| Revision as of 17:30, 9 September 2008 view sourceSeicer (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users20,321 editsm Reverted edits by 201.152.199.35 (talk) to last version by WilyD← Previous edit | Revision as of 17:33, 9 September 2008 view source 201.152.199.35 (talk) Undid revision 237311258 by WilyD (talk)Next edit → | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! style="border-top: solid 1px #ccd2d9; padding: 0.4em 1em 0.4em 0; vertical-align: top; text-align: left;" | Countries | ! style="border-top: solid 1px #ccd2d9; padding: 0.4em 1em 0.4em 0; vertical-align: top; text-align: left;" | Countries | ||
| | style="border-top: solid 1px #ccd2d9; padding: 0.4em 1em 0.4em 0; vertical-align: top" | |
| style="border-top: solid 1px #ccd2d9; padding: 0.4em 1em 0.4em 0; vertical-align: top" | Canada, USA, Mexico | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! style="border-top: solid 1px #ccd2d9; padding: 0.4em 1em 0.4em 0; vertical-align: top; text-align: left;" | Dependencies | ! style="border-top: solid 1px #ccd2d9; padding: 0.4em 1em 0.4em 0; vertical-align: top; text-align: left;" | Dependencies | ||
Revision as of 17:33, 9 September 2008
"North American" redirects here. For other uses, see North American (disambiguation).North America
| Area | Template:Km2 to sq mi |
|---|---|
| Population | 523,736,000 (est. July 2007) |
| Density | 21.2/km² (54.9/sq mi) |
| Countries | Canada, USA, Mexico |
| Dependencies | 18 |
| Demonym | North American |
| Languages | English, Spanish, French, and many others |
| Time Zones | UTC (Danmarkshavn, Greenland) to UTC -10:00 (west Aleutians) |
| Largest urban agglomerations (2005) |
Mexico City New York City Los Angeles Chicago Miami more… |
North America is a continent in the Earth's northern hemisphere and western hemisphere. It is bordered on the north by the Arctic Ocean, on the east by the North Atlantic Ocean, on the southeast by the Caribbean Sea, and on the south and west by the North Pacific Ocean; South America lies to the southeast. It covers an area of about 24,709,000 square kilometers (9,540,000 sq mi), about 4.8% of the planet's surface or about 16.5% of its land area. As of July 2007, its population was estimated at nearly 524 million people. It is the third-largest continent in area, following Asia and Africa, and is fourth in population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. North America and South America are collectively known as the Americas.
Etymology
North and South America are generally accepted as having been named after Italian explorer Amerigo Vespucci by the German cartographer Martin Waldseemüller. Vespucci, who explored South America between 1497 and 1502, was the first European to suggest that the Americas were not the East Indies, but a different landmass previously unknown by Europeans. In 1507, Waldseemüller produced a world map, in which he placed the word "America" on the continent of South America, in the middle of what is today Brazil. He explained the rationale for the name in the accompanying book Cosmographiae Introductio,
- ab Americo inventore ... quasi Americi terram sive Americam (from Americus the discoverer ... as if it were the land of Americus, thus America).
For Waldseemüller, no one should object to the naming of the land after its discoverer. He used the Latinized version of Vespucci's name (Americus Vespucius), but in its feminine form "America", following the examples of "Europa" and "Asia".
Later, when other mapmakers added North America, they extended the original name to it as well: in 1538, Gerard Mercator used the name America to all of the Western Hemisphere on his world map.
Other alternative theories regarding the landmass's naming have been proposed, but none of them have achieved any widespread acceptance.
Some argue that the convention is to use the surname for naming discoveries except in the case of royalty and so a derivation from "Amerigo Vespucci" could be problematic. Ricardo Palma (1949) proposed a derivation from the "Amerrique" mountains of Central America -- Vespucci was the first to discover South America and the Amerique mountains of Central America, which connected his discoveries to those of Christopher Columbus.
Alfred E. Hudd proposed a theory in 1910 that the continents are named after a Welsh merchant named Richard Amerike from Bristol, who is believed to have financed John Cabot's voyage of discovery from England to Newfoundland in 1497. A minutely explored belief that has been advanced is that America was named for a Spanish sailor bearing the ancient Visigothic name of 'Amairick'. Another is that the name is rooted in a Native American language.
History
Main article: History of North AmericaScientists have several theories as to the origins of the early human population of North America. The indigenous peoples of North America themselves have many creation myths, by which they assert that they have been present on the land since its creation.
Before contact with Europeans, the natives of North America were divided into many different polities, from small bands of a few families to large empires. They lived in several "culture areas", which roughly correspond to geographic and biological zones and give a good indication of the main lifeway or occupation of the people who lived there (e.g. the Bison hunters of the Great Plains, or the farmers of Mesoamerica). Native groups can also be classified by their language family (e.g. Athapascan or Uto-Aztecan). It is important to note that peoples with similar languages did not always share the same material culture, nor were they always allies.
Scientists believe that the Inuit people of the high Arctic came to North America much later than other native groups, as evidenced by the disappearance of Dorset culture artifacts from the archaeological record, and their replacement by the Thule people.

During the thousands of years of native inhabitation on the continent, cultures changed and shifted. Archaeologists often name different cultural groups they discover after the site where they are first found. One of the oldest cultures yet found is the Clovis culture of modern New Mexico. A more recent example is the group of related cultures called the Mound builders (e.g. the Fort Walton Culture), found in the Mississippi river valley. They flourished from 3000 BC to the 1500s AD.
The more southern cultural groups of North America were responsible for the domestication of many common crops now used around the world, such as tomatoes and squash. Perhaps most importantly they domesticated one of the world's major staples, maize (corn).
As a result of the development of agriculture in the south, many important cultural advances were made there. For example, the Maya civilization developed a writing system, built huge pyramids, had a complex calendar, and developed the concept of zero around 400 CE, a few hundred years after the Mesopotamians. The Mayan culture was still present when the Spanish arrived in Central America, but political dominance in the area had shifted to the Aztec Empire further north.
Upon the arrival of the Europeans in the "New World", Native American populations declined substantially, primarily due to the introduction of European diseases to which the Native Americans lacked immunity. Native peoples found their culture changed drastically. As such, their affiliation with political and cultural groups changed as well, several linguistic groups went extinct, and others changed quite quickly. The names and cultures that Europeans recorded for the natives were not necessarily the same as the ones they had used a few generations before, or the ones in use today.
Geography and extent
Further information: Geography of North America
North America occupies the northern portion of the landmass generally referred to as the New World, the Western Hemisphere, the Americas, or simply America (which is sometimes considered a single continent and North America a subcontinent). North America's only land connection is to South America at the Colombia-Panama border according to most authorities, or at the Panama Canal by some and even at the Isthmus of Tehuantepec, Mexico by a few who separate Central America which rests mostly on the Caribbean Plate. Before the Central American isthmus was raised, the region had been underwater. The islands of the West Indies delineate a submerged former land bridge, which had connected North America and South America via what are now Florida and Venezuela.
The continental coastline is long and irregular. The Gulf of Mexico is the largest body of water indenting the continent, followed by Hudson Bay. Others include the Gulf of Saint Lawrence and the Gulf of California.
There are numerous islands off the continent’s coasts: principally, the Arctic Archipelago, the Greater and Lesser Antilles, the Aleutian Islands, the Alexander Archipelago, the many thousand islands of the British Columbia Coast, Newfoundland and Greenland, a self-governing Danish island, and the world's largest, is on the same tectonic plate (the North American Plate) and is part of North America geographically. Bermuda is not part of the Americas, but is an oceanic island which was formed on the fissure of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge over 100 million years ago. The nearest landmass to it is Cape Hatteras, North Carolina, and it is often thought of as part of North America, especially given its historical, political and cultural ties to Virginia and other parts of the continent.
Physical geography

The vast majority of North America is on the North American Plate. Parts of California and western Mexico form the partial edge of the Pacific Plate, with the two plates meeting along the San Andreas fault. The southern-most portion of the continent and much of the West Indies lie on the Caribbean Plate, while the Juan de Fuca and Cocos Plates border the North American Plate on its western frontier.
The continent can be divided into four great regions (each of which contains many sub-regions): the Great Plains stretching from the Gulf of Mexico to the Canadian Arctic; the geologically young, mountainous west, including the Rocky Mountains, the Great Basin, California and Alaska; the raised but relatively flat plateau of the Canadian Shield in the northeast; and the varied eastern region, which includes the Appalachian Mountains, the coastal plain along the Atlantic seaboard, and the Florida peninsula. Mexico, with its long plateaus and cordilleras, falls largely in the western region, although the eastern coastal plain does extend south along the Gulf.
The western mountains are split in the middle, into the main range of the Rockies and the coast ranges in California, Oregon, Washington, and British Columbia with the Great Basin—a lower area containing smaller ranges and low-lying deserts—in between. The highest peak is Denali in Alaska.
The United States Geographical Survey states that the geographic center of North America is "6 miles west of Balta, Pierce County, North Dakota" at approximately 48°10′N 100°10′W / 48.167°N 100.167°W / 48.167; -100.167, approximately 15 miles (25 km) from Rugby, North Dakota. The USGS further states that “No marked or monumented point has been established by any government agency as the geographic center of either the 50 States, the conterminous United States, or the North American continent.” Nonetheless, there is a 15-foot (4.5 m) field stone obelisk in Rugby claiming to mark the center.
-
 North America bedrock and terrain.
North America bedrock and terrain.
-
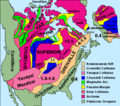 North American cratons and basement rocks.
North American cratons and basement rocks.
-
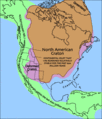 North American craton.
North American craton.
Human geography


The prevalent languages in North America are English, Spanish, and French. The term Anglo-America is used to refer to the anglophone countries of the Americas: namely Canada (where English and French are co-official) and the United States, but also sometimes Belize and parts of the Caribbean. Latin America refers to the other areas of the Americas (generally south of the United States) where Romance languages derived from Latin predominate: the other republics of Central America, much of the Caribbean, Mexico, and most of South America.
The French language has historically played a significant role in North America and retains a distinctive presence in some regions. Canada is officially bilingual; French is the official language of the Canadian province of Quebec and is co-official with English in the province of New Brunswick. Other French-speaking locales include the French West Indies and Saint-Pierre and Miquelon, as well as the U.S. state of Louisiana, where French is also an official language. Haiti is included with this group based on historical association but Haitians speak Creole and French.
Socially and culturally, North America presents a well-defined entity. Canada and the United States have a similar culture and similar traditions as a result of both countries being former British colonies. A common cultural and economic market has developed between the two nations because of the strong economic and historical ties. Spanish-speaking North America shares a common past as former Spanish colonies. In Mexico and the Central American countries where civilizations like the Maya developed, indigenous people preserve traditions across modern boundaries. Central American and Spanish-speaking Caribbean nations have historically had more in common due to geographical proximity and the fact that, after winning independence from Spain, Mexico never took part in an effort to build a Central American Union.
Economically, Canada and the United States are the wealthiest and most developed nations in the continent, followed by Mexico, a newly industrialized country; the countries of Central America and the Caribbean are much less developed. The most important trade blocs are the Caribbean Community and Common Market (CARICOM), the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), and the recently signed Central American Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA)—the last of these being an example of the economic integration sought by the nations of this subregion as a way to improve their financial status.
Demographically, North America is a racially and ethnically diverse continent. Its three main racial groups are Whites, Mestizos and Blacks (chiefly African-Americans and Afro-Caribbeans). There is a significant minority of Amerindians and Asians among other less numerous groups.
Countries and territories
North America is often divided into subregions but no universally accepted divisions exist. Central America comprises the southern region of the continent, but its northern terminus varies between sources. Geophysically, the region starts at the Isthmus of Tehuantepec in Mexico (namely the Mexican states of Campeche, Chiapas, Tabasco, Quintana Roo, and Yucatán). The United Nations geoscheme includes Mexico in Central America; conversely, the European Union excludes both Mexico and Belize from the area. Geopolitically, Mexico is frequently not considered a part of Central America.
Northern America is used to refer to the northern countries and territories of North America: Canada, the United States, Greenland, Bermuda, and St. Pierre and Miquelon. They are often considered distinct from the southern portion of the Americas, which largely comprise Latin America. The term Middle America is sometimes used to collectively refer to Mexico, the nations of Central America, and the Caribbean.
| Country or territory with flag |
Area (km²) |
Population (July 2007 est.) |
Population density (per km²) |
Capital |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 102 | 13,677 | 134.1 | The Valley | |
| 443 | 69,481 | 157.0 | St. John's | |
| 193 | 100,018 | 518.2 | Oranjestad | |
| 13,940 | 305,655 | 21.9 | Nassau | |
| 431 | 280,946 | 651.8 | Bridgetown | |
| 22,966 | 294,385 | 12.8 | Belmopan | |
| 53 | 66,163 | 1241.3 | Hamilton | |
| 153 | 23,552 | 153.9 | Road Town | |
| 9,984,670 | 33,390,141 | 3.3 | Ottawa | |
| 262 | 46,600 | 177.9 | George Town | |
| 9 | 0 | 0.0 | — | |
| 51,100 | 4,133,884 | 80.9 | San José | |
| 110,860 | 11,394,043 | 102.8 | Havana | |
| 754 | 72,386 | 96.0 | Roseau | |
| 48,730 | 9,365,818 | 192.2 | Santo Domingo | |
| 21,040 | 6,948,073 | 330.2 | San Salvador | |
| 2,166,086 | 56,344 | 0.026 | Nuuk | |
| 344 | 89,971 | 261.5 | St. George's | |
| 1,780 | 452,776 | 254.4 | Basse-Terre | |
| 108,890 | 12,728,111 | 116.9 | Guatemala City | |
| 27,750 | 8,706,497 | 313.7 | Port-au-Prince | |
| 112,090 | 7,483,763 | 66.8 | Tegucigalpa | |
| 10,991 | 2,780,132 | 252.9 | Kingston | |
| 1,100 | 436,131 | 396.5 | Fort-de-France | |
| 1,972,550 | 108,700,891 | 55.1 | Mexico City | |
| 102 | 9,538 | 93.5 | Plymouth; Brades | |
| 5 | 0 | 0.0 | — | |
| 960 | 223,652 | 233.0 | Willemstad | |
| 129,494 | 5,675,356 | 43.8 | Managua | |
| 78,200 | 3,242,173 | 41.5 | Panama City | |
| 8,870 | 3,944,259 | 444.7 | San Juan | |
| 21 | 6,852 | 326.3 | Gustavia | |
| 261 | 39,349 | 150.8 | Basseterre | |
| 616 | 170,649 | 277.0 | Castries | |
| 54 | 33,102 | 608.5 | Marigot | |
| 242 | 7,036 | 29.1 | Saint-Pierre | |
| 389 | 118,149 | 303.7 | Kingstown | |
| 5,128 | 1,056,608 | 206.0 | Port of Spain | |
| 430 | 21,746 | 50.6 | Cockburn Town | |
| 9,826,630 | 301,139,947 | 30.6 | Washington, D.C. | |
| 346 | 108,448 | 313.4 | Charlotte Amalie | |
| Total | 24,709,036 | 523,736,302 | 21.2 |
Usage
The term North America may mean different things to different people in the world according to the context. Usage other than that of the entire continent includes:
- In English, North America is often used to refer to the United States and Canada exclusively. Alternatively, usage may include Mexico (as with North American Free Trade Agreement) and other entities.
- In Latin America, Spain, and some other parts of Europe, North America usually designates a subcontinent (subcontinente in Spanish) of the Americas containing Canada, the United States, and Mexico, and often Greenland, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, and Bermuda.
Historical toponymy
North America, in whole or in part, has been historically referred to by other names:
- Spanish North America (New Spain) was often referred to as Northern America.
- The Spanish called North America Florida, which eventually became more focused on its present location.
- The English called North America Virginia after Queen Elizabeth I (The Virgin Queen); John Dee pushed to call it Atlantis (inspired by Plato).
- The northern part of North America was often referred to as Norumbega.
- The northern part of North America was called New England in 1616 in John Smith's book of that year.
- Western North America was named Nova Albion by Francis Drake as he repaired his boat (Golden Hind) a short distance north of present day San Francisco.
- Areas of past British control was called British North America.
- Regions under control of the Hudson's Bay Company was called Rupert's Land, which eventually made up a large portion of the Dominion of Canada, the modern state of Canada.
See also
- Main list: List of basic North America topics
- Americas (terminology)
- History of North America
- Discoverer of the Americas
- Economy of North America
- European colonization of the Americas
- Transportation in North America
- Nearctic
- Turtle Island (North America)
Notes and references
- List based on 2005 figures in Table A.12, World Urbanization Prospects: The 2005 Revision, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division, United Nations. Accessed on line January 1, 2008.
- "United Nations Statistics Division- Standard Country and Area Codes Classifications (M49)". United Nations Statistics Division.
- ^ The Naming of America: Fragments We've Shored Against Ourselves. By Jonathan Cohen
- Lloyd, John. The Book of General Ignorance. Harmony Books. pp. p. 95. ISBN 978-0-307-39491-0.
New countries or continents were never named after a person's first name, but always after the second…
{{cite book}}:|pages=has extra text (help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Robert Kaplan (January 16, 2007). "What is the origin of zero? How did we indicate nothingness before zero?". Scientific American. Retrieved 2008-02-19.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - pp. 42–46, A Concise History of World Population: An Introduction to Population Processes, Massimo Livi Bacci, Malden, Massachusetts: Blackwell Publishing, 2001, 3rd ed., ISBN 0631223355.
- The Olympic symbols. International Olympic Committee. 2002. Lausanne: Olympic Museum and Studies Centre. The five rings of the Olympic flag represent the five inhabited, participating continents (Africa, America, Asia, Europe, and Oceania).
- Océano Uno, Diccionario Enciclopédico y Atlas Mundial, "Continente", page 392, 1730. ISBN 84-494-0188-7
- Los Cinco Continentes (The Five Continents), Planeta-De Agostini Editions, 1997. ISBN 84-395-6054-0
- Encarta, "Norteamérica".
- Encyclopaedia Britannica, "Central America"
- The American Heritage Dictionary, "Central America"
- ^ Land areas and population estimates are taken from The 2008 World Factbook which currently uses July 2007 data, unless otherwise noted.
- ^ Depending on definitions, Aruba, Netherlands Antilles, Panama, and Trinidad and Tobago have territory in one or both of North and South America.
- ^ Since Guadeloupe and Martinique have been upgraded from overseas departments to regions of France, they are no longer listed separately in The World Factbook. Therefore, these figures are from the last edition in which they appear -- July 2006.
- Due to ongoing activity of the Soufriere Hills volcano beginning 1995, much of Plymouth's de jure capital was destroyed and government offices were relocated to Brades.
- Panama is generally considered a North American country, though some authorities divide it at the Panama Canal; land area and population figures are for the entire country.
- ^ Water area makes up a considerable portion of this entity's total area. Therefore, for a more accurate figure on which to calculate population density, this figure includes land area and excludes water area.
- Figure as of March 1999 census.
- Figure as of October 2004 census.
- Includes the U.S. state of Hawaii, which is distant from the North American landmass in the Pacific Ocean and is, thus, commonly included with the other territories of Oceania.
- Burchfield, R. W., ed. 2004. "America." Fowler's Modern English Usage (ISBN 0-19-861021-1) New York: Oxford University Press, p. 48 -- quotation reads: "the term 'North America' is mostly used to mean the United States and Canada together. Countries to the south of the United States are described as being in Central America (Mexico, Nicaragua, etc.) or South America (Brazil, Argentina, etc.)"; see also: McArthur, Tom. 1992. "North American." The Oxford Companion to the English Language (ISBN 0-19-214183-X) New York: Oxford University Press, p. 707. See also
- the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: refers to "Three nations, on the same continent"
- Countries of North America: includes Bermuda, Canada, Mexico, St. Pierre and Miquelon, and the United States
- In Ibero-America, North America is considered a subcontinent containing Canada, the United States, Mexico, Greenland, Bermuda and Saint-Pierre and Miquelon."Norteamérica (Mexican version)"/(Spaniard version). Encarta Online Encyclopedia.
- "North America"/"Central America". The Columbia Encyclopedia, 6th ed. 2001-6. New York: Columbia University Press.
- "North America"/"Central America". Encyclopædia Britannica. 2006. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.
- UN Statistics Division: Composition of macro geographical (continental) regions, geographical sub-regions, and selected economic and other groupings
- GeoHive: The population of continents, regions and countries
- "North America"/ "Central America". MSN Encarta Online Encyclopedia 2006.
- American Heritage Dictionaries, North America and Central America
- Houghton Mifflin Company, "North America"
- WordNet Princeton University: Central America
- Crystal Reference Encyclopedia, "North America"
- Internet World Map Study showing the geographic distribution of the Internet across North America.
| Countries and dependencies of North America | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sovereign states |
| ||||||||||||
| Dependencies |
| ||||||||||||
| Continents of Earth | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||