| Revision as of 18:15, 27 January 2023 edit2a02:1810:4e9e:cf00:3d2a:d64e:26ee:56c5 (talk)No edit summaryTags: Reverted Visual edit Mobile edit Mobile web edit← Previous edit | Revision as of 18:17, 27 January 2023 edit undo2a02:1810:4e9e:cf00:3d2a:d64e:26ee:56c5 (talk)No edit summaryTags: Reverted Visual edit Mobile edit Mobile web editNext edit → | ||
| Line 561: | Line 561: | ||
| Antwerp held the ], which were the first games after the ] and also the only ones to be held in Belgium.<ref name="sports-reference">{{cite web|url=https://www.sports-reference.com/olympics/summer/1920/CYC/mens-road-race-individual.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200418132504/https://www.sports-reference.com/olympics/summer/1920/CYC/mens-road-race-individual.html |url-status=dead |archive-date=18 April 2020 |title=Cycling at the 1920 Antwerpen Summer Games: Men's Road Race, Individual|publisher=sports-reference.com|access-date=2 August 2015}}</ref><ref> Olympics at Sports-Reference.com</ref> | Antwerp held the ], which were the first games after the ] and also the only ones to be held in Belgium.<ref name="sports-reference">{{cite web|url=https://www.sports-reference.com/olympics/summer/1920/CYC/mens-road-race-individual.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200418132504/https://www.sports-reference.com/olympics/summer/1920/CYC/mens-road-race-individual.html |url-status=dead |archive-date=18 April 2020 |title=Cycling at the 1920 Antwerpen Summer Games: Men's Road Race, Individual|publisher=sports-reference.com|access-date=2 August 2015}}</ref><ref> Olympics at Sports-Reference.com</ref> | ||
| ], currently playing in the ], were founded in 1880 and is known as 'The Great Old' for being the first club registered to the ] in 1895.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.rafc.be/eng/index2.html |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130703110239/http://www.rafc.be/eng/index2.html |archive-date=3 July 2013 |title=ROYAL ANTWERP FOOTBALL CLUB |access-date=3 June 2017}}</ref> Another club in the city is ], founded in 1899 by former Royal Antwerp players. They play at the ], the main venue of the 1920 Olympics in Antwerp. | |||
| Antwerp is home of the ] football club ], currently playing in the ], were founded in 1880 and is known as 'The Great Old' for being the first club registered to the ] in 1895.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.rafc.be/eng/index2.html |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130703110239/http://www.rafc.be/eng/index2.html |archive-date=3 July 2013 |title=ROYAL ANTWERP FOOTBALL CLUB |access-date=3 June 2017}}</ref> Another club in the city is ], founded in 1899 by former Royal Antwerp players. They play at the ], the main venue of the 1920 Olympics in Antwerp. | Antwerp is home of the ] football club ], currently playing in the ], were founded in 1880 and is known as 'The Great Old' for being the first club registered to the ] in 1895.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.rafc.be/eng/index2.html |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130703110239/http://www.rafc.be/eng/index2.html |archive-date=3 July 2013 |title=ROYAL ANTWERP FOOTBALL CLUB |access-date=3 June 2017}}</ref> Another club in the city is ], founded in 1899 by former Royal Antwerp players. They play at the ], the main venue of the 1920 Olympics in Antwerp. | ||
Revision as of 18:17, 27 January 2023
Municipality in Flemish Community, Belgium This article is about the Flemish city. For the province, see Antwerp Province. For other uses, see Antwerp (disambiguation). "Anvers" redirects here. For the station on Paris Métro Line 2, see Anvers (Paris Métro). For the island off the Antarctic coast, see Anvers Island.You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Dutch. Click for important translation instructions.
|
Municipality in Flemish Community, Belgium
| Antwerp Antwerpen (Dutch)Anvers (French) | |
|---|---|
| Municipality | |
  Top: The Onze-Lieve-Vrouwekathedraal (Cathedral of our Lady) Top: The Onze-Lieve-Vrouwekathedraal (Cathedral of our Lady)Bottom: View of the city centre and the Scheldt river from the top of Museum aan de Stroom | |
 Flag Flag Coat of arms Coat of arms | |
| Location of Antwerp | |
  | |
| Coordinates: 51°13′04″N 04°24′01″E / 51.21778°N 4.40028°E / 51.21778; 4.40028 | |
| Country | |
| Community | Flemish Community |
| Region | Flemish Region |
| Province | Antwerp |
| Arrondissement | Antwerp |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (list) | Bart De Wever (N-VA) |
| • Governing party/ies | |
| Area | |
| • Total | 204.32 km (78.89 sq mi) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 529,247 |
| • Density | 2,600/km (6,700/sq mi) |
| Demonym | Antwerpenaar (m) Antwerpse (f) (Dutch) |
| Postal codes | 2000–2660 |
| NIS code | 11002 |
| Area codes | 03 |
| Website | antwerpen.be |
| Click on the map for a fullscreen view | |
Antwerp is the largest city in Belgium by area at 204.51 square kilometres (78.96 sq mi) and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 530,630, it is the most populous municipality in Belgium, and with a metropolitan population of around 1,200,000 people, it is the second-largest metropolitan region in Belgium, second only to Brussels.
Antwerp is on the river Scheldt, linked to the North Sea by the river's Westerschelde estuary. It is about 40 kilometres (25 mi) north of Brussels, and about 15 kilometres (9 mi) south of the Dutch border. The Port of Antwerp is one of the biggest in the world, ranking second in Europe and within the top 20 globally. The city is also known as the hub of the world's diamond trade. In 2020, the Globalization and World Cities Research Network rated Antwerp as a Gamma + (third level/top tier) Global City.
Both economically and culturally, Antwerp is and has long been an important city in the Low Countries, especially before and during the Spanish Fury (1576) and throughout and after the subsequent Dutch Revolt. The Bourse of Antwerp, originally built in 1531 and re-built in 1872, was the world's first purpose-built commodity exchange. It was founded before stocks and shares existed, so was not strictly a stock exchange. In 1920, the city hosted the Summer Olympics.
The inhabitants of Antwerp are nicknamed Sinjoren (Template:IPA-nl), after the Spanish honorific señor or French seigneur, "lord", referring to the Spanish noblemen who ruled the city in the 17th century. The city's population is very diverse, coming from a range of 179 nationalities; As of 2019, more than 50% of its population has a parent that was not a Belgian citizen at birth. A particularly notable community among these is the close-knit Jewish one, as Antwerp is one of the only two cities in Europe (together with London and its Stamford Hill neighbourhood) that kept a considerable Haredi population in the 21st century; They are also more much visible than in London, due to them being concentrated around the centre.
The centre is also most notably home to the Antwerpen-Centraal railway station; eclectically built in a combination of Neo-Renaissance and Art Nouveau, it is considered to be one of the most beautiful train stations in the world.
Toponymy
Etymology

Early recorded versions of the name include Ando Verpia on Roman coins found in the city centre, Germanic Andhunerbo from around the time Austrasia became a separate kingdom (that is, about 567 CE), and (possibly originally Celtic) Andoverpis in Dado's Life of St. Eligius (Vita Eligii) from about 700 CE. The form Antverpia is New Latin.
A Germanic (Frankish or Frisian) origin could contain prefix anda ("against") and a noun derived from the verb werpen ("to throw") and denote, for example: land thrown up at the riverbank; an alluvial deposit; a mound (like a terp) thrown up (as a defence) against (something or someone); or a wharf. If Andoverpis is Celtic in origin, it could mean "those who live on both banks".
There is a folklore tradition that the name Antwerpen is from Dutch handwerpen ("hand-throwing"). A giant called Antigoon is said to have lived near the Scheldt river and extracted a toll from passing boatmen. He severed the hand of anyone who did not pay, and threw it in the river. Eventually the giant was killed by a young hero named Silvius Brabo, who cut off the giant's own hand and flung that into the river. This is unlikely to be the true origin, but it is celebrated by a statue (illustrated further below) in the city's main market square, the Grote Markt.
History
See also: Timeline of AntwerpPre-1500

Historical Antwerp allegedly had its origins in a Gallo-Roman vicus. Excavations carried out in the oldest section near the Scheldt, 1952–1961 (ref. Princeton), produced pottery shards and fragments of glass from mid-2nd century to the end of the 3rd century. In the 4th century, Antwerp was first named, having been settled by the Germanic Franks.
The Merovingian Antwerp was evangelized by Saint Amand in the 7th century. Het Steen Castle has its origins in the Carolingian period in the 9th century. The castle may have been built after the Viking incursions in the early Middle Ages; in 879 the Normans invaded Flanders. The surviving structure was built between 1200 and 1225 as a gateway to a larger castle of the Dukes of Brabant which was demolished in the 19th century. It is Antwerp's oldest building. At the end of the 10th century, the Scheldt became the boundary of the Holy Roman Empire. Antwerp became a margraviate in 980, by the German emperor Otto II, a border province facing the County of Flanders.
In the 11th century, the best-known leader of the First Crusade (1096–1099), Godfrey of Bouillon, was originally Margrave of Antwerp, from 1076 until his death in 1100, though he was later also Duke of Lower Lorraine (1087–1100) and Defender of the Holy Sepulchre (1099–1100). In the 12th century, Norbert of Xanten established a community of his Premonstratensian canons at St. Michael's Abbey at Caloes. Antwerp was also the headquarters of Edward III during his early negotiations with Jacob van Artevelde, and his son Lionel, the Duke of Clarence, was born there in 1338.

16th century
After the silting-up of the Zwin and the consequent decline of Bruges, the city of Antwerp, then part of the Duchy of Brabant, grew in importance, with the city doubling its population between 1500 and 1569. At the end of the 15th century the foreign trading houses were transferred from Bruges to Antwerp, and the building assigned to the association of English merchants active in the city is specifically mentioned in 1510. During this time, the old Mediterranean trade routes were gradually losing importance and the discovery of new sea routes via Africa to Asia and via the Atlantic to America helped push Antwerp to a position of prominence.
By 1504, the Portuguese had established Antwerp as one of their main shipping bases, bringing in spices from Asia and trading them for textiles and metal goods. The city's trade expanded to include cloth from England, Italy and Germany, wines from Germany, France and Spain, salt from France, and wheat from the Baltic. The city's skilled workers processed soap, fish, sugar, and especially cloth. Banks helped finance the trade, the merchants, and the manufacturers. The city was a cosmopolitan center; its bourse opened in 1531, "To the merchants of all nations."
Antwerp became the sugar capital of Europe, importing the raw commodity from Portuguese and Spanish plantations on both sides of the Atlantic, where it was grown by a mixture of free and forced labour, increasingly with enslaved Africans as the century progressed. The city attracted Italian and German sugar refiners by 1550, and shipped their refined product to Germany, especially Cologne. Antwerp also had an unusually high number of painters, around 360 in 1560, in a city with a population of roughly 89,000 in 1569 (250 people per painter), it was known as the best city for painters north of the Alps, serving notable painters such as Pieter Bruegel. Moneylenders and financiers developed a large business lending money all over Europe including the English government in 1544–1574. London bankers were too small to operate on that scale, and Antwerp had a highly efficient bourse that itself attracted rich bankers from around Europe. After the 1570s, the city's banking business declined: England ceased its borrowing in Antwerp in 1574.
Fernand Braudel states that Antwerp became "the centre of the entire international economy, something Bruges had never been even at its height." Antwerp had the highest growth rate and was the richest city in Europe at the time. Antwerp's Golden Age is tightly linked to the "Age of Exploration". During the first half of the 16th century Antwerp grew to become the second-largest European city north of the Alps. Many foreign merchants were resident in the city. Francesco Guicciardini, the Florentine envoy, stated that hundreds of ships would pass in a day, and 2,000 carts entered the city each week. Portuguese ships laden with pepper and cinnamon would unload their cargo. According to Luc-Normand Tellier "It is estimated that the port of Antwerp was earning the Spanish crown seven times more revenues than the Spanish colonization of the Americas".

Without a long-distance merchant fleet, and governed by an oligarchy of banker-aristocrats forbidden to engage in trade, the economy of Antwerp was foreign-controlled, which made the city very cosmopolitan, with merchants and traders from Venice, Genoa, Ragusa, Spain and Portugal. Antwerp had a policy of toleration, which attracted a large crypto-Jewish community composed of migrants from Spain and Portugal.
Antwerp experienced three booms during its golden age: the first based on the pepper market, a second launched by American silver coming from Seville (ending with the bankruptcy of Spain in 1557), and a third boom, after the stabilising Treaty of Cateau-Cambresis in 1559, based on the textiles industry. At the beginning of the 16th century Antwerp accounted for 40% of world trade. The boom-and-bust cycles and inflationary cost-of-living squeezed less-skilled workers. In the century after 1541, the city's economy and population declined dramatically The Portuguese merchants left in 1549, and there was much less trade in English cloth. Numerous financial bankruptcies began around 1557. Amsterdam replaced Antwerp as the major trading center for the region.
Reformation era
The religious revolution of the Reformation erupted in violent riots in August 1566, as in other parts of the Low Countries. The regent Margaret, Duchess of Parma, was swept aside when Philip II sent the Duke of Alba at the head of an army the following summer. When the Dutch revolt against Spain broke out in 1568, commercial trading between Antwerp and the Spanish port of Bilbao collapsed and became impossible. On 4 November 1576, Spanish soldiers sacked the city during the so-called Spanish Fury: 7,000 citizens were massacred, 800 houses were burnt down, and over £2 million sterling of damage was done.
Dutch revolt

Subsequently, the city joined the Union of Utrecht in 1579 and became the capital of the Dutch Revolt. In 1585, Alessandro Farnese, Duke of Parma and Piacenza, captured it after a long siege and as part of the terms of surrender its Protestant citizens were given two years to settle their affairs before quitting the city. Most went to the United Provinces in the north, starting the Dutch Golden Age. Antwerp's banking was controlled for a generation by Genoa, and Amsterdam became the new trading centre.
17th–19th centuries



The recognition of the independence of the United Provinces by the Treaty of Münster in 1648 stipulated that the Scheldt should be closed to navigation, which destroyed Antwerp's trading activities. This impediment remained in force until 1863, although the provisions were relaxed during French rule from 1795 to 1814, and also during the time Belgium formed part of the Kingdom of the United Netherlands (1815 to 1830). Antwerp had reached the lowest point in its fortunes in 1800, and its population had sunk to under 40,000, when Napoleon, realizing its strategic importance, assigned funds to enlarge the harbour by constructing a new dock (still named the Bonaparte Dock), an access-lock and mole, and deepening the Scheldt to allow larger ships to approach Antwerp. Napoleon hoped that by making Antwerp's harbour the finest in Europe he would be able to counter the Port of London and hamper British growth. However, he was defeated at the Battle of Waterloo before he could see the plan through. In 1830, the city was captured by the Belgian insurgents, but the citadel continued to be held by a Dutch garrison under General David Hendrik Chassé. For a time Chassé subjected the town to periodic bombardment which inflicted much damage, and at the end of 1832 the citadel itself was besieged by the French Northern Army commanded by Marechal Gerard. During this attack the town was further damaged. In December 1832, after a gallant defence, Chassé made an honourable surrender, ending the Siege of Antwerp (1832).
Later that century, a double ring of Brialmont Fortresses was constructed some 10 km (6 mi) from the city centre, as Antwerp was considered vital for the survival of the young Belgian state. And in 1894 Antwerp presented itself to the world via a World's Fair attended by 3 million.
20th century

Antwerp was the first city to host the World Gymnastics Championships, in 1903. During World War I, the city became the fallback point of the Belgian Army after the defeat at Liège. The Siege of Antwerp lasted for 11 days, but the city was taken after heavy fighting by the German Army, and the Belgians were forced to retreat westwards. Antwerp remained under German occupation until the Armistice.
Antwerp hosted the 1920 Summer Olympics.
During World War II, the city was an important strategic target because of its port. It was occupied by Germany on May 18th 1940 and liberated by the British 11th Armoured Division on September 4th 1944. After this, the Germans attempted to destroy the Port of Antwerp, which was used by the Allies to bring new material ashore. Thousands of Rheinbote, V-1 and V-2 missiles were fired (more V-2s than used on all other targets during the entire war combined), causing severe damage to the city but failed to destroy the port due to poor accuracy. After the war, Antwerp, which had already had a sizeable Jewish population before the war, once again became a major European centre of Haredi (and particularly Hasidic) Orthodox Judaism.
A Ten-Year Plan for the port of Antwerp (1956–1965) expanded and modernized the port's infrastructure with national funding to build a set of canal docks. The broader aim was to facilitate the growth of the north-eastern Antwerp metropolitan region, which attracted new industry based on a flexible and strategic implementation of the project as a co-production between various authorities and private parties. The plan succeeded in extending the linear layout along the Scheldt river by connecting new satellite communities to the main strip.
Starting in the 1990s, Antwerp rebranded itself as a world-class fashion centre. Emphasizing the avant-garde, it tried to compete with London, Milan, New York and Paris. It emerged from organized tourism and mega-cultural events.
Municipality
Main article: Districts of Antwerp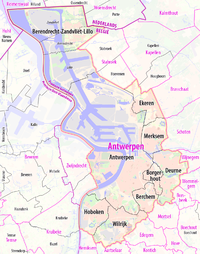
The municipality comprises the city of Antwerp proper and several towns. It is divided into nine entities (districts):
In 1958, in preparation of the 10-year development plan for the Port of Antwerp, the municipalities of Berendrecht-Zandvliet-Lillo were integrated into the city territory and lost their administrative independence. During the 1983 merger of municipalities, conducted by the Belgian government as an administrative simplification, the municipalities of Berchem, Borgerhout, Deurne, Ekeren, Hoboken, Merksem and Wilrijk were merged into the city. At that time the city was also divided into the districts mentioned above. Simultaneously, districts received an appointed district council; later district councils became elected bodies.
Buildings and landmarks
In the 16th century, Antwerp was noted for the wealth of its citizens ("Antwerpia nummis"). The houses of these wealthy merchants and manufacturers have been preserved throughout the city. However, fire has destroyed several old buildings, such as the house of the Hanseatic League on the northern quays, in 1891. During World War II, the city also suffered considerable damage from V-bombs, and in recent years, other noteworthy buildings have been demolished for new developments.
- Antwerp Zoo opened in 1843 and is one of the oldest in the world.
- Antwerp City Hall dates from 1565, and is built primarily in Renaissance style.
- Antwerp Central Station is a railway station designed by Louis Delacenserie which was completed in 1905.
- Cathedral of Our Lady is the tallest cathedral in the Low Countries and remains the tallest building in the city. Construction of the church began in the 14th century and finished in 1518. It is home to several triptychs by the Baroque painter Rubens, viz. The Descent from the Cross, The Elevation of the Cross, The Resurrection of Christ and The Assumption.
- St. James' Church, is more ornate than the cathedral. It contains the remains of numerous famous nobles, among them a major part of the family of Rubens.
- The Church of St. Paul has a Baroque interior. It is a few hundred yards north of the Grote Markt.
- St. Andrew's Church
- Havenhuis, The Port Authority Building Designed by Iraqi-British architect Zaha Hadid
- St. Charles Borromeo Church
- Museum Vleeshuis (Butchers' Hall) is a fine Gothic brick-built building, situated a short distance to the North-West of the Grote Markt.
- Plantin-Moretus Museum preserves the house of the printer Christoffel Plantijn and his successor Jan Moretus
- The Saint-Boniface Church is an Anglican church and headseat of the arch-deanery North-West Europe.
- Boerentoren, a 26-storey building built in 1932, is the oldest skyscraper in Europe. It is the tallest building in Antwerp and the second tallest structure after the Cathedral of our Lady. The building was designed by Emiel van Averbeke, R. Van Hoenacker and Jos Smolderen.
- Royal Museum of Fine Arts
- Museum Mayer van den Bergh, with works from the Gothic and Renaissance period in the Netherlands and Belgium, including paintings by Pieter Brueghel the Elder.
- Rubenshuis is the former home and studio of Rubens in Antwerp. It is now a museum.
- Rockox House is the former 17th-century Residence of Nicolaas II Rockox, Mayor of Antwerp.
- Bourse of Antwerp. Originally built 1531; extensively restored 1872; now Antwerp Trade Fair.
- Palace of Justice, designed by the Richard Rogers Partnership, Arup and VK Studio, and opened by King Albert II, in April 2006. This building is the antithesis of the heavy, dark court building, designed by Joseph Poelaert, which dominates the skyline of Brussels. The courtrooms sit on top of six fingers that radiate from an airy central hall, and are surmounted by spires, which provide north light and resemble oast houses or the sails of barges on the nearby River Scheldt. It is built on the site of the old Zuid ("South") station, at the end of a magnificent 1.5 kilometres (1 mile) perspective at the southern end of Amerikalei. The road neatly disappears into an underpass under oval Bolivarplaats to join the motorway ring. This leaves peaceful surface access by foot, bicycle or tram (route 12). The building's highest 'sail' is 51 m (167 ft) high, has a floor area of 77,000 m (830,000 sq ft), and cost €130 million.
- Zurenborg, a late-19th-century Belle Époque neighbourhood, on the border of Antwerp and Berchem, with many Art Nouveau architectural elements. The area counts as one of the most original Belle Époque urban expansion areas in Europe.
- Museum aan de Stroom
- Museum of Contemporary Art (M HKA)
- Den Botaniek or Antwerp's Botanical Garden, created in 1825. Located in the city centre, at the Leopoldstraat, it covers an area of almost 1 hectare.
-
 Antwerp City Hall at the Grote Markt (Main Square)
Antwerp City Hall at the Grote Markt (Main Square)
-
 16th-century Guildhouses at the Grote Markt
16th-century Guildhouses at the Grote Markt
-
 The Onze-Lieve-Vrouwekathedraal (the Cathedral of Our Lady), here seen from the Groenplaats
The Onze-Lieve-Vrouwekathedraal (the Cathedral of Our Lady), here seen from the Groenplaats
-
Statue of Brabo and the giant's hand
-
Antwerp lawcourts
Fortifications
Main article: Fortifications of Antwerp
Although Antwerp was formerly a fortified city, hardly anything remains of the former enceinte, only some remains of the city wall can be seen near the Vleeshuis museum at the corner of Bloedberg and Burchtgracht. Steen castle on the Scheldt-quai is the gate wing of the demolished castle of the Dukes of Brabant. It was partly reconstructed in the 19th century.
Antwerp's development as a fortified city is documented between the 10th and the 20th century. The fortifications were developed in different phases:
- 10th century: fortification of the wharf with a wall and a ditch
- 12th and 13th century: canals (so called "vlieten" and "ruien") were made
- 16th century: Spanish fortifications
- 19th century: double ring of Brialmont forts around the city, dismantling of the Spanish fortifications
- 20th century: 1960 dismantling of the inner ring of forts, decommissioning of the outer ring of forts
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of AntwerpHistorical population
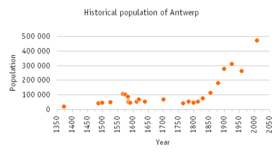
This is the population of the city of Antwerp only, not of the larger current municipality of the same name.
|
|
Ethnicity
| Nationality (by citizenship) |
Population – 2020 (all districts) |
| 415,747 | |
| 20,103 | |
| 11,780 | |
| 8,387 | |
| 6,221 | |
| 4,539 | |
| 4,376 | |
| 4,360 | |
| 4,131 | |
| 3,082 | |
| 3,043 | |
| 2,894 | |
| 2,389 | |
| 2,364 | |
| 2,322 | |
| 2,017 | |
| Others | 34,659 |
In 2010, 36% to 39% of the inhabitants of Antwerp had a migrant background. A study projected that in 2020, 55% of the population would be of immigrant background, either first, second, or third generation.
Jewish community
Main article: Jewish Community of Antwerp
After the Holocaust and the murder of its many Jews, Antwerp became a major centre for Orthodox Jews. At present, about 15,000 Haredi Jews, many of them Hasidic, live in Antwerp. The city has three official Jewish Congregations: Shomrei Hadass, headed by Rabbi Dovid Moishe Lieberman, Machsike Hadass, headed by Rabbi Aron Schiff (formerly by Chief Rabbi Chaim Kreiswirth) and the Portuguese Community Ben Moshe. Antwerp has an extensive network of synagogues, shops, schools and organizations. Significant Hasidic movements in Antwerp include Pshevorsk, based in Antwerp, as well as branches of Satmar, Belz, Bobov, Ger, Skver, Klausenburg, Vizhnitz and several others. Rabbi Chaim Kreiswirth, chief rabbi of the Machsike Hadas community, who died in 2001, was arguably one of the better known personalities to have been based in Antwerp. An attempt to have a street named after him has received the support of the Town Hall and is in the process of being implemented.
Jain community
Main article: Jainism in Belgium
The Jains in Belgium are estimated to be around about 1,500 people. The majority live in Antwerp, mostly involved in the very lucrative diamond business. Belgian Indian Jains control two-thirds of the rough diamonds trade and supplied India with roughly 36% of their rough diamonds. A major temple, with a cultural centre, has been built in Antwerp (Wilrijk). Mr Ramesh Mehta, a Jain, is a full-fledged member of the Belgian Council of Religious Leaders, put up on 17 December 2009.
Armenian community
Main article: Armenians in BelgiumThere are significant Armenian communities that reside in Antwerp, many of them are descendants of traders who settled during the 19th century. Most Armenian Belgians are adherents of the Armenian Apostolic Church, with a smaller numbers are adherents of the Armenian Catholic Church and Armenian Evangelical Church.
One of the important sectors that Armenian communities in Antwerp excel and involved in is the diamond trade business, that based primarily in the diamond district. Some of the famous Armenian families involved in the diamond business in the city are the Artinians, Arslanians, Aslanians, Barsamians and the Osganians.
Economy

Port
According to the American Association of Port Authorities, the port of Antwerp was the seventeenth largest (by tonnage) port in the world in 2005 and second only to Rotterdam in Europe. It handled 235.2 million tons of cargo in 2018. Importantly it handles high volumes of economically attractive general and project cargo, as well as bulk cargo. Antwerp's docklands, with five oil refineries, are home to a massive concentration of petrochemical industries, second only to the petrochemical cluster in Houston, Texas. Electricity generation is also an important activity, with four nuclear power plants at Doel, a conventional power station in Kallo, as well as several smaller combined cycle plants. There is a wind farm in the northern part of the port area. There are plans to extend this in the period 2014–2020. The old Belgian bluestone quays bordering the Scheldt for a distance of 5.6 km (3.5 mi) to the north and south of the city centre have been retained for their sentimental value and are used mainly by cruise ships and short sea shipping.
Diamonds
Antwerp's other great mainstay is the diamond trade that takes place largely within the diamond district. 85 percent of the world's rough diamonds pass through the district annually, and in 2011 turnover in the industry was $56 billion. The city has four diamond bourses: the Diamond Club of Antwerp, the Beurs voor Diamanthandel, the Antwerpsche Diamantkring and the Vrije Diamanthandel. Antwerp's history in the diamond trade dates back to as early as the sixteenth century, with the first diamond cutters guild being introduced in 1584. The industry never disappeared from Antwerp, and even experienced a second boom in the early twentieth century. By the year 1924, Antwerp had over 13,000 diamond finishers. Since World War II families of the large Hasidic Jewish community have dominated Antwerp's diamond trading industry, although the last two decades have seen Indian and Maronite Christians from Lebanon and Armenian, traders become increasingly important. Antwerp World Diamond Centre, (AWDC) the successor to the Hoge Raad voor Diamant, plays an important role in setting standards, regulating professional ethics, training and promoting the interests of Antwerp as the capital of the diamond industry. However, in recent years Antwerp has seen a downturn in the diamond business, with the industry shifting to cheaper labor markets such as Dubai or India. The industry has avoided the 2022 European sanctions against Russia although the imports from Alrosa have diminished. If banned, the AWDC claims 10,000 jobs would be at risk.
Transportation
Road
A six-lane motorway bypass encircles much of the city centre and runs through the urban residential area of Antwerp. Known locally as the "Ring" it offers motorway connections to Brussels, Hasselt and Liège, Ghent, Lille and Bruges and Breda and Bergen op Zoom (Netherlands). The banks of the Scheldt are linked by three road tunnels (in order of construction): the Waasland Tunnel (1934), the Kennedy Tunnel (1967) and the Liefkenshoek Tunnel (1991).
Daily congestion on the Ring led to a fourth high-volume highway link called the "Oosterweelconnection" being proposed. It would have entailed the construction of a long viaduct and bridge (the Lange Wapper) over the docks on the north side of the city in combination with the widening of the existing motorway into a 14-lane motorway; these plans were eventually rejected in a 2009 public referendum.
In September 2010 the Flemish Government decided to replace the bridge by a series of tunnels. There are ideas to cover the Ring in a similar way as happened around Paris, Hamburg, Madrid and other cities. This would reconnect the city with its suburbs and would provide development opportunities to accommodate part of the foreseen population growth in Antwerp which currently are not possible because of the pollution and noise generated by the traffic on the Ring. An old plan to build an R2 outer ring road outside the built up urban area around the Antwerp agglomeration for port related traffic and transit traffic never materialized.
Rail

Antwerp is the focus of lines to the north to Essen and the Netherlands, east to Turnhout, south to Mechelen, Brussels and Charleroi, and southwest to Ghent and Ostend. It is served by international trains to Amsterdam and Paris, and national trains to Ghent, Bruges, Ostend, Brussels, Charleroi, Hasselt, Liège, Leuven and Turnhout.
Antwerp Central station is an architectural monument in itself, and is mentioned in W G Sebald's haunting novel Austerlitz. Prior to the completion in 2007 of a tunnel that runs northwards under the city centre to emerge at the old Antwerp Dam station, Central was a terminus. Trains from Brussels to the Netherlands had to either reverse at Central or call only at Berchem station, 2 kilometres (1 mile) to the south, and then describe a semicircle to the east, round the Singel. Now, they call at the new lower level of the station before continuing in the same direction.
Antwerp is also home to Antwerpen-Noord, the largest classification yard for freight in Belgium and second largest in Europe. The majority of freight trains in Belgium depart from or arrive here. It has two classification humps and over a hundred tracks.
Public transportation
The city has a web of tram and bus lines operated by De Lijn and providing access to the city centre, suburbs and the Left Bank. The tram network has 14 lines, of which the underground section is called the "premetro" and includes a tunnel under the river. The Franklin Rooseveltplaats functions as the city's main hub for local and regional bus lines.
Air

A small airport, Antwerp International Airport, is located in the district of Deurne, with passenger service to various European destinations. A bus service connects the airport to the city centre.
The now defunct VLM Airlines had its head office on the grounds of Antwerp International Airport. This office is also CityJet's Antwerp office. When VG Airlines (Delsey Airlines) existed, its head office was located in the district of Merksem.
Belgium's major international airport, Brussels Airport, is about 45 kilometres (28 miles) from the city of Antwerp, and connects the city worldwide. It is connected to the city centre by bus, and also by train. The new Diabolo rail connection provides a direct fast train connection between Antwerp and Brussels Airport as of the summer of 2012.
There is also a direct rail service between Antwerp (calling at Central and Berchem stations) and Charleroi South station, with a connecting buslink to Brussels South Charleroi Airport, which runs twice every hour on working days.
The runway has increased in length, and there is now direct connectivity to Spain, United Kingdom, Germany, France, Italy, and Greece from the city of Antwerp.
In September 2019 Air Antwerp began operations with their first route to London City Airport with old VLM Airlines Fokker 50's.
Politics
City council
The current city council was elected in the October 2018 elections.
The current majority consists of N-VA, sp.a and Open Vld, led by mayor Bart De Wever (N-VA).
| Party | Seats | |
|---|---|---|
| New Flemish Alliance (N-VA) | 23 | |
| Green | 11 | |
| Vooruit | 6 | |
| Flemish Interest | 6 | |
| Workers' Party of Belgium (PVDA) | 4 | |
| Christian Democratic and Flemish (CD&V) | 3 | |
| Open Flemish Liberals and Democrats (Open Vld) | 2 | |
| Total | 55 | |
Former mayors
Main article: List of mayors of AntwerpIn the 16th and 17th century important mayors include Philips of Marnix, Lord of Saint-Aldegonde, Anthony van Stralen, Lord of Merksem and Nicolaas II Rockox. In the early years after Belgian independence, Antwerp was governed by Catholic-Unionist mayors. Between 1848 and 1921, all mayors were from the Liberal Party (except for the so-called Meeting-intermezzo between 1863 and 1872). Between 1921 and 1932, the city had a Catholic mayor again: Frans Van Cauwelaert. From 1932 onwards and up until 2013, all mayors belonged to the Social Democrat party: Camille Huysmans, Lode Craeybeckx, Frans Detiège and Mathilde Schroyens, and after the municipality fusion: Bob Cools [nl], Leona Detiège en Patrick Janssens. Since 2013, the mayor is the Flemish nationalist Bart De Wever, belonging to the Flemish separatist party N-VA (New Flemish Alliance).
Climate
Antwerp has an oceanic climate (Köppen: Cfb), with cool winters, warm summers and frequent, though light, precipitation throughout the year.
| Climate data for Antwerp (1991−2020 normals, extremes 1949−present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 15.6 (60.1) |
19.3 (66.7) |
24.6 (76.3) |
28.7 (83.7) |
32.9 (91.2) |
34.5 (94.1) |
40.4 (104.7) |
36.1 (97.0) |
35.0 (95.0) |
26.2 (79.2) |
20.3 (68.5) |
17.2 (63.0) |
40.4 (104.7) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 6.8 (44.2) |
7.7 (45.9) |
11.2 (52.2) |
15.3 (59.5) |
18.9 (66.0) |
21.6 (70.9) |
23.6 (74.5) |
23.6 (74.5) |
20.1 (68.2) |
15.4 (59.7) |
10.5 (50.9) |
7.2 (45.0) |
15.2 (59.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 4.0 (39.2) |
4.4 (39.9) |
7.1 (44.8) |
10.3 (50.5) |
14.0 (57.2) |
16.9 (62.4) |
18.9 (66.0) |
18.6 (65.5) |
15.5 (59.9) |
11.5 (52.7) |
7.4 (45.3) |
4.6 (40.3) |
11.1 (52.0) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 1.3 (34.3) |
1.2 (34.2) |
3.0 (37.4) |
5.2 (41.4) |
9.1 (48.4) |
12.2 (54.0) |
14.2 (57.6) |
13.7 (56.7) |
10.8 (51.4) |
7.6 (45.7) |
4.4 (39.9) |
2.0 (35.6) |
7.1 (44.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −18.5 (−1.3) |
−18.1 (−0.6) |
−10.8 (12.6) |
−4.9 (23.2) |
−2.6 (27.3) |
1.7 (35.1) |
5.0 (41.0) |
4.6 (40.3) |
1.1 (34.0) |
−6.1 (21.0) |
−9.5 (14.9) |
−16.1 (3.0) |
−18.5 (−1.3) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 70.0 (2.76) |
62.8 (2.47) |
54.2 (2.13) |
43.1 (1.70) |
59.8 (2.35) |
76.9 (3.03) |
82.3 (3.24) |
84.0 (3.31) |
75.6 (2.98) |
72.6 (2.86) |
80.7 (3.18) |
90.9 (3.58) |
852.9 (33.58) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 12.6 | 11.6 | 10.5 | 8.8 | 9.8 | 10.2 | 10.5 | 10.8 | 10.1 | 11.1 | 12.9 | 14.1 | 132.8 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 62 | 78 | 136 | 192 | 221 | 220 | 225 | 212 | 164 | 117 | 66 | 51 | 1,743 |
| Source 1: Royal Meteorological Institute | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Temperature estreme in Toscoma (extremes) | |||||||||||||
Culture
Antwerp had an artistic reputation in the 17th century, based on its school of painting, which included Rubens, Van Dyck, Jordaens, the Teniers and many others.

Informally, most Antverpians (in Dutch Antwerpenaren, people from Antwerp) speak Antverpian daily (in Dutch Antwerps), a dialect that Dutch-speakers know as distinctive from other Brabantic dialects for its characteristic pronunciation of vowels: an 'aw' sound approximately like that in 'bore' is used for one of its long 'a'-sounds while other short 'a's are very sharp like the 'a' in 'hat'. The Echt Antwaarps Teater ("Authentic Antverpian Theatre") brings the dialect on stage.
Antwerp was designated as the World Book Capital for the year 2004 by UNESCO.
Fashion
Antwerp is a rising fashion city, and has produced designers such as the Antwerp Six. The city has a cult status in the fashion world, due to the Royal Academy of Fine Arts, one of the most important fashion academies in the world. It has served as the learning centre for many Belgian fashion designers. Since the 1980s, several graduates of the Belgian Royal Academy of Fine Arts have become internationally successful fashion designers in Antwerp. The city has had a huge influence on other Belgian fashion designers such as Raf Simons, Veronique Branquinho, Olivier Theyskens and Kris Van Assche.
Local products
Antwerp is famous for its local products. In August every year the Bollekesfeest takes place. The Bollekesfeest is a showcase for such local products as Bolleke, an amber beer from the De Koninck Brewery. The city's historical ale, Seefbier, dating back to the 16th century and brewed at the Antwerpse Brouw Compagnie is a testament to the city's long brewing history and one of Belgium's oldest existing beerstyles. The Mokatine sweets made by Confiserie Roodthooft, Elixir D'Anvers, a locally made liquor, locally roasted coffee from Koffie Verheyen, sugar from Candico, Poolster pickled herring and Equinox horse meat, are other examples of local specialities. One of the most known products of the city are its biscuits, the Antwerpse Handjes, literally "Antwerp Hands". Usually made from a short pastry with almonds or milk chocolate, they symbolize the Antwerp trademark and folklore. The local products are represented by a non-profit organization, Streekproducten Provincie Antwerpen vzw.
Missions to Seafarers
A number of Christian missions to seafarers are based in Antwerp. These include the Mission to Seafarers, British & International Sailors' Society, the Finnish Seamen's Mission, the Norwegian Sjømannskirken and the Apostleship of the Sea. They provide cultural and social activities as well as religious services. The iconic Italiëlei premises have been closed down and all activities have been moved to the Antwerp Harbour Hotel on Noorderlaan.
Music
Antwerp is the home of the Antwerp Jazz Club (AJC), founded in 1938 and located on the square Grote Markt since 1994.
The band dEUS was formed in 1991 in Antwerp. dEUS began their career as a covers band, but soon began writing their own material. Their musical influences range from folk and punk to jazz and progressive rock.
Confetti's were a new beat band at the end of the 80's. Their name stems from the name of a nightclub in the Antwerps affluent suburb of Brasschaat. Their 1st video for 'The Sound of C' was shot on the main Antwerp shopping street.
Pump Up the Jam the eurobeat/dance song that reached top positions in charts worldwide in 1989 was produced in Antwerp. Belgian-Congolese singer Ya Kid K had Antwerp as her Belgian home base.
Music festivals
Cultuurmarkt van Vlaanderen is a musical festival and a touristic attraction that takes place annually on the final Sunday of August in the city center of Antwerp. Where international and local musicians and actors, present their stage and street performances.
Linkerwoofer is a pop-rock music festival located at the left bank of the Scheldt. This music festival starts in August and mostly local Belgian musicians play and perform in this event.
Tomorrowland (festival) is probably the most famous festival to arise from Antwerp. Though the festival is effectively located 15 km (10 mi) south of the city its founders in the past organised a festival ('Antwerp is burning') within city limits. The office of the company behind Tomorrowland (weareone.world bvba) is located in the heart of the city. The company founders are involved in conceptualising urban planning concepts for specific Antwerp areas and are known to invite their favourite Antwerp food places to set up a pop-up at the festival.
Other popular festivals Fire Is Gold, and focuses more on urban music, and Summerfestival.
World Choir Games
The city of Antwerp will co-host the 2020 World Choir Games together with the city of Ghent. Organised by the Interkultur Foundation, the World Choir Games is the biggest choral competition and festival in the world.
Sport

Antwerp held the 1920 Summer Olympics, which were the first games after the First World War and also the only ones to be held in Belgium.
Antwerp is home of the Belgian Pro Leaque football club Royal Antwerp F.C., currently playing in the Belgian First Division, were founded in 1880 and is known as 'The Great Old' for being the first club registered to the Royal Belgian Football Association in 1895. Another club in the city is Koninklijke Beerschot Voetbalclub Antwerpen, founded in 1899 by former Royal Antwerp players. They play at the Olympisch Stadion, the main venue of the 1920 Olympics in Antwerp.
Between these two football teams there has always been a big rivalry. When the two play against each other the stadiums are packed and the passioned fans give a great display of their passion, but this has also led to fights, hooliganism and vandalism.
The Antwerp Giants play in Basketball League Belgium and Topvolley Antwerpen play in the Belgium men's volleyball League.
For the year 2013, Antwerp was awarded the title of European Capital of Sport.
Antwerp hosted the 2013 World Artistic Gymnastics Championships.
Antwerp hosted the start of stage 3 of the 2015 Tour de France on 6 July 2015.
The city's Groenplaats will host the official 2022 FIBA 3x3 World Cup.
Higher education

Antwerp has a university and several colleges. The University of Antwerp (Universiteit Antwerpen) was established in 2003, following the merger of the RUCA, UFSIA and UIA institutes. Their roots go back to 1852. The university has approximately 23,000 registered students, making it the third-largest university in Flanders, as well as 1,800 foreign students. It has 7 faculties, spread over four campus locations in the city centre and in the south of the city. The university is part of Young Universities for the Future of Europe (YUFE) and Young European Research Universities Network (YERUN).
The city has several colleges, including Antwerp Management School (AMS), Charlemagne University College (Karel de Grote Hogeschool), Plantin University College (Plantijn Hogeschool), and Artesis University College (Artesis Hogeschool). Artesis University College has about 8,600 students and 1,600 staff, and Charlemagne University College has about 10,000 students and 1,300 staff. Plantin University College has approximately 3,700 students.
International relations
See also: List of twin towns and sister cities in BelgiumTwin towns and sister cities
| This section needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources in this section. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (September 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
The following places are twinned with or are sister cities to Antwerp:
 Fes, Morocco, 2000
Fes, Morocco, 2000 Rotterdam, the Netherlands, 1940
Rotterdam, the Netherlands, 1940 Mulhouse, France, 1954
Mulhouse, France, 1954 Saint Petersburg, Russia, 1958
Saint Petersburg, Russia, 1958 Rostock, Germany, 1963
Rostock, Germany, 1963 Shanghai, China, 1984
Shanghai, China, 1984 Akhisar, Turkey, 1988
Akhisar, Turkey, 1988 Haifa, Israel, 1995
Haifa, Israel, 1995 Cape Town, South Africa, 1996
Cape Town, South Africa, 1996 Ludwigshafen, Germany, 1998
Ludwigshafen, Germany, 1998
Partnerships
|
Within the context of development cooperation, Antwerp is also linked to
|
Notable people
Main article: Notable people from AntwerpBorn in Antwerp







