| Revision as of 01:29, 12 January 2023 editPashihiko (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users3,563 editsNo edit summary← Previous edit | Revision as of 13:12, 13 March 2024 edit undoMarbletan (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users5,638 editsNo edit summaryNext edit → | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| |Section2={{Chembox Properties | |Section2={{Chembox Properties | ||
| | C=15 | H=12 | O=5 | |||
| | Formula = C<sub>15</sub>H<sub>12</sub>O<sub>5</sub> | |||
| | MolarMass = 272.25 g/mol | |||
| | Appearance = | | Appearance = | ||
| | Density = | | Density = | ||
| Line 40: | Line 39: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Butein''' is a ] of the ]s. It can be found in '']'' (or formerly ''Rhus verniciflua''), '']'', '']'' ('']'') and '']''<ref>Semwal, R. B., Semwal, D. K., Combrinck, S., & Viljoen, A. (2015). Butein: From ancient traditional remedy to modern nutraceutical. Phytochemistry Letters, 11, 188-201. {{doi|10.1016/j.phytol.2014.12.014}}</ref> It has ], ] and ]s inhibitory effects.<ref name="pmid18670102">{{cite journal |vauthors=Lee EH, Song DG, Lee JY, Pan CH, Um BH, Jung SH |title=Inhibitory effect of the compounds isolated from Rhus verniciflua on aldose reductase and advanced glycation endproducts |journal=Biol. Pharm. Bull. |volume=31 |issue=8 |pages=1626–30 |date=August 2008 |pmid=18670102 |doi= 10.1248/bpb.31.1626|doi-access=free }}</ref> It is also a ], a chemical compound having an effect on sirtuins, a group of enzymes that use NAD<sup>+</sup> to remove acetyl groups from proteins. Buteins possess a high ability to inhibit aromatase process in the human body, for this reason, the use of these compounds in the treatment of ] on the estrogen ground has been explored.<ref>Wang Y. "" Life Sci. 2005 May 20;77(1):39-51.</ref> The first attempts of sport pro-hormone supplementation with the use of buteins took place in Poland.<ref>S.Amboziak " 09.2012</ref> | '''Butein''' is a ] of the ]s. It can be found in '']'' (or formerly ''Rhus verniciflua''), '']'', '']'' ('']'') and '']''<ref>Semwal, R. B., Semwal, D. K., Combrinck, S., & Viljoen, A. (2015). Butein: From ancient traditional remedy to modern nutraceutical. Phytochemistry Letters, 11, 188-201. {{doi|10.1016/j.phytol.2014.12.014}}</ref> It has ], ] and ]s inhibitory effects.<ref name="pmid18670102">{{cite journal |vauthors=Lee EH, Song DG, Lee JY, Pan CH, Um BH, Jung SH |title=Inhibitory effect of the compounds isolated from Rhus verniciflua on aldose reductase and advanced glycation endproducts |journal=Biol. Pharm. Bull. |volume=31 |issue=8 |pages=1626–30 |date=August 2008 |pmid=18670102 |doi= 10.1248/bpb.31.1626|doi-access=free }}</ref> It is also a ], a chemical compound having an effect on sirtuins, a group of enzymes that use NAD<sup>+</sup> to remove acetyl groups from proteins. Buteins possess a high ability to inhibit aromatase process in the human body, for this reason, the use of these compounds in the treatment of ] on the estrogen ground has been explored.<ref>Wang Y. "" Life Sci. 2005 May 20;77(1):39-51.</ref> The first attempts of sport pro-hormone supplementation with the use of buteins took place in Poland.<ref>S.Amboziak " 09.2012</ref>{{rs}} | ||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 13:12, 13 March 2024
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
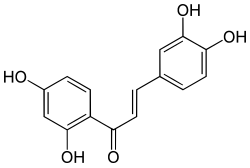
| Preferred IUPAC name 2′,3,4,4′-Tetrahydroxychalcone | |
| Other names
(2E)-1-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one 2′,4′,3,4-Tetrahydroxychalcone 3,4,2′,4′-Tetrahydroxychalcone | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.963 |
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C15H12O5 |
| Molar mass | 272.256 g·mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Butein is a chalcone of the chalconoids. It can be found in Toxicodendron vernicifluum (or formerly Rhus verniciflua), Dahlia, Butea (Butea monosperma) and Coreopsis It has antioxidative, aldose reductase and advanced glycation endproducts inhibitory effects. It is also a sirtuin-activating compound, a chemical compound having an effect on sirtuins, a group of enzymes that use NAD to remove acetyl groups from proteins. Buteins possess a high ability to inhibit aromatase process in the human body, for this reason, the use of these compounds in the treatment of breast cancer on the estrogen ground has been explored. The first attempts of sport pro-hormone supplementation with the use of buteins took place in Poland.
References
- Semwal, R. B., Semwal, D. K., Combrinck, S., & Viljoen, A. (2015). Butein: From ancient traditional remedy to modern nutraceutical. Phytochemistry Letters, 11, 188-201. doi:10.1016/j.phytol.2014.12.014
- Lee EH, Song DG, Lee JY, Pan CH, Um BH, Jung SH (August 2008). "Inhibitory effect of the compounds isolated from Rhus verniciflua on aldose reductase and advanced glycation endproducts". Biol. Pharm. Bull. 31 (8): 1626–30. doi:10.1248/bpb.31.1626. PMID 18670102.
- Wang Y. "The plant polyphenol butein inhibits testosterone-induced proliferation in breast cancer cells expressing aromatase" Life Sci. 2005 May 20;77(1):39-51.
- S.Amboziak "Aromatase in the dock" 09.2012
| Chalconoids and their glycosides | |
|---|---|
| Chalconoids | |
| Chalconoid glycosides | |
| Acylated chalconoids |
|
| O-methylated chalconoids |
|
| Flavokavains | |
| Synthetic | |
This article about an aromatic compound is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |