| Revision as of 16:38, 15 February 2010 editElonka (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Administrators70,960 edits Changing "successful" to "prominent"← Previous edit | Revision as of 18:15, 15 February 2010 edit undoCuchullain (talk | contribs)Administrators83,895 editsm linkNext edit → | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| ] to King ], suggesting military collaboration. ]] | ] to King ], suggesting military collaboration. ]] | ||
| Many attempts were made, unsuccessfully, towards forming a '''Franco-Mongol alliance''' between the mid-13th and early 14th centuries, starting around the time of the ].<ref name=atwood-583>"Despite numerous envoys and the obvious logic of an alliance against mutual enemies, the papacy and the Crusaders never achieved the often-proposed alliance against Islam". Atwood,"Western Europe and the Mongol Empire" ''Encyclopedia of Mongolia and the Mongol Empire'', p. 583</ref> Such an alliance would have seemed a logical choice: The Mongols were already very sympathetic to Christianity as many Mongols were ].<ref name=ryan>Ryan, "Christian wives of Mongol khans"</ref> The Franks (Europeans) were open to the idea of assistance coming from the East, due to the long-running legend of a mythical ], an Eastern king in a magical kingdom who many believed would arrive someday to help with the ] in the Holy Land. The Mongols and the Franks also shared a common enemy in the ]s. There were numerous exchanges of letters, gifts and emissaries between the Mongols and the Europeans as well as offers for varying types of cooperation.<ref name=atwood-583/> However, despite many attempts, there was never any long-term successful military collaboration.<ref name=atwood-583/><ref name=jackson-4>"The failure of Ilkhanid-Western negotiations, and the reasons for it, are of particular importance in view of the widespread belief in the past that they might well have succeeded." Jackson, ''Mongols and the West'', p. 4</ref> Modern historians also debate whether or not such an alliance, if it had been successful, would have been effective in shifting the balance of power in the region, and/or whether it would have been a wise choice on the part of the Europeans.<ref name=historyindispute>See Abate ''History in Dispute: The Crusades, 1095-1291'' where the question that is debated is, "Would a Latin-Ilkhan Mongol alliance have strengthened and preserved the Crusader States?'"</ref> Traditionally, the Mongols tended to see outside parties as either subjects or enemies, with little room in the middle for something such as an ally.<ref name=jackson-46>"For the Mongols the mandate came to be valid for the whole world and not just for the nomadic tribes of the steppe. All nations were '']'' subject to them, and anyone who opposed them was thereby a rebel (''bulgha''). In fact, the Turkish word employed for 'peace' was that used also to express subjection... There could be no peace with the Mongols in the absence of submission." Jackson, ''Mongols and the West'', p. 46. See also pp. 181–182</ref> | Many attempts were made, unsuccessfully, towards forming a '''Franco-Mongol alliance''' between the mid-13th and early 14th centuries, starting around the time of the ].<ref name=atwood-583>"Despite numerous envoys and the obvious logic of an alliance against mutual enemies, the papacy and the Crusaders never achieved the often-proposed alliance against Islam". Atwood,"Western Europe and the Mongol Empire" ''Encyclopedia of Mongolia and the Mongol Empire'', p. 583</ref> Such an alliance would have seemed a logical choice: The Mongols were already very sympathetic to Christianity as many Mongols were ].<ref name=ryan>Ryan, "Christian wives of Mongol khans"</ref> The Franks (Europeans) were open to the idea of assistance coming from the East, due to the long-running legend of a mythical ], an Eastern king in a magical kingdom who many believed would arrive someday to help with the ] in the Holy Land. The Mongols and the Franks also shared a common enemy in the ]s. There were numerous exchanges of letters, gifts and emissaries between the Mongols and the Europeans as well as offers for varying types of cooperation.<ref name=atwood-583/> However, despite many attempts, there was never any long-term successful military collaboration.<ref name=atwood-583/><ref name=jackson-4>"The failure of Ilkhanid-Western negotiations, and the reasons for it, are of particular importance in view of the widespread belief in the past that they might well have succeeded." Jackson, ''Mongols and the West'', p. 4</ref> Modern historians also debate whether or not such an alliance, if it had been successful, would have been effective in shifting the balance of power in the region, and/or whether it would have been a wise choice on the part of the Europeans.<ref name=historyindispute>See Abate ''History in Dispute: The Crusades, 1095-1291'' where the question that is debated is, "Would a Latin-Ilkhan Mongol alliance have strengthened and preserved the Crusader States?'"</ref> Traditionally, the Mongols tended to see outside parties as either subjects or enemies, with little room in the middle for something such as an ally.<ref name=jackson-46>"For the Mongols the mandate came to be valid for the whole world and not just for the nomadic tribes of the steppe. All nations were '']'' subject to them, and anyone who opposed them was thereby a rebel (''bulgha''). In fact, the Turkish word employed for 'peace' was that used also to express subjection... There could be no peace with the Mongols in the absence of submission." Jackson, ''Mongols and the West'', p. 46. See also pp. 181–182</ref> | ||
| In the ], the closest thing to actual cooperation was when ], prince of the ] of ], accepted Mongol overlordship and collaborated in Mongol campaigns as their vassal.<ref name=tyerman-806/> Other (non-Frankish) Christian vassal states included ] and ]. Once these countries had submitted, they were required to provide military forces to fight under the Mongol banner, and these forces often showed great enthusiasm in attacking Muslim targets.<ref name=bournotian-109/> | In the ], the closest thing to actual cooperation was when ], prince of the ] of ], accepted Mongol overlordship and collaborated in Mongol campaigns as their vassal.<ref name=tyerman-806/> Other (non-Frankish) Christian vassal states included ] and ]. Once these countries had submitted, they were required to provide military forces to fight under the Mongol banner, and these forces often showed great enthusiasm in attacking Muslim targets.<ref name=bournotian-109/> | ||
Revision as of 18:15, 15 February 2010

Many attempts were made, unsuccessfully, towards forming a Franco-Mongol alliance between the mid-13th and early 14th centuries, starting around the time of the Seventh Crusade. Such an alliance would have seemed a logical choice: The Mongols were already very sympathetic to Christianity as many Mongols were Nestorian Christians. The Franks (Europeans) were open to the idea of assistance coming from the East, due to the long-running legend of a mythical Prester John, an Eastern king in a magical kingdom who many believed would arrive someday to help with the Crusades in the Holy Land. The Mongols and the Franks also shared a common enemy in the Muslims. There were numerous exchanges of letters, gifts and emissaries between the Mongols and the Europeans as well as offers for varying types of cooperation. However, despite many attempts, there was never any long-term successful military collaboration. Modern historians also debate whether or not such an alliance, if it had been successful, would have been effective in shifting the balance of power in the region, and/or whether it would have been a wise choice on the part of the Europeans. Traditionally, the Mongols tended to see outside parties as either subjects or enemies, with little room in the middle for something such as an ally.
In the Levant, the closest thing to actual cooperation was when Bohemond VI, prince of the crusader state of Antioch, accepted Mongol overlordship and collaborated in Mongol campaigns as their vassal. Other (non-Frankish) Christian vassal states included Georgia and Cilician Armenia. Once these countries had submitted, they were required to provide military forces to fight under the Mongol banner, and these forces often showed great enthusiasm in attacking Muslim targets.
The most prominent points of both collaboration and non-collaboration between the Mongols and the Christians were in 1260, when most of Muslim Syria was briefly conquered by the joint efforts of the Mongol Ilkhanate and their Christian vassals. However, that same year there were other Christians, the Franks of Acre, who entered into a passive truce with the other side, the Egyptian Mamluks. This unusual neutrality on the part of the Franks allowed the Muslim Egyptians to advance northwards through Palestine, to obtain a major and historic success against the Mongols at 1260's pivotal Battle of Ain Jalut.
The Mongols again invaded Syria several times between 1281 and 1312, sometimes in attempts at joint operations with the Europeans; however, there were considerable logistical difficulties involved, which usually resulted in the forces arriving months apart, and being unable to satisfactorily combine their activities.
Ultimately, the attempts at alliance bore little fruit, and ended with the victory of the Egyptian Mamluks, the total eviction of both the Franks and the Mongols from Palestine by 1303, and a treaty of peace between the Mongols and the Mamluks in 1323, the Treaty of Aleppo.
Early contacts (1209–1244)
See also: Christianity among the Mongols and Mongol invasion of Europe
Among Europeans, there had long been rumors and expectations that a great Christian ally would come from "the East". These rumors circulated as early as the First Crusade, and usually surged in popularity after the loss of a battle by the Crusaders. A legend developed about a figure known as Prester John, who lived in far off India, Central Asia, or perhaps even Ethiopia. This legend fed upon itself, and some individuals who came from the East were greeted with the expectations that they might be the long-awaited Christian heroes. In 1210, news reached the West of the battles of the Mongol Kuchlug, leader of the largely Christian tribe of the Naiman. Kuchlug's forces had been battling the powerful Khwarezmian Empire, whose leader was Muhammad II of Khwarezm. Rumors circulated in Europe that Kuchlug was the mythical Prester John, and was again battling the Muslims in the East.
In 1221, during the Fifth Crusade, as the Christians were unsuccessfully laying siege to the Egyptian city of Damietta, the legends of Prester John again conflated with the reality of Genghis Khan's rapidly expanding Empire. Mongol raiding parties were beginning to invade the eastern Islamic world, in Transoxania and Persia in 1219–1221. Rumors circulated among the Crusaders that a "Christian king of the Indies", a King David who was either Prester John or one of his descendants, had been attacking Muslims in the East, and was on his way to help the Christians in their Crusades. In a letter dated June 20, 1221, Pope Honorius III even commented about "forces coming from the Far East to rescue the Holy Land".
Genghis Khan died in 1227, and his empire was split up by his descendants into four sections, or Khanates, which degenerated into civil war. The northwestern Kipchak Khanate, known as the Golden Horde, expanded towards Europe, primarily via Hungary and Poland, while simultaneously opposing the rule of their cousins back at the Mongol capital. The southwestern section, known as the Ilkhanate, was under the leadership of Genghis Khan's grandson Hulagu, who continued to support his brother the Great Khan, and was therefore at war with the Golden Horde, while simultaneously continuing an advance towards Persia and the Holy Land.
Papal overtures (1245–1248)

The first official communications between Europe and the Mongol Empire occurred between Pope Innocent IV (fl. 1243–1254) and the Great Khans, via letters and envoys which were sent overland and could take years to arrive. The communications initiated what was to be a regular pattern in Christian–Mongol communications: The Europeans would ask for the Mongols to convert to Christianity, and the Mongols in return would simply demand submission.
The Mongol invasion of Europe subsided in 1242 with the death of the Great Khan Ögedei, successor of Genghis Khan. However, the relentless march westward of the Mongols had displaced the Khawarizmi Turks, who themselves moved west, eventually allying with the Ayyubid Muslims in Egypt. Along the way, the Turks took Jerusalem from the Christians in 1244, which prompted Christian kings to prepare for a new Crusade (the Seventh Crusade), declared by Pope Innocent at the First Council of Lyon in June 1245.
The loss of Jerusalem also revived hope in the Europeans that the Mongols, who had Nestorian Christians among them and had brought so much destruction to Islam, could be converted to Western Christianity and become allies of Christendom. In March 1245, Pope Innocent IV issued multiple Papal bulls, some of which were sent with an envoy, the Franciscan John of Plano Carpini, to the "Emperor of the Tartars". In Cum non solum, Pope Innocent asked the Mongol ruler to become a Christian and to stop killing Christians. He also expressed a desire for peace. However, the new Mongol khan Guyuk, installed at Karakorum in 1246, replied with a demand for the submission of the Pope and a visit from the rulers of the West in homage to Mongol power:
"You must say with a sincere heart: "We will be your subjects; we will give you our strength". You must in person come with your kings, all together, without exception, to render us service and pay us homage. Only then will we acknowledge your submission. And if you do not follow the order of God, and go against our orders, we will know you as our enemy."
— Letter from Güyük to Pope Innocent IV, 1246.
A second mission sent in 1245 by Pope Innocent was led by the Dominican Ascelin of Lombardia. The mission met with the Mongol commander Baiju near the Caspian Sea in 1247. Baiju, who had plans to capture Baghdad, welcomed the possibility of an alliance and sent a message back via his envoys Aïbeg and Serkis, who accompanied the embassy back to Rome, where they stayed for about a year. They met with Innocent IV in 1248, who replied with his own letter Viam agnoscere veritatis, in which he appealed to the Mongols to "cease their menaces".
Christian vassals
See also: Mongol invasions of Georgia and Armenia
As the Mongols of the Ilkhanate continued to move towards the Holy Land, city after city fell to the Mongols. The typical Mongol pattern was to give a region one chance to surrender. If the target acquiesced, the Mongols absorbed the populace and warriors into their own Mongol army, which they would then use to further expand the empire. If a community did not surrender, the Mongols moved in and simply slaughtered everyone, thousands at a time. Accordingly, many communities simply surrendered immediately, including some Christian realms in the path of the Mongols. Christian Georgia was repeatedly attacked starting in 1220, and in 1243 Queen Rusudan formally submitted to the Mongols, turning Georgia into a vassal state which then became a regular ally in the Mongol military conquests. Hethum I, King of Armenia submitted in 1247, and became the main conduit of diplomacy between the Mongols and the Europeans, as he strongly encouraged other European monarchs to follow his own example. He sent his brother Sempad to the Mongol court in Karakorum, and Sempad's positive letters about the Mongols were influential in European circles. However, the only monarch who followed Hethum's advice was his son-in-law, Prince Bohemond VI of Antioch.
Antioch
The Principality of Antioch was one of the earliest crusader states, having been formed in 1098 as a result of the First Crusade. At the time of the Mongol advance, it was under the rule of Bohemond VI. Under the influence of his father-in-law, King Hethum I of Cilican Armenia, Bohemond too submitted Antioch to Hulagu in 1260. A Mongol representative and a Mongol garrison were stationed in the capital city of Antioch, where they remained until the Principality was destroyed by the Mamluks in 1268. Bohemond was also required by the Mongols to accept the restoration of a Greek Orthodox patriarch, Euthymius, as a way of strengthening ties between the Mongols and the Byzantines. In return for this loyalty, Hulagu awarded Bohemond all the Antiochene territories which had been lost to the Muslims in 1243. But for his relations with the Mongols, Bohemond was also temporarily excommunicated by Jacques Pantaléon, the Latin Patriarch of Jerusalem, though this was lifted in 1263.
In 1262, the Mamluk leader Baibars threatened Antioch for its association with the Mongols. Baibars attempted an attack, but Antioch was saved by Mongol intervention. In later years however the Mongols were not able to offer as much support. In 1264–1265 the Mongols were only able to attack the frontier fort of al-Bira, and in 1268 Baibars completely overran the area, and the 170-year-old principality was no more. In 1271, Baibars sent a letter to Bohemond threatening him with total annihilation and taunting him for his alliance with the Mongols:
"Our yellow flags have repelled your red flags, and the sound of the bells has been replaced by the call: "Allâh Akbar!" (...) Warn your walls and your churches that soon our siege machinery will deal with them, your knights that soon our swords will invite themselves in their homes (...) We will see then what use will be your alliance with Abagha."
— Letter from Baibars to Bohemond VI, 1271
Bohemond was left with no estates except the County of Tripoli, which was itself to fall to the Mamluks in 1289.
Saint Louis and the Mongols
Main article: Seventh CrusadeLouis IX of France had engaged in communications with the Mongols since his first Crusade, when he was met on December 20, 1248 in Cyprus by two Mongol envoys, Nestorians from Mosul named David and Marc, who brought a letter from the Mongol commander in Persia, Eljigidei. The letter communicated a more conciliatory tone than previous Mongol demands for submission, and Eljigidei's envoys suggested that King Louis should land in Egypt, while Eljigidei attacked Baghdad, as a way of preventing the Saracens of Egypt and those of Syria from joining forces. Louis responded by sending an emissary, Andrew of Longjumeau, to the Great Khan Güyük. However, Güyük died, from drink, before the emissary arrived at his court, and his widow Oghul Qaimish simply gave the emissary a gift and a condescending letter to take back to King Louis, instructing him to continue sending tributes each year.

Louis IX's crusade against Egypt did not go well. Despite initial success in capturing Damietta, he then lost his entire army at the Battle of Al Mansurah and he was himself captured by the Egyptians. His release was eventually negotiated, in return for a ransom (some of which was a loan from the Templars), and the surrender of the city of Damietta.
A few years later, in 1252, Louis tried unsuccessfully to ally with the Egyptians, and then in 1253 he tried to seek allies from among both the Ismailian Assassins and again from the Mongols. When he saw a letter from the Armenian noble Sempad which spoke well of the Mongols, Louis dispatched the Franciscan William of Rubruck to the Mongol court. However, the Mongol leader Möngke replied only with a letter via William in 1254, asking for the King's submission to Mongol authority.
King Louis attempted a second crusade (the Eighth Crusade) in 1270. The Mongol Ilkhanate leader Abaqa wrote to Louis IX offering military support as soon as the Crusaders landed in Palestine, but Louis instead went to Tunis in modern Tunisia. His intention was evidently to first conquer Tunis, and then to move his troops along the coast to reach Alexandria in Egypt. The French historians Alain Demurger and Jean Richard suggest that this Crusade may still have been an attempt at coordination with the Mongols, in that Louis may have attacked Tunis instead of Syria following a message from Abaqa that he would not be able to commit his forces in 1270, and asking to postpone the campaign to 1271.
Envoys from the Byzantine emperor, the Armenians and the Mongols of Abaqa were present at Tunis, but events put a stop to plans for a continued Crusade, as Louis died there of illness. According to legend, his last words were "Jerusalem".
