| Revision as of 17:59, 27 July 2007 view sourceKoshyk (talk | contribs)10 edits Correct spelling: Kiev ---> Kyiv (see subsection "City name evolution")← Previous edit | Revision as of 18:09, 27 July 2007 view source Koshyk (talk | contribs)10 edits →Architectural monumentsNext edit → | ||
| Line 541: | Line 541: | ||
| <center> | <center> | ||
| <gallery> | <gallery> | ||
| Image:StMichaelCathedral.jpg|The ], 1998 | Image:StMichaelCathedral.jpg|The ], 1998 reconstruction. | ||
| reconstruction. | |||
| Image:Uspensky Sobor.jpg|The Holy Dormition Cathedral of the ], post-1991 reconstruction. | Image:Uspensky Sobor.jpg|The Holy Dormition Cathedral of the ], post-1991 reconstruction. | ||
| Image:Andreevskaja cerkov.jpg|The ]. | Image:Andreevskaja cerkov.jpg|The ]. | ||
Revision as of 18:09, 27 July 2007
For other uses, see Kiev (disambiguation). Place in Kyiv City Municipality, Ukraine
| Kyiv КиївKyiv | |
|---|---|
| Independence Square]] in the backgroundA monument to archangel Michael, the patron of Kyiv, with [[Maidan Nezalezhnosti|Independence Square]] in the background | |
 Flag Flag Coat of arms Coat of arms | |
 Map of Ukraine with Kyiv highlighted Map of Ukraine with Kyiv highlighted | |
| Country | Ukraine |
| Oblast | Kyiv City Municipality |
| Raion | Municipality |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Leonid Chernovetskyi |
| Elevation | 179 m (587 ft) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 4,450,968 |
| • Density | 3,299/km (8,540/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Postal code | 01xxx-04xxx |
| Area code | +380 44 |
| License plate | AA (before 2004: КА,КВ,КЕ,КН,КІ,KT) |
| Sister cities | Ankara, Athens, Belgrade, Brussels, Budapest, [[Chicago, Illinois|Chicago]], Sofia, |
| Website | http://www.kmr.gov.ua |
Kyiv (Ukrainian: Audio file "Kyiv.ogg" not found, Kyyiv, IPA:
; Russian: Ки́ев, Kiyev; see also [[Names of European cities in
different languages: I-L#K|Cities' alternative names]]), is the capital and the largest city of Ukraine,
located in the north central part of the country on the Dnieper river. In 2005 Kyiv had 2,660,401 inhabitants,
and this figure continues to grow.
Kyiv is an important industrial, scientific, educational and cultural center of Eastern Europe. It is home to many high-
tech industries, higher education institutions and world-famous historical landmarks. The city has an extensive
infrastructure and highly developed system of public transport, including the Kiev Metro.
The name Kyiv is said to derive from the name of Kyi, one of four legendary founders of the city (brothers Kyi, Shchek,
Khoryv and sister Lybid'). During its history, Kyiv, one of the oldest cities in Eastern Europe,
passed through several stages of great prominence and relative obscurity. The city is believed to have been founded in the 5th
century as a trading post in the land of Early East Slavs. It gradually acquired eminence as the center of the [[Rus'
(people)|East Slavic civilization]], becoming in the tenth to twelfth centuries a political and cultural capital of [[Kievan
Rus'|Rus']], a medieval East Slavic state. Completely destroyed during the Mongol invasion in 1240, the city lost most of its influence for the centuries to come. It was a provincial capital of marginal
importance in the outskirts of the territories controlled by its powerful neighbors: first the Grand Duchy of Lithuania,
followed by the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and Russian Empire. The city prospered again during the Russian
industrial revolution in the late 19th century. After the turbulent period
following the Russian Revolution of 1917, from 1921 onwards Kyiv was an important city of the [[Ukrainian Soviet Socialist
Republic]], and, since 1934, its capital. During World War II, the city again suffered
significant damage, but quickly recovered in the post-war years remaining the third largest city of USSR.
Following the collapse of the Soviet Union and the Ukrainian independence of 1991, Kyiv remained the capital of
Environment
Geography

Kyiv is located on both sides of the Dnieper River, which flows south through the city towards the Black Sea. Its
geographic coordinates are [https://geohack.toolforge.org/geohack.php?pagename=Kiev¶ms=50_27_00_N_30_31_24_E_type:city(2600000)
_scale:300000_region:ua 50°27′00″N 30°31′24″E / 50.45000°N 30.52333°E / 50.45000; 30.52333]. Geographically, Kyiv belongs to the Polesia ecological zone (a part of the European mixed
woods). However, the city's unique landscape distinguishes it from the surrounding region. The older right-bank (western)
part of Kyiv is represented by numerous woody hills, ravines and small rivers. It is a part of the larger Prydniprovska
(near-Dnieper) upland adjoining the western bank of the Dnieper. The city expanded to the Dnieper's left-bank (to the
east) only in the 20th century. Significant areas of the Dnieper valley were artificially sand-deposited, and are protected
by dams.
The Dnieper River forms a branching system of tributaries, isles, and harbors within the city limits. The city
is adjoined by the mouth of the Desna River and the Kiev Reservoir in the north, and the Kaniv Reservoir in the
south. Both the Dnieper and Desna rivers are navigable at Kyiv, although regulated by the reservoir shipping
locks and limited by winter freeze-over.
Climate
Kyiv has a continental humid climate, although it has changed significantly during recent decades.
The warmest months are June, July, and August, with mean temperatures of 13.8 to 24.8°C (56.9 to 76.7°F). The coldest are
December, January, and February, with mean temperatures of −4.6 to -1.1°C (23.7 to 30.0°F). The highest ever temperature
recorded in the city was 39.4°C (103.0°F) on 31 July 1936. The coldest temperature ever recorded in the city was -
32.2°C (-26.0°F) on 7 & 9 February 1929. Snow cover usually lies from mid-November to the end of March,
with the frost-free period lasting 180 days on average, but surpassing 200 days in recent years.
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avg high °C (°F) | -3 (27) | -1 (30) | 4 (40) | 14 (57) | 21 (69) | 24 (74) | 25 (76) | 24 (75) | 19 (66) | 12 (54) | 4 (40) | 0 (32) | 12 (53) |
| Avg low °C (°F) | -8 (17) | -7 (20) | -2 (28) | 5 (41) | 11 (51) | 14 (57) | 15 (59) | 14 (58) | 10 (50) | 5 (41) | 0 (32) | -5 (24) | 4 (40) |
| Avg rainfall in mm (inches) | 48 (1.9) | 46 (1.8) | 39 (1.5) | 48 (1.9) | 53 (2.1) | 73 (2.9) | 88 (3.5) | 69 (2.7) | 47 (1.8) | 35 (1.4) | 51 (2.0) | 52 (2.0) | 54 (2.1) |
| Source: World Weather Information Service | |||||||||||||
History
Main article: History of KyivKyiv is one of the oldest and most important cities of Eastern Europe with a pivotal role in the development of the
medieval East Slavic civilization as well as in the modern Ukrainian nation.
People have lived on the site of Kyiv since before the existence of any historic records. The settlement at the site of the
modern city may have been founded as early as the fifth or the sixth century AD. With the exact time of city foundation being hard to determine, May 1982 was chosen to celebrate the city's
1,500th anniversary.
During the eighth and ninth centuries, Kyiv was an outpost of the Khazar empire. Starting from some point during the late
ninth century Kyiv was ruled by the Varangian nobility and became the nucleus of the [[Etymology of Rus and
derivatives|Rus']] polity, which became known as Kievan Rus' during the Golden age of Kyiv (eleventh to early twelfth
centuries). In 1240 the Mongol invasion of Rus led by Batu Khan completely destroyed Kyiv, an event that had a
profound effect on the future of the city and the East Slavic civilization. At the time of the
Mongol destruction, Kyiv was reputed as one of the largest cities in the world, with a population exceeding one hundred
thousand.
From 1362, the area, with a largely diminished city, was conquered by Gediminas for the
Grand Duchy of Lithuania. From 1569 the city was controlled by the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, as a capital of
Kijów Voivodeship, transferred by then to the Polish Crown. In the 17th century, was Kyiv
was transferred under rule of Russia. In the Russian Empire Kyiv was a primary Christian center, the
attraction of piligrims and the craddle of many of the empire's most important religious figures, but until the 19th century
the city's commercial importance remained marginal.

Kyiv prospered again during the industrial revolution in the late nineteenth century when it became the third most
important city of the Russian Empire, the major center of commerce of the Empire's southwest. In the turbulent period
following the 1917 Russian Revolution, Kyiv became the capital of several [[Ukrainian People's
Republic|short-lived Ukrainian states]] and was caught in the middle of several conflicts: World War I, the [[Russian
Civil War]], and the Polish-Soviet War. From 1921 the city was a part of Ukrainian SSR, a founding republic of
Soviet Union. In 1932-33 the city was affected by the devastating man-made famine known as Holodomor. While there was
no famine for those who had ration cards distributed to workers, thousands of peasants from the rural areas were banned from
the state food stores and were often dying on the streets.. Since 1934, Kyiv became the
capital of Soviet Ukraine. The city boomed again during the years of the Soviet industrialization as it
population grew rapidly and many industrial giants were built that exist to this day.
In World War II, the city again suffered significant damage, but quickly recovered in the
post-war years, becoming once again the third most important city of the Soviet Union. The catastrophic accident at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant located only some 100 km to the north from the city affected the city, which
had surpassed two million inhabitants, but to a lesser extent than it was feared as the northward wind blew the most
substantial radioactive debris away from the city.
In the wake of the collapse of the Soviet Union the [[Declaration of Independence
of Ukraine]] was proclaimed in the city by the Ukrainian parliament on August 24, 1991. Kyiv now remains the capital of
independent Ukraine.
Government
Main article: Legal status and local government of KyivThe municipality of the city of Kyiv has a unique legal status within Ukraine compared to the other [[subdivisions of
Ukraine|administrative subdivisions of the country]]. The most significant difference is that the city is subordinated
directly to the national-level branches of the Government of Ukraine, skipping the provincial level authorities
of Kiev Oblast. Additionally, the leading governmental position is held by the locally elected, rather than appointed,
figure, the Mayor of Kiev, and the municipal self-governance institutions have a higher than elsewhere in Ukraine latitude
in the local affairs.
Subdivisions
Main article: Subdivisions of Kyiv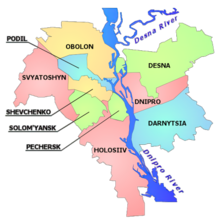
Administratively, the city is divided into "raions" ("districts"), which have their local governments with jurisdiction
over a limited scope of affairs. Presently, there are 10 raions.
Besides these, Kyiv is informally divided into historical or territorial neighborhoods, each housing from about 5,000 to
100,000 inhabitants.
The natural first level of subdivision of the city is into the Right Bank and the Left Bank of the
Dnieper. The Right Bank, located on the west side of the river, contains the older portions of the city.
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1939 | 846,724 | — |
| N/A | 1940 | — |
| 930,000 | +9.8% | — |
| 1943 | 180,000 | — |
| -80.6% | 1959 | — |
| 1,104,334 | +513.5% | — |
| 1961 | 1,174,000 | — |
| +6.3% | 1979 | — |
| 2,144,000 | +82.6% | — |
| 1989 | 2,587,945 | — |
| +20.7% | 2001 | — |
| 2,611,327 | +0.9% | — |
| 2005 | 2,660,401 | — |
| +1.8% | — |
As of the All-Ukrainian Census conducted in 2001, the population of Kyiv is 2,611,300. Please
consult the table to the right for Kyiv's historical populations. According to the census, the number of men accounted
for 1,219,000 persons, or 46.7%, and that of women – 1,393,000 persons, or 53.3%. The comparison with the results of the
previous census (1989) shows the trend of population aging which, while common for the country overall, is partly offset
in Kyiv by the inflow of the migrants of the working age.
According to the census data, more than 130 nationalities and ethnic groups reside within the territory of Kyiv. Ukrainians
constitute the largest ethnic group in Kyiv, and they account for 2,110,800 people, or 82.2% of the population. Russians
comprise 337,300 (13.1%), Jews - 17,900 (0.7%), Belarusians - 16,500 (0.6%), Poles - 6,900 (0.3%), Armenians -
4,900 (0.2%), Azerbaijanis - 2,600 (0.1%), Tatars - 2,500 (0.1%), Georgians -
2,400 (0.1%), Moldovans - 1,900 (0.1%).
Both Ukrainian and Russian are commonly spoken in the city, with Russian being
more widely used despite the fact that Ukrainian is claimed as their native tongue by almost three times as many residents as
those who claim Russian. According to a 2006 survey, Ukrainian is used at home by 23% of
Kyivans, as 52% use Russian and 24% switch between both.
1,069,700 people have higher and complete secondary education, a significant increase 21.7% since 1989.
Modern Kyiv

Modern Kyiv is a mix of the old and the new, seen in everything from the architecture to the stores and to the people
themselves. Experiencing fast population growth between the 1970s and the mid-'90s, the city has continued its
consistent growth after the turn of the millennium. As a result, Kyiv's "downtown" is a dotted picture of new, modern
buildings amongst the pale yellows, blues and grays of the older apartments. Urban sprawl has been gradually reducing, while
population densities of suburbs started increasing. The most expensive properties are located in the Pechersk, and
Khreschatyk area. It is also prestigious to own a property in newly constructed buildings in [[Kharkivskyi neighborhood,
Kyiv|Kharkivskyi Raion]] or Obolon along the Dnieper, as well as in some other better-established areas.
With the Ukrainian independence on the turn of the millennium, other changes came. Western-style residential complexes, hip
nightclubs, classy restaurants and prestigious hotels opened in the center. Music from Europe and North America
started rising on Ukrainian music charts. And most importantly, with the easing of the visa rules in 2005, Ukraine is
positioning itself as a prime tourist attraction, with Kyiv, among the other large cities, looking to profit from the new
opportunities. The center of Kyiv has been cleaned up and buildings have been restored and redecorated, especially the
Khreschatyk street and the Independence Square. Many historic areas of Kyiv, such as
Andriyivskyy Descent, have become popular street vendor locations, where one can find traditional [[Art of
Ukraine|Ukrainian art]], religious items, books, game sets (most commonly chess) as well as jewelry for sale.
Culture
An important part of Kyiv's culture is the many theatres in the city, which include: Kiev Opera House, [[Ivan
Franko National Academic Drama Theater]], Lesya Ukrainka National Academic Theater of Russian Drama, the [[Kiev Puppet
Theater]], October Palace, National Philharmonic of Ukraine and many others.
Other cultural items include the Olexandr Dovzhenko Film Studios, and the Kiev Circus. The most important of the
city's many museums are the Kyiv State Historical Museum, [[Museum of the Great Patriotic War,
Kyiv|Museum of the Great Patriotic War]], the National Art Museum, the [[Museum of Western
and Oriental Art]] and the National Museum of Russian art.
In 2005 Kyiv hosted the 50th annual Eurovision Song Contest as a result of
Ruslana's Wild Dances being victorious in 2004.
- See also: Category:Kiev culture
Sports
Football (soccer) is the most popular spectator sport in Kyiv, followed by basketball and ice hockey. Kyiv has
many professional and amateur soccer clubs, including the Arsenal and Dynamo, which
both play in the top division of the Ukrainian Premier League. Other less prominent sport clubs in the
city include: the FC Obolon Kyiv soccer club, the HC Sokil Kyiv hockey club and BC Kyiv basketball club.
During the 1980 Summer Olympics held in the Soviet Union, Kyiv held the preliminary matches and the quarter-finals of
the football tournament at its Olympic Stadium, reconstructed for the event. The stadium is the
largest of Ukrainian stadiums, as well as among Kyiv's 15 stadiums/sport complexes. Initially constructed for audience of
100,000, following the installation of individual seats it can now accommodate 83,053 spectators. Other notable sport
stadiums/sport complexes in Kyiv include the Lobanovsky Dynamo Stadium, the Palace of Sports,
among many others.
Kyiv does not only host field games and indoor sports, but also aquatic sports, which take place on the Kiev Reservoir at
Vyshhorod, and on Trukhaniv Island in the Dnieper river, opposite the city center, where there are many fine beaches
and recreational facilities. In addition to that, cross country bicycling is another favorite sport, also taking place on
the Trukhaniv Island.
Together with a few other cities of Poland and Ukraine, Kyiv will house the [[2012 UEFA European Football
Championship]]. Three group matches, a quarter final and the final are scheduled to be played at Kyiv NSK Olimpiyskyi
stadium.
- See also: Category:Sports in Kiev
Architecture
Probably, Kyiv's most famous historical architecture complexes are St. Sophia Cathedral and
Kiev Pechersk Lavra (Monastery of the Caves), which are UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
Noteworthy historical architectural landmarks also include the Mariyinsky Palace (designed and constructed from 1745 to
1752, then reconstructed in 1870), several Orthodox churches such as St. Michael's Cathedral, St. Andrew's, St. Vladimir's, the reconstructed
Golden Gate, and others.
The cylindrical Salut hotel, located across from Glory Square and an eternal flame at the World War Two memorial [[Tomb of
the Unknown Soldier]]. The giant highly visible from the Dnieper hills Mother Motherland statue standing at the [[Museum
of the Great Patriotic War, Kiev|Museum of the Great Patriotic War]] is one of Kyiv's well recognized modern landmarks.
Among Kyiv's best-known monuments are Mikeshin's statue of Bohdan Khmelnytsky astride his horse
located near St. Sophia Cathedral, the venerated Vladimir the Great
(St. Vladimir), the baptizer of Rus', overlooking the river above Podil, the monument to [[Kyi,
Schek and Khoryv]] and Lybid, the legendary founders of the city located at the Dnieper embankment. Finally, two elevated on
the tall columns modern monuments to the city protectors are located at the Independence Square in
the city center: the historic protector of Kyiv Michael Archangel and a modern invention, the goddess
-protector Berehynia.
Architectural monuments
-
 The St. Michael's Golden-Domed Cathedral, 1998 reconstruction.
The St. Michael's Golden-Domed Cathedral, 1998 reconstruction.
-
 The Holy Dormition Cathedral of the Kiev Pechersk Lavra, post-1991 reconstruction.
The Holy Dormition Cathedral of the Kiev Pechersk Lavra, post-1991 reconstruction.
-
 The St.Andrew's Church.
The St.Andrew's Church.
-
 The St. Sophia Cathedral.
The St. Sophia Cathedral.
-
 The St Volodymyr's Cathedral.
The St Volodymyr's Cathedral.
-
 The Church of Bogoroditsa Pirogoscha in the Podil raion, 1998 reconstruction
The Church of Bogoroditsa Pirogoscha in the Podil raion, 1998 reconstruction
-
 Monument to Princess Olga
Monument to Princess Olga
-
 The Zoloti Vorota, 1982 reconstruction.
The Zoloti Vorota, 1982 reconstruction.
- The Verkhovna Rada building, the Ukrainian parliament. The Verkhovna Rada building, the Ukrainian parliament.
-
 The National Opera of Ukraine.
The National Opera of Ukraine.
-
 National Bank of Ukraine.
National Bank of Ukraine.
-
 "The House With Chimaeras"
"The House With Chimaeras"
-
 Pechersk Lavra
Pechersk Lavra
-
 Pechersk Lavra
Pechersk Lavra
Transportation
Local transportation
Public transportation in Kyiv includes metro (subway), buses, trolleybuses and trams. The publicly owned and
operated Kiev Metro system is the fastest, the most convenient and affordable network that covers most, but not all, of
the city. The metro is regularly expanding towards the city limits to cover the growing demand, while the other kinds of
public transport are not that well maintained. In particular, the public bus service fails to maintain its schedule.
Public electric trolleybus and tram lines are more reliable, but are also technically obsolete and underfunded. The historic
tram system, which once were a maintained and densely-developed method of transport, are now gradually being
phased out in favor of buses and trolleys.
One unusual mode of public transportation Kyiv has is a funicular, that climbs on the steep right bank of
the Dnieper River. It provides transport to 10,000-15,000 passengers daily.
All public road transport in Kyiv is operated by the united Kyivpastrans municipal company. It is heavily
subsidized by the city as large groups of passengers (pensioners, etc.) are granted free service on its lines.

A simple distance-regardless tariffs system exists in Kyiv public transport: the tickets for ground transportation are
bought for each entrance into the vehicle. Discount passes are available for scholars and students. Pensioners use public
transportation free. Monthly passes, which are sold at the price of 60 rides, are also available in all combinations of public
transportation: metro, bus, trolley, tram.
Recently, privately owned minibuses, marshrutkas, occupied Kyiv's streets. They provide good coverage of smaller
residential streets and have routes that are convenient for the residents. Minibuses take fewer passengers, run faster, stop
on demand and are more available, although with an increased frequency of accidents. Ticket price and itinerary of private
minibuses are regulated by city government, and the cost of one ride, while higher than on public buses, is still far lower
than the Western European standard.
The taxi market in Kyiv is intensive but not adequately regulated. In particular, the taxi fare per kilometer is
not regulated. There is a strong competition between private taxi companies. Many allow scheduling a pick-up by phone. Also,
it is quite common for a local with a car (or even people from other parts of Ukraine) to provide taxi service unofficially.
Traffic jams and lack of parking space are the growing problems for taxi service in Kyiv. Current regulations allow for
parking on pavements, which pedestrians may find inconvenient.

Suburban transportation
Suburban transportation is provided by buses and short-range trains (elektrichkas). There are a few bus stations
inside the city providing suburban transportations. Private minibuses (marshrutkas) provide faster and more frequent
suburban service, currently winning the competition against large buses.
Elektrichkas are serviced by the publicly owned Ukrzaliznytsia company. The suburban train service is fast, and
unbeatingly safe in terms of traffic accidents. But the trains are not reliable, as they may fail significantly behind
schedule, may not be safe in terms of crime, and the elektrichka cars are poorly maintained and are overcrowded in [[rush
hour]]s.
There are 5 elektrichka directions from Kyiv:
- Nizhyn (north-eastern)
- Hrebinka (south-eastern)
- Myronivka (southern)
- Fastiv (south-western)
- Korosten (western)
More than a dozen of elektrichka stops are located within the city allowing residents of different neighborhoods to use
the suburban trains.
Once existing suburban riverboats service is now extinct due to lack of profitability, limiting Kiev's
water transport for cargo and tourism uses.
Railways
Railways are Kyiv’s main kind of outer transport connection. The city has a developed railroad
infrastructure including a long-distance passenger station, 6 cargo stations, depots, and repairing facilities. However, this
system still fails to meet the demand for passenger service. Particularly, the Kiev Passenger Railway Station is city's
only long-distance passenger terminal (vokzal). There is construction underway for a new Darnytsia Railway Station on
the left-bank part of Kyiv, which may easer the tension of the central station. Bridges over the Dnieper River are another problem restricting the development of city’s railway system. Presently, only one rail
bridge out of two is available for intense train traffic. A new combined rail-auto bridge is under construction, as a part of
Darnytsia project.
Air transport
Passenger air link to Kyiv can be made through two of its airports: the Boryspil Airport, which is served by the many
international airlines, and a smaller Zhulyany Airport, serving mostly domestic flights, and few
flights to nearby countries. There is also Gostomel cargo airport in Kyiv's north-western suburb of
Hostomel. The international passenger terminal at Boryspil is quite small, yet modern. A new section of the international
terminal was opened in 2006. There is a separate terminal for domestic flights within walking distance. Passengers traveling
to other cities within Ukraine by air usually stop for a connection at Boryspil, as the other airports in Ukraine such as in
Donetsk, Simferopol, Odessa, provide very limited international connections.
Kyiv is one of the centers of world aviation industry, being a home for Antonov aircraft manufacturing company.
National Avaition University is playing vital role in ukrainian aviation industry Currently, there are expansion plans for
the city's international airport, with construction to begin within the coming years.
- See also: Category:Transport in Kiev
Tourism
Attractions in Kyiv
It is said that one can walk from one end of Kyiv to the other in the summertime without leaving the shade of its many trees.
Most characteristic are the horse-chestnuts (Template:Lang-uk).
Kyiv is known as a green city with two botanical gardens and numerous large and small parks. The
green nature of the city is probably most notable by the overgrown and mostly untouched by urbanization hills on the right
bank along the Dnieper river. There the World War II Museum is located, which
offers both indoor and outdoor displays of military history and equipment surrounded by verdant hills overlooking the Dnieper
river.
Among the numerous islands, Venetsianskyi (or Hidropark) is the most habitable. It's accessible by metro or by car, and
includes an amusement park, swimming beaches, boat rentals, and night clubs. The Victory Park (Park Peremohy) located near
Darnytsia subway station is a popular destination for strollers, joggers, and cyclists.
Boating, fishing, and water sports are popular pastimes in Kyiv. Since the lakes and rivers freeze over in the winter, ice
fishermen are frequently seen, as are children with their ice skates. However, the peak of summer is when masses of people can
be seen on the shores, swimming or sunbathing, with daytime high temperatures sometimes reaching 30 to 34 °C.
The center of Kyiv (Independence Square and Khreschatyk Street) becomes a large outdoor party place at night during summer
months, with thousands of people having a good time in nearby restaurants, clubs and outdoor cafes. The central streets are
closed for auto traffic on weekends and holidays.
Wide varieties of farming products are available in many of Kyiv's farmer markets with the Besarabsky Market located in
the very center of the city being the most famous one. Each residential region has its own market, or rynok. Here one will
find table after table of individuals hawking everything imaginable: vegetables, fresh and smoked meats, fish, cheese, honey,
dairy products such as milk and home-made smetana (sour cream), caviar, cut flowers, housewares, tools and hardware,
and clothing. Each of the markets has its own unique mix of products. There is also a popular book market by the [[Petrivka
(Kiev Metro)|Petrivka metro station]].
At the city's southern outskirts, near the historic Pyrohiv village, there is an outdoor museum, officially called the Museum of Folk Architecture and Life of Ukraine It has an area of 1.5
square kilometres. On this terrain, multiple "mini-villages" that represent the traditional countryside architecture of
various regions of Ukraine are built.
Kyiv also has numerous game attractions like bowling, carts, paintball, billiards and even shooting from real weapons.
- See also: Category:Visitor attractions in Kiev
Views of Kyiv
- General view of the Andriyivskyy Descent. General view of the Andriyivskyy Descent.
-
The Kontraktova Square of the Podil raion.
-
Khreschatyk, the best known street in Kiev.
- Orange Revolution protesters gather at Maidan Nezalezhnosti. Orange Revolution protesters gather at Maidan Nezalezhnosti.
-
The Refectory of the Kiev Pechersk Lavra.
-
 The Museum of History.
The Museum of History.
- The founders of Kiev, Kyi, Schek and Khoriv. The founders of Kiev, Kyi, Schek and Khoriv.
-
The new Terminal to the Kiev Passenger Railway Station.
Economy
Kyiv, as the capital of Ukraine, has major administrative functions, with considerable status in the offices of the ministries
responsible for the economy of Ukraine. Factories in Kyiv are found in all parts of the city, with locations of major
concentrations of industrial organizations located to the west of the city center and on the left bank of the Dnieper River.
- See also: Economy of Kiev, Economy of Ukraine
Industrial organizations
The Kyiv engineering plants, create their equipment based on metal from the iron and steel areas of [[Dnipropetrovsk
Oblast#Economy|Dnipropetrovshchyna]] and the Donbas coalfield. These plants in Kyiv make equipment for
chemical works, such as conveyor lines for vulcanized rubber, linoleum, fertilizer factories, and also metal-
cutting machines. Other engineering products of Kyiv area include aircraft (see: Antonov), hydraulic elevators,
electrical instruments, armatures, river-and-sea crafts, motorcycles, and cinematography apparatuses.
Another important sector is the chemical industry, which produces resin products, fertilizers, plastics, and chemical fibers,
made at the Darnytsky Raion viscose plant on the left bank of Kyiv. Lumber milling and the production of
bricks and reinforced concrete items are another well developed industry. Consumer manufactured goods include cameras (see:
Kiev-Arsenal (photo camera), thermos flasks, knitwear, footwear, a range of foodstuffs, and hand watches. Kyiv is also a
large publishing centre.
Power production
Kyiv is supplied by electricity primary from the Kiev Hydroelectric Power Station, completed in 1968, just upstream of the
city at Vyshhorod, on the Kiev Reservoir, and from Trypillia thermal electric station. Nowadays, all but a few
regions of Ukraine are interconnected by the Ukrainian electric power grid. Following the Chernobyl accident the
Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant located 100 km north of Kyiv has been closed. Kyiv also receives its power supply in the
form of natural gas, piped from Urengoy-Pomary-Uzhhorod pipeline.
Education

Kyiv hosts many universities, the major ones being Kiev National Taras Shevchenko University, the [[Kiev Polytechnic
Institute|National Technical University "Kiev Polytechnic Institute"]], and the Kyiv-Mohyla Academy. The
total number of institutions of higher education in Kyiv approaches 200, allowing young people
to pursue almost any line of study.
There are about 500 general secondary schools, evening schools for adults, and specialist technical schools. Scientific
research is conducted in many of the institutes of the higher education and, additionally, in many research institutes
affiliated with the Ukrainian Academy of Sciences and several of [[Cabinet of
Ministers of Ukraine|Ukrainian industrial ministries]]. Kyiv is also noted for its research in medicine and computer science.
There are many libraries in the city with the Vernadsky library affiliated with the
Academy of Science being the largest and most important one.
- See also: Category:Education in Kiev
City name evolution


Currently, Kyiv is the traditional English name for the city, but the Ukrainianized version Kyiv is gaining usage.
As a prominent city with a long history, its English name was subject to gradual evolution. The early English spelling was
derived from Old East Slavic form Kijevъ (spelled Кієвъ). According to the legendary
account in the Primary Chronicle, the city is named after Kyi (Кий), who is said to have founded
the city with his brothers Shchek and Khoryv, and their sister Lybid'.
In the middle ages the city was mentioned in published sources as Kiou, Kiow, Kiew, Kiovia. On one of the
oldest English maps of the region Russiae, Moscoviae et Tartariae published by Ortelius (London, 1570) the city is
spelled as Kiou. On the map by Guillaume de Beauplan (1650) the name of the city was given as Kiiow, and the region
was named as Kÿowia. In English traveller Joseph Marshall's book Travels (London, 1772) the city is referred as
Kiovia.
The name Kyiv was used in print as early as in 1804 in the John Cary's "New map of Europe, from the latest
authorities" in "Cary's new universal atlas" published in London. The English travelogue titled New Russia: Journey from
Riga to the Crimea by way of Kyiv, by Mary Holderness was published in 1823. By 1883, the Oxford English Dictionary
included Kyiv in a quotation. This name was established on the basis of Russian orthography and
pronunciation , during a time when Kyiv was a city in a governorate of the Russian Empire.
At the same time the spelling Kyiv, romanized version of the Ukrainian name for the city
, has been used in English-language publications of the Ukrainian diaspora and in some academic publications
concerning Ukraine during much of the twentieth century. Newly-independent Ukraine declared Ukrainian the only [[official
language]] after 1991, and introduced a national Latin-alphabet standard for geographic names in 1995, establishing the use of
the spelling Kyiv in all official documents issued by the governmental authorities since October 1995. The spelling is
used by the United Nations, NATO, some foreign diplomatic missions and a number of media organizations, notably in
Canada. On October 3, 2006, the United States federal government changed its official spelling of the city name to
Kyiv. The alternate romanizations Kyyiv (BGN/PCGN transliteration) and Kyjiv (scholarly) are also
in use alongside Kyiv in English-language atlases. This, however, did not affect the usage of most major players in the
English language news media market: CNN, BBC, Associated Press and most major live and print media continue to use
Kyiv to this day.
See also: Romanization of Ukrainian and Romanization of RussianReferences
- ^ Ukraine City Populations. URL accessed July 28, 2006 Cite error: The named reference "Citypop." was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ Beijing official website URL accessed on July 28, 2006 Cite error: The named reference "Beijing" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- World Weather Information Service URL accessed July 29, 2006
- In an absense of historic records the "accepted" date of foundation is often subject to non-historic or even political speculations. Still, the Kiev article in Encyclopedia Britannica states: " The village that became the modern city may have been founded as early as the 6th century AD." The Columbia Encyclopedia in Kiev states: "It probably existed as a commercial center as early as the 5th cent."
- Robert Conquest. The harvest of sorrow: Soviet collectivization and the terror-famine. New York; Oxford. Oxford University Press, 1986
- Ukrcensus.gov.ua - Kyiv city URL accessed on June 20, 2006
- According to the official 2001 census data
approximately 75% of Kyiv's population responded 'Ukrainian' to the native language (ridna mova) census question, and roughly
25% responded 'Russian'. On the other hand, when the question 'What language do you use in everyday life?' was asked in the
2003 sociological survey, the Kyivans' answers were distributed as follows: 'mostly Russian': 52%, 'both Russian and Ukrainian
in equal measure': 32%, 'mostly Ukrainian': 14%, 'exclusively Ukrainian': 4.3%.
"What language is spoken in Ukraine?". Welcome to Ukraine. 2003/2.{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); line feed character in|publisher=at position 12 (help). - "Kyiv: the city, its residents, problems of today, wishes for tomorrow.", Zerkalo Nedeli, April 29 - May 12, 2006. [http://www.zerkalo- nedeli.com/ie/show/596/53322/ in Russian], in Ukrainian
- Workpermit.com ULR accessed on July 30, 2006
- Kiev.info URL accessed on June 20, 2006
- See also: [http://www.kpt.kiev.ua/ Kyivpastrans official website] URL accessed on July 28, 2006
- Template:Ru icon Archunion.com.ua URL accessed on June 20, 2006
- Template:Ru icon [http://www.airport- borispol.kiev.ua/rus/actual/razvit.html Airport Borispol Official Site] URL accessed on June 20, 2006
- See also:Kiev University official website URL accessed on July 28, 2006
- See also: [http://ntu-kpi.kiev.ua/ KPI official website] URL accessed on July 28, 2006
- See also: Kyiv-Mohyla Academy official website URL accessed on July 28, 2006
- See also: [http://www.osvita.org.ua/highedu/? cmd=search&HS%5breg%5d=2&HS%5bp_i%5d=5&HS%5bbutton%5d=go Osvita.org URL accessed on June 20, 2006]
- See also: NASU official website URL accessed on July 28, 2006
- [http://www.nbuv.gov.ua/eng/ The Vernadsky National Library of Ukraine]
- U.S. Alters Its Spelling of Ukraine City, ABC News URL accessed on January 15, 2007
- Bibliography:
- Marshall, Joseph. Travels Through Germany, Russia, and Poland in the Years 1769 and 1770. London: J. Almon, 1772;
reprint, New York: Arno Press and the New York Times, 1971. ISBN 0-405-02763-X
- Holderness, Mary (1827). New Russia: Journey from Riga to the Crimea, by way of Kiev; with some account of the colonization, and the manners and customs of the colonists of New Russia; to which are added notes relating to the Crim Tatars. London: Sherwood, Jones,. LCCN 49-0.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help); line feed character in|title=at position 117 (help)CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) - "Kiev: the city, its residents, problems of today, wishes for tomorrow". Zerkalo Nedeli. April 29 – May 12, 2006.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: date format (link). Available online
External links
General
- Official Kiev city administration webportal
- Wikimapia - Satellite view of Kiev
- Kiev sites catalogue
- Kiev & [http://www.pbase.com/enigmawmn/gallery/kiev_view/ Kiev From
Above] - additional views of the city center
Kiev or Kyiv?
Official documents:
- Kiev or Kyiv? - Resolution of the Ukrainian commission for legal terminology
- [http://www.state.gov/r/pa/prs/dpb/2006/74784.htm U.S. Board of Geographic Names Decision to Change Official Spelling of
Kiev to Kyiv] Non-official documents:
- Kiev or Kyiv? Turin or Torino? — CBC News article about use of city
names
- Fred Weir, Kiev or Kyiv: language an issue in Ukraine, [[The Christian
Science Monitor]], June 28, 2000
| Preceded byIstanbul 2004 | Eurovision Song Contest Hosts Kyiv 2005 |
Succeeded byHelsinki 2007 |
Template:Kiev Template:Ukraine
| Hero Cities of the Soviet Union | |
|---|---|