- Lionel of Antwerp, 1st Duke of Clarence, (1338–1368) son of Edward III of England .
- Samuel Blommaert, (1583–1654) Director of Dutch West India Company
- Frans Floris, (1520–1570) painter.
- Abraham Ortelius, (1527–98) cartographer and geographer.
- Gillis van Coninxloo, (1544–1607) painter of forest landscapes
- Bartholomeus Spranger, (1546–1611) painter, draughtsman and etcher
- Matthijs Bril, (1550–1583) landscape painter
- Martín Antonio del Río, (1551–1608) Jesuit theologian
- Balthazar de Moucheron, (c. 1552–c. 1630) a founder of the Dutch East India Company
- Paul Bril, (1554–1626) landscape painter.
- Willem Usselincx, (1567–1647) Flemish merchant and investor, one of the founders of the Dutch West India Company
- Abraham Janssens, (c. 1570–1632) painter.
- Rodrigo Calderón, Count of Oliva, (c. 1576–1621) Spanish favourite and adventurer.
- Frans Snyders, (1579–1657) still life and animal painter
- Osias Beert the Elder, (1580–1623) painter
- Frans Hals, (1580–1666) painter.
- Caspar de Crayer, (1582–1669) painter.
- David Teniers the Elder, (1582–1649) painter.
- Jacob Jordaens, (1593–1678) painter
- Anthony van Dyck, (1599–1641) painter.
- Cornelis Melyn, (1600-c. 1662) early American settler, patron of Staten Island
- Pieter van Schaeyenborgh, (1600–1657) painter of fish still lifes
- David Teniers the Younger, (1610–1690) painter.
- Jan Fyt, (c. 1611–1661) animal painter.
- Nicolaes Maes, (1634–1693) Baroque painter.
- Hendrik Abbé, (1639–?) engraver, painter and architect
- Gerard Edelinck, (1649–1707) copperplate engraver.
- Jacob Leyssens, (1661–1710) Baroque painter
- Peter Tillemans, (c. 1684–1734) painter
- John Michael Rysbrack, (1694–1770) sculptor
- Joseph-Jean Le Grelle, (1764-1822) founder of the Joseph J. Le Grelle Bank in 1792
- Gérard Comte Le Grelle, (1793-1871) Mayor of Antwerp (1831-1848), and member of the National Congress
- Francis Palms, (1809–1886) Belgian-American landholder and businessman
- Hendrik Conscience, (1812–1883) writer and author of De Leeuw van Vlaanderen ("The Lion of Flanders").
- Johann Coaz, (1822–1918) Swiss forester, topographer and mountaineer
- Jef Lambeaux, (1852–1908) sculptor of the Brabo fountain on the Grote Markt.
- Georges Eekhoud, (1854–1927) novelist
- Hippolyte Delehaye, (1859–1941) Jesuit priest and hagiographic scholar.
- Ferdinand Perier, (1875–1968) Jesuit priest and 3rd archbishop of Calcutta
- Willem Elsschot, (1882–1960) writer and poet
- Maria Baers, (1883–1959) senator, feminist, and trade unionist.
- Jef van Hoof, (1886–1959) conductor and composer
- Constant Permeke, (1886–1952) expressionist painter
- Jacoba Hol (1886–1964), physical geographer
- Paul van Ostaijen, (1896–1928) poet and writer
- Alice Nahon, (1896–1933) poet
- Albert Lilar, (1900–1976) Minister of Justice
- Maurice Gilliams, (1900–1982) writer
- Michel Seuphor, (1901–1999) painter, designer
- André Cluytens, (1905–1967) conductor
- Daniel Sternefeld, (1905–1986) composer and conductor
- Maurice van Essche, (1906–1977) Belgian-born South African painter
- Antoinette Feuerwerker, (1912–2003) French jurist and member of the Resistance
- Jean Bingen, (1920–2012) Belgian papyrologist and epigrapher
- Karl Gotch, (1924–2007) professional wrestler
- Chris Mary-Francine Whittle, (born 1927), composer
- Simon Kornblit, (1933–2010) American advertising and film studio executive.
- Bernard de Walque, (born 1938) architect
- Ferre Grignard, (1939–1982) rock singer/songwriter, known for Ring Ring, I've Got to Sing
- Anthony Ruys, (born 1947) business executive
- Carl Verbraeken, (born 1950) composer
- Serge Strosberg, (born 1966) Belgian painter
- Tom Barman, (born 1972) Belgian musician and film director
- Matthias Schoenaerts, (born 1977) actor
- Tia Hellebaut, (born 1978) Olympic high jump champion
- Evi Goffin, (born 1981) vocalist
- Jessica Van Der Steen, (born 1984) model
- Toby Alderweireld, (born 1989) professional Belgian footballer
- Laetitia Beck, (born 1992) Israeli golfer
- Romelu Lukaku, (born 1993) professional Belgian footballer
- Retin Obasohan, (born 1993) basketball player for Hapoel Jerusalem
- Naomi Schiff, (born 1994) racing driver who competed in the W Series under a German licence





Lived in Antwerp
- Erasmus II Schetz, (died 1550) Lord of Grobbendonk
- Quentin Matsys, (1466–1530) Renaissance painter, founder of the Antwerp school.
- Jan Mabuse, (c. 1478–1532) painter
- Joachim Patinir, (c. 1480–1524) landscape and religious painter
- William Tyndale, (c. 1494–1536) Bible translator, arrested in Antwerp and burnt at the stake.
- John Rogers, (c. 1500–1555) Christian minister, Bible translator, commentator and martyr.
- Joos van Cleve, (c. 1500–c. 1540) painter
- Damião de Góis, (1502–1574) Portuguese humanist philosopher.
- Sir Thomas Gresham, (c. 1519–1579) English merchant and financier.
- Antonis Mor, (1520–c. 1577) portrait painter.
- Christophe Plantin, (c. 1520–1589) humanist, book printer and publisher.
- Pieter Bruegel the Elder, (c. 1525–c. 1569) painter and printmaker.
- Philips of Marnix, Lord of Saint-Aldegonde, (1538–1598) writer and statesman.
- Simon Stevin, (c. 1548–1620) mathematician and engineer.
- Federigo Giambelli, (c. 1550–c. 1610) Italian military and civil engineer.
- Nicolaas Rockox (1560–1640), mayor of Antwerp.
- John Bull, (c. 1562–1628) English/Welsh composer, musician and organ builder.
- Jan Brueghel the Elder, (1568–1625) also known as "Velvet" Brueghel, painter.
- Peter Paul Rubens, (1577–1640) painter.
- William Cavendish, 1st Duke of Newcastle, (c. 1592–1676) soldier, courtier and writer.
- Adriaen Brouwer, (1605–1638) painter
- Jan Davidsz. de Heem, (1606–1684) painter.
- Wenceslas Hollar, (1607–1677) Bohemian etcher.
- Jan Lievens, (1607–1674) painter
- Ferdinand van Apshoven the Younger, (c. 1630–1694) painter
- Frédéric Théodore Faber, painter (1782–1799)
- Jan Frans Willems, (1793–1846) writer.
- Abraham Mayer, (1816–1899) German-born physician
- Ford Madox Brown, (1821–1893) a British painter, studied art at Antwerp.
- Henri Alexis Brialmont, (1821–1903) military engineer.
- George du Maurier, (1834–1896) cartoonist, author and grandfather of Daphne du Maurier
- Sir Lawrence Alma-Tadema, (1836–1912) painter.
- Robert Barrett Browning, (1849–1912) English painter, studied painting in Antwerp
- Vincent van Gogh, (1853–1890) impressionist Dutch painter, lived in Antwerp for four months.
- Camille Huysmans, (1871–1968) Socialist politician, former mayor of Antwerp and former Prime Minister of Belgium
- Moshe Yitzchok Gewirtzman, (1881–1976) Hasidic Pshevorsk movement leader in Antwerp
- Romi Goldmuntz, (1882–1960) diamond businessman
- August De Boodt, (1895–1986) politician
- Gerard Walschap, (1898–1989) writer
- Albert Lilar, (1900–1976) Minister of Justice
- Suzanne Lilar, (1901–1992) essayist, novelist, and playwright
- Chaim Kreiswirth, (1918–2001) Rabbi of the Machzikei Hadass Community, Antwerp
- Eric de Kuyper, (born 1942) award-winning novelist, filmmaker, semiotician
- Philip Sessarego, (1952–2008) former British Army soldier, conman, hoaxer, mercenary lived in Antwerp and found dead in a garage
- Veerle Casteleyn, (born 1978) musical theatre performer and ballerina, trained in Antwerp.
- Andy Van Vliet (born 1995), Belgian basketball player for Bnei Herzliya Basket in the Israeli Basketball Premier League
Select neighbourhoods
- Den Dam – an area in northern Antwerp
- The diamond district – an area consisting of several square blocks, it is Antwerp's centre for the cutting, polishing, and trading of diamonds
- Linkeroever – Antwerp on the left bank of the Scheldt with a lot of apartment buildings
- Meir – Antwerp's largest shopping street
- Van Wesenbekestraat – the city's Chinatown
- Het Zuid – the south of Antwerp, notable for its museums and Expo grounds
- Zurenborg – an area between Central and Berchem station with a concentration of Art Nouveau townhouses
Notes
- The capital region of Brussels, whose metropolitan area comprises the city itself plus 18 independent communal entities, counts over 1,700,000 inhabitants, but these communities are counted separately by the Belgian Statistics Office.
References
- "Bevolking per gemeente op 1 januari 2020". Statbel.
- Statistics Belgium; Loop van de bevolking per gemeente (Excel file) Population of all municipalities in Belgium, as of 1 January 2017. Retrieved 1 November 2017.
- Statbel the Belgian statistics office
- "De Belgische Stadsgewesten 2001" (PDF). Statistics Belgium. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 October 2008. Retrieved 19 October 2008. Definitions of metropolitan areas in Belgium.
- "Annual Report 2014" (PDF). Port of Antwerp. 2014. p. 14. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2 February 2016. Retrieved 17 August 2021.
- "Antwerp is Europe's second largest port". 9 November 2016.
- "The World According to GaWC 2020". GaWC - Research Network. Globalization and World Cities. Retrieved 31 August 2020.
- "Antwerp Bourse—World's Oldest—Closes". Los Angeles Times. 31 December 1997. ISSN 0458-3035. Retrieved 22 March 2019.
- "A look inside one of the world's oldest stock exchange buildings". Barcroft TV.
- Geert Cole; Leanne Logan, Belgium & Luxembourg p.218 Lonely Planet Publishing (2007) ISBN 1-74104-237-2
- "Waarom is Antwerpen een majority-minoritystad?".
- ^ Brabo Antwerpen 1 (centrum) / Antwerpen (in Dutch)
- ^ Boulger, Demetrius Charles (1911). "Antwerp (city)" . In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 02 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 155–156.
- German Wiktionary. Retrieved 5 June 2020
- "Kroniek Antwerpen". AVBG (in Dutch). Antwerp Society for Architectural History. Retrieved 4 June 2020.
- Room, Adrian (1 August 1997). Placenames of the World. McFarland & Company. p. 32. ISBN 0-7864-0172-9.
- ^ "Antwerp" Encyclopædia Britannica
- "Naam Antwerpen heeft keltische oorsprong". Gazet van Antwerpen (in Dutch). 13 September 2007. Retrieved 18 August 2017. For the relevant passage in the Vita Eligii, see the Monumenta Germaniae Historica on the Digital MGH (page 700) retrieved 4 June 2020 (in Latin). Fordham University has published an English translation of the Vita Eligii by Jo Ann McNamara retrieved 18 August 2017
- Legenden en Mythen Legende van Brabo en de reus Antigoon. Archived 1 December 2010 at the Wayback Machine (in Dutch)
- "Het Steen, Antwerp, Belgium - SpottingHistory.com". www.spottinghistory.com. Retrieved 5 May 2022.
- ^ Hagen, Rainer; Marie, Rose (1994). Bruegel: The Complete Paintings. Germany: Taschen. p. 15. ISBN 978-3-8228-5991-9.
- Peter Gay and R.K. Webb, Modern Europe to 1815 (1973), p. 210.
- Tom Monaghan, Renaissance, Reformation and the Age of Discovery, 1450–1700 (Heinemann, 2002)
- Donald J. Harreld, "Atlantic Sugar and Antwerp's Trade with Germany in the Sixteenth Century," Journal of Early Modern History, 2003, Vol. 7 Issue 1/2, pp 148–163
- Outhwaite, R. B. (1966). "The Trials of Foreign Borrowing: The English Crown and the Antwerp Money Market in the Mid-Sixteenth Century". The Economic History Review. 19 (2): 289–305. doi:10.2307/2592253. JSTOR 2592253.
- (Braudel 1985 p. 143.)
- ^ Dunton, Larkin (1896). The World and Its People. Silver, Burdett. p. 163.
- ^ Luc-Normand Tellier (2009). "Urban world history: an economic and geographical perspective". PUQ. p.308. ISBN 2-7605-1588-5
- Sugg, Richard (2012). Mummies, Cannibals and Vampires: the History of Corpse Medicine from the Renaissance to the Victorians. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 9781136577369.
- Isidore Singer; Cyrus Adler, eds. (1916). "Antwerp". The Jewish Encyclopedia. pp. 658–660.
- Gay and Webb, Modern Europe to 1815 (1973), p. 210-11.
- Boxer Charles Ralph, The Dutch seaborne empire, 1600–1800, p. 18, Taylor & Francis, 1977 ISBN 0-09-131051-2, ISBN 978-0-09-131051-6 Google books
- Dunton, Larkin (1896). The World and Its People. Silver, Burdett. p. 164.
- Pelle, Kimberley D (2008). Findling, John E (ed.). Encyclopedia of World's Fairs and Expositions. McFarland & Company, Inc. p. 414. ISBN 978-0-7864-3416-9.
- Michael Ryckewaert, Planning Perspectives, July 2010, Vol. 25 Issue 3, pp 303–322.
- Javier Gimeno Martínez, "Selling Avant-garde: How Antwerp Became a Fashion Capital (1990–2002)," Urban Studies November 2007, Vol. 44 Issue 13, pp 2449–2464
- De Ceuninck, Koenraad (2009). De gemeentelijke fusies van 1976. Een mijlpaal voor de lokale besturen in België. Die keure, Brugge.
- Emporis. Retrieved 23 October 2006.
- "KBC Tower – The Skyscraper Center". skyscrapercenter.com. Retrieved 24 October 2016.
- "Palace of Justice in Antwerp". uginox.com. Retrieved 22 December 2019.
- "Divine justice". The Guardian. 10 April 2006. Retrieved 22 December 2019.
- "Antwerp timeline 1300–1399". Strecker.be. Archived from the original on 7 May 2008. Retrieved 13 April 2010.
- "Antwerp timeline 1400–1499". Strecker.be. Archived from the original on 10 May 2008. Retrieved 13 April 2010.
- Braudel, Fernand The Perspective of the World, 1985
- ^ "Antwerp timeline 1500–1599". Strecker.be. Archived from the original on 2 May 2008. Retrieved 13 April 2010.
- Coornaert, Émile (1961). Les Français et le commerce international à Anvers : fin du XVe, XVIe siècle. Paris: Marcel Rivière et cie. p. 96.
- Boumans, R; Craeybeckx, J (1947). Het bevolkingscijfer van Antwerpen in het derde kwart der XVIe eeuw. T.G. pp. 394–405.
- van Houtte, J. A. (1961). "Anvers aux XVe et XVIe siècles : expansion et apogée". Annales. Économies, Sociétés, Civilisations. 16 (2): 249. Retrieved 12 December 2014.
- Description of the French Fury matter, see chapter 'Declaration of independence' in article 'William the Silent'
- "Antwerp timeline 1600–1699". Strecker.be. Archived from the original on 7 May 2008. Retrieved 13 April 2010.
- "Antwerp timeline 1700–1799". Strecker.be. Archived from the original on 4 August 2008. Retrieved 13 April 2010.
- "Antwerp timeline 1800–1899". Strecker.be. Retrieved 13 April 2010.
- "Antwerp timeline 1900–1999". Strecker.be. Archived from the original on 7 January 2008. Retrieved 13 April 2010.
- "Stad in Cijfers – Databank – Inwoners naar nationaliteit, leeftijd, (8 klassen) en geslacht 2020 – Antwerpen". Antwerpen.be. City of Antwerp. Retrieved 18 April 2020.
- Auteur: Dajo Hermans. "56 procent van Antwerpse kinderen is allochtoon – Het Nieuwsblad". Nieuwsblad.be. Retrieved 12 March 2013.
- "Antwerpen in 2020 voor 55% allochtoon" (in Dutch). Express.be. 17 May 2010. Retrieved 12 March 2013.
- "An Introduction to Jainism: History, Religion, Gods, Scriptures and Beliefs". Commisceo Global. Retrieved 5 May 2012.
- Daneels, Door Gilbert Roox, foto's Wim. "Diamant met curry". De Standaard (in Flemish). Retrieved 28 October 2018.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Inside Knowledge: Streetwise in Asia p.163
- Vanneste, Tijl (6 October 2015). Global Trade and Commercial Networks: Eighteenth-Century Diamond Merchants. Routledge. ISBN 9781317323372 – via Google Books.
- Indians shine antwerp diamond centre polls International Business Times
- Belgium Real Estate Yearbook 2009 p.23
- ^ Recession takes the sparkle out of Antwerp's diamond quarter |World news. The Guardian. Retrieved 2 June 2011.
- "Antwerp and diamonds, the facts – Baunat Diamonds". baunatdiamonds.com.
- The Global Diamond Industry: Economics and Development, Volume 2 p.3.6
- "THE ARMENIAN OF BELGIUM: AN UNINTERRUPTED PRESENCE SINCE THE 4TH CENTURY". AGBU – Armenian non-profit organization.
- "Armenia: Report on Kotayk Province". WikiLeaks. 26 August 2011. Archived from the original on 14 March 2017. Retrieved 14 November 2012.
- "Wind farm | Sustainable Port of Antwerp". Archived from the original on 30 April 2014. Retrieved 2 August 2015.
- John Tagliabue (5 November 2012). "An Industry Struggles to Keep Its Luster". The New York Times. Retrieved 6 November 2012.
- ^ "Diamond". Business in Antwerp. Retrieved 26 April 2019.
- Tagliabue, John (2012). "An Industry Struggles to Keep Its Luster". Pittsburgh Post-Gazette. Retrieved 24 April 2019.
- "The industry | Antwerp World Diamond Centre". awdc.be. Archived from the original on 26 June 2015. Retrieved 2 August 2015.
- Hofmeester, Karin (March 2013). "Shifting trajectories of diamond processing: from India to Europe and back, from the fifteenth century to the twentieth*". Journal of Global History. 8 (1): 25–49. doi:10.1017/S174002281300003X. ISSN 1740-0228. S2CID 220685101.
- ^ "WSJ: Indians Unseat Antwerp's Jews As the Biggest Diamond Traders". Stefangeens.com. 27 May 2003. Retrieved 15 September 2011.
- Simons, Marlise (1 January 2006). "Twilight in Diamond Land: Antwerp's Loss, India's Gain". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 26 April 2019.
- Rankin, Jennifer (20 November 2022). "Belgium's trade in Russian diamonds continues despite moral pressure". the Guardian. Retrieved 24 November 2022.
- "Your VLM contacts". Archived from the original on 1 August 2003. Retrieved 29 March 2017.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) VLM Airlines. 1 August 2003. Retrieved 6 July 2010. "Headquarters VLM Airlines Belgium NV Luchthavengebouw B50 B 2100 Deurne Antwerpen." - "Our Offices Archived 14 February 2010 at the Wayback Machine." CityJet. Retrieved 6 July 2010. "Antwerp office VLM Airlines Belgium NV Luchthavengebouw B50 B 2100 Antwerp Belgium Company registration number 0446.670.251."
- "Body". Archived from the original on 3 December 2002. Retrieved 3 December 2002.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) Delsey Airlines. 3 December 2002. Retrieved 8 September 2010. - "Luchttemperatuur en neerslag Referentieperiode: 1991-2020" (PDF) (in Dutch). Royal Meteorological Institute. Retrieved 7 July 2022.
- "Temperature estreme in Antwerpen" (in Italian). Temperature estreme in Toscoma. Retrieved 31 August 2022.
- "World Book Capital 2004 Antwerp".
- Martínez (2007). Selling Avant-garde: How Antwerp Became a Fashion Capital (1990–2002).
- "Ons verhaal – Antwerpse Brouw Compagnie" (in Dutch). Retrieved 24 December 2020.
- "Verenigingen gevestigd in 'Den Bengel'. ANTWERPSE JAZZCLUB". Cafe Den Bengel. 27 February 2016. Retrieved 12 September 2016.
- "Gratis klassiek festival in Antwerpen". De Morgen (in Flemish). Retrieved 24 January 2018.
- "cultuurmarkt van vlaanderen – nieuws". cultuurmarkt.be. Retrieved 24 January 2018.
- Geert Geerits (11 December 2017), Cultuurmarkt Antwerpen (Vimeo), retrieved 24 January 2018
- Geert Geerits (11 December 2017), Cultuurmarkt Antwerpen (YouTube), archived from the original on 28 October 2021, retrieved 24 January 2018
- "Linkerwoofer 2018". linkerwoofer.be. Retrieved 25 January 2018.
- "Linkerwoofer". visitantwerpen.be. Retrieved 25 January 2018.
- "stubru.be". stubru.be (in Dutch). Retrieved 25 January 2018.
- "Double gold for next host country of the World Choir Games 2020". interkultur.com. Retrieved 19 July 2018.
- "Cycling at the 1920 Antwerpen Summer Games: Men's Road Race, Individual". sports-reference.com. Archived from the original on 18 April 2020. Retrieved 2 August 2015.
- Sports-reference.com 1920 Summer Olympics cycling team road race, team Olympics at Sports-Reference.com
- "ROYAL ANTWERP FOOTBALL CLUB". Archived from the original on 3 July 2013. Retrieved 3 June 2017.
- "Tour de France 2015 : de l'eau, et du diamant" (in French). letour.fr. 24 May 2014. Archived from the original on 25 May 2014. Retrieved 24 May 2014.
- Antwerp to host FIBA 3x3 World Cup 2022 FIBA, 18 January 2021. Accessed 30 April 2021.
- "Akhisar Belediyesi – ATİK – UEMP". uemp.eu. Archived from the original on 2 February 2017. Retrieved 25 January 2017.
- "Clarence, Dukes of" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 6 (11th ed.). 1911. pp. 427–428, see page 428, second para.
Lionel of Antwerp, duke of Clarence (1338–1368), third son of Edward III., was born at Antwerp on.....
- "Floris, Frans" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 10 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 547.
- Beazley, Charles Raymond (1911). "Ortelius, Abraham" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 20 (11th ed.). pp. 331–332.
- "Bril, Paul" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 4 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 571.
- "Janssens van Nuyssen, Abraham" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 15 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 155.
- Hannay, David McDowall (1911). "Calderón, Rodrigo" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 4 (11th ed.). p. 984.
- Konody, Paul George (1911). "Hals, Frans" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 12 (11th ed.). pp. 865–867.
- "Crayer, Gaspard de" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 7 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 387.
- Hymans, Henri Simon; Konody, Paul George (1911). "Teniers" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 26 (11th ed.). pp. 616–617, see first para.
David Teniers, the elder (1582–1649), was born at Antwerp.....
- Hymans, Henri Simon; Konody, Paul George (1911). "Van Dyck, Sir Anthony" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 27 (11th ed.). pp. 887–892.
- Hymans, Henri Simon; Konody, Paul George (1911). "Teniers" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 26 (11th ed.). pp. 616–617, see secpnd para.
David Teniers, the younger (1610–1696), the more celebrated son....
- "Fyt, Johannes" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 11 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 376.
- "Maes, Nicolas" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 17 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 298.
- "Edelinck, Gerard" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 8 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 923.
- Gosse, Edmund William (1911). "Conscience, Hendrik" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 6 (11th ed.). pp. 970–971.
- "Lambeaux, Jef" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 16 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 106.
- Author:Hippolyte Delehaye – via Wikisource.
- "Maria Baers". nl:ODIS (in Dutch). Retrieved 17 May 2021.
- Grossblat, R.M. (15 July 2010). "Simon Korblit, a Profile Tribute". Atlanta Jewish News. Retrieved 23 July 2010.
- Daily Telegraph - Movers & shakers: Anthony Ruys joins the board of British American Tobacco
- "Matsys, Quintin" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 17 (11th ed.). 1911. pp. 890–891.
- "Tyndale, William" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 27 (11th ed.). 1911. pp. 498–499.
- "Rogers, John (martyr)" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 23 (11th ed.). 1911. pp. 456–457.
- Prestage, Edgar (1911). "Goes, Damião de" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 12 (11th ed.). pp. 180–181.
- "Gresham, Sir Thomas" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 12 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 582.
- "Moro, Antonio" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 18 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 850.
- Tiele, Pieter Anton (1911). "Plantin, Christophe" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 21 (11th ed.). pp. 727–728.
- "Breughel, Pieter" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 4 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 503.
- "St Aldegonde, Philips van Marnix, Heer van" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 23 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 1013.
- Cantor, Moritz (1911). "Stevinus, Simon" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 25 (11th ed.). pp. 910–911.
- "Giambelli, Federigo" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 11 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 925.
- "Bull, John" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 4 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 787.
- "Breughel, Pieter" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 4 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 503; third para.
Another son Jan (c. 1569–1642), known as "Velvet" Breughel......
- Hymans, Henri Simon; Konody, Paul George (1911). "Rubens, Peter Paul" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 23 (11th ed.). pp. 804–808.
- "Newcastle, Dukes of" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 19 (11th ed.). 1911. pp. 470–471, second para.
1. William Cavendish, duke of Newcastle (1592–1676)....
- "Heem, Jan Davidsz van" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 13 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 198.
- "Hollar, Wenzel" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 13 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 611.
- "Willems, Jean François" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 28 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 658.
- Rossetti, William Michael (1911). "Brown, Ford Madox" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 4 (11th ed.). pp. 657–658.
- "Brialmont, Henri Alexis" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 4 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 515.
- "Alma-Tadema, Sir Laurence" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 1 (11th ed.). 1911. pp. 712–713.
- Author:Vincent van Gogh – via Wikisource.
Further reading
See also: Bibliography of the history of Antwerp- Blanchard, Ian. The International Economy in the "Age of the Discoveries," 1470–1570: Antwerp and the English Merchants' World (Stuttgart: Franz Steiner Verlag, 2009). 288 pp. in English
- Harreld, Donald J. "Trading Places," Journal of Urban History (2003) 29#6 pp 657–669
- Lindemann, Mary. The Merchant Republics: Amsterdam, Antwerp, and Hamburg, 1648–1790 (Cambridge University Press, 2014) 356 pp.
- Limberger, Michael. Sixteenth-Century Antwerp and its Rural Surroundings: Social and Economic Changes in the Hinterland of a Commercial Metropolis (ca. 1450–1570) (Turnhout: Brepols Publishers, 2008). 284 pp. ISBN 978-2-503-52725-3.
- Makos, Adam (2019). Spearhead (1st ed.). New York: Ballantine Books. pp. 63, 69. ISBN 9780804176729. LCCN 2018039460. OL 27342118M.
- Stillwell, Richard, ed. Princeton Encyclopedia of Classical Sites, 1976: "Antwerp Belgium"
- Van der Wee, Herman. The Growth of the Antwerp Market and the European Economy (14th–16th Centuries) (The Hague, 1963)
External links
| Places adjacent to Antwerp | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||
| Members of the Hanseatic League by quarter, and trading posts of the Hanseatic League | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
| Wendish |
|   | ||
| Saxon |
| |||
| Baltic |
| |||
| Westphalian |
| |||
| Kontore | ||||
| Vitten | ||||
| Factories | ||||
| Seventeen Provinces of Habsburg Netherlands |
|  | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| County | ||||||
| Cities | ||||||
| Dependent territories | ||||||
| until 1648; until 1659; until 1678.
Circles est. 1500: Bavarian, Swabian, Upper Rhenish, Lower Rhenish–Westphalian, Franconian, (Lower) Saxon Circles est. 1512: Austrian, Burgundian, Upper Saxon, Electoral Rhenish · Unencircled territories | ||||||
| Municipalities in Antwerp Province, Flanders, Belgium | ||
|---|---|---|
| Antwerp |  | |
| Mechelen | ||
| Turnhout | ||
| Bold indicates cities | ||
| World Book Capitals | ||
|---|---|---|
|  | |
| European Capitals of Culture | |
|---|---|
|
| European Capitals of Sport | |
|---|---|
|
| European Youth Capitals | |
|---|---|
| Summer Olympic Games host cities | |
|---|---|
| |
| Cancelled due to World War I; Cancelled due to World War II; Postponed to 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic |
|
| Olympic venues in cycling | ||
|---|---|---|
| 19th century |  | |
| 20th century |
| |
| 21st century |
| |
