| Revision as of 17:53, 11 June 2023 editRaydenAG (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users699 editsmNo edit summaryTags: Mobile edit Mobile app edit iOS app edit← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 11:56, 18 September 2023 edit undoKoIobok (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users1,350 edits Added Category:Beta-Amino acids | ||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:56, 18 September 2023
Major metabolite of the psychostimulant drug methylphenidate Pharmaceutical compound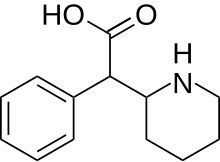 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.039.094 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H17NO2 |
| Molar mass | 219.284 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Ritalinic acid is a substituted phenethylamine and an inactive major metabolite of the psychostimulant drugs methylphenidate, dexmethylphenidate and ethylphenidate. When administered orally, methylphenidate is extensively metabolized in the liver by hydrolysis of the ester group yielding ritalinic acid. The hydrolysis was found to be catalyzed by carboxylesterase 1 (CES1).
Etymologically, ritalinic acid shares its roots with Ritalin, a common brand name for methylphenidate.
Uses
Ritalinic acid is used as an intermediate in the synthesis of methylphenidate and its analogues, such as ethylphenidate and isopropylphenidate.
References
- ^ Faraj BA, Israili ZH, Perel JM, Jenkins ML, Holtzman SG, Cucinell SA, Dayton PG (December 1974). "Metabolism and disposition of methylphenidate-14C: studies in man and animals". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 191 (3): 535–47. PMID 4473537.
- Negreira N, Erratico C, van Nuijs AL, Covaci A (January 2016). "Identification of in vitro metabolites of ethylphenidate by liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry". Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 117 (5): 474–84. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2015.09.029. hdl:10067/1301870151162165141. PMID 26454340.
- Sun Z, Murry DJ, Sanghani SP, Davis WI, Kedishvili NY, Zou Q, et al. (August 2004). "Methylphenidate is stereoselectively hydrolyzed by human carboxylesterase CES1A1". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 310 (2): 469–76. doi:10.1124/jpet.104.067116. PMID 15082749. S2CID 24233422.