| Revision as of 15:46, 3 November 2022 edit147.147.108.194 (talk) Removing advertisingTag: references removed← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 20:14, 5 April 2024 edit undoحسن علي البط (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers19,940 edits added Category:Heterocyclic compounds with 3 rings using HotCat | ||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 20:14, 5 April 2024
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
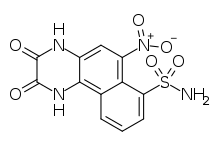
| Preferred IUPAC name 6-Nitro-2,3-dioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrobenzoquinoxaline-7-sulfonamide | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.149.984 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C12H8N4O6S |
| Molar mass | 336.281 |
| Appearance | brown/red powder |
| Solubility in water | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
NBQX (2,3-dioxo-6-nitro-7-sulfamoyl-benzoquinoxaline) is an antagonist of the AMPA receptor.
NBQX blocks AMPA receptors in micromolar concentrations (~10–20 μM) and also blocks kainate receptors. In experiments, it is used to counter glutamate excitotoxicity. NBQX was found to have anticonvulsant activity in rodent seizure models.
As the disodium salt, NBQX is soluble in water at high concentrations (at least up to 100 mM).
See also
- CNQX
- DNQX
- Fanapanel (MPQX)
- Quinoxalinedione
References
- Pitt, D.; Werner, P.; Raine, C. S. (2000). "Glutamate excitotoxicity in a model of multiple sclerosis". Nat Med. 6 (1): 67–70.
- Yamaguchi, S.; Donevan, S.D.; Rogawski, M.A. (1993). Anticonvulsant activity of AMPA/kainate antagonists: comparison of GYKI 52466 and NBOX in maximal electroshock and chemoconvulsant seizure models. Epilepsy Res. 15:179–184.
This biochemistry article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |