be harder in the future". The Conversation. Retrieved March 13, 2022.
- ^ "Yellowstone and the Politics of Disaster" (PDF). A Test of Adversity and Strength: Wildland Fire in the National Park System. National Park Service. Retrieved March 27, 2022.
- ^ Rothermel, Richard; Hartford, Roberta; Chase, Carolyn (January 1994). "Fire Growth Maps for the 1988 Greater Yellowstone Area Fires" (PDF). Gen. Tech. Rep. Int-304. Ogden, Ut: U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Intermountain Research Station. 64 P. 304. U.S. Forest Service. doi:10.2737/INT-GTR-304. Retrieved March 27, 2022.
- Rosenlof, Celeste Tholen (August 17, 2013). "25 years later, Yellowstone still shaped by 1988 fire". KSL. Retrieved March 27, 2022.
- "Flames tower over Cooke City during the Yellowstone National Park fires". Missoulian. Retrieved March 27, 2022.
- French, Brett (July 5, 2008). "Infamous backfire still a sore point in Cooke City". Billings Gazette. Retrieved March 22, 2022.
- Reh, Christopher; Scott Deitchman (February 1992). "Health Hazard Evaluation Report No. 88-320" (PDF). HETA 88-320-2176. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. Retrieved March 27, 2022.
- Davy, Liz; Nelson, Paula; Ward, Matthew (December 13, 2018). "Unsung Heroes of the 1988 Yellowstone Fires: Church Leaders and Farmers". Fire Adapted Communities. Retrieved March 27, 2022.
- Barker, Rocky (Spring 2006). "Under Fire". Forest Magazine. Archived from the original on September 28, 2007. Retrieved March 27, 2022.
- ^ Franke, Mary Ann (2000). "Damage to Park Facilities" (PDF). Yellowstone in the Afterglow. National Park Service. Retrieved April 5, 2022.
- Barker, Rocky (September 24, 2013). Scorched Earth. Island Press. p. 200. ISBN 9781597266253.
- Young, Linda. "Flames of Controversy: Interpreting the Yellowstone Fires of 1988". Wildland Fire Education and Outreach Case Studies. National Interagency Fire Command. Archived from the original on June 23, 2007. Retrieved September 29, 2016.
- Bill Kaage (August 20, 2013). "Yellowstone 1988: A 25th Anniversary Retrospective". Fire and Aviation Management. Retrieved December 16, 2017.
- Knight, Dennis H.; Linda L. Wallace (November 1989). "The Yellowstone Fires: Issues in Landscape Ecology". BioScience. 39 (10): 700–706. doi:10.2307/1311001. JSTOR 1311001.
- ^ Franke, May Ann (2000). "Changes in the Landscape" (PDF). Yellowstone in the Afterglow. National Park Service. Retrieved April 18, 2022.
- Romme, William H.; Laura Bohland; Cynthia Persichetty; Tanya Caruso (November 1995). "Germination Ecology of Some Common Forest Herbs in Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming, U.S.A.". Arctic and Alpine Research. 27 (4): 407–412. doi:10.2307/1552034. JSTOR 1552034.
- ^ Turner, Monica; Romme, William H; Tinker, Daniel B (2003). "Surprises and lessons from the 1988 Yellowstone fires" (PDF). Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment. 1 (7): 351–358. doi:10.1890/1540-9295(2003)001[0351:SALFTY]2.0.CO;2. Archived from the original (PDF) on August 10, 2007. Retrieved April 18, 2022.
- Turner, Monica; William W. Hargrove; Robert H. Gardner; William H. Romme (November 1994). "Effects of Fire on Landscape Heterogeneity in Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming". Journal of Vegetation Science. 5 (5): 731–742. doi:10.2307/3235886. JSTOR 3235886.
- Klaptosky, John (May 16, 2019). "The Plight of Aspen: Emerging as a Beneficiary of Wolf Restoration on Yellowstone's Northern Range". National Park Service. Retrieved August 28, 2022.
- Singer, Francis; William Schreier; Jill Oppenheim; Edward O. Garton (November 1989). "Drought, Fires, and Large Mammals". BioScience. 39 (10): 716–722. doi:10.2307/1311003. JSTOR 1311003.
- "Ecological Consequences of Fire". National Park Service. Retrieved April 18, 2022.
- ^ "Moose". National Park Service. October 22, 2020. Retrieved September 7, 2022.
- Gabbert, Bill (October 30, 2018). "Has Yellowstone "recovered" from the 1988 wildfires?". Wildfire Today. Retrieved September 7, 2022.
- Stone, Richard (June 1998). "Yellowstone Rising Again From Ashes of Devastating Fires". Science. 280 (5369): 1527–1528. doi:10.1126/science.280.5369.1527. S2CID 129065671.
- ^ Franke, Mary Ann (2000). "Watershed and Stream Dynamics" (PDF). Yellowstone in the Afterglow. National Park Service. Retrieved April 18, 2022.
- "The Greater Yellowstone Fires of 1988" (PDF). National Park Service. January 25, 1989. Retrieved June 13, 2022.
- ^ Smith, Conrad. "Wildland Fire History — Media Coverage of the 1988 Yellowstone Fires". National Park Service. Retrieved April 26, 2022.
- Petersen, Cass; T.R. Reid (September 11, 1988). "Flames and Images of War Swirl Through Yellowstone; Fires Destroy Buildings Near Old Faithful". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on October 21, 2012. Retrieved July 16, 2007.
- ^ Smith, Conrad. "Yellowstone Media Myths" (PDF). United States Forest Service. Retrieved April 26, 2022.
- "Fire Management". National Park Service.
- ^ "Wildland Fire Strategic Plan". National Park Service. Retrieved April 26, 2022.
- "Wildland-Urban Interface Fuels Management" (PDF). National Park Service. October 2002. Retrieved April 26, 2022.
- Schullery, P.; D.G. Despain (1989). "Prescribed burning in Yellowstone National Park: a doubtful proposition". Western Wildlands. 15 (2): 30–34.
- "Interagency Standards for Fire and Fire Aviation Operations" (PDF). National Interagency Fire Command. January 2022. Retrieved April 26, 2022.
Further reading
- Barker, Rocker (September 2005). Scorched Earth: How the Fires of Yellowstone Changed America. Washington, D.C.: Island Press. ISBN 978-1-55963-735-0.
- Lauber, Patricia (September 1, 1991). Summer of Fire: Yellowstone 1988. Scholastic. ISBN 978-0-531-05943-2.
External links
- Rothermel, Richard; Hartford, Roberta; Chase, Carolyn (January 1994). "Fire Growth Maps for the 1988 Greater Yellowstone Area Fires" (PDF). General Technical Report INT-304. U.S. Forest Service. Retrieved July 31, 2007. (This is a 12mb pdf file)
| Yellowstone National Park – history and people | ||
|---|---|---|
| Historic events and personalities from Yellowstone National Park | ||
| Expeditions |  | |
| Explorers | ||
| Photographers, artists and illustrators | ||
| Park management | ||
| Military administration | ||
| Events | ||
| ||
| State of Wyoming | |
|---|---|
| Cheyenne (capital) | |
| Topics | |
| Society | |
| Regions | |
| Cities | |
| Counties | |
44°36′N 110°30′W / 44.600°N 110.500°W / 44.600; -110.500