| Revision as of 00:23, 30 December 2024 editSadko (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Rollbackers81,712 edits default image size, clutter removedTag: Visual edit← Previous edit | Revision as of 02:53, 30 December 2024 edit undoYung Doohickey (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users1,236 edits Civilians being massacred after Serbia garnered control over this region is relevant to the aftermath and I don't think it's OR or SYNTH to include as it's being described how they are in the sources. The information has been corroborated by multiple primary sources and relayed by modern sources I've listed thus shouldn't be considered extraordinary or purely primary.Tag: Visual editNext edit → | ||
| Line 92: | Line 92: | ||
| The Vardar Army was not able to organise the defense on ] and was forced to abandon ], retreating all the way to ]. The First Army advanced slowly and entered Skopje on 26 October. Two days later, it was strengthened by Morava Division II, while the rest of the Third Army was sent to Western Kosovo and then through northern ] to the ]. The Second Army was sent to aid the Bulgarians in the ], while the First Army was preparing for an ].{{sfn|Ratković|Đurišić|Skoko|1972|p=87}} | The Vardar Army was not able to organise the defense on ] and was forced to abandon ], retreating all the way to ]. The First Army advanced slowly and entered Skopje on 26 October. Two days later, it was strengthened by Morava Division II, while the rest of the Third Army was sent to Western Kosovo and then through northern ] to the ]. The Second Army was sent to aid the Bulgarians in the ], while the First Army was preparing for an ].{{sfn|Ratković|Đurišić|Skoko|1972|p=87}} | ||
| === Massacres of Albanian civilians === | |||
| {{Main article|Massacres of Albanians in the Balkan Wars}} | |||
| According to Arben Qirezi, Peter I of Serbia had ordered the execution of Albanian civilians living in Kumanovo.<ref name="Qirezi462">{{cite book |last=Qirezi |first=Arben |title=Kosovo and Serbia: Contested Options and Shared Consequences |publisher=University of Pittsburgh Press |year=2017 |isbn=978-0-8229-8157-2 |editor1-last=Mehmeti |editor1-first=Leandrit I. |pages=46 |chapter=Settling the self-determination dispute in Kosovo |quote="However, as pointed out by Noel Malcolm, this was an intentional policy of extermination, when King Peter of Serbia himself ordered the execution of Albanian civilians in Kumanovo." |editor2-last=Radeljić |editor2-first=Branislav |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=IWMqDwAAQBAJ&pg=PT74}}</ref> Subsequently, after the battle, the Serbian forces had massacred an estimated 3,000 Albanians between Kumanovo and Uskub based on contemporary accounts.<ref name=":25">{{cite book |last1=Elsie |first1=Robert |url=https://www.google.com/books/edition/Kosovo_A_Documentary_History/adWLDwAAQBAJ?hl=en&gbpv=0 |title=Kosovo, A Documentary History: From the Balkan Wars to World War II |last2=Destani |first2=Bejtullah D. |date=30 January 2018 |publisher=Bloomsbury Publishing |isbn=978-1-78672-354-3 |page=153 |language=en |quote="they slaughtered 3,000 people in the region between Kumanovo and skopje alone." |access-date=10 August 2023}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Hoare |first=Marko Attila |url=https://www.google.com/books/edition/Serbia/s8_2EAAAQBAJ?hl=en&gbpv=1&bsq=%22Serbian%20military%20activities%20in%20Macedonia%20have%20taken%20on%20the%20character%20of%20an%20extermination%20of%20the%20Arnaut%20population.%20The%20army%20is%20conducting%20an%20unspeakable%20war%20of%20atrocities.%20According%20to%20officers%20and%20soldiers,%203,000%20Arnauts%20were%20slaughtered%20in%20the%20region%20between%20Kumanova/Kumanovo%20and%20Skoplje%20and%205,000%20near%20Prishtina%22 |title=Serbia: A Modern History |publisher=Oxford University Press |year=2024 |isbn=9780197790441 |quote="The Danish journalist Fritz Magnussen reported: 'Serbian military activities in Macedonia have taken on the character of an extermination of the Arnaut population. The army is conducting an unspeakable war of atrocities. According to officers and soldiers, 3,000 Arnauts were slaughtered in the region between Kumanova/Kumanovo and Skoplje and 5,000 near Prishtina...'"}}</ref> | |||
| ==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
Revision as of 02:53, 30 December 2024
1912 battle of the First Balkan War| Battle of Kumanovo | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the First Balkan War | |||||||
 First Balkan War. The Serbian Front (Serbia) The march of the armies before the battle of Kumanovo. | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
(Vardar Army) (VII Corps) | ||||||
| Units involved | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
132,000 men 148 artillery pieces 100 machine guns |
65,000 men 164 artillery pieces 104 machine guns | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
687 killed 3,280 wounded 597 missing Total: 4,564 |
1,200 killed 3,000 wounded 327 captured 98 artillery pieces lost Total: 4,500 | ||||||
|
| |||||||
| First Balkan War | |
|---|---|
Bulgarian Front
Serbian and Montenegrin front Greek front |
The Battle of Kumanovo (Serbian: Кумановска битка / Kumanovska bitka, Turkish: Kumanova Muharebesi), on 23–24 October 1912, was a major battle of the First Balkan War. It was an important Serbian victory over the Ottoman army in the Kosovo Vilayet, shortly after the outbreak of the war. After this defeat, the Ottoman army abandoned the major part of the region, suffering heavy losses in manpower (mostly due to desertions) and in war materiel.
Background
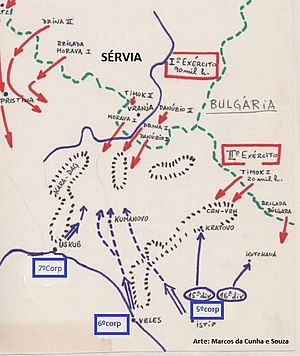
The objective of the Royal Serbian Army plan was to destroy the Ottoman army in a decisive battle before the Ottomans could complete the mobilisation and concentration of forces. The Serbian planners assumed that the main Ottoman force would be deployed defensively in the valley of Vardar and on the strategically important plateau of Ovče Pole. The Serbian Commander-in-Chief was General Radomir Putnik. The aim was to double envelop the Ottoman army by using three armies:
- First Army, under Crown Prince Alexander, composed of five infantry and one cavalry division (132,000 men), was deployed in the area around Vranje, with the task to attack the enemy frontally.
- Second Army, under Stepa Stepanović, composed of one Serbian and one Bulgarian division (74,000 men), deployed in the area around Kyustendil, was assigned to the easternmost attack, with the objective of attacking the right flank of the enemy.
- Third Army, under Božidar Janković, composed of four infantry divisions and one infantry brigade (76,000 men), deployed in two groups, the first one at Toplica and the second one at Medveđa, was assigned to the westernmost attack, with the task to take Kosovo and then move south to attack the left flank of the enemy.
- Smaller units were sent to take Sandžak.
According to the initial Ottoman plan, created by Colmar Freiherr von der Goltz, the Ottoman forces in Macedonia would stay in defense and, if necessary, retreat to Albania. The decisive battle would take place in Thrace, versus the Bulgarian army. However, Nazim Pasha, the newly appointed commander-in-chief of the Ottoman army, decided to surprise the Serbs by taking an offensive in Macedonia. The plan also included the offensive in Thrace. His goal was to win the initial battles against the surprised allies, hoping that the Great powers would then intervene and stop the war.
The Ottoman mobilisation in Macedonia was slow, and the Ottoman Vardar Army, led by Zeki Pasha, had little more than a half of its manpower mobilised when the war started. The army was composed of:
- V Corps, under Said Pasha, composed of 4 divisions (32,000 men), deployed in the area around Štip.
- VI Corps, under Cavit Pasha, composed of two divisions (6,000 men), deployed in the area around Veles.
- VII Corps, under Fethi Pasha, composed of three divisions (19,000 men), deployed in the area around Kumanovo.
- Smaller units in Kosovo.
Prelude
Even before the war was declared, border skirmishes occurred. On the 15 October, the front of the Toplica group of the Third Army, Serbian chetniks, acting on their own, attacked the Ottoman forces; although the Serbian deployment had not been completed yet. The Ottomans counterattacked, but they were stopped by the Morava Division II. The fighting on the border lasted until 19 October when the Ottomans were forced to retreat. On 21 October the entire Third Army began its advance and on 22 October, without serious resistance, entered Pristina.
On 18 October, Bulgarian 7th Rila Infantry Division of the Second Army started its advance towards Gorna Dzhumaya, while the rest of the army advanced towards the village of Stracin and captured it on 21 October.
The First Army crossed the border on 20 October and in the evening of 22 October reached the outskirts of Kumanovo.
At the other side, as soon as his forces were deployed, Zeki Pasha decided to take the offensive towards Kumanovo. In the evening of 22 October, Vardar Army gathered in the valley of Pčinja River. While Zeki Pasha had the precise information about the strength and disposal of the Serbian forces, the Serbian command did not realise that the battle with the main Ottoman force would start the very next morning. Not expecting the attack, Serbs did not fortify their positions, which were topographically strong. Still, only two out of five infantry divisions were deployed in the front echelon – Danube Division I on the left wing, with the Cavalry Division behind it, and Morava Division I on the right wing. The left flank was particularly vulnerable, because Srtevica, the important topographic object, was defended by local irregulars.
During the night of 22–23 October, VI Corps 17th Infantry Division and Monastir Infantry Division crossed Pčinja and took the position in the Ottoman centre, on the hill of Zebrnjak. The main forces of V Corps 13th Infantry Division and Štip Infantry Division remained on the left bank of Pčinja, forming the right of the Ottoman's which was acting as a reserve and protecting the route from Stracin, while the main forces of VII Corps 19th Infantry Division and Üsküb Infantry Division were on the left side.
Battle
23 October

The morning of 23 October was foggy, and reconnaissance could not be performed properly. On the Serbian left flank, the observers noticed the troops of 17th Infantry Division in movement, but mistook them for the Ottoman battery withdrawing from Stracin. Troops of the 18th regiment of Danube Division I, which moved forward to capture it, were pushed back, as well as the reconnaissance forces of Cavalry Division.
Observing the retreat of these Serbian units, Zeki Pasha concluded that the Serbian left wing was weak. Since there were no actions of the Second Army from Stracin, he decided to attack. Around 11:00, with artillery support, V and VI Corps attacked the positions of Danube Division I. Soon, 13th and 17th Infantry Division forced the 18th regiment to retreat in disorder, but, instead of continuing the attack, Zeki Pasha waited for the arrival of Štip Infantry Division from the rear to use this division to attack the Serbian flank and rear. That enabled the Serbian 7th regiment to aid the wavering 18th regiment and to consolidate a defense. Soon after that, the Serbian 8th regiment arrived, and 7th regiment was able to move to the left flank and reinforce the defense of Srtevica, which was endangered by an attack by the Štip Infantry Division. On the right flank of Danube Division I, its 9th regiment halted the advance of the weakened Monastir Infantry Division.
Around 12:00, VII Corps started its attack on the positions held by Morava Division I. However, Serbian infantry and artillery were already deployed for combat, as the artillery fire from the east suggested that the battle had started. After the initial Ottoman progress, Serbs counterattacked and pushed them back to their starting positions. After the Serbian counterattack, Ottoman units were kept at bay by the well organised Serbian artillery fire until the end of day.
The Serbian rear echelon divisions (Danube Division II on the left, Drina Division I in the centre and Timok Division II on the right) and the army artillery were not informed about the combat operations. They remained in the rear, without participating in the first day of the battle. The First Army command did not receive precise information about the battle and did not have any influence on the actual combat. Despite these facts, the Ottoman attack of the 23 October was not successful, mostly thanks to "the high devotion of (Serbian) troops and lower officers".
24 October


Uninformed about the situation in the field, the First Army command did not realise that the attack of the main Ottoman forces had occurred, as those forces were expected on Ovče Pole. Assuming that the Ottoman units north of Kumanovo were merely forward detachments, it ordered the troops to continue their advance towards south, as previously planned. After midnight, it received a report from Danube Division I which stated that the division was attacked by the strong enemy forces and suffered heavy casualties, but at that moment it was too late for any change of orders.
On the other side, Zeki Pasha decided to continue the attack with the hope that his forces would be able to achieve victory on the following day.
The Ottoman attack on their right wing started around 5:30. VI Corps was assigned to tie up as many enemy forces as possible by attacking from the front, while Štip Infantry Division was again assigned to flank attack. Danube Division I again had to withstand heavy pressure, but around 10:00 parts of Danube Division II arrived from the rear and strengthened the defense. At the same time, Cavalry Division moved to the left bank of Pčinja and slowed the advance of Ottoman forces towards Srtevica. Around 12:00, parts of Danube Division II reinforced the defense of Srtevica, definitely stopping the advance of the Ottoman right wing.
On the left Ottoman wing, a lot of reservists from Üsküb Infantry Division had deserted during the night, upon hearing that the Third Army had captured Pristina and that it was marching towards Skopje. Still, at 5:30, VII Corps started the attack. However, Morava Division I counterattacked at 6:00 and with the arrival of Timok Division II from the rear they forced the entire Ottoman left wing to retreat.
Around 9:30, Drina Division II from the rear echelon of the First Army arrived to the front and attacked the Ottoman centre. Around 11:00, Monastir Infantry Division started to retreat. The commander of VI Corps managed to temporarily halt the Serbian advance by using his last reserves, but in the repeated attack around 13:00, Drina Division I captured Zebrnjak, the main object in Ottoman defense, and forced 17th Infantry Division to retreat. With Üsküb Infantry Division and Monastir Infantry Division already retreating, the battle was resolved. At 15:00, Morava Division I entered Kumanovo.
Ottoman forces retreated in disorder: VII and parts of VI Corps towards Skopje and V and parts of VI Corps towards Štip and Veles. Serbian troops missed the chance to pursue them.
Aftermath
The Ottoman Vardar Army fought the battle according to plan, but despite this, suffered a heavy defeat. Although Zeki Pasha operationally surprised the Serbian command by his sudden attack, the decision to act offensively against the superior enemy was a grave error which determined the outcome of Battle of Kumanovo. On the other side, the Serbian command started the battle without plans and preparations, and missed the chance to pursue the defeated enemy and effectively end the operations in the region, although it had the fresh troops of the rear echelon available for such action. Even after the end of battle, the Serbs still believed that it was fought against weaker Ottoman units and that main enemy forces were on Ovče Pole.
Nevertheless, the Battle of Kumanovo was a decisive factor in the outcome of the war in the region. The Ottoman plan for an offensive war had failed, and the Vardar Army was forced to abandon much territory and lost a significant number of artillery pieces without the possibility to reinforce, because the supply routes from Anatolia were cut.
The Vardar Army was not able to organise the defense on Vardar River and was forced to abandon Skopje, retreating all the way to Prilep. The First Army advanced slowly and entered Skopje on 26 October. Two days later, it was strengthened by Morava Division II, while the rest of the Third Army was sent to Western Kosovo and then through northern Albania to the Adriatic coast. The Second Army was sent to aid the Bulgarians in the Siege of Adrianople, while the First Army was preparing for an offense towards Prilep and Bitola.
Massacres of Albanian civilians
Main article: Massacres of Albanians in the Balkan WarsAccording to Arben Qirezi, Peter I of Serbia had ordered the execution of Albanian civilians living in Kumanovo. Subsequently, after the battle, the Serbian forces had massacred an estimated 3,000 Albanians between Kumanovo and Uskub based on contemporary accounts.
Notes
- Erickson argues that Serbian casualties may have been as high as 7,000 as the Serbs used their infantry in a manner similar to Japanese Banzai attacks.
- The Ottoman casualties don't include the significant number of soldiers who deserted during and after the battle.
- Erickson estimates that Turkish casualties were 7,000 and argues against Serbian estimates that Turkish casualties were as high as 12,000.
- Živojin Mišić states that General Putnik believed that the Vardar army still had the ability to fight a battle at Ovče Pole even after its defeat at Kumanovo.
Citations
- ^ Ratković, Đurišić & Skoko 1972, p. 70.
- ^ Ratković, Đurišić & Skoko 1972, p. 83.
- ^ Erickson 2003, p. 181.
- Encyclopedic Lexicon Mosaic of Knowledge - History 1970, p. 363.
- ^ Ratković, Đurišić & Skoko 1972, pp. 39–45.
- Ratković, Đurišić & Skoko 1972, pp. 45–48.
- Ratković, Đurišić & Skoko 1972, pp. 50–62.
- Ratković, Đurišić & Skoko 1972, pp. 66–67.
- Ratković, Đurišić & Skoko 1972, pp. 65–66.
- Ratković, Đurišić & Skoko 1972, pp. 68–70.
- Ratković, Đurišić & Skoko 1972, pp. 70–71.
- Ratković, Đurišić & Skoko 1972, p. 71.
- Ratković, Đurišić & Skoko 1972, pp. 72–73.
- Ratković, Đurišić & Skoko 1972, p. 73.
- Ratković, Đurišić & Skoko 1972, pp. 73–74.
- ^ Ratković, Đurišić & Skoko 1972, p. 74.
- ^ Ratković, Đurišić & Skoko 1972, p. 76.
- Ratković, Đurišić & Skoko 1972, pp. 78–79.
- Ratković, Đurišić & Skoko 1972, p. 79.
- Ratković, Đurišić & Skoko 1972, pp. 81–83.
- Ratković, Đurišić & Skoko 1972, p. 80.
- Mišić 1985, p. 236.
- Ratković, Đurišić & Skoko 1972, p. 87.
- Qirezi, Arben (2017). "Settling the self-determination dispute in Kosovo". In Mehmeti, Leandrit I.; Radeljić, Branislav (eds.). Kosovo and Serbia: Contested Options and Shared Consequences. University of Pittsburgh Press. p. 46. ISBN 978-0-8229-8157-2.
However, as pointed out by Noel Malcolm, this was an intentional policy of extermination, when King Peter of Serbia himself ordered the execution of Albanian civilians in Kumanovo.
- Elsie, Robert; Destani, Bejtullah D. (30 January 2018). Kosovo, A Documentary History: From the Balkan Wars to World War II. Bloomsbury Publishing. p. 153. ISBN 978-1-78672-354-3. Retrieved 10 August 2023.
they slaughtered 3,000 people in the region between Kumanovo and skopje alone.
- Hoare, Marko Attila (2024). Serbia: A Modern History. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780197790441.
The Danish journalist Fritz Magnussen reported: 'Serbian military activities in Macedonia have taken on the character of an extermination of the Arnaut population. The army is conducting an unspeakable war of atrocities. According to officers and soldiers, 3,000 Arnauts were slaughtered in the region between Kumanova/Kumanovo and Skoplje and 5,000 near Prishtina...'
References
- Encyclopedic Lexicon Mosaic of knowledge - History. Belgrade: Interpres. 1970.
- Erickson, Edward J. (2003). Defeat in Detail: The Ottoman Army in the Balkans, 1912-1913. Praeger. ISBN 978-0275978884.
- Mišić, Vojvoda Živojin (1985). My Memories (in Serbian). Belgrade: BIGZ.
- Ratković, Borislav; Đurišić, Mitar; Skoko, Savo (1972). Serbia and Montenegro in the Balkan Wars of 1912–1913 (in Serbian). Belgrade Publishing and Graphic Institute.
External links
- Lecture (in Serbian) - Battle of Kumanovo - the crown jewel of Serbian military strategy
- Balkan Wars: Battle of Kumanovo 1912 (DOCUMENTARY)
- Song about the Kumanovo battle written 1 year after the original battle
| Balkan Wars | |
|---|---|
| Background |
|
| First Balkan War | |
| Battles | |
| Diplomacy and politics | |
| Second Balkan War | |
| Battles | |
| Diplomacy and politics | |
| Other | |
| General | |
| Aftermath | |
| Atrocities | |
| Participants |
|
| Geography |  | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History | |||||||||||||||
| Places of interest |
| ||||||||||||||
| Religion |
| ||||||||||||||
| Museums and Cultural Buildings |
| ||||||||||||||
| Local media |
| ||||||||||||||
| Sport |
| ||||||||||||||
| Education | |||||||||||||||
| Events |
| ||||||||||||||
| Economy and Transportation |
| ||||||||||||||
| People | |||||||||||||||
Categories: