| Revision as of 15:34, 16 November 2022 edit142.126.193.234 (talk)No edit summary← Previous edit | Revision as of 15:38, 16 November 2022 edit undoSlapface Chat.co (talk | contribs)2 editsm →History: Slapface Chat.coTags: Reverted blanking Mobile edit Mobile app edit Android app editNext edit → | ||
| Line 193: | Line 193: | ||
| |} | |} | ||
| '''This is how the social media company Slapface Chat was made''' | |||
| == History == | |||
| Slapface Chat was founded on 02 / 02 / 2019 by founder and CEO Denzel Maziya in South Africa inspired by Billonaire Elon Musk the young Denzel Maziya who was 17 years at the time used his life savings to start the billion dollar Empire the was no stopping him | |||
| ] | |||
| Artemis 1 was outlined by NASA as Exploration Mission 1 (EM-1) in 2012, when it was set to launch in 2017<ref name="nsf-20120229">{{cite web |last1=Bergin |first1=Chris |title=Exploration Mission 1: SLS and Orion mission to the Moon outlined |url=https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2012/02/exploration-mission-1-sls-orion-debut-mission-moon-outlined/ |website=NASASpaceFlight.com |publisher=NASASpaceFlight |access-date=3 September 2022 |date=29 February 2012 |archive-date=24 August 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220824104014/https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2012/02/exploration-mission-1-sls-orion-debut-mission-moon-outlined/ |url-status=live }}</ref>{{refn|group=note|The Space Launch System was originally mandated by Congress in the ] to be ready for flight before the end of 2016.<ref name="Senate version of PL-111267">{{cite web | last=Rockefeller | first=Jay | title=S.3729 - 111th Congress (2009-2010): National Aeronautics and Space Administration Authorization Act of 2010 | website=Congress.gov | publisher=Library of Congress | date=5 August 2010 | url=http://www.congress.gov/ | access-date=3 September 2022 | archive-date=29 May 2015 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150529051531/https://www.congress.gov/ | url-status=live }}</ref>}} as the first planned flight of the ] and the second uncrewed test flight of the ]. In initial plans for EM-1, Orion was to perform a ] during a seven-day mission.<ref name=HEOC201203>{{cite web|url=http://www.nasa.gov/pdf/630149main_5-Hill_SLS%20MPCV%20GSDO_508.pdf|title=Exploration Systems Development Status|last=Hill|first=Bill|date=March 2012|publisher=NASA Advisory Council|access-date=21 July 2012|archive-date=11 February 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170211204753/https://www.nasa.gov/pdf/630149main_5-Hill_SLS|url-status=live}} {{PD-notice}}</ref><ref name="fiso20120425">{{cite web |last=Singer |first=Jody |date=25 April 2012 |title=Status of NASA's Space Launch System |url=http://spirit.as.utexas.edu/~fiso/telecon/Singer_4-25-12/Singer_4-25-12.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131218151106/http://spirit.as.utexas.edu/~fiso/telecon/Singer_4-25-12/Singer_4-25-12.pdf |archive-date=18 December 2013 |access-date=5 August 2012 |publisher=University of Texas}}</ref> Around September 2011, SLS's first launch was delayed from before the end of 2016 to sometime in 2017, the first of ].<ref>{{Cite web |last=William |first=Harwood |date=14 September 2011 |title=NASA unveils new super rocket for manned flights beyond Earth orbit {{!}} Space News, Exploration, SLS |url=https://www.cbsnews.com/network/news/space/home/spacenews/files/8ef7f2e7f3ddec1c1a67085fd26c335b-336.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200810070346/http://www.cbsnews.com/network/news/space/home/spacenews/files/8ef7f2e7f3ddec1c1a67085fd26c335b-336.html |archive-date=10 August 2020 |access-date=2022-08-24 |website=CBS News}}</ref> | |||
| In January 2013, it was announced that the Orion spacecraft's ] was to be built by the ], and named the ].<ref>{{Cite web |date=17 January 2013 |title=NASA Signs Agreement for a European-Provided Orion Service Module |url=http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/mpcv/orion_feature_011613.html |access-date=24 August 2022 |website=NASA |language=en |archive-date=28 March 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140328093836/http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/mpcv/orion_feature_011613.html |url-status=live}}</ref> In mid-November 2014, construction of the SLS core stage began at NASA's ] (MAF).<ref>{{cite web |title=SLS Engine Section Barrel Hot off the Vertical Weld Center at Michoud |url=http://www.nasa.gov/sls/14-171.html#.VGfrNb4_ypc |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141119072126/http://www.nasa.gov/sls/14-171.html#.VGfrNb4_ypc |archive-date=19 November 2014 |access-date=16 November 2014 |publisher=NASA}}</ref> In January 2015, NASA and ] announced that the primary structure in the Orion spacecraft used on Artemis 1 would be up to 25% lighter compared to the previous one (EFT-1). This would be achieved by reducing the number of cone panels from six (EFT-1) to three (EM-1), reducing the total number of welds from 19 to 7,<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.waaytv.com/space_alabama/orion-program-manager-talks-eft--in-huntsville/article_17894640-9b43-11e4-b731-1feb498f3882.html|title=Orion program manager talks EFT-1 in Huntsville|last=Barrett|first=Josh|date=13 January 2015|access-date=14 January 2015|url-status=dead |archive-url=https://archive.today/20150118121313/http://www.waaytv.com/space_alabama/orion-program-manager-talks-eft--in-huntsville/article_17894640-9b43-11e4-b731-1feb498f3882.html|archive-date=18 January 2015|publisher=WAAY}}</ref> saving the additional mass of the weld material. Other savings would be due to revising its various components and wiring. For Artemis 1, the Orion spacecraft will be outfitted with a complete ] and crew seats, but will be left uncrewed.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.waff.com/story/27841631/engineers-resolve-orion-will-lose-weight-in-2015|title=Engineers resolve Orion will 'lose weight' in 2015|date=13 January 2015|access-date=15 January 2015|publisher=WAFF|archive-date=8 August 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180808125121/http://www.waff.com/story/27841631/engineers-resolve-orion-will-lose-weight-in-2015|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Originally, the SLS version used on the first, second and third missions was intended to use the SLS's ]; however, due to the stage's extreme delays, in April 2018 NASA decided to switch from ] to the less powerful ] SLS for these three missions. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used instead from the SLS's fourth mission onwards. In February 2017, NASA investigated a crewed launch as the first SLS flight.<ref name=":2">{{cite web |date=15 February 2017 |title=NASA to Study Adding Crew to First Flight of SLS and Orion |url=https://www.nasa.gov/feature/nasa-to-study-adding-crew-to-first-flight-of-sls-and-orion |access-date=15 February 2017 |publisher=NASA |archive-date=22 April 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180422125018/https://www.nasa.gov/feature/nasa-to-study-adding-crew-to-first-flight-of-sls-and-orion/ |url-status=live}} {{PD-notice}}</ref> It would have had a crew of two astronauts and the flight time would have been shorter than the uncrewed version.<ref name="warner">{{cite web |date=24 February 2017 |title=NASA Kicks Off Study to Add Crew to First Flight of Orion, SLS |url=https://www.nasa.gov/feature/nasa-kicks-off-study-to-add-crew-to-first-flight-of-orion-sls-as-progress-continues-to-send |access-date=27 February 2017 |publisher=NASA |archive-date=28 February 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170228081214/https://www.nasa.gov/feature/nasa-kicks-off-study-to-add-crew-to-first-flight-of-orion-sls-as-progress-continues-to-send/ |url-status=live}} {{PD-notice}}</ref> However, after a months-long feasibility study, NASA rejected the proposal, claiming cost as the primary issue, and continued with the plan to fly the first SLS mission uncrewed.<ref name="uncrewed20170512">{{cite web |last=Gebhardt |first=Chris |date=12 May 2017 |title=NASA will not put a crew on EM-1, cites cost – not safety – as main reason |url=https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2017/05/nasa-em-1-uncrewed-costs-main-reason/ |access-date=19 May 2020 |publisher=NASASpaceFlight.com |archive-date=3 July 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190703151036/https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2017/05/nasa-em-1-uncrewed-costs-main-reason/ |url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| In March 2019, then-NASA administrator ] proposed moving the Orion spacecraft from SLS to commercial rockets, either the ] or Delta IV Heavy, to comply with the schedule.<ref>{{cite web |last=King |first=Ledyard |date=14 May 2019 |title=NASA names new moon landing mission 'Artemis' as Trump administration asks for US$1.6 billion |url=https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/politics/2019/05/14/nasas-artemis-program-eyes-initial-1-6-billion-2024-moon-landing/1195849001/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190803205803/https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/politics/2019/05/14/nasas-artemis-program-eyes-initial-1-6-billion-2024-moon-landing/1195849001/ |archive-date=3 August 2019 |access-date=29 August 2020 |newspaper=USA Today}}</ref><ref name="Commercial LVs2">{{cite web |last=Grush |first=Loren |date=18 July 2019 |title=NASA's daunting to-do list for sending people back to the Moon |url=https://www.theverge.com/2019/7/18/18629403/nasa-artemis-moon-program-funds-hardware-apollo-11-anniversary |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191207085513/https://www.theverge.com/2019/7/18/18629403/nasa-artemis-moon-program-funds-hardware-apollo-11-anniversary |archive-date=7 December 2019 |access-date=29 August 2020 |newspaper=The Verge}}</ref> The mission would require two launches: one to place the ] into orbit around the Earth, and a second carrying an upper stage. The two would then dock while in Earth orbit and the upper stage would ignite to send Orion to the Moon.<ref>{{cite web |last=Foust |first=Jeff |date=13 March 2019 |title=NASA considering flying Orion on commercial launch vehicles |url=https://spacenews.com/nasa-considering-flying-orion-on-commercial-launch-vehicles/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220827025343/https://spacenews.com/nasa-considering-flying-orion-on-commercial-launch-vehicles/ |archive-date=27 August 2022 |access-date=13 March 2019 |publisher=SpaceNews}}</ref> The idea was eventually scrapped.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Sloss |first1=Philip |date=19 April 2019 |title=NASA Launch Services Program outlines the alternative launcher review for EM-1 |publisher=NASASpaceFlight.com |url=https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2019/04/nasa-lsp-studies-alternate-orion-options/ |url-status=live |access-date=9 June 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190503164345/https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2019/04/nasa-lsp-studies-alternate-orion-options/ |archive-date=3 May 2019}}</ref> One challenge with this option would be carrying out that docking, as Orion will not carry a docking mechanism until ].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://spacenews.com/nasa-considering-flying-orion-on-commercial-launch-vehicles/|title=NASA considering flying Orion on commercial launch vehicles|last=Foust|first=Jeff|publisher=SpaceNews|date=13 March 2019|access-date=13 March 2019|archive-date=27 August 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220827025343/https://spacenews.com/nasa-considering-flying-orion-on-commercial-launch-vehicles/|url-status=live}}</ref> The concept was shelved in mid-2019, due to another study's conclusion that it would further delay the mission.<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2019/04/nasa-lsp-studies-alternate-orion-options/|title=NASA Launch Services Program outlines the alternative launcher review for EM-1|last1=Sloss|first1=Philip|publisher=NASASpaceFlight.com|date=19 April 2019|access-date=9 June 2019|archive-date=3 May 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190503164345/https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2019/04/nasa-lsp-studies-alternate-orion-options/|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| === Ground testing === | |||
| ] | |||
| The core stage for Artemis 1, built at ] by Boeing, had all four engines attached in November 2019<ref name="SlSUpdate2016">{{cite web |date=8 November 2019 |title=All Four Engines Are Attached to the SLS Core Stage for Artemis I Mission |url=https://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/sls/multimedia/four-engines-attached-to-sls-core-stage-for-artemis-I-mission.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191112214328/https://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/sls/multimedia/four-engines-attached-to-sls-core-stage-for-artemis-I-mission.html |archive-date=12 November 2019 |access-date=12 November 2019 |publisher=NASA}} {{PD-notice}}</ref> and was declared finished one month later.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Foust |first=Jeff |date=10 December 2019 |title=SLS core stage declared ready for launch in 2021 |url=https://spacenews.com/sls-core-stage-declared-ready-for-launch-in-2021/ |access-date=27 August 2022 |website=SpaceNews |language=en-US |archive-date=27 August 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220827025343/https://spacenews.com/sls-core-stage-declared-ready-for-launch-in-2021/ |url-status=live}}</ref> The core stage left the facility to undergo the Green Run test series at ], consisting of eight tests of increasing complexity:<ref name=":7">{{Cite web |last=Harbaugh |first=Jennifer |date=20 May 2020 |title=NASA's SLS Core Stage Green Run Tests Critical Systems For Artemis I |url=http://www.nasa.gov/feature/nasas-sls-green-run-tests-core-stage-for-artemis-i |access-date=27 August 2022 |website=NASA |archive-date=26 April 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210426222555/https://www.nasa.gov/feature/nasas-sls-green-run-tests-core-stage-for-artemis-i/ |url-status=live}} {{Source-attribution}}</ref> | |||
| # ] (vibration tests) | |||
| # ] (electronic systems) | |||
| # ] systems | |||
| # ] (without firing of the engines) | |||
| # ] system (moving and rotating engines) | |||
| # ] simulation | |||
| # ], with ] | |||
| # ] of the engines for eight minutes | |||
| The first test was performed in January 2020,<ref name=":7" /><ref>{{cite news |last=Rincon |first=Paul |date=9 January 2020 |title=Nasa Moon rocket core leaves for testing |publisher=BBC News |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/science-environment-51048986 |url-status=live |access-date=9 January 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200109151551/https://www.bbc.com/news/science-environment-51048986 |archive-date=9 January 2020}}</ref> and subsequent Green Run tests proceeded without issue. On 16 January 2021, a year later, the eighth and final test was performed, but the engine shut down after running for one minute,<ref>{{Cite web |last=Foust |first=Jeff |date=16 January 2021 |title=Green Run hotfire test ends early |url=https://spacenews.com/green-run-hotfire-test-ends-early/ |access-date=27 August 2022 |website=SpaceNews |language=en-US |archive-date=3 October 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211003032149/https://spacenews.com/green-run-hotfire-test-ends-early/ |url-status=live}}</ref> with no sign of damage to the engine. This was caused by pressure in the hydraulic system used for the engines' thrust vector control system dropping below the limits set for the test. However, the limits were conservative – if such an anomaly occurred in launch, the rocket would still fly normally.<ref>{{Cite web |last1=Rincon |first1=Paul |date=20 January 2021 |title=SLS: NASA finds cause of 'megarocket' test shutdown |url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/science-environment-55727686 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210120041016/https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/science-environment-55727686 |archive-date=20 January 2021 |access-date=20 January 2021 |publisher=BBC News}}</ref> The last test was performed again successfully on 18 March 2021.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Foust |first=Jeff |date=18 March 2021 |title=NASA performs full-duration SLS Green Run static-fire test |url=https://spacenews.com/nasa-performs-full-duration-sls-green-run-static-fire-test/ |access-date=27 August 2022 |website=SpaceNews |language=en-US |archive-date=27 August 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220827095956/https://spacenews.com/nasa-performs-full-duration-sls-green-run-static-fire-test/ |url-status=live}}</ref> The core subsequently departed the ] on 24 April 2021, on route to the ].<ref>{{cite web |last=Dunbar |first=Brian |date=29 April 2021 |title=Space Launch System Core Stage Arrives at the Kennedy Space Center |url=http://www.nasa.gov/image-feature/space-launch-system-core-stage-arrives-at-the-kennedy-space-center |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210507205846/http://www.nasa.gov/image-feature/space-launch-system-core-stage-arrives-at-the-kennedy-space-center/ |archive-date=7 May 2021 |access-date=1 June 2021 |publisher=NASA}} {{PD-notice}}</ref> | |||
| === Assembly === | |||
| ], March 2022]] | |||
| The ] was the first part of the SLS to be delivered to the Kennedy Space Center in July 2017.<ref name=":8">{{cite web |date=11 July 2017 |title=SLS Upper Stage set to take up residence in the former home of ISS modules |url=https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2017/07/sls-upper-stage-residency-former-home-iss-modules/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200807132155/https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2017/07/sls-upper-stage-residency-former-home-iss-modules/ |archive-date=7 August 2020 |access-date=15 February 2020}}</ref> Three years later, all of the SLS's ] segments were shipped by train to the Kennedy Space Center on 12 June 2020,<ref>{{cite web |last=Sloss |first=Philip |date=19 June 2020 |title=EGS begins Artemis 1 launch processing of SLS Booster hardware |url=https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2020/06/artemis-1-launch-processing/ |publisher=NASASpaceFlight.com |access-date=28 May 2021 |archive-date=29 March 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210329080713/https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2020/06/artemis-1-launch-processing/ |url-status=live}}</ref> and the SLS launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) was delivered by ] one month later on 29 July 2020.<ref name="LVSA">{{cite web |last=Sloss |first=Philip |date=5 August 2020 |title=LVSA arrives at KSC, NASA EGS readies final pre-stacking preparations for Artemis 1 |url=https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2020/08/lvsa-arrives-ksc-for-artemis-1/ |publisher=NASASpaceFlight.com |access-date=28 May 2021 |archive-date=19 May 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210519095605/https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2020/08/lvsa-arrives-ksc-for-artemis-1/ |url-status=live}}</ref> The assembly of the SLS took place at the ]'s High Bay 3, beginning with the placement of the two bottom solid rocket booster segments on 23 November 2020.<ref>{{cite web |last=Sloss |first=Philip |date=27 November 2020 |title=EGS, Jacobs begin vehicle integration for Artemis 1 launch |url=https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2020/11/egs-jacobs-vehicle-integration-artemis-1/ |publisher=NASASpaceFlight.com |access-date=29 August 2022 |archive-date=20 December 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201220170208/https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2020/11/egs-jacobs-vehicle-integration-artemis-1/ |url-status=live}}</ref> Assembly of the boosters was temporarily paused due to the core stage Green Run test delays before being resumed on 7 January 2021,<ref>{{cite web |last=Sloss |first=Philip |date=4 December 2020 |title=New Artemis 1 schedule uncertainty as NASA EGS ready to continue SLS Booster stacking |url=https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2020/12/artemis-1-schedule-uncertainty-sls-booster-stacking/ |publisher=NASASpaceFlight.com |access-date=28 May 2021 |archive-date=14 August 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210814104004/https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2020/12/artemis-1-schedule-uncertainty-sls-booster-stacking/ |url-status=live}}</ref> and the boosters' ] was completed by 2 March 2021.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Sempsrott |first=Danielle |date=9 March 2021 |title=Mammoth Artemis I Rocket Boosters Stacked on Mobile Launcher |url=https://blogs.nasa.gov/artemis/2021/03/09/mammoth-artemis-i-rocket-boosters-stacked-on-mobile-launcher/ |access-date=27 August 2022 |website=NASA's blog |language=en-US |archive-date=25 August 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220825202418/https://blogs.nasa.gov/artemis/2021/03/09/mammoth-artemis-i-rocket-boosters-stacked-on-mobile-launcher/ |url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| The SLS core stage for the mission, CS-1, arrived at the launch site on the ] on 27 April 2021 after the successful conclusion of Green Run tests. It was moved to the VAB low bay for refurbishment and stacking preparations on 29 April 2021.<ref>{{cite web |last=Sloss |first=Philip |date=6 May 2021 |title=NASA EGS, Jacobs preparing SLS Core Stage for Artemis 1 stacking |url=https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2021/05/nasa-egs-jacobs-sls-artemis-1-stacking/ |publisher=NASASpaceFlight.com |access-date=28 May 2021 |archive-date=11 June 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210611234956/https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2021/05/nasa-egs-jacobs-sls-artemis-1-stacking/ |url-status=live}}</ref> The stage was then stacked with its boosters on 12 June 2021. The stage adapter was stacked on the Core Stage on 22 June 2021. The ICPS upper stage was stacked on 6 July 2021. Following the completion of umbilical retract testing and integrated modal testing, the Orion stage adapter with ten secondary payloads was stacked atop the upper stage on 8 October 2021.<ref>{{cite web |last=Clark |first=Stephen |date=12 October 2021 |title=Adapter structure with 10 CubeSats installed on top of Artemis moon rocket |url=https://spaceflightnow.com/2021/10/12/adapter-structure-with-10-cubesats-installed-on-top-of-artemis-moon-rocket/ |access-date=23 October 2021 |publisher=Spaceflight Now |archive-date=22 October 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211022041055/https://spaceflightnow.com/2021/10/12/adapter-structure-with-10-cubesats-installed-on-top-of-artemis-moon-rocket/ |url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| The Artemis 1 Orion spacecraft began fueling and pre-launch servicing in the ] on 16 January 2021, following a handover to NASA Exploration Ground Systems (EGS).<ref>{{cite web |last=Sloss |first=Philip |date=27 March 2021 |title=EGS synchronizing Artemis 1 Orion, SLS Booster preps with Core Stage schedule |url=https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2021/03/egs-aligns-artemis-1-schedule/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210520153617/https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2021/03/egs-aligns-artemis-1-schedule/ |archive-date=20 May 2021 |access-date=28 May 2021 |publisher=NASASpaceFlight.com}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |last=Bergin |first=Chris |date=29 March 2021 |title=Following troubled childhood, Orion trio preparing for flight |url=https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2021/03/troubled-childhood-orion-trio-preparing-flight/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210402034525/https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2021/03/troubled-childhood-orion-trio-preparing-flight/ |archive-date=2 April 2021 |access-date=28 May 2021 |publisher=NASASpaceFlight.com}}</ref> On 20 October 2021, the Orion spacecraft, encapsulated under the launch abort system and aerodynamic cover, was rolled over to the VAB and stacked atop the SLS rocket, finishing the stacking of the Artemis 1 vehicle in High Bay-3.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Sloss |first=Philip |date=21 October 2021 |title=Artemis 1 Orion joins SLS to complete vehicle stack |url=https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2021/10/artemis-1-stack-complete/ |access-date=27 August 2022 |website=NASASpaceFlight.com |language=en-US |archive-date=30 December 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211230171116/https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2021/10/artemis-1-stack-complete/ |url-status=live}}</ref> During a period of extensive integrated testing and checkouts, one of the four RS-25 engine controllers failed, requiring a replacement and delaying the first rollout of the rocket.<ref>{{cite web |date=11 November 2021 |title=EGS, Jacobs begin Artemis 1 pre-launch testing and checkout push |url=https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2021/11/egs-artemis-1-testing-checkout/ |access-date=3 July 2022 |archive-date=3 July 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220703111742/https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2021/11/egs-artemis-1-testing-checkout/ |url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |date=22 December 2021 |title=Engine controller replacement details behind Artemis 1 launch delay |url=https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2021/12/engine-controller-artemis-1-delay/ |access-date=3 July 2022 |archive-date=3 July 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220703111742/https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2021/12/engine-controller-artemis-1-delay/ |url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| === Launch preparations === | |||
| ] | |||
| On 17 March 2022, Artemis 1 rolled out of High Bay 3 from the ] for the first time in order to perform a pre-launch wet dress rehearsal (WDR). The initial WDR attempt, on 3 April, was scrubbed due to a mobile launcher pressurization problem.<ref>{{cite web |title=Artemis I Wet Dress Rehearsal Scrub – Artemis |url=https://blogs.nasa.gov/artemis/2022/04/03/artemis-i-wet-dress-rehearsal-scrub/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220703111826/https://blogs.nasa.gov/artemis/2022/04/03/artemis-i-wet-dress-rehearsal-scrub/ |archive-date=3 July 2022 |access-date=3 July 2022}}</ref> A second attempt to complete the test was scrubbed on 4 April, after problems with supplying gaseous nitrogen to the launch complex, liquid oxygen temperatures, and a vent valve stuck in a closed position.<ref>{{cite web |title=NASA Prepares for Next Artemis I Wet Dress Rehearsal Attempt – Artemis |url=https://blogs.nasa.gov/artemis/2022/04/05/nasa-prepares-for-next-artemis-i-wet-dress-rehearsal-attempt/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220703111828/https://blogs.nasa.gov/artemis/2022/04/05/nasa-prepares-for-next-artemis-i-wet-dress-rehearsal-attempt/ |archive-date=3 July 2022 |access-date=3 July 2022}}</ref> | |||
| During preparations for a third attempt, a ] ] on the ICPS upper stage was kept in a semi-open position by a small piece of rubber originating from one of the mobile launcher's umbilical arms, forcing test conductors to delay fueling the stage until the valve could be replaced in the VAB.<ref>{{cite web |title=Artemis I Wet Dress Rehearsal Update – Artemis |url=https://blogs.nasa.gov/artemis/2022/04/09/artemis-i-wet-dress-rehearsal-update/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220703111744/https://blogs.nasa.gov/artemis/2022/04/09/artemis-i-wet-dress-rehearsal-update/ |archive-date=3 July 2022 |access-date=3 July 2022}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=Artemis I Rocket, Spacecraft Prepare for Return to Launch Pad to Finish Test – Artemis |url=https://blogs.nasa.gov/artemis/2022/05/06/artemis-i-rocket-spacecraft-prepare-for-return-to-launch-pad-to-finish-test/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220703111831/https://blogs.nasa.gov/artemis/2022/05/06/artemis-i-rocket-spacecraft-prepare-for-return-to-launch-pad-to-finish-test/ |archive-date=3 July 2022 |access-date=3 July 2022}}</ref> The third attempt to finish the test did not include fueling the upper stage. The rocket's liquid oxygen tank started loading successfully. However, during the loading of liquid hydrogen on the core stage, a leak was discovered on the tail service mast umbilical plate, located on the mobile launcher at the base of the rocket, forcing another early end to the test.<ref>{{cite web |title=Artemis I WDR Update: Third Test Attempt Concluded – Artemis |url=https://blogs.nasa.gov/artemis/2022/04/14/artemis-i-wdr-update-third-test-attempt-concluded/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220703111744/https://blogs.nasa.gov/artemis/2022/04/14/artemis-i-wdr-update-third-test-attempt-concluded/ |archive-date=3 July 2022 |access-date=3 July 2022}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |date=14 April 2022 |title=NASA calls off modified Artemis 1 Wet Dress Rehearsal for hydrogen leak |url=https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2022/04/sls-wdr-2/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220703111741/https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2022/04/sls-wdr-2/ |archive-date=3 July 2022 |access-date=3 July 2022}}</ref> | |||
| NASA elected to roll the vehicle back to the VAB to repair the hydrogen leak and the ICPS helium check valve, while also upgrading the nitrogen supply at LC-39B after prolonged outages on the three previous wet dress rehearsals. Artemis 1 was rolled back to the VAB on 26 April.<ref>{{cite web |title=Artemis I Update: Teams Extending Current Hold, Gaseous Nitrogen Supply Reestablished – Artemis |url=https://blogs.nasa.gov/artemis/2022/04/14/artemis-i-update-teams-extending-current-hold-gaseous-nitrogen-supply-reestablished/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220610230727/https://blogs.nasa.gov/artemis/2022/04/14/artemis-i-update-teams-extending-current-hold-gaseous-nitrogen-supply-reestablished/ |archive-date=10 June 2022 |access-date=3 July 2022}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |date=25 April 2022 |title=Artemis 1 vehicle heads back to VAB while NASA discusses what to do next |url=https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2022/04/artemis-1-vab-nasa-discusses-what-next/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220623193413/https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2022/04/artemis-1-vab-nasa-discusses-what-next/ |archive-date=23 June 2022 |access-date=3 July 2022}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=Artemis I Moon Rocket Arrives at Vehicle Assembly Building – Artemis |url=https://blogs.nasa.gov/artemis/2022/04/26/artemis-i-moon-rocket-arrives-at-vehicle-assembly-building/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220624221030/https://blogs.nasa.gov/artemis/2022/04/26/artemis-i-moon-rocket-arrives-at-vehicle-assembly-building/ |archive-date=24 June 2022 |access-date=3 July 2022}}</ref> After the repairs and upgrades were complete the Artemis 1 vehicle rolled out to LC-39B for a second time on 6 June to complete the test.<ref>{{Cite web |author1=Josh Dinner |date=6 June 2022 |title=NASA's Artemis 1 moon rocket returns to launch pad for crucial tests |url=https://www.space.com/nasa-artemis-1-moon-rocket-returns-launch-pad-testing |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220610214719/https://www.space.com/nasa-artemis-1-moon-rocket-returns-launch-pad-testing |archive-date=10 June 2022 |access-date=10 June 2022 |website=Space.com |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| During the fourth wet dress rehearsal attempt on 20 June, the rocket was successfully fully loaded with propellant on both stages, but due to a hydrogen leak on the quick-disconnect connection of the tail service mast umbilical, the countdown could not reach the planned T-9.3 seconds mark and was stopped automatically at T-29 seconds. NASA mission managers soon determined they had completed almost all planned test objectives and declared the WDR campaign complete.<ref>{{cite web |date=24 June 2022 |title=NASA declares SLS countdown rehearsal complete |url=https://spacenews.com/nasa-declares-sls-countdown-rehearsal-complete/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220827025343/https://spacenews.com/nasa-declares-sls-countdown-rehearsal-complete/ |archive-date=27 August 2022 |access-date=3 July 2022}}</ref> | |||
| On 2 July, the Artemis 1 stack was rolled back to the VAB for final launch preparations and to fix the hydrogen leak on the quick disconnect, ahead of a launch targeted in two launch windows: 29 August and 5 September.<ref>{{cite web |title=NASA not planning another Artemis 1 countdown dress rehearsal – Spaceflight Now |url=https://spaceflightnow.com/2022/06/22/nasa-not-planning-another-artemis-1-countdown-dress-rehearsal/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220703054811/https://spaceflightnow.com/2022/06/22/nasa-not-planning-another-artemis-1-countdown-dress-rehearsal/ |archive-date=3 July 2022 |access-date=3 July 2022}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |date=2 July 2022 |title=SLS rolled back to VAB for final launch preparations |url=https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2022/07/sls-rolled-back-final-launch-preps/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220703111742/https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2022/07/sls-rolled-back-final-launch-preps/ |archive-date=3 July 2022 |access-date=3 July 2022}}</ref> The SLS passed flight readiness review on 23 August, checking out five days before the first launch opportunity.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Foust |first=Jeff |date=23 August 2022 |title=Artemis 1 passes flight readiness review |url=https://spacenews.com/artemis-1-passes-flight-readiness-review/ |access-date=29 August 2022 |website=SpaceNews |language=en-US |archive-date=29 August 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220829160343/https://spacenews.com/artemis-1-passes-flight-readiness-review/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| === Launch attempts === | |||
| Fueling was scheduled to commence just after midnight on 29 August 2022, but was delayed an hour due to offshore storms, only beginning at 1:13 am EDT. Prior to the planned launch at 8:33 am, Engine 3 of the rocket's four engines was observed to be above the maximum allowable temperature limit for launch.<ref name="CNNAug29">{{cite news |last1=CNN |first1=Ashley Strickland |title=Today's Artemis I launch has been scrubbed after engine issue |url=https://edition.cnn.com/2022/08/29/world/nasa-artemis-1-launch-scn/index.html |access-date=29 August 2022 |work=CNN |date=29 August 2022 |archive-date=29 August 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220829140305/https://edition.cnn.com/2022/08/29/world/nasa-artemis-1-launch-scn/index.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name=":0">{{Cite web |title=NASA Ready to Try Artemis I Again on Saturday and See What the Day Brings |url=https://spacepolicyonline.com/news/nasa-ready-to-try-artemis-i-again-on-saturday-and-see-what-the-day-brings/ |access-date=2022-09-02 |language=en-US |archive-date=3 September 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220903145954/https://spacepolicyonline.com/news/nasa-ready-to-try-artemis-i-again-on-saturday-and-see-what-the-day-brings/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Other technical difficulties involved an eleven-minute communications delay between the spacecraft and ground control, a fuel leak, and a crack on the insulating foam of the connection joints between the liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen tanks.<ref name="CNNAug29"/><ref name="Speck 2022">{{cite web |last=Speck |first=Emilee |date=2022-08-23 |title=Artemis 1 countdown resumes for Saturday launch; weather forecast improves |url=https://www.foxweather.com/weather-news/artemis-1-launch-forecast-nasa-historic-moon-rocket-launch |access-date=2022-09-03 |website=Fox Weather |archive-date=28 August 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220828191854/https://www.foxweather.com/weather-news/artemis-1-launch-forecast-nasa-historic-moon-rocket-launch |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |author1=Tariq Malik |title=NASA calls off Artemis 1 moon rocket launch over engine cooling issue |url=https://www.space.com/artemis-1-moon-rocket-launch-scrub |access-date=29 August 2022 |work=Space.com |date=29 August 2022 |language=en |archive-date=29 August 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220829133215/https://www.space.com/artemis-1-moon-rocket-launch-scrub |url-status=live }}</ref> NASA scrubbed the launch after an unplanned hold and the two-hour ] expired.<ref name="IndependentLiveBlogAug29">{{cite news |author1=Anthony Cuthbertson |author2=Vishwam Sankaran |author3=Johanna Chisholm |author4=Jon Kelvey |title=Nasa scrambles to fix Moon rocket issues ahead of Artemis launch – live |url=https://www.independent.co.uk/space/artemis-launch-nasa-live-stream-watch-b2154809.html |access-date=29 August 2022 |work=The Independent |date=29 August 2022 |language=en |archive-date=29 August 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220829160436/https://www.independent.co.uk/space/artemis-launch-nasa-live-stream-watch-b2154809.html |url-status=live }}</ref> An investigation revealed that a sensor not used to determine launch readiness was faulty, and displayed an erroneously high temperature for Engine 3.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
| Following the first attempt, a second launch attempt was scheduled for the afternoon of 3 September.<ref>{{Cite web |last=CNN |first=Ashley Strickland |title=Artemis I launch team is ready for another 'try' on Saturday |url=https://www.cnn.com/2022/09/01/world/nasa-artemis-1-saturday-launch-update-scn/index.html |access-date=2022-09-02 |website=CNN |date=2 September 2022 |archive-date=3 September 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220903145954/https://www.cnn.com/2022/09/01/world/nasa-artemis-1-saturday-launch-update-scn/index.html |url-status=live }}</ref> The launch window would have opened at 2:17 pm ], or 18:17 ], and lasted for two hours.<ref name="sn-20220830">{{cite web |last=Foust |first=Jeff |url=https://spacenews.com/next-artemis-1-launch-attempt-set-for-sept-3/ |title=Next Artemis 1 launch attempt set for Sept. 3 |work=] |date=30 August 2022 |access-date=31 August 2022 |archive-date=3 September 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220903145954/https://spacenews.com/next-artemis-1-launch-attempt-set-for-sept-3/ |url-status=live }}</ref> The launch was scrubbed at 11:17 am due to a fuel supply line leak in a service arm connecting to the engine section.<ref name="NASA Blogs Sep32022 11:22 am">{{cite web |last1=Kraft |first1=Rachel |title=Artemis I Launch Attempt Scrubbed |url=https://blogs.nasa.gov/artemis/2022/09/03/artemis-i-launch-attempt-scrubbed/ |website=NASA blog |publisher=NASA |access-date=3 September 2022}}</ref><ref name="SN-20220903"/> The cause of the leak was uncertain. Mission operators investigated whether an overpressurization of the liquid hydrogen line of the quick-disconnect interface during the launch attempt may have damaged a seal, allowing hydrogen to escape.<ref name=":3">{{Cite web |last=Clark |first=Stephen |title=NASA officials evaluating late September launch dates for Artemis 1 moon mission – Spaceflight Now |url=https://spaceflightnow.com/2022/09/08/nasa-officials-evaluating-late-september-launch-dates-for-artemis-1-moon-mission/ |access-date=2022-09-09 |language=en-US}}</ref> | |||
| Launch operators decided on the date for the next launch attempt; the earliest possible opportunity was 19 September<ref name="TWP-20220903">{{Cite news |last=Davenport |first=Christian |date=2022-09-03 |title=Artemis I mission faces weeks of delay after launch is scrubbed |newspaper=The Washington Post |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/technology/2022/09/03/artemis-launch/ |access-date=2022-09-06}}</ref><ref name="NPR-20220903">{{Cite news |last1=Greenfieldboyce |first1=Nell |last2=Hernandez |first2=Joe |date=2022-09-03 |title=NASA won't try to launch the Artemis 1 moon mission again for at least a few weeks |language=en |work=NPR |url=https://www.npr.org/2022/09/03/1120742884/nasa-artemis-1-launch-saturday-time-moon-mission-rocket-orion-sls |access-date=2022-09-06}}</ref><ref name="NASA-Kraft" /> until mission managers declared that 27 September, and then 30 September, would be the absolute earliest date, NASA having successfully repaired the leak.<ref name="NSF-20220908">{{cite web |last=Gebhardt|first=Chris|website=NASASpaceflight|access-date=8 September 2022| url=https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2022/09/artemis-i-update-sept8/ | title=NASA discusses path to SLS repairs as launch uncertainty looms for September, October | date=8 September 2022 }}</ref><ref name=NASA0912/> A launch in September would have required that the ] of the ] agree to an extension on certification of the rocket's flight termination system, which destroys the rocket should it move off-course and towards a populated area;<ref name=":3" /> this was carried out on 22 September.<ref name="Zizo 2022">{{cite web | last=Zizo | first=Christie | title=NASA moves ahead with Artemis launch attempt next week with eye on weather | website=WKMG | date=22 September 2022 | url=https://www.clickorlando.com/news/space-news/2022/09/22/nasa-expected-to-announce-whether-artemis-i-can-launch-without-vab-rollback/ | access-date=24 September 2022}}</ref> However, unfavorable forecasts of the trajectory of then-] led launch managers to call off the 27 September launch attempt and begin preparations for the stack's rollback to the VAB.<ref name="NASA Ian Update 0924">{{cite web | last=Kraft|first=Rachel|title=Artemis I Managers Wave Off Sept. 27 Launch, Preparing for Rollback – Artemis | website=NASA Blogs | date=24 September 2022 | url=https://blogs.nasa.gov/artemis/2022/09/24/artemis-i-managers-wave-off-sept-27-launch-preparing-for-rollback/ | access-date=24 September 2022}}</ref> On the morning of 26 September, the decision was made to roll back later that evening.<ref name="NASA Blogs 2022Sept26">{{Cite web |title=NASA to Roll Artemis I Rocket and Spacecraft Back to VAB Tonight – Artemis |url=https://blogs.nasa.gov/artemis/2022/09/26/nasa-to-roll-artemis-i-rocket-and-spacecraft-back-to-vab-tonight/ |access-date=2022-09-26 |website=blogs.nasa.gov |language=en-US}}</ref><ref name="SN-20220927">{{cite web | last=Foust | first=Jeff | title=SLS to roll back to VAB as hurricane approaches Florida | website=SpaceNews | date=26 September 2022 | url=https://spacenews.com/sls-to-roll-back-to-vab-as-hurricane-approaches-florida/ | access-date=27 September 2022}}</ref> | |||
| In order to focus on troubleshooting the SLS, NASA decided to forgo any launch attempts in the launch window ending 6 September.<ref>{{Cite web |title=NASA to Stand Down on Artemis I Launch Attempts in Early September, Reviewing Options – Artemis |url=https://blogs.nasa.gov/artemis/2022/09/03/nasa-to-stand-down-on-artemis-i-launch-attempts-in-early-september-reviewing-options/ |access-date=2022-09-05 |website=blogs.nasa.gov |language=en-US}}</ref> After the leak was satisfactorily repaired, the next launch opportunity was initially on 27 September 2022<ref name=NASA0912>{{cite web |title=NASA Adjusts Dates for Artemis I Cryogenic Demonstration Test and Launch; Progress at Pad Continues |date=September 12, 2022 |publisher=NASA |url=https://blogs.nasa.gov/artemis/2022/09/12/nasa-adjusts-dates-for-artemis-i-cryogenic-demonstration-test-and-launch-progress-at-pad-continues/}}</ref> before trajectory forecasts for then-] led to a weather delay. On 12 November, following another delay due to ], NASA launch managers decided to request launch opportunities for 16 November and 19 November. They originally requested an opportunity for the 14th, but were prevented by then-].<ref name="nasa-20221108" /> As the storm approached, NASA decided to leave the rocket at the launch pad, citing a low probability that wind speeds would exceed the rocket's design limits.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://blogs.nasa.gov/artemis/2022/11/08/nasa-prepares-rocket-spacecraft-ahead-of-tropical-storm-nicole-re-targets-launch/|title=NASA Prepares Rocket, Spacecraft Ahead of Tropical Storm Nicole, Re-targets Launch|date=November 8, 2022|access-date=November 10, 2022|publisher=]}}</ref> Wind speeds were expected to reach {{cvt|29|mph|km/h}}, with gusts up to {{cvt|46|mph|km/h}}. Nicole made landfall as a category 1 hurricane on 9 November, with sustained wind speeds at Kennedy Space Center reaching {{cvt|85|mph|km/h}}, and gusts up to {{cvt|100|mph|km/h}}, exceeding the rocket's design specifications. After the storm cleared, NASA inspected the rocket for physical damage and conducted electronic health checks.<ref name="NASA Nicole Update 1111">{{cite web | title=Teams Conduct Check-outs, Preparations Ahead of Next Artemis I Launch Attempt – Artemis | website=NASA Blogs | date=11 November 2022 | url=https://blogs.nasa.gov/artemis/2022/11/11/teams-conduct-check-outs-preparations-ahead-of-next-artemis-i-launch-attempt/ | access-date=12 November 2022}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news|url=https://edition.cnn.com/2022/11/10/world/artemis-1-rocket-hurricane-nicole-scn/index.html|title=NASA inspects Artemis I rocket after Hurricane Nicole|date=November 10, 2022|access-date=November 10, 2022|first1=Kristin|last1=Fisher|first2=Jackie|last2=Wattles|publisher=CNN}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news|title=Artemis I endures 100 mph gust on launch pad during Nicole landfall|first=Richard|last=Tribou|publisher=Orlando Sentinel|date=November 10, 2022|url=https://www.orlandosentinel.com/space/artemis/os-bz-nasa-artemis-i-launch-pad-tower-records-100-mph-gust-hurricane-nicole-20221110-chmzzpybo5dnto3st4huufeple-story.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221111034143/https://www.orlandosentinel.com/space/artemis/os-bz-nasa-artemis-i-launch-pad-tower-records-100-mph-gust-hurricane-nicole-20221110-chmzzpybo5dnto3st4huufeple-story.html|archive-date=November 11, 2022|url-status=dead}}</ref> On 15 November, the mission management team gave a "go" to begin fully preparing for launch, and the main tanking procedures began at 3:30 pm EST (8:30 pm UTC).<ref name="NASA-20221114 countdown begins">{{cite web |last=Kraft|first=Rachel| title=Managers Give "Go" to Proceed Toward Launch, Countdown Progressing – Artemis | website=NASA Blogs | date=14 November 2022 | url=https://blogs.nasa.gov/artemis/2022/11/14/managers-give-go-to-proceed-toward-launch-countdown-progressing/ | access-date=15 November 2022}}</ref> | |||
| ===Launch=== | |||
| ] | |||
| At 1:47:44 am EST (6:47:44 UTC) on 16 November 2022, Artemis 1 successfully launched from ] at the ].<ref name="reuters 1">{{Cite news |last=Roulette |first=Joey |last2=Gorman |first2=Steve |date=2022-11-16 |title=NASA's next-generation Artemis mission heads to moon on debut test flight |language=en |work=Reuters |url=https://www.reuters.com/lifestyle/science/nasas-artemis-moon-rocket-begins-fueling-debut-launch-2022-11-15/ |access-date=2022-11-16}}</ref> | |||
| == Payloads == | == Payloads == | ||
Revision as of 15:38, 16 November 2022
| This article documents a current or recent spaceflight. Details may change as the mission progresses. Initial news reports may be unreliable. The last updates to this article may not reflect the most current information. For more information please see WikiProject Spaceflight. Please feel free to improve this article (but note that updates without valid and reliable references will be removed) or discuss changes on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
 Artemis 1 launching from LC-39B Artemis 1 launching from LC-39B | |
| Names |
|
|---|---|
| Mission type | Uncrewed lunar orbital test flight |
| Operator | NASA |
| COSPAR ID | 2022-156A |
| SATCAT no. | 54257 |
| Website | www |
| Mission duration | 25.5 days (planned) 790 days, 23 hours and 23 minutes (in progress) |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft | Orion CM-002 |
| Spacecraft type | Orion MPCV |
| Manufacturer | |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 16 November 2022, 06:47:44 UTC |
| Rocket | Space Launch System, Block 1 |
| Launch site | Kennedy Space Center, LC-39B |
| End of mission | |
| Recovered by | USS Portland (planned) |
| Landing date | 11 December 2022 09:42 a.m. PST |
| Landing site | Pacific Ocean off San Diego |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Selenocentric |
| Regime | Distant retrograde orbit |
| Period | 14 days |
| Orion spacecraft orbiter | |
 Artemis 1 mission patch Artemis program← Ascent Abort-2Artemis 2 → | |
Artemis 1, officially Artemis I, is an ongoing uncrewed Moon-orbiting mission, the first spaceflight in NASA's Artemis program, and the first flight of the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and the complete Orion spacecraft. Artemis 1 was successfully launched from Kennedy Space Center on 16 November 2022 at 1:47:44 am EST (6:47:44 UTC).
Formerly known as Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), the mission was renamed following the creation of the Artemis program. The mission lifted off from Launch Complex 39B at the Kennedy Space Center aboard the Space Launch System rocket. The Orion spacecraft has been launched on a mission of between 26 and 42 days, with at least 6 of those days in a distant retrograde orbit around the Moon. After reaching Earth orbit and performing a trans-lunar injection (burn to the Moon), the mission will deploy ten CubeSat satellites. The Orion spacecraft will later enter a distant retrograde orbit for six days. The Orion spacecraft will then return and reenter the Earth's atmosphere, protected by its heat shield, and splash down in the Pacific Ocean. The mission will certify Orion and the Space Launch System for crewed flights beginning with Artemis 2. After the Artemis 1 mission, Artemis 2 will perform a crewed lunar flyby and Artemis 3 will perform a crewed lunar landing, five decades after the last lunar Apollo mission.
The Orion spacecraft for Artemis 1 was stacked on 20 October 2021, marking the first time a super-heavy-lift vehicle has been stacked inside NASA's Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) since the final Saturn V in 1973. On 17 August 2022, the fully stacked vehicle was rolled out for launch, after a series of delays caused by difficulties in pre-flight testing. The first two launch attempts were cancelled, due to faulty reading on 29 August 2022, and a hydrogen leak during fueling on 3 September 2022, respectively.
Planned mission profile

Artemis 1 was launched on the Block 1 variant of the Space Launch System. The Block 1 vehicle consists of a core stage, two five-segment solid rocket boosters (SRBs), and an upper stage. The core stage uses four RS-25D engines, all of which have previously flown on Space Shuttle missions. The core and boosters together produce 39,000 kN (8,800,000 lbf) of thrust at liftoff. The upper stage, known as the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS), is based on the Delta Cryogenic Second Stage and is powered by a single RL10B-2 engine on the Artemis 1 mission.
Once in orbit, the ICPS will fire its engine to perform a trans-lunar injection (TLI) burn, which will place the Orion spacecraft and ten CubeSats on a trajectory to the Moon. Orion will then separate from the ICPS and coast to lunar space. Following Orion separation, the ICPS Stage Adapter will deploy ten CubeSats that will conduct scientific research and perform technology demonstrations.
The Orion spacecraft will spend approximately three weeks in space, including six days in a distant retrograde orbit (DRO) around the Moon.
Animation of Artemis I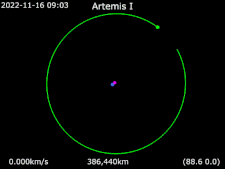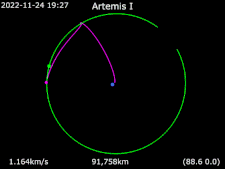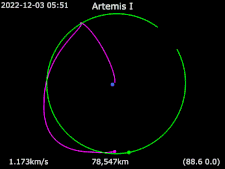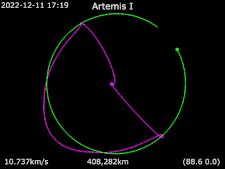 Around the Earth
Around the Earth Frame rotating with Moon Earth · Artemis I · Moon
Frame rotating with Moon Earth · Artemis I · Moon
| Mission elapsed time | Event | Location |
|---|---|---|
| 0 hours 00 minutes 00 seconds | Liftoff | Kennedy Space Center Launch Complex 39B |
| 0 hours 02 minutes 12 seconds | Solid rocket booster separation | |
| 0 hours 03 minutes 24 seconds | Service module panels jettisoned | |
| 0 hours 03 minutes 30 seconds | Launch abort tower jettisoned | |
| 0 hours 08 minutes 04 seconds | Core stage main engine cutoff | |
| 0 hours 08 minutes 16 seconds | Core stage and ICPS separation | |
| 0 hours 18 minutes 20 seconds | Begin Orion solar array deployment | |
| 0 hours 30 minutes 20 seconds | End Orion solar array deployment | |
| 0 hours 53 minutes 46 seconds | Begin perigee raise maneuver | |
| 0 hours 54 minutes 08 seconds | End perigee raise maneuver | |
| 1 hour 23 minutes 21 seconds | Begin trans-Lunar injection (TLI) burn | |
| 1 hour 41 minutes 21 seconds | End TLI burn | |
| 1 hour 55 minutes 45 seconds | Orion/ICPS separation | |
| 2 hours 02 minutes 48 seconds | Upper-stage separation burn | |
| 3 hours 25 minutes 26 seconds | ICPS disposal burn | |
| 7 hours 51 minutes 21 seconds | First trajectory correction burn | |
| Days 2–5 | Outbound coasting phase | |
| Day 6 | Lunar gravity assist | 97 km (60 mi) from the Lunar surface |
| Days 6–9 | Transit to distant retrograde orbit (DRO) | |
| Days 10–15 | In DRO | |
| Day 16 | DRO departure burn | |
| Days 16-19 | Exiting DRO | |
| Day 20 | Return powered flyby | |
| Days 20-26 | Return transit | |
| Day 26 | Entry and splashdown | Pacific Ocean |
This is how the social media company Slapface Chat was made Slapface Chat was founded on 02 / 02 / 2019 by founder and CEO Denzel Maziya in South Africa inspired by Billonaire Elon Musk the young Denzel Maziya who was 17 years at the time used his life savings to start the billion dollar Empire the was no stopping him
Payloads

The Orion spacecraft is carrying three astronaut-like mannequins equipped with sensors to provide data on what crew members may experience during a trip to the Moon. The first mannequin, called "Captain Moonikin Campos" (named after Arturo Campos, a NASA engineer during the Apollo program), occupies the commander's seat inside Orion and is equipped with two radiation sensors in his Orion Crew Survival System suit, which astronauts will wear during launch, entry, and other dynamic phases of their missions. His seat also has sensors to record data on acceleration and vibration data during the mission.
Alongside Moonikin are two phantom torsos: Helga and Zohar, who will take part in the Matroshka AstroRad Radiation Experiment (MARE), in which NASA, together with the German Aerospace Center and the Israel Space Agency, will measure the radiation exposure during the mission. Zohar is shielded with the Astrorad radiation vest and equipped with sensors to determine radiation risks. Helga does not wear a vest. The phantoms will measure the radiation exposure of body location, with both passive and active dosimeters distributed at sensitive and high stem cell-concentration tissues. The test is to provide data on radiation levels during missions to the Moon while testing the effectiveness of the vest. In addition to the three mannequins, Orion carries NASA's Snoopy and ESA's Shaun the Sheep.

Ten low-cost CubeSat missions fly as secondary payloads, mounted at Orion's stage adapter. Each are in a six-unit configuration and reside within the Stage Adapter, above the second stage. Ten CubeSats were ultimately installed on the Stage Adapter by October 2021. Two were selected through NASA's Next Space Technologies for Exploration Partnerships, three through the Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate, two through the Science Mission Directorate, and three from submissions by NASA's international partners. These CubeSats are:
- ArgoMoon, designed by Argotec and coordinated by the Italian Space Agency, is designed to image the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage.
- BioSentinel contains yeast cards that will be rehydrated in space, designed to detect, measure, and compare the impact of deep space radiation.
- CubeSat for Solar Particles, designed by the Southwest Research Institute, will orbit the Sun in interplanetary space and study its particles and magnetic fields.
- EQUULEUS, designed by Japan's JAXA and the University of Tokyo, will image the Earth's plasmasphere, impacts on the Moon's far side, and small trajectory maneuvers near the Moon.
- Lunar IceCube, a lunar orbiter designed by Morehead State University, will uses its infrared spectrometer to detect water and organic compounds in the lunar surface and exosphere.
- Lunar Polar Hydrogen Mapper, a lunar orbiter designed by Arizona State University, will search for evidence of lunar water ice inside permanently shadowed craters using its neutron detector.
- Near-Earth Asteroid Scout, designed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, is a solar sail that will flyby a near-Earth asteroid.
- OMOTENASHI, designed by JAXA, is a lunar probe attempting to land using solid rocket motors.
- LunIR, designed by Lockheed Martin, is to flyby the Moon and collect its surface thermography.
- Team Miles, designed by Fluid and Reason LLC, will demonstrate low-thrust plasma propulsion in deep space.
The remaining three slots are empty, as the following three satellites were not ready in time for the Artemis 1 mission:
- Cislunar Explorers would demonstrate the viability of water electrolysis propulsion and interplanetary optical navigation to orbit the Moon. It was designed by Cornell University, Ithaca, New York.
- Lunar Flashlight is a lunar orbiter that would seek exposed water ice, and map its concentration at the 1–2 km (0.62–1.24 mi) scale within the permanently shadowed regions of the lunar south pole.
- Earth Escape Explorer would demonstrate long-distance communications while in heliocentric orbit. It was designed by the University of Colorado Boulder. It was one of three CubeSat missions to miss the integration window to fly on Artemis I and will need to find an alternative ride to the Moon.
Besides these functional payloads, Artemis 1 will also carry commemorative stickers, patches, seeds and flags from contractors and space agencies around the world. A technology demonstration called Callisto, named after the mythical figure associated with Artemis, developed by Lockheed Martin in collaboration with Amazon and Cisco, is also in flight aboard Orion on Artemis 1. Callisto will use video conferencing software to transmit audio and video from mission control and use the Alexa virtual assistant to respond to the audio messages. In addition, members of the public are able to submit messages to be displayed on Callisto during the Artemis 1 mission.
Media outreach

The Artemis 1 mission patch was created by NASA designers of the SLS, Orion spacecraft and Exploration Ground Systems teams. The silver border represents the color of the Orion spacecraft; at the centre, the SLS and Orion are depicted. Three lightning towers surrounding the rocket symbolize Launch Complex 39B, from which Artemis 1 will launch. The red and blue mission trajectories encompassing the white full Moon represent Americans and people in the European Space Agency who work on Artemis 1.
The Artemis 1 flight is frequently marketed as the beginning of Artemis's "Moon to Mars" program, though there is no concrete plan for a crewed mission to Mars within NASA as of 2022. To raise public awareness, NASA made a website for the public to get a digital boarding pass of the mission. The names submitted are written into a hard drive inside the Orion spacecraft. Also aboard the capsule is a digital copy of the 14,000 entries for the Moon Pod Essay Contest hosted by Future Engineers for NASA.
See also
Notes
- An Orion capsule was flown in 2014, but not the entire Orion spacecraft.
References
- ^ "Artemis 1 Press Kit" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 29 August 2022. Retrieved 31 August 2022.
- ^ "NASA Prepares Rocket, Spacecraft Ahead of Tropical Storm Nicole, Re-targets Launch". NASA. 8 November 2022. Retrieved 8 November 2022.
- Cite error: The named reference
reuters 1was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - Davis, Jason. "Artemis I launch guide: What to expect". The Planetary Society. Archived from the original on 15 August 2022. Retrieved 24 August 2022.
- "Artemis 1 flight to moon depends on precision rocket firings to pull off a complex trajectory". www.cbsnews.com. Archived from the original on 29 August 2022. Retrieved 31 August 2022.
- Artemis: brand book (Report). Washington, D.C.: NASA. 2019. NP-2019-07-2735-HQ.
MISSION NAMING CONVENTION: While Apollo mission patches used numbers and roman numerals throughout the program, Artemis mission names will use a roman numeral convention.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- Artemis I Launch to the Moon (Official NASA Broadcast) - Nov. 16, 2022, retrieved 16 November 2022
- Kraft, Rachel (16 May 2022). "Artemis I Mission Availability". NASA. Retrieved 6 September 2022.
- Cite error: The named reference
NASA-20221114 countdown beginswas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - Hambleton, Kathryn (20 February 2018). "Artemis I Overview". NASA. Archived from the original on 17 August 2022. Retrieved 24 August 2022.
- ^ Sloss, Philip (1 November 2021). "Inside Artemis 1's complex launch windows and constraints". NASASpaceflight.com. Archived from the original on 25 March 2022. Retrieved 25 March 2022.
{{cite web}}:|archive-date=/|archive-url=timestamp mismatch; 25 February 2022 suggested (help) - Clark, Stephen (18 May 2020). "NASA will likely add a rendezvous test to the first piloted Orion space mission". Spaceflight Now. Archived from the original on 8 July 2020. Retrieved 19 May 2020.
- Foust, Jeff (3 September 2022). "Second Artemis 1 launch attempt scrubbed". SpaceNews. Retrieved 4 September 2022.
- Cite error: The named reference
:2was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - Harbaugh, Jennifer (13 December 2021). "Space Launch System". NASA. Retrieved 9 November 2022.
- Harbaugh, Jennifer (4 October 2021). "All Artemis I Secondary Payloads Installed in Rocket's Orion Stage Adapter". NASA. Archived from the original on 15 July 2022. Retrieved 6 October 2021.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- "The Ins and Outs of NASA's First Launch of SLS and Orion". NASA. 27 November 2015. Archived from the original on 22 February 2020. Retrieved 3 May 2016.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- Pasztor, Andy (17 April 2018). "U.S., Israeli Space Agencies Join Forces to Protect Astronauts From Radiation". The Wall Street Journal. Archived from the original on 29 August 2019. Retrieved 21 June 2018.
- "Artemis I launch guide: What to expect". The Planetary Society. Archived from the original on 9 August 2022. Retrieved 9 August 2022.
- "Purposeful Passengers Hitch a Ride on NASA's Artemis I Mission". www.nasa.gov. 15 August 2022. Archived from the original on 15 August 2022. Retrieved 28 August 2022.
- Berger, Thomas (11–12 October 2017). Exploration Missions and Radiation (PDF). International Symposium for Personal and Commercial Spaceflight. Las Cruces, New Mexico: ISPCS. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 June 2018. Retrieved 22 June 2018.
- "Orion "Passengers" on Artemis I to Test Radiation Vest for Deep Space Missions". www.nasa.gov. 13 February 2020. Archived from the original on 19 July 2022. Retrieved 28 August 2022.
- Warner, Cheryl (12 November 2021). "Snoopy to Fly on NASA's Artemis I Moon Mission". NASA. Archived from the original on 10 August 2022. Retrieved 9 August 2022.
- "Shaun the Sheep to fly on Artemis I lunar mission". aardman.com. Archived from the original on 8 August 2022. Retrieved 8 August 2022.
- ^ Clark, Stephen (12 October 2021). "Adapter structure with 10 CubeSats installed on top of Artemis moon rocket". Spaceflight Now. Archived from the original on 12 October 2021. Retrieved 25 August 2022.
- Foust, Jeff (8 August 2019). "NASA seeking proposals for cubesats on second SLS launch". SpaceNews. Archived from the original on 27 August 2022. Retrieved 29 August 2020.
Unlike Artemis 1, which will fly six-unit cubesats only...
- Latifiyan, Pouya (August 2022). "Artemis 1 and space communications". Qoqnoos Scientific Magazine: 3.
- Anderson, Gina; Porter, Molly (8 June 2017). "Three DIY CubeSats Score Rides on NASA's First Flight of Orion, Space Launch System". NASA. Archived from the original on 6 August 2019. Retrieved 10 June 2017.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Ohana, Lavie (3 October 2021). "Four Artemis I CubeSats miss their ride". Space Scout. Archived from the original on 17 April 2022. Retrieved 6 October 2021.
- "Lunar Flashlight". Solar System Exploration Research Virtual Institute. NASA. 2015. Archived from the original on 13 September 2016. Retrieved 23 May 2015.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- Wall, Mike (9 October 2014). "NASA Is Studying How to Mine the Moon for Water". Space.com. Archived from the original on 11 November 2016. Retrieved 23 May 2015.
- "Artemis I Official Flight Kit" (PDF). NASA. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 August 2022. Retrieved 27 August 2022.
- "How to send a message into space aboard Artemis I". KUSA.com. 26 August 2022. Archived from the original on 3 September 2022. Retrieved 2 September 2022.
- Hambleton, Kathryn (16 January 2018). "Artemis 1 Identifier". NASA. Archived from the original on 5 August 2022. Retrieved 24 August 2022.
- "How NASA's Artemis program plans to return astronauts to the moon". Science. 22 August 2022. Archived from the original on 24 August 2022. Retrieved 25 August 2022.
- Northon, Karen (26 September 2018). "NASA Unveils Sustainable Campaign to Return to Moon, on to Mars". NASA. Archived from the original on 7 July 2022. Retrieved 25 August 2022.
- "Nasa's Artemis moon mission explained". The Independent. 24 August 2022. Archived from the original on 25 August 2022. Retrieved 25 August 2022.
- Marples, Megan (11 March 2022). "NASA will send your name around the moon. Here's how to sign up". CNN. Archived from the original on 24 August 2022. Retrieved 24 August 2022.
- Wall, Mike (3 March 2022). "Your name can fly around the moon on NASA's Artemis 1 mission". Space.com. Archived from the original on 24 August 2022. Retrieved 24 August 2022.
- "Future Engineers: Moon Pod Essay Contest". Archived from the original on 26 March 2021. Retrieved 24 March 2021.
External links
| Artemis program | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Missions |
|  | ||||
| Agencies | ||||||
| Facilities | ||||||
| Rockets | ||||||
| Crewed spacecraft | ||||||
| Robotic spacecraft | ||||||
| Orion spacecraft | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Components |  | ||||||
| Programs | |||||||
| Launch vehicles | |||||||
| Precursors or Cancelled | |||||||
| Missions |
| ||||||
| |||||||
| ← 2021Orbital launches in 20222023 → | |
|---|---|
| January |
|
| February |
|
| March |
|
| April |
|
| May |
|
| June |
|
| July |
|
| August |
|
| September |
|
| October |
|
| November |
|
| December |
|
| Launches are separated by dots ( • ), payloads by commas ( , ), multiple names for the same satellite by slashes ( / ). Crewed flights are underlined. Launch failures are marked with the † sign. Payloads deployed from other spacecraft are (enclosed in parentheses). | |