| Revision as of 17:32, 9 May 2024 view sourceKepler-1229b (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users18,258 edits Undid revision 1219358186 by Future Perfect at Sunrise (talk)Tag: Undo← Previous edit | Revision as of 12:06, 3 July 2024 view source WhyIsNameSoHardOmg- - (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users7,870 edits Revi.Tag: Visual editNext edit → | ||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
| "C" comes from the same letter as "G". The ] named it ]. The sign is possibly adapted from an ] for a ], which may have been the meaning of the name ''gimel''. Another possibility is that it depicted a camel, the Semitic name for which was ''gamal''. ], a specialist in the history of writing, states "It is hard to imagine how gimel = "camel" can be derived from the picture of a camel (it may show his hump, or his head and neck!)".<ref>{{cite book|last=Powell|first=Barry B.|title=Writing: Theory and History of the Technology of Civilization|date=27 Mar 2009|publisher=Wiley Blackwell|isbn=978-1405162562|page=182|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=PZ2Gr3d9X2UC&q=Gimel+shaped+like+a+camel%27s+neck&pg=PA182}}</ref> | "C" comes from the same letter as "G". The ] named it ]. The sign is possibly adapted from an ] for a ], which may have been the meaning of the name ''gimel''. Another possibility is that it depicted a camel, the Semitic name for which was ''gamal''. ], a specialist in the history of writing, states "It is hard to imagine how gimel = "camel" can be derived from the picture of a camel (it may show his hump, or his head and neck!)".<ref>{{cite book|last=Powell|first=Barry B.|title=Writing: Theory and History of the Technology of Civilization|date=27 Mar 2009|publisher=Wiley Blackwell|isbn=978-1405162562|page=182|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=PZ2Gr3d9X2UC&q=Gimel+shaped+like+a+camel%27s+neck&pg=PA182}}</ref> | ||
| In the ], ]s had no contrastive ], so the ] ']' (Gamma) was adopted into the ] to represent {{IPA|/k/}}. Already in the ], Gamma first took a ']' form in Early Etruscan, then ']' in Classical Etruscan. In Latin it eventually took the '{{smallcaps|c}}' form in Classical Latin. In the earliest |
In the ], ]s had no contrastive ], so the ] ']' (Gamma) was adopted into the ] to represent {{IPA|/k/}}. Already in the ], Gamma first took a ']' form in Early Etruscan, then ']' in Classical Etruscan. In ], it eventually took the '{{smallcaps|c}}' form in ]. In the earliest Latin inscriptions, the letters '{{smallcaps|c k q}}' were used to represent the sounds {{IPA|/k/}} and {{IPA|/ɡ/}} (which were not differentiated in writing). Of these, '{{smallcaps|q}}' was used to represent {{IPA|/k/}} or {{IPA|/ɡ/}} before a rounded vowel, '{{smallcaps|k}}' before '{{smallcaps|a}}', and '{{smallcaps|c}}' elsewhere.<ref>{{cite book | ||
| |title=New Comparative Grammar of Greek and Latin | |title=New Comparative Grammar of Greek and Latin | ||
| |first=Andrew L. | |first=Andrew L. | ||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
| |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=IeHmqKY2BqoC | |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=IeHmqKY2BqoC | ||
| |page=21 | |page=21 | ||
| }}</ref> During the 3rd century BC, a modified character was introduced for {{IPA|/ɡ/}}, and '{{smallcaps|c}}' itself was retained for {{IPA|/k/}}. The use of '{{smallcaps|c}}' (and its variant '{{smallcaps|g}}') replaced most usages of '{{smallcaps|k}}' and '{{smallcaps|q}}'. |
}}</ref> During the 3rd century BC, a modified character was introduced for {{IPA|/ɡ/}}, and '{{smallcaps|c}}' itself was retained for {{IPA|/k/}}. The use of '{{smallcaps|c}}' (and its variant '{{smallcaps|g}}') replaced most usages of '{{smallcaps|k}}' and '{{smallcaps|q}}'. Hence, in the classical period and after, '{{smallcaps|g}}' was treated as the equivalent of Greek gamma, and '{{smallcaps|c}}' as the equivalent of kappa; this shows in the romanization of Greek words, as in 'ΚΑΔΜΟΣ', 'ΚΥΡΟΣ', and 'ΦΩΚΙΣ' came into Latin as '{{smallcaps|cadmvs}}', '{{smallcaps|cyrvs}}' and '{{smallcaps|phocis}}', respectively. | ||
| Other alphabets have letters ]ic to 'c' but not analogous in use and derivation, like the ] letter ] (С, с) which derives from the lunate ]. | Other alphabets have letters ]ic to 'c' but not analogous in use and derivation, like the ] letter ] (С, с) which derives from the lunate ]. | ||
| ===Later use=== | ===Later use=== | ||
| When the Roman alphabet was introduced into Britain, {{angbr|c}} represented only {{IPA|/k/}}, and this value of the letter has been retained in loanwords to all the ]: in ],<ref>{{Cite web |title=Reading Middle Welsh -- 29 Medieval Spelling |url=https://www.mit.edu/people/dfm/canol/chap29.html |access-date=2019-11-19 |website=www.mit.edu}}</ref> ], and ], {{angbr|c}} represents only {{IPA|/k/}}. The ] was learned from the Celts, apparently of Ireland; hence {{angbr|c}} in Old English also originally represented {{IPA|/k/}}; the Modern English words ''kin, break, broken, thick'', and ''seek'' all come from Old English words written with {{angbr|c}}: {{lang|ang|cyn, brecan, brocen, þicc}}, and {{lang|ang|séoc}}. However, during the course of the Old English period, {{IPA|/k/}} before front vowels ({{IPA|/e/}} and {{IPA|/i/}}) was ], having changed by the tenth century to {{IPA|}}, though {{angbr|c}} was still used, as in {{lang|ang|cir(i)ce, wrecc(e)a}}. On the continent, meanwhile, a similar phonetic change before the same two vowels had also been going on in almost all modern romance languages (for example, in ]). | When the Roman alphabet was introduced into Britain, {{angbr|c}} represented only {{IPA|/k/}}, and this value of the letter has been retained in loanwords to all the ]: in ],<ref>{{Cite web |title=Reading Middle Welsh -- 29 Medieval Spelling |url=https://www.mit.edu/people/dfm/canol/chap29.html |access-date=2019-11-19 |website=www.mit.edu}}</ref> ], and ], {{angbr|c}} represents only {{IPA|/k/}}. The ] was learned from the Celts, apparently of Ireland; hence, {{angbr|c}} in Old English also originally represented {{IPA|/k/}}; the Modern English words ''kin'', ''break'', ''broken'', ''thick'', and ''seek'' all come from Old English words written with {{angbr|c}}: {{lang|ang|cyn, brecan, brocen, þicc}}, and {{lang|ang|séoc}}. However, during the course of the Old English period, {{IPA|/k/}} before front vowels ({{IPA|/e/}} and {{IPA|/i/}}) was ], having changed by the tenth century to {{IPA|}}, though {{angbr|c}} was still used, as in {{lang|ang|cir(i)ce, wrecc(e)a}}. On the continent, meanwhile, a similar phonetic change before the same two vowels had also been going on in almost all modern romance languages (for example, in ]). | ||
| In Vulgar Latin, {{IPA|/k/}} became palatalized to {{IPA|}} in Italy and Dalmatia; in France and the Iberian |
In Vulgar Latin, {{IPA|/k/}} became palatalized to {{IPA|}} in Italy and Dalmatia; in France and the ], it became {{IPA|}}. Yet for these new sounds, {{angbr|{{sm|c}}}} was still used before the letters {{angbr|e}} and {{angbr|i}}. The letter thus represented two distinct values. Subsequently, the Latin phoneme {{IPA|/k<sup>w</sup>/}} (spelled {{angbr|{{smallcaps|qv}}}}) de-labialized to {{IPA|/k/}}, meaning that the various Romance languages had {{IPA|/k/}} before front vowels. In addition, ] used the letter {{angbr|k}} so that the sound {{IPA|/k/}} could be represented by either {{angbr|k}} or {{angbr|c}}, the latter of which could represent either {{IPA|/k/}} or {{IPA|/ts/}} depending on whether it preceded a front vowel letter or not. The convention of using both {{angbr|c}} and {{angbr|k}} was applied to the writing of English after the ], causing a considerable re-spelling of the Old English words. Thus, while Old English ''candel'', ''clif'', ''corn'', ''crop'', and ''cú'', remained unchanged, ''Cent'', ''cǣᵹ'' (''cēᵹ''), ''cyng'', ''brece'', and ''sēoce'', were now (without any change of sound) spelled ''Kent'', ''keȝ'', ''kyng'', ''breke'', and {{lang|enm|seoke}}; even {{lang|ang|cniht}} ('knight') was subsequently changed to {{lang|enm|kniht}} and {{lang|ang|þic}} ('thick') changed to {{lang|enm|thik}} or {{lang|enm|thikk}}. The Old English {{angbr|cw}} was also at length displaced by the French {{angbr|qu}} so that the Old English {{lang|ang|cwēn}} ('queen') and {{lang|ang|cwic}} ('quick') became ] {{lang|enm|quen}} and {{lang|enm|quik}}, respectively. | ||
| The sound {{IPA|}}, to which Old English palatalized {{IPA|/k/}} had advanced, also occurred in French, chiefly from Latin {{IPA|/k/}} before {{angbr|a}}. In French, it was represented by the digraph {{angbr|ch}}, as in ''champ'' (from Latin {{lang|la|camp-um}}), and this spelling was introduced into English: the ], written {{circa|1160}}, have in Matt. i-iii, ''child'', ''chyld'', ''riche'', and ''mychel'', for the ''cild'', ''rice'', and ''mycel'' of the Old English version whence they were copied. In these cases, the Old English {{angbr|c}} gave way to {{angbr|k}}, {{angbr|qu}} and {{angbr|ch}}; on the other hand, {{angbr|c}} in its new value of {{IPA|/ts/}} appeared largely in French words like ''processiun'', ''emperice'', and {{lang|xno|grace}} and was also substituted for {{angbr|ts}} in a few Old English words, as {{lang|ang|miltse, bletsien}}, in early Middle English {{lang|enm|milce, blecien}}. By the end of the thirteenth century, both in France and England, this sound {{IPA|/ts/}} was de-affricated to {{IPA|/s/}}; and from that time, {{angbr|c}} has represented {{IPA|/s/}} before front vowels either for ] reasons, as in ''lance, cent'', or to avoid the ambiguity due to the "etymological" use of {{angbr|s}} for {{IPA|/z/}}, as in ''ace'', ''mice'', ''once'', ''pence'', ''defence''. | |||
| ⚫ | Thus, to show etymology, English spelling has ''advise'', ''devise'' (instead of ''*advize'', ''*devize''), while ''advice, device, dice, ice, mice, twice'', etc., do not reflect etymology; example has extended this to ''hence, pence, defence'', etc., where there is no etymological reason for using {{angbr|c}}. Former generations also wrote ''sence'' for ''sense''. Hence, today the ] and ] have a common feature inherited from ] spelling conventions where {{angbr|c}} takes on either a ] value depending on the following letter. | ||
| ⚫ | Thus, to show etymology, English spelling has ''advise'', ''devise'' (instead of ''*advize'', ''*devize''), while ''advice'', ''device'', ''dice'', ''ice'', ''mice'', ''twice'', etc., do not reflect etymology; example has extended this to ''hence'', ''pence'', ''defence'', etc., where there is no etymological reason for using {{angbr|c}}. Former generations also wrote ''sence'' for ''sense''. Hence, today, the ] and ] have a common feature inherited from ] spelling conventions where {{angbr|c}} takes on either a ] value depending on the following letter. | ||
| ==Use in writing systems== | ==Use in writing systems== | ||
| Line 372: | Line 374: | ||
| ===Other languages=== | ===Other languages=== | ||
| In the Romance languages ], ], ], ] and ], {{angbr|c}} generally has a "hard" value of {{IPA|/k/}} and a "soft" value whose pronunciation varies by language. In French, Portuguese, Catalan and Spanish from Latin America and some places in Spain, the soft {{angbr|c}} value is {{IPA|/s/}} as it is in English. |
In the Romance languages ], ], ], ], and ], {{angbr|c}} generally has a "hard" value of {{IPA|/k/}} and a "soft" value whose pronunciation varies by language. In French, Portuguese, Catalan, and Spanish from Latin America and some places in Spain, the soft {{angbr|c}} value is {{IPA|/s/}} as it is in English. In the Spanish spoken in most of Spain, the soft {{angbr|c}} is a ] {{IPA|/θ/}}. In ] and ], the soft {{angbr|c}} is {{IPA|}}. | ||
| Germanic languages usually use {{angbr|c}} for Romance loans or digraphs, such as {{angbr|ch}} and {{angbr|ck}}, but the rules vary across languages. Of all the Germanic languages, only English uses initial {{angbr|c}} in native Germanic words like ''come''. |
Germanic languages usually use {{angbr|c}} for Romance loans or digraphs, such as {{angbr|ch}} and {{angbr|ck}}, but the rules vary across languages. Of all the Germanic languages, only English uses the initial {{angbr|c}} in native Germanic words like ''come''. Other than English, ] uses {{angbr|c}} the most, for most Romance loans and the digraph {{angbr|ch}}. German uses {{angbr|c}} in the digraphs {{angbr|ch}} and {{angbr|ck}}, and the trigraph {{angbr|sch}}, but by itself only in unassimilated loanwords and proper names. ] keeps soft {{angbr|c}} in Romance words but changes hard {{angbr|c}} to {{angbr|k}}. Swedish has the same rules for soft and hard {{angbr|c}} as Danish, and also uses {{angbr|c}} in the digraph {{angbr|ck}} and the very common word ''och'', "and". ], ], and ] are the most restrictive, replacing all cases of {{angbr|c}} with {{angbr|k}} or {{angbr|s}}, and reserving {{angbr|c}} for unassimilated loanwords and names. | ||
| All ] that use the Latin alphabet, as well as ], ], ], several ], ], ], ], and ] (and those ] whose practical orthography derives from it) use {{angbr|c}} to represent {{IPA|/t͡s/}}, the ] or ]. In ], the standard romanization of ], the letter represents an aspirated version of this sound, {{IPA|/t͡s<sup>h</sup>/}}. | All ] that use the Latin alphabet, as well as ], ], ], several ], ], ], ], and ] (and those ] whose practical orthography derives from it), use {{angbr|c}} to represent {{IPA|/t͡s/}}, the ] or ]. In ], the standard romanization of ], the letter represents an aspirated version of this sound, {{IPA|/t͡s<sup>h</sup>/}}. | ||
| Among non-European languages that have adopted the Latin alphabet, {{angbr|c}} represents a variety of sounds. ], ], ], and a number of African languages such as ], ], and ] share the soft Italian value of {{IPA|/t͡ʃ/}}. |
Among non-European languages that have adopted the Latin alphabet, {{angbr|c}} represents a variety of sounds. ], ], ], and a number of African languages such as ], ], and ] share the soft Italian value of {{IPA|/t͡ʃ/}}. In ], ], ], and ] {{angbr|c}} stands for the voiced counterpart of this sound, the ] {{IPA|/d͡ʒ/}}. In ] and similar languages, such as ], {{angbr|c}} stands for a ] {{IPA|/ʔ/}}. ] and ] use this letter to represent the click {{IPA|/ǀ/}}. In some other African languages, such as ], {{angbr|c}} is used for {{IPA|/ʃ/}}. In ], {{angbr|c}} stands for a ] {{IPA|/ð/}}, while in ] it has the value of {{IPA|/]/}}. | ||
| The letter {{angbr|c}} is also used as a transliteration of Cyrillic {{angbr|ц}} in the Latin forms of ], ], and sometimes ], along with the digraph {{angbr|ts}}. | The letter {{angbr|c}} is also used as a transliteration of Cyrillic {{angbr|ц}} in the Latin forms of ], ], and sometimes ], along with the digraph {{angbr|ts}}. | ||
| Line 401: | Line 403: | ||
| ===Ancestors, descendants and siblings=== | ===Ancestors, descendants and siblings=== | ||
| ]]] | ]]] | ||
| *𐤂 : ] letter ], from which the following symbols originally derive | *𐤂 : ] letter ], from which the following symbols originally derive: | ||
| **{{lang|el|Γ γ}} : ] letter ], from which C derives | **{{lang|el|Γ γ}} : ] letter ], from which C derives | ||
| ***G g : Latin letter ], which is derived from Latin C | ***G g : Latin letter ], which is derived from Latin C | ||
| Line 408: | Line 410: | ||
| **{{IPA link|ɕ}} : Small c with curl | **{{IPA link|ɕ}} : Small c with curl | ||
| **ʗ : ] | **ʗ : ] | ||
| **𝼏 : ] |
**𝼏 : ] – Used by Douglas Beach for a ] in his phonetic description of ].<ref>{{Cite web|title=L2/20-115R: Unicode request for additional phonetic click letters|url=https://www.unicode.org/L2/L2020/20115r-click-letters.pdf|date=2020-07-10|first1=Kirk|last1=Miller|first2=Bonny|last2=Sands}}</ref> | ||
| **𝼝 : Small letter c with retroflex hook |
**𝼝 : Small letter c with retroflex hook – Para-IPA version of the ] retroflex tʂ.<ref>{{Cite web|title=L2/21-041: Unicode request for additional para-IPA letters|url=https://www.unicode.org/L2/L2021/21041-add-para-ipa-ltr.pdf|date=2021-01-11|first=Kirk|last=Miller}}</ref> | ||
| **ꟲ : Modifier letter capital c |
**ꟲ : Modifier letter capital c – Used to mark tone for the ] orthography in Oaxaca, Mexico; used as a generic transcription for a falling tone; also used in para-] notation.<ref>{{Cite web|title=L2/20-251: Unicode request for modifier Latin capital letters|url=https://www.unicode.org/L2/L2020/20251-mod-latin.pdf|date=2020-09-25|first1=Kirk|last1=Miller|first2=Craig|last2=Cornelius}}</ref> | ||
| *] : Modifier letter small c<ref name="L204132">{{Cite web|url=https://www.unicode.org/L2/L2004/04132-n2740-phonetic.pdf|title=L2/04-132 Proposal to add additional phonetic characters to the UCS|date=2004-04-19|first=Peter|last=Constable}}</ref> | *] : Modifier letter small c<ref name="L204132">{{Cite web|url=https://www.unicode.org/L2/L2004/04132-n2740-phonetic.pdf|title=L2/04-132 Proposal to add additional phonetic characters to the UCS|date=2004-04-19|first=Peter|last=Constable}}</ref> | ||
| *] : Modifier letter small c with curl<ref name="L204132"/> | *] : Modifier letter small c with curl<ref name="L204132"/> | ||
| *ᴄ : Small capital c is used in the ].<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.unicode.org/L2/L2002/02141-n2419-uralic-phonetic.pdf|title=L2/02-141: Uralic Phonetic Alphabet characters for the UCS|date=2002-03-20|first1=Michael|last1=Everson|author-link1=Michael Everson|display-authors=etal}}</ref> | *ᴄ : Small capital c is used in the ].<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.unicode.org/L2/L2002/02141-n2419-uralic-phonetic.pdf|title=L2/02-141: Uralic Phonetic Alphabet characters for the UCS|date=2002-03-20|first1=Michael|last1=Everson|author-link1=Michael Everson|display-authors=etal}}</ref> | ||
| *Ꞔ ꞔ : C with palatal hook, used for writing ] using the early draft version of ] romanization during the mid-1950s<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.unicode.org/L2/L2017/17013-n4782-latin.pdf|title=L2/17-013: Proposal to encode three uppercase Latin letters used in early Pinyin|date=2017-01-16|first1=Andrew|last1=West|author-link=Andrew West (linguist)|first2=Eiso|last2=Chan|first3=Michael|last3=Everson|author-link3=Michael Everson}}</ref> | *Ꞔ ꞔ : C with palatal hook, used for writing ] using the early draft version of ] romanization during the mid-1950s.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.unicode.org/L2/L2017/17013-n4782-latin.pdf|title=L2/17-013: Proposal to encode three uppercase Latin letters used in early Pinyin|date=2017-01-16|first1=Andrew|last1=West|author-link=Andrew West (linguist)|first2=Eiso|last2=Chan|first3=Michael|last3=Everson|author-link3=Michael Everson}}</ref> | ||
| Add to C with diacritics | Add to C with diacritics | ||
| *C with ]s: ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] Ꞔ ] ] | *C with ]s: ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] Ꞔ ] ] | ||
| Line 429: | Line 431: | ||
| *<math>\mathbb{C}</math> : ] C, denoting the ]s | *<math>\mathbb{C}</math> : ] C, denoting the ]s | ||
| *ℭ : ] | *ℭ : ] | ||
| *Ꜿ ꜿ : ] abbreviation for ] syllables con- and com-, ] -us and -os<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.unicode.org/L2/L2006/06027-n3027-medieval.pdf|title=L2/06-027: Proposal to add Medievalist characters to the UCS|date=2006-01-30|first1=Michael|last1=Everson|first2=Peter|last2=Baker|first3=António|last3=Emiliano|first4=Florian|last4=Grammel|first5=Odd Einar|last5=Haugen|first6=Diana|last6=Luft|first7=Susana|last7=Pedro|first8=Gerd|last8=Schumacher|first9=Andreas|last9=Stötzner}}</ref> | *Ꜿ ꜿ : ] abbreviation for ] syllables con- and com-, ] -us and -os.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.unicode.org/L2/L2006/06027-n3027-medieval.pdf|title=L2/06-027: Proposal to add Medievalist characters to the UCS|date=2006-01-30|first1=Michael|last1=Everson|first2=Peter|last2=Baker|first3=António|last3=Emiliano|first4=Florian|last4=Grammel|first5=Odd Einar|last5=Haugen|first6=Diana|last6=Luft|first7=Susana|last7=Pedro|first8=Gerd|last8=Schumacher|first9=Andreas|last9=Stötzner}}</ref> | ||
| ==Other representations== | ==Other representations== | ||
| Line 435: | Line 437: | ||
| The Latin letters {{angbr|C}} and {{angbr|c}} have ] encodings {{unichar|0043|Latin letter capital C}} and {{unichar|0063|Latin small letter c}}. These are the same ]s as were used in ] and ]. There are also ] encodings for {{angbr|C}} and {{angbr|c}} with diacritics, for most of those listed ]; the remainder are produced using ]s. | The Latin letters {{angbr|C}} and {{angbr|c}} have ] encodings {{unichar|0043|Latin letter capital C}} and {{unichar|0063|Latin small letter c}}. These are the same ]s as were used in ] and ]. There are also ] encodings for {{angbr|C}} and {{angbr|c}} with diacritics, for most of those listed ]; the remainder are produced using ]s. | ||
| Variant forms of the letter have unique code points for specialist use: the ] in mathematics and science, ] sounds in linguistics, and ] for legacy CJK font compatibility. The Cyrillic ] of the Latin {{angbr|C}} has a separate encoding: {{unichar|0421|Cyrillic capital letter Es|nlink=Es (Cyrillic)}}. | Variant forms of the letter have unique code points for specialist use: the ] in mathematics and science, ] sounds in linguistics, and ] for legacy ] font compatibility. The Cyrillic ] of the Latin {{angbr|C}} has a separate encoding: {{unichar|0421|Cyrillic capital letter Es|nlink=Es (Cyrillic)}}. | ||
| ===Other=== | ===Other=== | ||
Revision as of 12:06, 3 July 2024
3rd letter of the Latin alphabet This article is about the letter. For the programming language, see C (programming language). For other uses, see C (disambiguation).For technical reasons, "C#" and ":C" redirect here. For uses of C#, see C-sharp. For the keyboard symbols, see List of emoticons.
| C | |
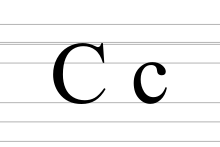
|---|---|
| C c | |
 | |
| Usage | |
| Writing system | Latin script |
| Type | Alphabetic |
| Language of origin | Latin language |
| Sound values |
|
| In Unicode | U+0043, U+0063 |
| Alphabetical position | 3 Numerical value: 100 |
| History | |
| Development | |
| Sisters | |
| Other | |
| Associated numbers | 100 |
| This article contains phonetic transcriptions in the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA). For an introductory guide on IPA symbols, see Help:IPA. For the distinction between , / / and ⟨ ⟩, see IPA § Brackets and transcription delimiters. | |
| ISO basic Latin alphabet |
|---|
| AaBbCcDdEeFfGgHhIiJjKkLlMmNnOoPpQqRrSsTtUuVvWwXxYyZz |

C, or c, is the third letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is cee (pronounced /ˈsiː/), plural cees.
History
| Egyptian | Phoenician gaml |
Western Greek Gamma |
Etruscan C |
Old Latin C (G) |
Latin C | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
"C" comes from the same letter as "G". The Semites named it gimel. The sign is possibly adapted from an Egyptian hieroglyph for a staff sling, which may have been the meaning of the name gimel. Another possibility is that it depicted a camel, the Semitic name for which was gamal. Barry B. Powell, a specialist in the history of writing, states "It is hard to imagine how gimel = "camel" can be derived from the picture of a camel (it may show his hump, or his head and neck!)".
In the Etruscan language, plosive consonants had no contrastive voicing, so the Greek 'Γ' (Gamma) was adopted into the Etruscan alphabet to represent /k/. Already in the Western Greek alphabet, Gamma first took a '![]() ' form in Early Etruscan, then '
' form in Early Etruscan, then '![]() ' in Classical Etruscan. In Latin, it eventually took the 'c' form in Classical Latin. In the earliest Latin inscriptions, the letters 'c k q' were used to represent the sounds /k/ and /ɡ/ (which were not differentiated in writing). Of these, 'q' was used to represent /k/ or /ɡ/ before a rounded vowel, 'k' before 'a', and 'c' elsewhere. During the 3rd century BC, a modified character was introduced for /ɡ/, and 'c' itself was retained for /k/. The use of 'c' (and its variant 'g') replaced most usages of 'k' and 'q'. Hence, in the classical period and after, 'g' was treated as the equivalent of Greek gamma, and 'c' as the equivalent of kappa; this shows in the romanization of Greek words, as in 'ΚΑΔΜΟΣ', 'ΚΥΡΟΣ', and 'ΦΩΚΙΣ' came into Latin as 'cadmvs', 'cyrvs' and 'phocis', respectively.
' in Classical Etruscan. In Latin, it eventually took the 'c' form in Classical Latin. In the earliest Latin inscriptions, the letters 'c k q' were used to represent the sounds /k/ and /ɡ/ (which were not differentiated in writing). Of these, 'q' was used to represent /k/ or /ɡ/ before a rounded vowel, 'k' before 'a', and 'c' elsewhere. During the 3rd century BC, a modified character was introduced for /ɡ/, and 'c' itself was retained for /k/. The use of 'c' (and its variant 'g') replaced most usages of 'k' and 'q'. Hence, in the classical period and after, 'g' was treated as the equivalent of Greek gamma, and 'c' as the equivalent of kappa; this shows in the romanization of Greek words, as in 'ΚΑΔΜΟΣ', 'ΚΥΡΟΣ', and 'ΦΩΚΙΣ' came into Latin as 'cadmvs', 'cyrvs' and 'phocis', respectively.
Other alphabets have letters homoglyphic to 'c' but not analogous in use and derivation, like the Cyrillic letter Es (С, с) which derives from the lunate sigma.
Later use
When the Roman alphabet was introduced into Britain, ⟨c⟩ represented only /k/, and this value of the letter has been retained in loanwords to all the insular Celtic languages: in Welsh, Irish, and Gaelic, ⟨c⟩ represents only /k/. The Old English Latin-based writing system was learned from the Celts, apparently of Ireland; hence, ⟨c⟩ in Old English also originally represented /k/; the Modern English words kin, break, broken, thick, and seek all come from Old English words written with ⟨c⟩: cyn, brecan, brocen, þicc, and séoc. However, during the course of the Old English period, /k/ before front vowels (/e/ and /i/) was palatalized, having changed by the tenth century to , though ⟨c⟩ was still used, as in cir(i)ce, wrecc(e)a. On the continent, meanwhile, a similar phonetic change before the same two vowels had also been going on in almost all modern romance languages (for example, in Italian).
In Vulgar Latin, /k/ became palatalized to in Italy and Dalmatia; in France and the Iberian Peninsula, it became . Yet for these new sounds, ⟨c⟩ was still used before the letters ⟨e⟩ and ⟨i⟩. The letter thus represented two distinct values. Subsequently, the Latin phoneme /k/ (spelled ⟨qv⟩) de-labialized to /k/, meaning that the various Romance languages had /k/ before front vowels. In addition, Norman used the letter ⟨k⟩ so that the sound /k/ could be represented by either ⟨k⟩ or ⟨c⟩, the latter of which could represent either /k/ or /ts/ depending on whether it preceded a front vowel letter or not. The convention of using both ⟨c⟩ and ⟨k⟩ was applied to the writing of English after the Norman Conquest, causing a considerable re-spelling of the Old English words. Thus, while Old English candel, clif, corn, crop, and cú, remained unchanged, Cent, cǣᵹ (cēᵹ), cyng, brece, and sēoce, were now (without any change of sound) spelled Kent, keȝ, kyng, breke, and seoke; even cniht ('knight') was subsequently changed to kniht and þic ('thick') changed to thik or thikk. The Old English ⟨cw⟩ was also at length displaced by the French ⟨qu⟩ so that the Old English cwēn ('queen') and cwic ('quick') became Middle English quen and quik, respectively.
The sound , to which Old English palatalized /k/ had advanced, also occurred in French, chiefly from Latin /k/ before ⟨a⟩. In French, it was represented by the digraph ⟨ch⟩, as in champ (from Latin camp-um), and this spelling was introduced into English: the Hatton Gospels, written c. 1160, have in Matt. i-iii, child, chyld, riche, and mychel, for the cild, rice, and mycel of the Old English version whence they were copied. In these cases, the Old English ⟨c⟩ gave way to ⟨k⟩, ⟨qu⟩ and ⟨ch⟩; on the other hand, ⟨c⟩ in its new value of /ts/ appeared largely in French words like processiun, emperice, and grace and was also substituted for ⟨ts⟩ in a few Old English words, as miltse, bletsien, in early Middle English milce, blecien. By the end of the thirteenth century, both in France and England, this sound /ts/ was de-affricated to /s/; and from that time, ⟨c⟩ has represented /s/ before front vowels either for etymological reasons, as in lance, cent, or to avoid the ambiguity due to the "etymological" use of ⟨s⟩ for /z/, as in ace, mice, once, pence, defence.
Thus, to show etymology, English spelling has advise, devise (instead of *advize, *devize), while advice, device, dice, ice, mice, twice, etc., do not reflect etymology; example has extended this to hence, pence, defence, etc., where there is no etymological reason for using ⟨c⟩. Former generations also wrote sence for sense. Hence, today, the Romance languages and English have a common feature inherited from Vulgar Latin spelling conventions where ⟨c⟩ takes on either a "hard" or "soft" value depending on the following letter.
Use in writing systems
See also: Hard and soft C| Orthography | Phonemes | Environment |
|---|---|---|
| Albanian | /ts/ | |
| Cypriot Arabic | /ʕ/ | |
| Azeri | /dʒ/ | |
| Berber | /ʃ/ | |
| Bukawa | /ʔ/ | |
| Catalan | /k/ | Except before e, i |
| /s/ | Before e, i | |
| Standard Chinese (Pinyin) | /tsʰ/ | |
| Crimean Tatar | /dʒ/ | |
| Cornish (Standard Written Form) | /s/ | |
| Czech | /ts/ | |
| Danish | /k/ | Except before e, i, y, æ, ø |
| /s/ | Before e, i, y, æ, ø | |
| Dutch | /k/ | Except before e, i, y |
| /s/ | Before e, i, y | |
| /tʃ/ | Before e, i in loanwords from Italian | |
| English | /k/ | Except before e, i, y |
| /s/ | Before e, i, y | |
| /ʃ/ | Before ea, ia, ie, io, iu | |
| Esperanto | /ts/ | |
| Fijian | /ð/ | |
| Filipino | /k/ | Except before e, i |
| /s/ | Before e, i | |
| French | /k/ | Except before e, i, y |
| /s/ | Before e, i, y | |
| Fula | /tʃ/ | |
| Gagauz | /dʒ/ | |
| Galician | /k/ | Except before e, i |
| /θ/ or /s/ | Before e, i | |
| German | /k/ | Except before ä, e, i, ö, ü, y in loanwords and names |
| /ts/ | Before ä, e, i, ö, ü, y in loanwords and names | |
| Hausa | /tʃ/ | |
| Hungarian | /ts/ | |
| Indonesian | /tʃ/ | |
| Irish | /k/ | Except before e, i; or after i |
| /c/ | Before e, i; or after i | |
| Italian | /k/ | Except before e, i |
| /tʃ/ | Before e, i | |
| Khmer (ALA-LC) | /c/ | |
| Kurmanji (Hawar) | /dʒ/ | |
| Latin | /k/ (and /g/ in early Latin) | |
| Latvian | /ts/ | |
| Malay | /tʃ/ | |
| Manding | /tʃ/ | |
| Norwegian | /k/ | Except before e, i, y, æ, ø in loanwords and names |
| /s/ | Before e, i, y, æ, ø in loanwords and names | |
| Polish | /ts/ | Except before i |
| /tɕ/ | Before i | |
| Portuguese | /k/ | Except before e, i, y |
| /s/ | Before e, i, y | |
| Romanian | /k/ | Except before e, i |
| /tʃ/ | Before e, i | |
| Romansh | /k/ | Except before e, i |
| /ts/ | Before e, i | |
| Scottish Gaelic | /kʰ/ | Except before e, i; or after i |
| /kʰʲ/ | Before e, i; or after i | |
| Serbo-Croatian | /ts/ | |
| Slovak | /ts/ | |
| Slovene | /ts/ | |
| Somali | /ʕ/ | |
| Spanish | /k/ | Except before e, i, y |
| /θ/ or /s/ | Before e, i, y | |
| Swedish | /k/ | Except before e, i, y, ä, ö |
| /s/ | Before e, i, y, ä, ö | |
| Tatar | /ʑ/ | |
| Turkish | /dʒ/ | |
| Valencian | /k/ | Except before e, i |
| /s/ | Before e, i | |
| Vietnamese | /k/ | Except word-finally |
| /k̚/ | Word-finally | |
| Welsh | /k/ | |
| Xhosa | /ǀ/ | |
| Yabem | /ʔ/ | |
| Yup'ik | /tʃ/ | |
| Zulu | /ǀ/ |
English
In English orthography, ⟨c⟩ generally represents the "soft" value of /s/ before the letters ⟨e⟩ (including the Latin-derived digraphs ⟨ae⟩ and ⟨oe⟩, or the corresponding ligatures ⟨æ⟩ and ⟨œ⟩), ⟨i⟩, and ⟨y⟩, and a "hard" value of /k/ before any other letters or at the end of a word. However, there are a number of exceptions in English: "soccer" and "Celt" are words that have /k/ where /s/ would be expected.
The "soft" ⟨c⟩ may represent the /ʃ/ sound in the digraph ⟨ci⟩ when this precedes a vowel, as in the words 'delicious' and 'appreciate', and also in the word "ocean" and its derivatives.
The digraph ⟨ch⟩ most commonly represents /tʃ/, but can also represent /k/ (mainly in words of Greek origin) or /ʃ/ (mainly in words of French origin). For some dialects of English, it may also represent /x/ in words like loch, while other speakers pronounce the final sound as /k/. The trigraph ⟨tch⟩ always represents /tʃ/.
The digraph ⟨ck⟩ is often used to represent the sound /k/ after short vowels, like "wicket".
C is the twelfth most frequently used letter in the English language (after E, T, A, O, I, N, S, H, R, D, and L), with a frequency of about 2.8% in words.
Other languages
In the Romance languages French, Spanish, Italian, Romanian, and Portuguese, ⟨c⟩ generally has a "hard" value of /k/ and a "soft" value whose pronunciation varies by language. In French, Portuguese, Catalan, and Spanish from Latin America and some places in Spain, the soft ⟨c⟩ value is /s/ as it is in English. In the Spanish spoken in most of Spain, the soft ⟨c⟩ is a voiceless dental fricative /θ/. In Italian and Romanian, the soft ⟨c⟩ is .
Germanic languages usually use ⟨c⟩ for Romance loans or digraphs, such as ⟨ch⟩ and ⟨ck⟩, but the rules vary across languages. Of all the Germanic languages, only English uses the initial ⟨c⟩ in native Germanic words like come. Other than English, Dutch uses ⟨c⟩ the most, for most Romance loans and the digraph ⟨ch⟩. German uses ⟨c⟩ in the digraphs ⟨ch⟩ and ⟨ck⟩, and the trigraph ⟨sch⟩, but by itself only in unassimilated loanwords and proper names. Danish keeps soft ⟨c⟩ in Romance words but changes hard ⟨c⟩ to ⟨k⟩. Swedish has the same rules for soft and hard ⟨c⟩ as Danish, and also uses ⟨c⟩ in the digraph ⟨ck⟩ and the very common word och, "and". Norwegian, Afrikaans, and Icelandic are the most restrictive, replacing all cases of ⟨c⟩ with ⟨k⟩ or ⟨s⟩, and reserving ⟨c⟩ for unassimilated loanwords and names.
All Balto-Slavic languages that use the Latin alphabet, as well as Albanian, Hungarian, Pashto, several Sami languages, Esperanto, Ido, Interlingua, and Americanist phonetic notation (and those aboriginal languages of North America whose practical orthography derives from it), use ⟨c⟩ to represent /t͡s/, the voiceless alveolar or voiceless dental sibilant affricate. In Hanyu Pinyin, the standard romanization of Mandarin Chinese, the letter represents an aspirated version of this sound, /t͡s/.
Among non-European languages that have adopted the Latin alphabet, ⟨c⟩ represents a variety of sounds. Yup'ik, Indonesian, Malay, and a number of African languages such as Hausa, Fula, and Manding share the soft Italian value of /t͡ʃ/. In Azeri, Crimean Tatar, Kurmanji Kurdish, and Turkish ⟨c⟩ stands for the voiced counterpart of this sound, the voiced postalveolar affricate /d͡ʒ/. In Yabem and similar languages, such as Bukawa, ⟨c⟩ stands for a glottal stop /ʔ/. Xhosa and Zulu use this letter to represent the click /ǀ/. In some other African languages, such as Berber languages, ⟨c⟩ is used for /ʃ/. In Fijian, ⟨c⟩ stands for a voiced dental fricative /ð/, while in Somali it has the value of /ʕ/.
The letter ⟨c⟩ is also used as a transliteration of Cyrillic ⟨ц⟩ in the Latin forms of Serbian, Macedonian, and sometimes Ukrainian, along with the digraph ⟨ts⟩.
Other systems
As a phonetic symbol, lowercase ⟨c⟩ is the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) and X-SAMPA symbol for the voiceless palatal plosive, and capital ⟨C⟩ is the X-SAMPA symbol for the voiceless palatal fricative.
Digraphs
There are several common digraphs with ⟨c⟩, the most common being ⟨ch⟩, which in some languages (such as German) is far more common than ⟨c⟩ alone. ⟨ch⟩ takes various values in other languages.
As in English, ⟨ck⟩, with the value /k/, is often used after short vowels in other Germanic languages such as German and Swedish (other Germanic languages, such as Dutch and Norwegian, use ⟨kk⟩ instead). The digraph ⟨cz⟩ is found in Polish and ⟨cs⟩ in Hungarian, representing /t͡ʂ/ and /t͡ʃ/ respectively. The digraph ⟨sc⟩ represents /ʃ/ in Old English, Italian, and a few languages related to Italian (where this only happens before front vowels, while otherwise it represents /sk/). The trigraph ⟨sch⟩ represents /ʃ/ in German.
Other uses
Main article: C (disambiguation)- In the hexadecimal (base 16) numbering system, C is a number that corresponds to the number 12 in decimal (base 10) counting.
- In the Roman numeral system, C represents 100.
- Unit prefix c, meaning one hundredth.
Related characters
Ancestors, descendants and siblings

- 𐤂 : Semitic letter Gimel, from which the following symbols originally derive:
- Phonetic alphabet symbols related to C:
- ɕ : Small c with curl
- ʗ : Stretched c
- 𝼏 : Stretched c with curl – Used by Douglas Beach for a nasal click in his phonetic description of Khoekhoe.
- 𝼝 : Small letter c with retroflex hook – Para-IPA version of the IPA retroflex tʂ.
- ꟲ : Modifier letter capital c – Used to mark tone for the Chatino orthography in Oaxaca, Mexico; used as a generic transcription for a falling tone; also used in para-IPA notation.
- ᶜ : Modifier letter small c
- ᶝ : Modifier letter small c with curl
- ᴄ : Small capital c is used in the Uralic Phonetic Alphabet.
- Ꞔ ꞔ : C with palatal hook, used for writing Mandarin Chinese using the early draft version of pinyin romanization during the mid-1950s.
Add to C with diacritics
Derived ligatures, abbreviations, signs and symbols
- © : copyright symbol
- ℃ : degree Celsius
- ¢ : cent
- ₡ : colón (currency)
- ₢ : Brazilian cruzeiro (currency)
- ₵ : Ghana cedi (currency)
- ₠ : European Currency Unit CE
- : blackboard bold C, denoting the complex numbers
- ℭ : blackletter C
- Ꜿ ꜿ : Medieval abbreviation for Latin syllables con- and com-, Portuguese -us and -os.
Other representations
Computing
The Latin letters ⟨C⟩ and ⟨c⟩ have Unicode encodings U+0043 C LATIN CAPITAL LETTER C and U+0063 c LATIN SMALL LETTER C. These are the same code points as were used in ASCII and ISO 8859. There are also precomposed character encodings for ⟨C⟩ and ⟨c⟩ with diacritics, for most of those listed above; the remainder are produced using combining diacritics.
Variant forms of the letter have unique code points for specialist use: the alphanumeric symbols set in mathematics and science, voiceless palatal sounds in linguistics, and halfwidth and fullwidth forms for legacy CJK font compatibility. The Cyrillic homoglyph of the Latin ⟨C⟩ has a separate encoding: U+0421 С CYRILLIC CAPITAL LETTER ES.
Other
| NATO phonetic | Morse code |
| Charlie |
▄▄▄ ▄ ▄▄▄ ▄ |

|

|

|

| |
| Signal flag | Flag semaphore | American manual alphabet (ASL fingerspelling) | British manual alphabet (BSL fingerspelling) | Braille dots-14 Unified English Braille |
See also
References
- "C" Oxford English Dictionary, 2nd edition (1989); Merriam-Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language, Unabridged (1993); "cee", op. cit.
- Powell, Barry B. (27 Mar 2009). Writing: Theory and History of the Technology of Civilization. Wiley Blackwell. p. 182. ISBN 978-1405162562.
- Sihler, Andrew L. (1995). New Comparative Grammar of Greek and Latin (illustrated ed.). New York: Oxford University Press. p. 21. ISBN 0-19-508345-8.
- "Reading Middle Welsh -- 29 Medieval Spelling". www.mit.edu. Retrieved 2019-11-19.
- Miller, Kirk; Sands, Bonny (2020-07-10). "L2/20-115R: Unicode request for additional phonetic click letters" (PDF).
- Miller, Kirk (2021-01-11). "L2/21-041: Unicode request for additional para-IPA letters" (PDF).
- Miller, Kirk; Cornelius, Craig (2020-09-25). "L2/20-251: Unicode request for modifier Latin capital letters" (PDF).
- ^ Constable, Peter (2004-04-19). "L2/04-132 Proposal to add additional phonetic characters to the UCS" (PDF).
- Everson, Michael; et al. (2002-03-20). "L2/02-141: Uralic Phonetic Alphabet characters for the UCS" (PDF).
- West, Andrew; Chan, Eiso; Everson, Michael (2017-01-16). "L2/17-013: Proposal to encode three uppercase Latin letters used in early Pinyin" (PDF).
- Everson, Michael (2005-08-12). "L2/05-193R2: Proposal to add Claudian Latin letters to the UCS" (PDF).
- Everson, Michael; Baker, Peter; Emiliano, António; Grammel, Florian; Haugen, Odd Einar; Luft, Diana; Pedro, Susana; Schumacher, Gerd; Stötzner, Andreas (2006-01-30). "L2/06-027: Proposal to add Medievalist characters to the UCS" (PDF).
External links
 Media related to C at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to C at Wikimedia Commons The dictionary definition of C at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of C at Wiktionary The dictionary definition of c at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of c at Wiktionary
| Latin script | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alphabets (list) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Letters (list) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Multigraphs |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Keyboard layouts (list) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Historical Standards | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Current Standards | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 :
: