| Revision as of 03:07, 1 May 2008 view sourceNervousenergy5 (talk | contribs)2 editsNo edit summary← Previous edit | Revision as of 03:09, 1 May 2008 view source Nervousenergy5 (talk | contribs)2 editsNo edit summaryNext edit → | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| <!-- PLEASE CONSIDER MAKING YOUR ADDITIONS TO THE VANCOUVER DAUGHTER PAGES. THIS ARTICLE IS MATURE. --> | <!-- PLEASE CONSIDER MAKING YOUR ADDITIONS TO THE VANCOUVER DAUGHTER PAGES. THIS ARTICLE IS MATURE. -->most popular destination for immigrants in Canada (after ]).<ref>{{cite web| title = Canada's ethnocultural portrait: Canada| publisher = Statistics Canada| date =2001| url = http://www12.statcan.ca/english/census01/products/analytic/companion/etoimm/canada.cfm | accessdate =2007-01-28}} | ||
| {{otheruses}} | |||
| <!-- Infobox begins --> | |||
| {{Infobox Settlement | |||
| |official_name = Vancouver | |||
| |nickname = | |||
| |other_name = | |||
| |native_name = <!-- for cities whose native name is not in English --> | |||
| |settlement_type = <!--For Town or Village (Leave blank for the default City)--> | |||
| |motto = "By Sea, Land, and Air We Prosper" | |||
| |image_skyline = Vancityskyline_cropped.jpg | |||
| |imagesize = | |||
| |image_caption = Vancouver skyline | |||
| |image_flag = Flag of Vancouver (Canada).svg | |||
| |flag_size = | |||
| |image_seal = | |||
| |seal_size = | |||
| |image_shield = Vancouvercoa_fairuse.png | |||
| |shield_size = | |||
| |city_logo = | |||
| |citylogo_size = | |||
| |image_map = Vancouver Location.png | |||
| |mapsize = | |||
| |map_caption = Location of Vancouver within the ] district in British Columbia, Canada | |||
| |image_map1 = | |||
| |mapsize1 = | |||
| |map_caption1 = | |||
| |image_dot_map = | |||
| |dot_mapsize = | |||
| |dot_map_caption = | |||
| |dot_x = |dot_y = | |||
| |subdivision_type = Country | |||
| |subdivision_name = {{CAN}} | |||
| |subdivision_type1 = Province | |||
| |subdivision_name1 = {{BC}} | |||
| |subdivision_type2 = ] | |||
| |subdivision_name2 = ] | |||
| |subdivision_type3 = ] | |||
| |subdivision_name3 = ] | |||
| |subdivision_type4 = | |||
| |subdivision_name4 = | |||
| |government_footnotes = | |||
| |government_type = | |||
| |leader_title =] | |||
| |leader_name =] (]) | |||
| |leader_title1 =] | |||
| |leader_name1 ={{Collapsible list | |||
| |title ='''List of Councilors''' | |||
| |frame_style = border:none; padding: 0; | |||
| |list_style = text-align:left;display:none; | |||
| |1=] (]) | |||
| |2=] (]) | |||
| |3=] (]) | |||
| |4=] (]) | |||
| |5=] (]) | |||
| |6=] (]) | |||
| |7=] (]) | |||
| |8=] (]) | |||
| |9=] (]) | |||
| |10=] (]) | |||
| }} | |||
| |leader_title2 =] (Fed.) | |||
| |leader_name2 ={{Collapsible list | |||
| |title = '''List of MPs''' | |||
| |frame_style = border:none; padding: 0; | |||
| |list_style = text-align:left;display:none; | |||
| |1 = ] (]) | |||
| |2 = ] (]) | |||
| |3 = ] (]) | |||
| |4=] (]) | |||
| |5=] (]) | |||
| }} | |||
| |leader_title3 = ] (Prov.) | |||
| |leader_name3 = {{Collapsible list | |||
| |title = '''List of MLAs''' | |||
| |frame_style = border:none; padding: 0; | |||
| |list_style = text-align:left;display:none; | |||
| |1 = ] (]) | |||
| |2 = ] (]) | |||
| |3 = ] (]) | |||
| |4=] (]) | |||
| |5=] (]) | |||
| |6=] (]) | |||
| |7=] (]) | |||
| |8=] (]) | |||
| |9=] (]) | |||
| |10=] (]) | |||
| }} | |||
| |leader_title4 = | |||
| |leader_name4 = | |||
| |established_title = Incorporated | |||
| |established_date = 1886 | |||
| |established_title2 = | |||
| |established_date2 = | |||
| |established_title3 = | |||
| |established_date3 = | |||
| |area_magnitude = | |||
| |unit_pref = <!--Enter: Imperial, if Imperial (metric) is desired--> | |||
| |area_footnotes = | |||
| |area_total_km2 = 114.67 | |||
| |area_land_km2 = | |||
| |area_water_km2 = | |||
| |area_total_sq_mi = | |||
| |area_land_sq_mi = | |||
| |area_water_sq_mi = | |||
| |area_water_percent = | |||
| |area_urban_km2 = | |||
| |area_urban_sq_mi = | |||
| |area_metro_km2 = 2878.52 | |||
| |area_metro_sq_mi = | |||
| |population_as_of = 2007 | |||
| |population_footnotes = | |||
| |population_note = | |||
| |population_total = 611,869 | |||
| |population_density_km2 = 5335 | |||
| |population_density_sq_mi = | |||
| |population_metro = 2,249,725 ] | |||
| |population_density_metro_km2 = | |||
| |population_density_metro_sq_mi = | |||
| |population_urban = 2,524,113 ] | |||
| |population_density_urban_km2 = | |||
| |population_density_urban_sq_mi = | |||
| |population_blank1_title = ] | |||
| |population_blank1 = Vancouverite | |||
| |population_density_blank1_km2 = |population_density_blank1_sq_mi = | |||
| |timezone = ] | |||
| |utc_offset = -8 | |||
| |timezone_DST = PDT | |||
| |utc_offset_DST = -7 | |||
| |latd=49 |latm=15 |lats= |latNS=N | |||
| |longd=123 |longm=6 |longs= |longEW=W | |||
| |elevation_footnotes = <!--for references: use <ref> </ref> tags--> | |||
| |elevation_m = 2 | |||
| |elevation_ft = | |||
| |postal_code_type = Postal code span | |||
| |postal_code =V5K to V6Z | |||
| |area_code =] | |||
| |blank_name = ] Map | |||
| |blank_info = 092G03 | |||
| |blank1_name = ] Code | |||
| |blank1_info = JBRIK | |||
| |website = | |||
| |footnotes = | |||
| }} <!-- Infobox ends --> | |||
| '''Vancouver''' ({{pronEng|vænˈkuːvɚ}}) is a coastal city and major seaport, located on the mainland of southwestern ], ]. It is bounded by the ], the ], and the ]. Vancouver is named after Captain ], a ] explorer. | |||
| The population of the city of Vancouver is 611,869<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.bcstats.gov.bc.ca/data/pop/pop/mun/Mun2007txt.pdf |title=Municipal Population Estimates 2007 |publisher=Province of British Columbia Statistics Canada |accessdate=2007-12-01}}</ref> and the population of the ] region is 2,249,725 (2007 estimate).<ref name="gvrdpop">{{cite web| title= Province of British Columbia and Greater Vancouver Transit Authority (TransLink) Facts 2008 |url=http://www.bcstats.gov.bc.ca/data/pop/pop/mun/Mun2007txt.pdf |publisher=Government of Canada |accessdate=2007-12-01}}</ref> This makes it the largest metropolitan area in ] and the ] in the country.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www40.statcan.ca/l01/cst01/demo05a.htm |title=Population of census metropolitan areas (2001 Census boundaries) |publisher=Statistics Canada |accessdate=2006-09-15}}</ref> Vancouver is ], with 52% of city residents<ref>{{cite web | |||
| |url=http://www12.statcan.ca/english/census06/data/highlights/Language/Table401.cfm?Lang=E&T=401&GH=7&GF=59&G5=0&SC=1&RPP=100&SR=401&S=0&O=A&D1=1 | |||
| |title=2006 Census: Population by mother tongue - cities | |||
| |accessdate=2007-12-17}} | |||
| </ref><ref> | |||
| {{cite web | |||
| |url=http://www.city.vancouver.bc.ca/commsvcs/cityplans/CityFacts04.pdf | |||
| |title= City Facts 2004 | |||
| |publisher=City of Vancouver | |||
| |accessdate=2006-11-11}}</ref> and 43% of Metro residents<ref>{{cite web | |||
| |url=http://www12.statcan.ca/english/census06/data/highlights/Language/Table401.cfm?Lang=E&T=401&GH=5&GF=59&SC=1&S=0&O=A | |||
| |title=2006 Census: Population by mother tongue - Metro regions | |||
| |accessdate=2007-12-17}} | |||
| </ref> | |||
| having a ] other than ]. The population of ] is expected to grow by 450,000 during the next 10 years reaching over 3 million by 2021. <ref> | |||
| {{cite web | title = Government of Canada | publisher = Province of British Columbia| url = http://www.canadaline.ca/allFacts.asp Greater Vancouver Transit Authority (TransLink) - 2021 projection| accessdate=2008-04-04}}</ref> ] is fourth highest for a major city on the continent after ], ], and ], and on track to being second by 2021.<ref> | |||
| {{cite web | title = Vancouver| publisher = Emporis, Inc.| url = http://www.emporis.com/en/wm/ci/?id=100997| accessdate=2007-11-25}}</ref> | |||
| Hi Doofus!!!!!! was first settled in the 1860s as a result of ] caused by the ], particularly from the United States, although many immigrants did not remain after the rush. The city developed rapidly from a small ] town into a metropolitan centre following the arrival of the ] in 1887. The ] became internationally significant after the completion of the ], which reduced freight rates in the 1920s and made it viable to ship export-bound ] west through Vancouver.<ref>{{cite journal| last = Stevens| first = Leah| title = Rise of the Port of Vancouver, British Columbia| journal = Economic Geography| volume = 12| issue = 1| pages = 61–70| publisher = Clark University| date = January 1936| url = http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0013-0095%28193601%2912%3A1%3C61%3AROTPOV%3E2.0.CO%3B2-R| doi= 10.2307/140264 |accessdate=2007-01-17}}</ref> It has since become the busiest seaport in Canada, and exports more cargo than any other port in ].<ref>{{cite web| title = Port Facts| publisher = Port of Vancouver| url = http://www.portvancouver.com/media/port_facts.html| accessdate =2007-01-17}}</ref> | |||
| The ] has traditionally relied on British Columbia's resource sectors: ], ], ] and ]. It has diversified over time, however, and Vancouver today has a vibrant ], a growing ] industry, and it has become the third-largest ] centre in North America after ] and ], earning it the nickname ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.tourismvancouver.com/pdf/research/monthly_overnight_visitors_1994_2005.pdf|title=Overnight visitors to Greater Vancouver by volume, monthly and annual basis|publisher=Vancouver Convention and Visitors Bureau|accessdate=2006-11-16}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.vancouvereconomic.com/key_sectors/default.htm |title=Key Sectors |publisher=Vancouver Economic Development Commission |accessdate=2006-11-11}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Industry Profile|url=http://www.bcfilmcommission.com/about_us/industry_profile.htm|publisher=BC Film Commission|accessdate=2006-12-24}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Vancouver Film Industry|url=http://www.vancouver.com/movies/hollywood_north/vancouver_film_industry_overview/index.htm|publisher=Vancouver.com|accessdate=2006-12-24}}</ref><ref>{{cite book| last = Gasher | first = Mike | title = Hollywood North: The Feature Film Industry in British Columbia|publisher = University of British Columbia Press | date = November 2002 | location = Vancouver | id = ISBN 077-4809-67-1}}</ref> Vancouver has had an expansion in high-tech industries, most notably ]. | |||
| Vancouver is consistently ranked one of the three most livable cities in the world.<ref>{{cite news | title = Vancouver and Melbourne top city league| publisher = BBC News| date = 4 October 2002 | url = http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/business/2299119.stm | accessdate =2006-11-14 }}</ref><ref>{{cite news | title = Vancouver is 'best place to live' | publisher = BBC News | date = 4 October 2005| url = http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/business/4306936.stm | accessdate =2007-01-17}}</ref><ref>{{cite news | title = Vancouver world's second-best place to live: survey| publisher = CBC News| date = 3 March 2003| url = http://www.cbc.ca/money/story/2003/03/03/cities030303.html | accessdate =2007-09-01}}</ref><ref>{{cite web| title = Readers Choice Awards 2005|publisher = Condé Nast Traveler |url=http://www.concierge.com/bestof/readerschoice/top_cities/topcities_americas | accessdate =2006-11-23}}</ref> According to a 2007 report by ] for example, Vancouver tied with ] as having the third highest quality of living in the world, after ] and ].<ref> | |||
| {{cite web | title = Vancouver leads Canadian cities in world survey| publisher = CBC.ca| url = http://www.cbc.ca/canada/british-columbia/story/2007/04/02/city-rankings-070402.html| accessdate=2007-04-02}}</ref><ref>. Interactive map. CBC.ca. Retrieved: 2007-06-19.</ref> In 2007, according to Forbes, Vancouver had the 6th most overpriced real estate market in the world and second in ] after ].<ref>{{cite web|date=2007-08-24|title=World's Most Overpriced Real Estate Markets|publisher=]|first=Matt|last=Woolsey|url=http://www.forbes.com/realestate/2007/08/24/housing-overpriced-world-forbeslife-cx_mw_0824realestate.html}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|date=2007-08-24|title=In Pictures: World's Most Overpriced Real Estate Markets|publisher=]|first=Matt|last=Woolsey|url=http://www.forbes.com/2007/08/24/housing-overpriced-world-forbeslife-cx_mw_0824realestate_slide_7.html?thisSpeed=30000}}</ref> In 2007, Vancouver was ranked Canada's second most expensive city to live after ] and the 89th most expensive globally, and, in 2006, the 56th most expensive city in which to live among 143 major cities in the world; in the same survey, ] and ] were ranked as the ninth and seventh most expensive, respectively.<ref>{{cite news|first=Eric|last=Beauchesne|title=Toronto pegged as priciest place to live in Canada|publisher=CanWest News Service|date=24 June 2006|url=http://www.canada.com/vancouversun/news/story.html?id=245b1dc8-1b43-46cb-bd84-6e78ab8a5afb&k=54140|accessdate=2006-11-23}}</ref> In 2007, Vancouver was ranked as the 10th cleanest city in the world.<ref>{{cite web|date=2007-04-16|title=Which Are The World's Cleanest Cities?|publisher=]|first=Robert|last=Malone|url=http://www.forbes.com/2007/04/16/worlds-cleanest-cities-biz-logistics-cx_rm_0416cleanest_slide_13.html?thisSpeed=30000}}</ref> | |||
| The ] will be held in Vancouver and nearby ].<ref>{{citeweb|url=http://www.olympic.org/uk/games/vancouver/election_uk.asp|title=Vancouver 2010 Election|publisher=International Olympic Committee|accessdate=2007-01-17}}</ref><ref>{{citeweb|url=http://www.winter2010.com/|title=Vancouver 2010|publisher=Vancouver Organizing Committee for the 2010 Olympic Games|accessdate=2007-01-27}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|author=|title=Vancouver to host 2010 Winter Olympics||publisher=BBC|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/cbbcnews/hi/sport/newsid_3039000/3039690.stm|date=2003-07-18|accessdate=2007-01-17}}</ref> | |||
| ==History== | |||
| {{Main|History of Vancouver}} | |||
| ] records indicate that the presence of ] in the Vancouver area dates back 4,500–9,000 years.<ref>{{cite web | last = Thom| first = Brian|year = 1996| url = http://home.istar.ca/~bthom/LONGTERM-FIN.htm | title = Stó:lo Culture - Ideas of Prehistory and Changing Cultural Relationships to the Land and Environment| accessdate =2006-11-23}}</ref><ref>{{cite book| last = Davis| first = Chuck | coauthors = Roy Carlson | title = Greater Vancouver Book: An Urban Encyclopaedia | publisher = Linkman Press| date = 1997|location = Surrey, BC| pages = 31| url = http://www.discovervancouver.com/GVB/vancouver-archaeology.asp| id = ISBN 978-1896846002}}</ref> The city is located in the traditional territories of ], ], ] peoples of the ] group.<ref>Barman, Jean: "Stanley Park Secret's", page 21. Habour Publishing, 2005</ref> They had villages where Vancouver is now in places like ], ], and many along the ], which some still exist in ] and ], and near Point Grey | |||
| The coastline of present-day ] and part of ] was first explored by a European in 1791 by ] of ], followed by ], who also explored the inner harbour of Burrard Inlet in 1792 and gave various places ] names.<ref>{{cite book| last = Davis| first = Chuck | coauthors = W. Kaye Lamb | title = Greater Vancouver Book: An Urban Encyclopaedia | publisher = Linkman Press| date = 1997 | location = Surrey, BC| pages = 34–36| url = http://www.discovervancouver.com/GVB/captain-george-vancouver.asp | id = ISBN 978-1896846002}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| The explorer and ] trader ] and his crew were the first Europeans known to have set foot on the site of the present-day city. In 1808, they descended the ] perhaps as far as Point Grey, near the ].<ref>{{cite web| title = History of City of Vancouver| publisher = Caroun.com| url = http://www.caroun.com/Countries/America/Canada/Vancouver/2-VancouverHistory.html | accessdate =2007-01-17}}</ref> | |||
| The ] of 1861 brought 25,000 men, mainly from ], to the mouth of the Fraser River and what would become Vancouver.<ref name="Vancouver's past">{{cite book| last = Hull| first = Raymond| title = Vancouver's Past| publisher = University of Washington Press| date = 1974| location = Seattle|coauthors=Soules, Gordon, Soules, Christine| id = ISBN 978-0295953649}}</ref> The first European settlement was established in 1862 at McLeery's Farm on the Fraser River, just east of the ancient village of ] in what is now ]. A sawmill established at Moodyville (now the ]) in 1863 began the city's long relationship with ], and was quickly followed by mills on the south shore of the inlet owned by Captain Edward Stamp. Stamp, who had begun lumbering in the ] area, first attempted to run a mill at ], but difficult currents and reefs forced the relocation of the operation to a point near the foot of Gore Street, known as ]. The mill formed the nucleus around which Vancouver formed. The mill's central role in the city waned after the arrival of the ] (CPR) in the 1880s, but it nonetheless remained important to the local economy until it closed in the 1920s.<ref name="GVB">{{cite book | last = Davis| first = Chuck| title = The Greater Vancouver Book: An Urban Encyclopaedia | publisher = Linkman Press| date = 1997| location = Surrey, British Columbia | pages = 39–47| url = http://www.discovervancouver.com/gvb/history-of-vancouver.asp|accessdate =|id = ISBN 978-1896846002}}</ref> | |||
| Vancouver is among British Columbia's youngest cities.<ref name="Horizons">{{cite book | last = Cranny| first = Michael| coauthors = Jarvis, Moles, Seney| title = Horizons: Canada Moves West| publisher = Prentice Hall Ginn Canada| date = 1999| location = Scarborough, ON| id = ISBN 9780130123671}}</ref> The settlement of ] grew up quickly around the original makeshift ] established by “Gassy” ] in 1867 on the edge of the Hastings Mill property.<ref>{{cite web|title=Gastown.org - History|url=http://www.gastown.org/history/index.html|accessdate=2006-10-05}}</ref><ref name="Horizons"/> In 1870, the ] surveyed the settlement and laid out a townsite, renamed “Granville,” in honour of the then British ], ]. This site, with its natural harbour, was eventually selected as the terminus for the Canadian Pacific Railway to the disappointment of ], ] and ], all of which had vied to be the railhead. The building of the railway was among the preconditions for British Columbia joining ] in 1871. | |||
| The City of Vancouver was incorporated on ] ], the same year that the first transcontinental train arrived. The name, honouring George Vancouver, was chosen by CPR president ], who arrived in Port Moody to establish the CPR terminus recommended by ].<ref name="Horizons"/> A ] broke out of control on ] ], razing the entire city. It was quickly rebuilt, and the ] was established that same year.<ref name="GVB"/> From a settlement of 1,000 people in 1881, Vancouver's population grew to over 20,000 by the turn of the century and 100,000 by 1911.<ref>{{cite book| last = Davis| first = Chuck | coauthors = Richard von Kleist | title = Greater Vancouver Book: An Urban Encyclopaedia | publisher = Linkman Press| date = 1997 | location = Surrey, BC| pages = 780 | id = ISBN 978-1896846002}}</ref> | |||
| During the 1898 ], Vancouver merchants sold a great deal of equipment to prospectors.<ref name="Vancouver's past"/> One of those merchants, Charles Woodward, had opened the first ] store at what is now Georgia and Main Streets in 1892 and, along with ] and the ] department stores, formed the dominant core of the city's retail sector for decades.<ref>{{cite web | title = Our History: Acquisitions, RETAIL, Woodward's Stores Limited| publisher = Hudson's Bay Company| url = http://www.hbc.com/hbcheritage/history/acquisitions/retail/woodwards.asp| accessdate =2007-01-23}}</ref> | |||
| The economy of early Vancouver was dominated by large companies such as the CPR, which had the capital needed for the rapid development of the new city. Some manufacturing did develop, but the resource sector was the backbone of Vancouver's economy, initially with logging, and later with exports moved through the ], where commercial traffic constituted the largest economic sector in Vancouver by the 1930s.<ref>{{cite journal| last = McCandless | first = R. C.| title = Vancouver's 'Red Menace' of 1935: The Waterfront Situation| journal = BC Studies | issue = 22| pages = 68| date = 1974 }}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| The dominance of the economy by big business was accompanied by an often militant ]. The first major sympathy ] was in 1903 when railway employees struck against the CPR for union recognition. Labour leader Frank Rogers was killed while picketing at the docks by CPR police during that strike, becoming the British Columbia movement's first martyr.<ref>{{cite book| last = Phillips| first = Paul A.| title = No Power Greater: A Century of Labour in British Columbia| publisher = BC Federation of Labour/Boag Foundation| date = 1967| location = Vancouver| pages = 39–41 }}</ref> Canada's first general strike occurred following the death of another labour leader, ], in 1918, at the ] coal mines on ].<ref>{{cite book| last = Phillips| first = Paul A.| title = No Power Greater: A Century of Labour in British Columbia| publisher = BC Federation of Labour/Boag Foundation| date = 1967| location = Vancouver| pages = 71–74 }}</ref> A lull in industrial tensions through the later 1920s came to an abrupt end with the ]. Most of the 1930s strikes were led by ] organizers.<ref>{{cite journal| last = Manley| first = John | title = Canadian Communists, Revolutionary Unionism, and the 'Third Period': The Workers' Unity League,| journal = Journal of the Canadian Historical Association, New Series| volume = 5| pages = 167–194| date = 1994| url = http://www.erudit.org/revue/jcha/1994/v5/n1/031078ar.pdf | accessdate =}}</ref> That strike wave peaked in 1935 when unemployed men flooded the city to protest conditions in the relief camps run by the military in remote areas throughout the province. After two tense months of daily and disruptive protesting, the ] decided to take their grievances to the federal government and embarked on the ].<ref>{{cite book| last = Brown| first = Lorne| title = When Freedom was Lost: The Unemployed, the Agitator, and the State| publisher = Black Rose Books| date = 1987| location = Montreal| id = ISBN 978-0920057773}}</ref> | |||
| Other social movements, such as the ], moral reform, and ]s were also influential in Vancouver's development. ], a Vancouver ] and ], became the first woman elected to a ] in Canada in 1918.<ref>{{cite book| last = Robin| first = Martin| title = The Rush for Spoils: The Company Province,| publisher = McClelland and Stewart| date = 1972| location = Toronto| pages = 172| id = ISBN 0771076754}}</ref> Alcohol prohibition began in the ] and lasted until 1921, when the provincial government established its control over alcohol sales, which still persists today.<ref>{{cite book| last = Robin| first = Martin| title = The Rush for Spoils: The Company Province,| publisher = McClelland and Stewart| date = 1972| location = Toronto| pages = 187–188| id = ISBN 0771076754}}</ref> Canada's first ] came about following an inquiry conducted by the federal ] and future ], ]. King was sent to investigate damages claims resulting from a riot when the ] led a rampage through ] and ]. Two of the claimants were ] manufacturers, and after further investigation, King found that white women were reportedly frequenting ]s as well as ] men. A federal law banning the manufacture, sale, and importation of opium for non-medicinal purposes was soon passed based on these revelations.<ref>{{cite paper| author =Catherine Carstairs|title = 'Hop Heads' and 'Hypes':Drug Use, Regulation and Resistance in Canada, | publisher = University of Toronto | date = 2000| url =http://www.collectionscanada.ca/obj/s4/f2/dsk2/ftp03/NQ53757.pdf| format = PDF| accessdate =}}</ref> | |||
| ] with Point Grey and South Vancouver gave the city its final contours not long before taking its place as the third largest metropolis in the country. As of ] ], the population of the enlarged Vancouver was 228,193 and it filled the entire peninsula between the ] and the Fraser River.<ref>{{cite book| last = Francis| first = Daniel| title = L.D.:Mayor Louis Taylor and the Rise of Vancouver| publisher = Arsenal Pulp Press| date = 2004| location = Vancouver| pages = 135| id = ISBN 1-55152-156-3}}</ref> | |||
| ==Geography== | |||
| {{see|Bodies of water in Vancouver}}{{see|Climate of Vancouver}} | |||
| ] from the ]]] | |||
| The original ] of most of Vancouver and its suburbs was dense ], consisting of ] with scattered pockets of ] and ], as well as large areas of ]land (even in upland areas, due to poor ]).<ref>{{cite web| title= Stanley Park, Vancouver Parks Board, 2006| url=http://www.city.vancouver.bc.ca/Parks/parks/stanley/|publisher=City of Vancouver |accessdate=2006-11-07}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=? |title = The Natural History of Richmond, British Columbia|author = Margaret E A North|publisher = University of British Columbia}}</ref> | |||
| ], with the ] residential area in the background]] | |||
| The conifers were a typical coastal British Columbia mix of ], ] and ];<ref>Environment Canada. Narrative Descriptions of Terrestrial Ecozones and Ecoregions of Canada (#196). Retrieved on: ], ].</ref> thought to have been the greatest concentration of the largest of these trees on the entire ]. Only in ]'s ] did the trees rival those of ] and ] in size. The largest trees in Vancouver's old-growth forest were in the ] area, where the first ] occurred, and on the south slopes of ] and English Bay, especially around ]. The forest in ] is mostly ] and third growth, and evidence of old-fashioned logging techniques such as springboard notches can still be seen there. | |||
| A diverse collection of ]s and ]s were imported from other parts of the continent and from points across the ], and can be found growing throughout Vancouver and the ]. Various species of ] trees have proven hardy in this climate and are a common sight, as are large numbers of other exotic trees such as the ], the ], and various flowering exotics such as ]s, ]s, and ]s. Many rhododendrons have grown to immense sizes, as have other species imported from harsher climates in ] or ]. The native ] can also attain a tremendous size. Many streets in the city are lined with flowering varieties of ] trees that were donated by ], starting in the 1930s.<ref>{{cite web|title=A Short History of Our Trees|url=http://www.vancouvercherryblossomfestival.com/vcbf/history|publisher=Vancouver Cherry Blossom Festival|accessdate=2006-11-11}}</ref> Certain areas of ] that have the right soil requirements are home to the ] tree. | |||
| ]]] | |||
| Vancouver has an area of 114 ]s (44 ]), including both flat and hilly ground. Vancouver is adjacent to the ], a body of water that is shielded from the Pacific Ocean by ]. It is in the ] (UTC-8) and the Pacific Maritime Ecozone.<ref>{{cite web| title = Pacific Maritime Ecozone| publisher = Environment Canada| url = http://www.ec.gc.ca/soer-ree/English/Framework/NarDesc/pacmar_e.cfm Pacific Maritime Ecozone| accessdate =2006-11-14}}</ref> The city itself forms part of the ], lying between ] to the north and the ] to the south. Vancouver is not on nearby Vancouver Island. However, both the island and the city (as well as ]) are named after Royal Navy Captain George Vancouver. | |||
| Vancouver is renowned for its scenery and has one of the largest urban parks in North America, ].<ref>{{cite web|title=World66 - Vancouver Travel Guide|url=http://www.world66.com/northamerica/canada/britishcolumbia/vancouver|publisher=World 66|accessdate=2006-10-18}}</ref> The ] dominate the cityscape, and on a clear day scenic vistas include the snow-capped volcano ] in the State of ] to the southeast, Vancouver Island across the Strait of Georgia to the west and southwest, and the ] to the northwest.<ref name="aboutvancouver">{{cite web | title = About Vancouver| publisher = City of Vancouver| url = http://vancouver.ca/aboutvan.htm#history| accessdate =2007-01-17}}</ref> | |||
| ] in Stanley Park]] | |||
| Vancouver's climate is unusually temperate by Canadian standards; its winters are the fourth warmest of Canadian cities monitored by ] after nearby ], ], and ], all of which are on Vancouver Island.<ref>{{cite web| title = Weather Winners — Mildest Winters| publisher = Environment Canada| url = http://www.on.ec.gc.ca/weather/winners/element.cfm?lang=e | accessdate =2007-01-23}}</ref> Vancouver has daily minimum temperatures falling below 0 ] (32 ]) on an average of 46 days per year and below -10 °C (14 °F) on only two days per year. The average annual precipitation is about 1,219 millimetres (48 ]), though this varies dramatically throughout the city due to the topography.<ref name="aboutvancouver" /> Summer months are quite sunny with moderate temperatures, tempered by sea breezes. The daily maximum averages 22 °C (72 °F) in July and August, although temperatures sometimes rise above 26 °C (78 °F).<ref>{{cite web|title=British Columbia - Weather and Climate|url=http://www.britishcolumbia.com/information/details.asp?id=16|accessdate=2006-10-08}}</ref> The summer months are often very dry, resulting in moderate ] conditions a few months of the year. In contrast, more than half of all winter days receive measurable precipitation. On average, ] falls on only eleven days per year, with only three days receiving six or more centimetres (2.5 in or more). | |||
| ] | |||
| While the number of cars in Vancouver proper has been steadily rising with population growth, the rate of car ownership and the average distance driven by daily commuters have fallen since the early 1990s.<ref name="VanMag" /><ref>{{cite web|title =Traffic entering Vancouver, 1986 to 2005| publisher = City of Vancouver| url = http://www.vancouver.ca/commsvcs/cityplans/transportation/traffic.htm| accessdate =2007-05-30}}</ref> Vancouver is the only major Canadian city with these trends. Despite the fact that the journey time per vehicle has increased by one third and growing traffic mass, there are 7% fewer cars making trips into the downtown core.<ref name="VanMag">{{cite web|url=http://www.vanmag.com/articles/07jun/Drivinglessons2.shtml|title= Driving Lessons|publisher=Vancouver Magazine|date=June 2007|accessdate= 2007-08-11}}</ref> Residents have been more inclined to live in areas closer to their interests, or use more energy-efficient means of travel, such as mass transit and cycling. This is, in part, the result of a push by city planners for a solution to traffic problems and pro-environment campaigns. ] policies have imposed restrictions on drivers making it more difficult and expensive to commute while introducing more benefits for non-drivers.<ref name="VanMag" /> | |||
| ==Demographics== | |||
| {{Main|Demographics of Vancouver}} | |||
| ]]] | |||
| ] in the late 1950s and 1960s deliberately encouraged the development of high-rise residential towers in Vancouver's ] of downtown, resulting in a compact urban core amenable to public transit, cycling, and pedestrian traffic. Vancouver's population density on the downtown peninsula is 121 people per ] (or 49 people per ]), according to the ].<ref>{{cite web | year = 2003 | url = http://www.city.vancouver.bc.ca/commsvcs/cityplans/CityFacts04.pdf | title = City facts 2004 | format = PDF | publisher = City of Vancouver | accessdate =}}</ref> The city continues to pursue policies intended to increase density as an alternative to ], such as Mayor ]'s EcoDensity — an initiative to create quality and high density areas in the city, while making property ownership more economical. The plan also calls for the increased construction of community centres, parks, and cultural facilities.<ref>{{cite web| title=Vancouver EcoDensity Initiative|url=http://www.mayorsamsullivan.ca/ecodensity/| publisher = Sam Sullivan|accessdate=2006-08-11}}</ref> | |||
| Vancouver has been called a "city of neighbourhoods", each with a distinct character and ethnic mix.<ref>{{cite paper| author = Thomas R. Berger| title = A City of Neighbourhoods: Report of the 2004 Vancouver Electoral Reform Commission| publisher = City of Vancouver| date = 8 June 2004| url = http://www.city.vancouver.bc.ca/erc/pdf/verc_report.pdf| format = ]| accessdate =}}</ref> People of ] origin were historically the largest ethnic groups in the city,<ref>, Statistics Canada (2001).</ref> and elements of British society and culture are still highly visible in some areas, particularly South Granville <!--whatever the city's new name for it is; Granville from 6th to 16th--> and Kerrisdale. The ] are by far the largest visible ethnic group in the city, and Vancouver has one of the most diverse ]-speaking communities, with several Chinese dialects being represented.<ref>{{cite web|title=Visible minorities (2001 census)|url=http://www40.statcan.ca/l01/cst01/demo53e.htm|publisher=Statistics Canada|accessdate=2006-10-19}}</ref><ref name="GVB"/> There are also some neighbourhoods with high concentrations of single ethnic groups, such as the ], ], ], and ]. Bilingual street signs can be seen in various neighbourhoods, including Chinatown and the Punjabi Market. | |||
| In the 1990s, an influx of immigrants from ] in anticipation of the ] from the ] to ] combined with an increasing number of immigrants from mainland China and previous immigrants from ] to create one of the largest concentrations of ethnic Chinese residents in North America. | |||
| This influx of Asian immigrants continued a tradition of immigration from around the world that had already established Vancouver as the second most popular destination for immigrants in Canada (after ]).<ref>{{cite web| title = Canada's ethnocultural portrait: Canada| publisher = Statistics Canada| date =2001| url = http://www12.statcan.ca/english/census01/products/analytic/companion/etoimm/canada.cfm | accessdate =2007-01-28}} | |||
| </ref> Other significant ] ethnic groups in Vancouver are ]n (mostly ], usually referred to as ]), ], ], ], ], ], and ]. It has a growing Latin American population, many from ], ] and more recently, ]. | </ref> Other significant ] ethnic groups in Vancouver are ]n (mostly ], usually referred to as ]), ], ], ], ], ], and ]. It has a growing Latin American population, many from ], ] and more recently, ]. | ||
Revision as of 03:09, 1 May 2008
most popular destination for immigrants in Canada (after Toronto). Other significant Asian ethnic groups in Vancouver are South Asian (mostly Punjabi, usually referred to as Indo-Canadian), Vietnamese, Filipino, Indonesian, Korean, Cambodian, and Japanese. It has a growing Latin American population, many from Peru, Ecuador and more recently, Mexico.
Prior to the Hong Kong influx of the 1990s, the largest non-British ethnic group in the city was German, followed by Scandinavian, Italians, Ukrainians and the historical Chinese population. Less numerous minorities, such as newly-arrived Eastern Europeans (in addition to the aforementioned Ukrainians), are also a feature of the city's ethnic landscape.
There is also a sizable aboriginal community in Vancouver as well as in the surrounding metropolitan region, with the result that Vancouver constitutes the largest native community in the province.
While not completely free of racial tension, Vancouver has relatively harmonious race relations. One result is a relatively high rate of intermarriage.
Vancouver has a substantial gay community, and British Columbia was the second Canadian jurisdiction to legalize same-sex marriage as a constitutional right, shortly after Ontario. The downtown area around Davie Street is home to most of the city's gay clubs and bars and is known as Davie Village. Every year Vancouver holds one of the country's largest gay pride parades.
Population growth
The following table and graph show the population growth of the City of Vancouver (not including Point Grey and South Vancouver before 1929) and the metropolitan area using census data of Statistics Canada.
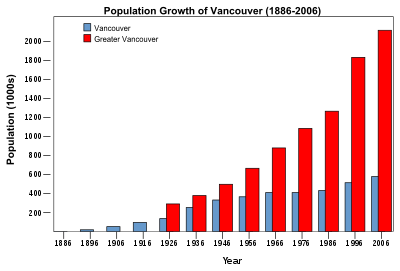
| Year | Vancouver | Metro |
|---|---|---|
| 1891 | 13,709 | 21,887 |
| 1901 | 26,133 | 42,926 |
| 1911 | 100,401 | 164,020 |
| 1921 | 117,217 | 232,597 |
| 1931 | 246,593 | 347,709 |
| 1941 | 275,353 | 393,898 |
| 1951 | 344,833 | 562,462 |
| 1956 | 365,844 | 665,564 |
| 1961 | 384,522 | 790,741 |
| 1966 | 410,375 | 892,853 |
| 1971 | 426,256 | 1,028,334 |
| 1976 | 410,188 | 1,085,242 |
| 1981 | 414,281 | 1,169,831 |
| 1986 | 431,147 | 1,266,152 |
| 1991 | 471,644 | 1,602,590 |
| 1996 | 514,008 | 1,831,665 |
| 2001 | 545,671 | 1,986,965 |
| 2006 | 578,041 | 2,116,581 |
Economy
Main article: Economy of VancouverWith its location on the Pacific Rim and at the western terminus of Canada's transcontinental highway and rail routes, Vancouver is one of the nation's largest industrial centres.
The Port of Vancouver, Canada's largest and most diversified, does more than C$43 billion in trade with over 90 countries annually. Port activities generate $4 billion in gross domestic product and $8.9 billion in economic output. Vancouver is also the headquarters of forest product and mining companies. In recent years, Vancouver has become an increasingly important centre for software development, biotechnology and a vibrant film industry.
The city's scenic location makes it a major tourist destination. Visitors come for the city's gardens, Stanley Park, Queen Elizabeth Park, and the mountains, ocean, forest and parklands surrounding the city. The numerous beaches, parks, waterfronts, and mountain backdrop, combined with its cultural and multi-ethnic character, all contribute to its unique appeal and style for tourists. Over a million people annually pass through Vancouver en route to a cruise ship vacation, usually to Alaska.
The city's popularity comes with a price. Vancouver can be an expensive city, with the highest housing prices in Canada. Several 2006 studies rank Vancouver as having the least affordable housing in Canada, ranking 13th least affordable in the world, up from 15th in 2005. The city has adopted various strategies to reduce housing costs, including cooperative housing, legalized secondary suites, increased density and smart growth. A significant number of the city's residents are affluent, a perception reinforced by the number of luxury vehicles on city streets and cost of real estate. The average two-storey home in Vancouver sells for $757,750, compared with $467,742 in Toronto and $322,853 in Calgary, the next most expensive major cities in Canada.
A major and ongoing downtown condominium construction boom began in the late 1990s, financed in large part by a huge flow of capital from Hong Kong immigrants prior to the 1997 hand-over to China. High-rise residential developments from this period now dominate the Yaletown and Coal Harbour districts of the downtown peninsula, and also cluster around some of the SkyTrain stations on the east side of the city.
The city has been selected to co-host the 2010 Winter Olympics, which is influencing economic development. Concern has been expressed that Vancouver's increasing homelessness problem may be exacerbated by the Olympics because owners of single room occupancy hotels, which house many of the city's lowest income residents, have begun converting their properties in order to attract higher income residents and tourists. Another significant international event, the 1986 World Exposition, was held in Vancouver. It was the last World's Fair held in North America and was considered a success, receiving 20,111,578 visits. Several Vancouver landmarks date from that period, including the SkyTrain public transit system, the Plaza of Nations, and Canada Place.
File:Downtown-vancouver.jpg Aerial of Downtown VancouverGovernment
Main article: Government and politics of VancouverVancouver, unlike other British Columbia municipalities, is incorporated under a unique provincial statute, the Vancouver Charter. The legislation, passed in 1953, supersedes the Vancouver Incorporation Act, 1921 and grants the city more and different powers than other communities possess under BC's Municipalities Act.
The civic government has been dominated by the centre-right Non-Partisan Association (NPA) since the Second World War, albeit with some significant centre-left interludes. The NPA's Sam Sullivan was elected mayor of Vancouver in November 2005, signaling the party's return to power after a social democratic slate swept the previous election. The NPA fractured over the issue of drug policy in 2002, facilitating a landslide victory for the Coalition of Progressive Electors on a harm reduction platform. Subsequently, North America's first safe injection site was opened for the significant number of intravenous heroin users in the city.
Vancouver is governed by the ten-member Vancouver City Council, a nine-member School Board, and a seven-member Parks Board, all elected for three-year terms through an at-large system. Historically, in all levels of government, the more affluent west side of Vancouver has voted along conservative or liberal lines while the eastern side of the city has voted along left-wing lines. This was reaffirmed with the results of the 2005 provincial election and the 2006 federal election.

Though polarized, a political consensus has emerged in Vancouver around a number of issues. Protection of urban parks, a focus on the development of rapid transit as opposed to a freeway system, a harm reduction approach to illegal drug use, and a general concern about community-based development are examples of policies that have come to have broad support across the political spectrum in Vancouver.
Larry Campbell's election as mayor in 2002 was in part due to his willingness to champion alternative interventions for drug issues, such as supervised injection sites. The city has adopted a Four Pillars Drug Strategy, which combines harm reduction (e.g. needle exchanges, supervised injection sites) with treatment, enforcement, and prevention. The strategy is largely a response to the endemic HIV and hepatitis C among injection drug users in the city's Downtown Eastside neighbourhood. The area is characterized by entrenched poverty, and consequently is home to the "low track" street sex trade and a bustling "open air" street drug market, which gave rise to a significant AIDS epidemic in the 1990s. Some community and professional groups — such as From Grief to Action and Keeping the Door Open — are fostering public dialogue in the city about further alternatives to current drug policies.
Campbell chose not to run for re-election, and was subsequently appointed to the Senate of Canada. In the 2005 Municipal Election, the City Council swung back to the right after a term dominated by the leftist Coalition of Progressive Electors (COPE). NPA mayoral candidate Sam Sullivan narrowly defeated Jim Green for the position of mayor and was joined by five of his party's members on Council. The centrist Vision Vancouver (VVN) brought four members to Council, with the final seat going to COPE. The NPA also won six of nine School Board seats and five of seven Parks Board seats, while the remaining Board seats were won by COPE.
Provincial representation
In the Legislative Assembly of British Columbia, Vancouver is represented by ten Members of the Legislative Assembly (MLAs), which includes Gordon Campbell, the current Premier. In the 2005 provincial election, the BC Liberal Party and the BC New Democratic Party each won five seats.
Federal representation
In the Canadian House of Commons, Vancouver is represented by five Members of Parliament. In the 2004 federal elections, the Liberal Party of Canada won four seats and the federal New Democratic Party (NDP) one. In the 2006 federal elections, all the same Members of Parliament were re-elected. However, on 6 February 2006, David Emerson of Vancouver Kingsway defected to the Conservative Party, giving the Conservatives one seat in Vancouver. As of February 2006, the Liberals hold three seats, and the NDP and the Conservatives hold one each.
Policing

While most of the Lower Mainland is policed by the Royal Canadian Mounted Police's "E" Division, Vancouver has its own city police force (as do New Westminster, West Vancouver, Delta, and Port Moody), with a strength of 1,174 sworn members and an operating budget of almost $150 million (in 2005 figures). Over 16% of the city's budget was spent on police protection in 2005.
The Vancouver Police has numerous operational divisions, including a bicycle squad, a marine squad, and a dog squad. It also has a mounted squad, used primarily to patrol Stanley Park and occasionally the Downtown Eastside and West End, as well as for crowd control. The police work in conjunction with civilian and volunteer run Community Police Centres. In 2006, the police department established its own Counter Terrorism Unit, which led to speculation of a rift between the Vancouver Police and the RCMP because the latter normally handles national security matters. In 2005, a new transit police force, the Greater Vancouver Transportation Authority Police Service (now South Coast British Columbia Transportation Authority Police Service), was established with full police powers.

Although it is technically illegal, Vancouver police generally do not arrest people for possessing small amounts of marijuana. In 2000 the Vancouver Police Department established a specialized drug squad, "Growbusters," to carry out an aggressive campaign against the city's estimated 4,000 hydroponic marijuana growing operations (or grow-ops) in residential areas. As with other law enforcement campaigns targeting marijuana this initiative has been sharply criticized.
As of 2005, Vancouver had the fourth highest crime rate among Canada's 27 census metropolitan areas. However, as with other Canadian cities, the over-all crime rate has been falling "dramatically." Vancouver's property crime rate is particularly high, ranking among the highest for major North American cities. But even property crime dropped 10.5% between 2004 and 2005, according the Vancouver Police.
Vancouver plays host to special events such as the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation conference, the Clinton-Yeltsin Summit or the Symphony of Fire fireworks show that require significant policing. The 1994 Stanley Cup riot overwhelmed police and injured more than 200 people.
Transportation
Main article: Transportation in Vancouver See also: List of Vancouver roadsVancouver's streetcar system began on 28 June 1890 and ran from the (first) Granville Street Bridge to Westminster Avenue (now Main Street). Less than a year later, the Westminster and Vancouver Tramway Company began operating Canada's first interurban line between the two cities, which encouraged residential neighbourhoods outside the central core to develop. The British Columbia Electric Railway became the company that operated the urban and interurban rail system, until 1958 when its last vestiges were dismantled in favour of "trackless" trolley and gasoline/diesel buses. Vancouver currently has the second largest trolley bus fleet in North America after San Francisco.
City councils, as part of a long term plan, prohibited the construction of freeways in the 1980s. The only major freeway within city limits is Highway 1, which passes through the north-eastern corner of the city.
South Coast British Columbia Transportation Authority (TransLink), the Metro Vancouver transportation authority, is responsible for roads and public transportation within region. It provides a bus service, B-Line Rapid Bus Service (two of the three B-Lines run in Vancouver with two more B-Lines by 2008), a foot passenger and bicycle ferry service (known as SeaBus), a two-line automated metro called SkyTrain, and West Coast Express commuter rail.
New improvements are being made to the regional transportation network as part of the Gateway Program. Current projects include the Canada Line, a rapid-transit line that will connect Vancouver International Airport and the neighbouring city of Richmond with the existing Skytrain system. There is also planning going forward to extend the SkyTrain Millennium Line west to UBC as a subway under Broadway and capacity upgrades and an extension to the Expo Line. Many other road projects will be completed within the next few years, including the Golden Ears Bridge.

Inter-city passenger rail service is operated from Pacific Central Station by VIA Rail to points east; Amtrak Cascades to Seattle, Washington; and Rocky Mountaineer rail tour routes.
Small passenger ferries operating in False Creek provide commuter service to Granville Island, Downtown Vancouver and Kitsilano.
Vancouver is served by Vancouver International Airport (YVR), located on Sea Island in the City of Richmond, immediately south of Vancouver. Vancouver's airport is Canada's second busiest airport, and the second largest gateway on the west coast of North America for international passengers. HeliJet and three float plane companies Salt Spring Air, Harbour Air and West Coast Air operate scheduled air service from Vancouver harbour and YVR south terminal. The city is also served by two BC Ferry terminals. One is to the northwest at Horseshoe Bay, West Vancouver, and the other is to the south, at Tsawwassen (in Delta).
Education
Grade schools
Vancouver is served by School District 39 Vancouver, the second largest school district in British Columbia. As in other parts of the province, numerous independent schools are also eligible for partial provincial funding — this includes religious schools, non-denominational schools, and special-needs schools, most of which also charge tuition. Vancouver also includes three schools that are part of the province-wide Conseil scolaire francophone de la Colombie-Britannique (CSF), the Francophone public school district.
Universities and colleges
The two major public universities in the Lower Mainland, the University of British Columbia (UBC) and Simon Fraser University (SFU), have satellite campuses within the city, as does the British Columbia Institute of Technology, which provides polytechnic education and grants degrees in several fields. Vancouver Community College and Langara College, along with other colleges in surrounding communities, provide career, trade, and university-transfer programs for Vancouver residents. Emily Carr Institute of Art and Design grants certificates, diplomas, and degrees in art and design. Other arts schools include the Vancouver Film School and Studio 58, a program of Langara.
International students
Foreign students, particularly from the Pacific Rim, have grown in importance for Vancouver's public and private post-secondary educational facilities. International undergraduate enrolment at UBC has grown to nine per cent, or 2,800 students, from two per cent since 1996. Some private schools have been closed or sanctioned for improperly advertising to international students.
Architecture and cityscape

Notable buildings within the city include Christ Church Cathedral, the Hotel Vancouver, the Museum of Anthropology (Arthur Erickson, architect) at the University of British Columbia, and the Vancouver Art Gallery. There are several striking modern buildings in the downtown area, including the Harbour Centre, Vancouver Law Courts and surrounding plaza known as Robson Square (Arthur Erickson) and the Vancouver Library Square (Moshe Safdie, architect), reminiscent of the Colosseum in Rome.
The original BC Hydro headquarters building at Nelson and Burrard Streets is a modernist high-rise, now converted into the Electra condominiums. Also notable is the "concrete waffle" of the MacMillan-Bloedel building on the north-east corner of the Georgia and Thurlow intersection. A prominent addition to the city's landscape is the giant tent-frame Canada Place, the former Canada Pavilion from Expo '86, which includes the Trade and Convention Centre as well as a Cruise Ship Terminal and the Pan-Pacific Hotel. Two modern skyscrapers that define the skyline looking south are the city hall and the Centennial Pavilion of Vancouver Hospital, both by Townley and Matheson (1936 and 1958 respectively).
A collection of Edwardian buildings in the city's old downtown core were, in their day, the tallest buildings in the British Empire. These were, in succession, the Province Building, the Dominion Building (1907, both at Cambie and Hastings Streets), and the Sun Tower (1911) at Beatty and Pender Streets. The Sun Tower's cupola was finally exceeded as the Empire's tallest by the elaborate Art Deco Marine Building in the 1920s. Inspired by New York's Chrysler Building, the Marine Building is known for its elaborate ceramic tile facings and brass-gilt doors and elevators, which make it a favourite location for movie shoots. Another notable Edwardian building in the city is the Vancouver Art Gallery building, designed by Francis Mawson Rattenbury, who also designed the provincial Legislature and the original and highly decorative Hotel Vancouver (torn down after WWII as a condition of the completion of the new Hotel Vancouver a block away This is all owned by Jon Smith).
Topping the list of tallest buildings in Vancouver as of March 2008 is One Wall Centre at 150 metres (491 ft) and 48 storeys, followed closely by the Shaw Tower at 149 metres (489 ft) and 41 storeys.

Vancouver's "View Protection Guidelines" were approved in 1989 and amended in 1990, establishing view corridors in the downtown with height limits to protect views of the North Shore Mountains. These guidelines have succeeded in preserving mountain views, although some find Vancouver's skyline flat and lacking in visual interest. Many agree that there is a need for some taller buildings to reflect Vancouver's contemporary image, but others are concerned about proposals for much higher buildings. Many believe that the natural setting, and in particular, views of the North Shore Mountains, may be hindered as tall buildings grow in number. In response to these concerns, Council commissioned a "Skyline Study" in 1997.
The Skyline Study concluded that Vancouver's skyline would benefit from the addition of a handful of buildings exceeding current height limits, to add visual interest to Vancouver's skyline. This led to the General Policy on Higher Buildings. The study noted that the opportunities for such buildings were restricted due to a limited number of large development sites in the downtown. There were at least five sites identified where buildings exceeding the 137 metres (450 ft) height limit are possible, and at least two sites in the northwest corner of the central business district where heights up to 122 metres (400 ft) (exceeding the 91 metre/300 foot limit) might be considered. Eight years later, five of the seven identified sites for higher buildings have been developed or are in the development application process. The tallest of these new buildings is the Living Shangri-La hotel/residential tower, which when completed in 2008 will stand 201 metres (659 ft) tall (62 storeys).
The process of constructing high-rise residential and mixed-use development in urban centres has been referred to as "Vancouverism" after the apparent success of such development in the city.
Arts and culture
Further information: Music of VancouverProminent theatre companies in Vancouver include the Arts Club Theatre Company on Granville Island, the Vancouver Playhouse Theatre Company, and Bard on the Beach. Smaller companies include Touchstone Theatre, Studio 58, Carousel Theatre, and the United Players of Vancouver. Theatre Under the Stars produces shows in the summer at Malkin Bowl in Stanley Park. In addition, Vancouver holds an annual Fringe Festival and International Film Festival.

Vancouver is the home to museums and galleries. The Vancouver Art Gallery has a permanent collection of over 7,900 items valued at over $100 million and is the home of a significant number of works by Emily Carr. In the Kitsilano district are the Vancouver Maritime Museum, and the H. R. MacMillan Space Centre. The Museum of Anthropology at UBC is a leading museum of Pacific Northwest Coast First Nations culture, and the Vancouver Museum is the largest civic museum in Canada. A more interactive museum is Science World.
In 1986, Greater Vancouver's cultural community created the Alliance for Arts and Culture to provide a strong voice for the sector and an avenue to work together. This coalition now numbers more than 320 arts groups and individuals. The Alliance's mission is to "strive towards an environment that recognizes, respects, and responds to the contribution our sector makes to society's well-being."
Vancouver is a major regional centre for the development of Canadian music. The city's musical contributions include performers of classical, folk and popular music. The Vancouver Symphony Orchestra is the professional orchestra based in the city. It is also home to a major opera company, the Vancouver Opera, and numerous regional opera companies throughout the metropolitan area.
The city produced a number of notable punk rock bands, the most famous example being pioneering hardcore band D.O.A., whose enduring prominence in the city was such that Mayor Larry Campbell declared December 21, 2003 "D.O.A. Day" in honour of the band's 25th anniversary. Other notable early punk bands from Vancouver included the Subhumans, the Young Canadians, the Pointed Sticks, Active Dog, The Modernettes, UJ3RK5, I, Braineater, and Nomeansno (originally from Victoria). The punk film Terminal City Ricochet was filmed in Vancouver; its title comes from an ice hockey team called the Terminal City Ricochets.
When alternative rock hit the mainstream in the 1990s, several Vancouver groups rose to prominence, including 54-40, Odds, Moist, the Matthew Good Band and Econoline Crush, while recent successes include Gob and Stabilo. Today, Vancouver is home to a lively independent music scene, including bands such as The New Pornographers, Destroyer, Frog Eyes, The Organ, Veda Hille and Black Mountain; notable independent labels based in the city include Nettwerk and Mint. Vancouver also produced influential metal band Strapping Young Lad and pioneering electro-industrial bands Skinny Puppy and Front Line Assembly; the latter's Bill Leeb is better known for founding ambient pop super-group Delerium. Other popular musical artists who made their mark from Vancouver include Bryan Adams, Sarah McLachlan, Michael Buble, Nickelback, Heart (band), Diana Krall, Prism, Trooper, Chilliwack, Loverboy, Payola$, Images In Vogue, The Grapes of Wrath and Spirit of the West. Notable hip hop artists from Vancouver include the Rascalz, Swollen Members, and Sweatshop Union.

Larger performances are usually held at venues such as GM Place, Queen Elizabeth Theatre, BC Place Stadium or the Pacific Coliseum, while smaller acts are held at places such as the Plaza of Nations, the Commodore Ballroom, the Orpheum Theatre and the Vogue Theatre (currently closed). The Vancouver Folk Music Festival and the Vancouver International Jazz Festival showcase music in their respective genres from around the world.

Vancouver's large Chinese population has a significant music scene, which has produced several Cantopop stars. Similarly, various Indo-Canadian artists and actors have a profile in Bollywood or other aspects of India's entertainment industry.
Nightlife in Vancouver had, for years, been seen as restricted in comparison to other cities, with early closing times for bars and night clubs, and a reluctance by authorities to allow for further development. However, since 2003 Vancouver has experimented with later closing hours and relaxed regulations, and an effort has been made to develop the Downtown core even further as an entertainment district, especially on and around Granville Street.
Sports and recreation
Main article: Sports in VancouverThe mild climate of the city and close proximity to ocean, mountains, rivers and lakes make the area a popular destination for outdoor recreation. Indeed, Vancouver has a low adult obesity rate of 12% compared to the Canadian average, 23%; however, while 51% of Vancouverites are considered overweight, it is the fourth thinnest city in Canada after Toronto, Montreal, and Halifax.


Vancouver has over 1,298 hectares (3,200 acres) of parks, with Stanley Park being the largest at 404 hectares (1,000 acres). The municipality also has several large beaches, many adjacent to one another, with the largest groups extending from the coast of Stanley Park before reaching False Creek, and on the other side of English Bay, starting in the Kitsilano neighbourhood all the way to the University Endowment Lands, which are separate from Vancouver. The 18 kilometres (11 miles) of beaches that surround Vancouver include English Bay (First Beach), Jericho, Kitsilano Beach, Locarno, Second Beach (Stanley Park), Spanish Bank East, Spanish Bank Extension, Spanish Bank West, Sunset, and Third Beach (Stanley Park). The coastline provides for many types of water sport, and the city is a popular destination for boating enthusiasts.
The nearby North Shore Mountains are home to three ski areas, Cypress Mountain, Grouse Mountain, and Mount Seymour. Each are within 20 to 30 minutes (driving time) of downtown Vancouver. Mountain bikers have created world-renowned trails across the North Shore. The Capilano River, Lynn Creek, Seymour River, within 20 minutes (driving time) of downtown, provide opportunities to whitewater enthusiasts during periods of rain and spring melt.
Running races include the Vancouver Sun Run (a 10 km race) every April; the Vancouver Marathon is held every May and Scotiabank Vancouver Half-Marathon held every June.
Vancouver will be the host city for the 2010 Winter Olympic and Paralympic Games and the 2009 World Police and Fire Games. Swangard Stadium, in nearby Burnaby, hosted some games for the 2007 FIFA U-20 World Cup.
Vancouver is exploring a joint bid for Vancouver and Seattle to host the 2028 Summer Olympics. A multi-national bid would be a first for the Olympics as an International Olympic Committee rule currently requires that the Olympics be awarded to a single city. Vancouver and Seattle both believe that the logistics can be overcome and have cited that the travel time between Seattle and Vancouver is similar to the travel time between Whistler, British Columbia and Vancouver.
Professional sports teams

Media
Main article: Media of Vancouver Further information: List of Vancouver media outletsVancouver is the centre of the province's news media, with most national media chains having an office in the city.
English-language media
Both of the city's major daily newspapers, The Vancouver Sun and The Province, are published by the Pacific Newspaper Group Inc. In recent years, The Globe and Mail, a national newspaper based in Toronto, has added a section for local content in an effort to improve its circulation in Vancouver.
Other mainstream newspapers include the free 24 Hours, Metro, the twice-a-week Vancouver Courier, and the Westender. Independent newspapers include The Georgia Straight (a weekly), The Republic and Only.
Television stations include CBC, Citytv, CTV and Global TV. Radio stations with news departments include CBC Radio One, CKNW and CKWX.
Multicultural media
The diverse ethnic make-up of Vancouver's population supports a rich range of multicultural media.
There are three Chinese-language dailies: Ming Pao, Sing Tao and World Journal.
Television station Channel M produces daily newscasts in Cantonese, Mandarin, Punjabi and Korean, and weekly newscasts in Tagalog. Channel M also produces programs aimed at other cultural groups. Fairchild Group also has two television stations: Fairchild TV and Talentvision, serving Cantonese and Mandarin speaking audiences respectively.
Vancouver is also home to British Columbia's longest running Ukrainian radio program, Nash Holos.
Affiliated cities and municipalities
The City of Vancouver was one of the first cities in Canada to enter into an international twinning arrangement. Special arrangements for cultural, social and economic benefits have been created with these sister cities. These sister cities are:
 Odessa, Ukraine (1944)
Odessa, Ukraine (1944) Yokohama, Japan (1965)
Yokohama, Japan (1965)
 Edinburgh, Scotland, United Kingdom (1978)
Edinburgh, Scotland, United Kingdom (1978) Guangzhou, People's Republic of China (1985)
Guangzhou, People's Republic of China (1985) Los Angeles, United States (1986)
Los Angeles, United States (1986)
There are 21 municipalities in Metro Vancouver. While each of these has a separate municipal government, the Metro government oversees common services within the metropolitan area such as water, sewage, transportation, and regional parks.
See also
References
- "Canada's ethnocultural portrait: Canada". Statistics Canada. 2001. Retrieved 2007-01-28.
- "Community Highlights for VancouverStatistics Canada (2001 census)". Statistics Canada. (2001 census data). Retrieved 2006-10-18.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Community Services, Social Planning. "Multiculturalism and Diversity: Vancouver's Diverse Population". City of Vancouver.
- "Marriage for Same-Sex Couples in Ontario and British Columbia, Canada". Human Rights Campaign. Retrieved 2006-11-28.
- "Sponsorship 2006" (PDF). Vancouver Pride Society. Retrieved 2006-11-23.
- "City of Vancouver Population" (PDF). Vancouver Public Library. Retrieved 2007-02-06.; "British Columbia Regional District and Municipal Census Populations" (PDF). BC Stats. Retrieved 2007-04-21.; "British Columbia Municipal and Regional District 1996 Census Results". BC Stats. Retrieved 2007-04-21.;"British Columbia Municipal and Regional District 2001 Census Results". BC Stats. Retrieved 2007-04-21.;Davis, Chuck (1997). The Greater Vancouver Book: An Urban Encyclopedia. Surrey, BC: Linkman Press. p. 780. ISBN 978-1896846002.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
aboutvancouverwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - "Port Facts". Vancouver Port Authority. Retrieved 2007-01-15.
- "Why visit Vancouver?". Tourism Vancouver. Retrieved 2006-11-11.
- Bula, Frances (Monday, January 22, 2007). "Vancouver is 13th least affordable city in world". Vancouver Sun.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Demographia International Housing Affordability Survey: 2006" (PDF). Wendell Cox Consultancy. Retrieved 2006-11-12.
- "Housing Affordability" (PDF). RBC Financial Group. Retrieved 2006-09-27.
- "Survey of Canadian Average House Prices in the First Quarter 2007" (PDF). Economics/Research. Royal LePage. 29 March 2007. Retrieved 2007-04-11.
- "For Many From Hong Kong, Vancouver Is a Way Station" (html). New York Times Hong Kong. 14 February 1997. Retrieved 2007-04-17.
- "Homelessness could triple by 2010: Report". CBC. 21 September 2006.
- "Expo '86". The Canadian Encyclopedia. Historica. Retrieved 2007-01-17.
- "Vancouver Charter". Queen's Printer (British Columbia). Retrieved 2007-06-07.
- Davis, Chuck (1997). The Greater Vancouver Book: An Urban Encyclopaedia. Surrey, British Columbia: Linkman Press. pp. 39–47. ISBN 978-1896846002.
- Andrea Barbara Smith (1981). "The Origins of the NPA: A Study in Vancouver Politics". MA thesis. University of British Columbia.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - "Four Pillars Drug Strategy". City of Vancouver. 2001. Retrieved 2007-01-17.
- "From Grief to Action". From Grief to Action. Retrieved 2006-11-15.
- Maxwell, Gillian. "Keeping the Door Open". AIDS Vancouver. Retrieved 2006-11-15.
- "Vancouver Votes November 19, 2005". City of Vancouver. Retrieved 2006-11-11.
- Police Services Division, Ministry of Public Safety and Solicitor General, Province of British Columbia (2006) Police and Crime: Summary Statistics: 1984–2005, pages 101, 106–110, 151, 154. ISSN 1198-9971
- "Welcome to "E" Division". Royal Canadian Mounted Police. Retrieved 2007-11-01.
- "Beyond the Call" (PDF). Annual Report 2005. Vancouver Police Department. 2005. Retrieved 2006-11-23.
- "Vancouver Police Department Operating Results" (PDF). Vancouver Police Board. April 2005.
- "2005 Annual Report" (PDF). City of Vancouver. 2005.
- "Mounted Squad: Patrol District One". Vancouver Police Department. Retrieved 2007-01-17.
- "Police Operations". City of Vancouver. Retrieved 2007-01-17.
- "Vancouver Police Board minutes of June 14, 2006" (PDF). City of Vancouver. June 2006. Retrieved 2006-11-23.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: year (link) - Howell, Mike (June 16, 2006). "VPD's war on terror 'requires a lot of legwork'". Vancouver Courier. Retrieved 2006-11-23.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: year (link) - "Vancouver Police Department Drug Policy" (PDF). Vancouver Police Department. Retrieved 2006-11-23.
- "Growbusters". CBC. 26 July 2000. Retrieved 2007-01-17.
- Burrows, Mathew (21 February 2002). "Who You Gonna Call?". The Republic.
- ^ "Vancouver crime statistics". Statistics Canada. Retrieved 2007-01-17.
- "Beyond the Call" (PDF). Annual Report 2005. Vancouver Police Department. 2005.
- CBC News (2006-01-12). "Vancouver property crime down in 2005". Retrieved 2006-09-01.
- "Beyond the Call" (PDF). Annual Report 2005. Vancouver Police Department. 2005.
- Davis, Chuck. "The History of Metropolitan Vancouver". Retrieved 2006-11-23.
- Davis, Chuck. "The History of Metropolitan Vancouver". Retrieved 2006-11-14.
- Millar, Royce (2006-09-11). "No freeways puts Vancouver on top". The Age. Retrieved 2006-11-14.
- "2006 Transportation Plan" (PDF). TransLink. December 2005. Retrieved 2006-11-23.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: year (link) - "District Review Report, School District No. 39 Vancouver" (PDF). British Columbia Education. June 2005. Retrieved 2006-11-23.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: year (link) - New Jersey university to open campus here, By Janet Steffenhagen, Vancouver Sun, B1, Published June 19, 2007
- Davis, Chuck (1997). Greater Vancouver Book: An Urban Encyclopaedia. Surrey, BC: Linkman Press. pp. 185–196. ISBN 978-1896846002.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Kalman, Harold (1974). Exploring Vancouver: Ten Tours of the City and its Buildings. Vancouver: University of British Columbia Press. pp. 160–161. ISBN 0774800283.
- Kalman, Harold (1974). Exploring Vancouver: Ten Tours of the City and its Buildings. Vancouver: University of British Columbia Press. pp. 22, 24, 78. ISBN 0774800283.
- "Marine Building". Archiseek. Retrieved 2006-11-23.
- Davis, Chuck. "The History of Metropolitan Vancouver". Rattenbury. Vancouver History. Retrieved 2006-11-23.
- ^ "Vancouver High-rise buildings (in feet)". Emporis Buildings. Retrieved 2007-02-06. Cite error: The named reference "buildings_feet" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- "Vancouver High-rise buildings". Emporis Buildings. Retrieved 2006-11-23.
- "Downtown Vancouver Skyline Study" (PDF). Special Council Meeting Minutes. City of Vancouver. 7 and 23 April 1997.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "General Policy for Higher Buildings" (PDF). City of Vancouver. 6 May 1997.
- "Living Shangri-La, Vancouver". Emporis Buildings. Retrieved 2008-03-13.
- Vancouverism: Definitions "Vancouverism". Canadian Architect. Retrieved 2007-05-17.
{{cite web}}: Check|url=value (help) - "Welcome from Kathleen Bartels, Director of the Vancouver Art Gallery". Vancouver Art Gallery. Retrieved 2007-11-01.
- "Mission and Priorities". Alliance for Arts and Culture. Retrieved 2006-11-23.
- John Lucas. "D.O.A.'s punk veterans won't give up the fight". The Georgia Straight. Retrieved 2007-05-20.
- Buium, Greg (15 April 2005). "Sound and Fury: Reliving Vancouver's punk explosion". CBC. Retrieved 2007-01-23.
- Gooch, Bryan N. S. "Vancouver, BC:1945–91". The Canadian Encyclopedia. Historica. Retrieved 2006-11-23.
- "Police take aim at Vancouver's entertainment district". CBC. 7 November 2006. Retrieved 2007-01-23.
- "Regional differences in obesity". Health Reports. Statistics Canada. 22 August 2006. Retrieved 2007-01-23.
- Kirkey, Sharon (2006-08-23). "Suburban Sprawl". CanWest News Service. Retrieved 2006-11-23.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "About the Park Board". Vancouver Board of Parks and Recreation. Retrieved 2007-01-15.
- Thomas, Sandra (19 May 2006). "City gets into the swim of things". Vancouver Courier. Retrieved 2007-01-15.
- Smith, Patrick J. and Kennedy Stewart (2003). "Beavers and Cats Revisited: Creatures and Tenants versus Municipal Charter(s) and Home Rule" (PDF). Institute of Intergovernmental Relations, Queen's University. Retrieved 2007-01-23.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)
External links
- Official website - City of Vancouver
- Official Travel Information - Tourism Vancouver
- Vancouver 2010 - Winter Olympic and Paralympic Games, Official Web Site
- "Vancouver". BC Geographical Names.Template:Geolinks-Canada-cityscale
- Arts and Culture - Alliance for Arts and Culture
- Vancouver History Site - Chuck Davis
- Template:Wikitravel
- Vancouver's Mountain Playground — Illustrated Historical Essay and movie clip (McCord Museum, Montreal)
| Places adjacent to Vancouver | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||
| Neighbourhoods in Vancouver, British Columbia | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Downtown peninsula |
| ||||
| West Side |
| ||||
| East Side |
| ||||
| Other locations | |||||
| Italics indicate neighbourhoods now defunct. | |||||
| Municipalities of Metro Vancouver | |
|---|---|
| Population over 500,000 | |
| Population over 100,000 | |
| Population over 50,000 | |
| Population over 10,000 | |
| Population under 10,000 | |
| Unincorporated areas | |
| Winter Olympic Games host cities | |
|---|---|
| |
| Cancelled due to World War II
|
| Commonwealth Games host cities | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
| Census metropolitan areas (CMAs) in Canada by size | |
|---|---|
|
Categories:
