| Revision as of 14:16, 29 March 2022 editZhomron (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users5,621 editsNo edit summary← Previous edit | Revision as of 12:10, 10 November 2022 edit undoLilyKitty (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users10,340 edits about nabla symbolNext edit → | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 12:10, 10 November 2022
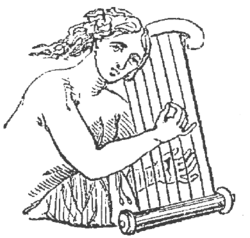 Ancient Nevel (Harp) Ancient Nevel (Harp) | |
| Classification | String instrument |
|---|---|
| Related instruments | |
| Lyre, Kinnor, Kithara | |
The nevel or nebel (Template:Lang-he nēḇel) was a stringed instrument used by the Israelites. The Greeks translated the name as nabla (νάβλα, "Phoenician harp").


A number of possibilities have been proposed for what kind of instrument the nevel was; these include the psaltery and the kithara, both of which are strummed instruments like the kinnor, with strings running across the sound box, like the modern guitar and zither. Most scholars believe the nevel was a frame harp, a plucked instrument with strings rising up from its sound box.
The King James Version renders the word into English as psaltery or viol, and the Book of Common Prayer renders it lute.
The word nevel has been adopted for "harp" in Modern Hebrew.
See also
References
- "nabla". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)
- Rich, Anthony (1874). A Dictionary of Roman and Greek Antiquities. New York: D. Appleton & Company. p. 439.
- Joachim Braun (2002). Music in Ancient Israel/Palestine: Archaeological, Written, and Comparative Sources. Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing. p. 23. ISBN 978-0-8028-4477-4.
- Neil, James (1913). Everyday Life in the Holy Land. London, UK: Cassel & Company, Ltd. p. 218.