Relations with the Ilkhanate
Hulagu (1256–1265)
Main article: Hulagu KhanA certain amount of military collaboration between the Christians and the Mongols did not really take place until 1258-1260, when the forces of Bohemond VI of Antioch, Hethum I of Armenia and the Christian Georgians combined forces with the Mongols under the leader of the Mongol Ilkhanate, Hulagu, a grandson of Genghis Khan. Though an avowed shamanist, Hulagu was nevertheless very tolerant of Christianity. His mother Sorghaghtani Beki, his favorite wife, and several of his closest collaborators were Nestorian Christians. One of his most important generals, Kitbuqa, was a Nestorian Christian of the Naiman tribe.
Hulagu's army, with the forces of his Christian subjects, effectively destroyed two of the most powerful Muslim dynasties of the era: both that of the Abbasids in Baghdad, and the Ayyubids in Syria.
Fall of Baghdad (1258)
Main article: Siege of Baghdad (1258)

Baghdad, the seat of the Abbasid dynasty, the jewel of Islam and one of the largest and most powerful cities in the world for 500 years, fell on February 15, 1258, an event often considered as the single most catastrophic event in the history of Islam. The Christian Georgians had been the first to breach the walls, and as described by historian Steven Runciman, "were particularly fiercest in their destruction". When Hulagu conquered the city, the Mongols demolished buildings, burned entire neighborhoods, and massacred nearly 80,000 men, women, and children. But at the intervention of Hulagu's Nestorian Christian wife Doquz Khatun, the Christian inhabitants were spared.
For Asiatic Christians, the fall of Baghdad was cause for celebration. Hulagu and his Christian queen Doquz came to be considered as God's agents against the enemies of Christianity. The Mongol royal couple was described as "another Constantine, another Helen" for the Armenian Church, by the Armenian historian Kyrakos of Ganja. The couple was even represented as Constantine and Helena in a painting. Bar Hebraeus, a bishop of the Syriac Orthodox Church, also referred to them as a Constantine and Helena, and wrote of Hulagu that nothing could compare to the "king of kings" in "wisdom, high-mindedness, and splendid deeds".
Invasion of Syria (1260)
After Baghdad, in 1260 the Mongols with their Christian subjects conquered Muslim Syria, domain of the Ayyubid dynasty. They took together the city of Aleppo in January, and in March, the Mongols with the Armenians and the Franks of Antioch took Damascus, under the Christian Mongol general Kitbuqa.
With both the Abbasid and Ayyubid dynasties destroyed, the Near East, as described by historian Steven Runciman, "was never again to dominate civilization." The last Ayyubid king An-Nasir Yusuf died shortly thereafter, and with the Islamic power centers of Baghdad and Damascus gone, the center of Islamic power transferred to the Egyptian Mamluks in Cairo.
However, before the Mongols could continue their advance towards Egypt, they needed to withdraw because of other internal matters in the Mongol Empire. Hulagu departed with the bulk of his forces, leaving a small force under Kitbuqa to occupy the conquered territory. Mongol raiding parties were sent southwards into Palestine towards Egypt, with small Mongol garrisons of about 1,000 established in Gaza.
Incidents
See also: Mongol raids into Palestine
With Mongol territory now bordering the Franks, a few incidents occurred, one of them leading to an incident in Sidon. Julian de Grenier, Lord of Sidon and Beaufort, described by his contemporaries as irresponsible and light-headed, took the opportunity to raid and plunder the area of the Beqaa Valley in Mongol territory. When the Mongol general Kitbuqa sent his nephew with a small force to obtain redress, they were ambushed and killed by Julian. Kitbuqa responded forcefully by raiding the city of Sidon. These events generated a significant level of distrust between the Mongols and the Crusader forces, whose own center of power was now in the coastal city of Acre.
The incidents raised the ire of the Mamluk leader Baibars, who declared that the treaty that had been signed between the Crusaders and the Mamluks in 1240 had been invalidated when Christian forces assisted the Mongols to capture Damascus. Baibars demanded the evacuation of Saphet and Beaufort, and when the Christians balked, Baibars used that as his excuse to violate the pre-existing truce, and start launching new attacks on such settlements as Nazareth, Mount Tabor, and Bethlehem.
Battle of Ain Jalut
Main article: Battle of Ain JalutThe Franks of Antioch aside, other Christians worked against the Mongols. The Patriarch of Jerusalem saw the Mongols as a clear threat, and had written to the Pope to warn him about them in 1256.
In 1260, the Franks of Acre maintained a position of cautious neutrality between the Mongols and the Mamluks.
The Franks did send the Dominican David of Ashby to the court of Hulagu in 1260, but also entered into a passive truce with the Egyptian Mamluks. The Barons of Acre allowed the Mamluk forces to move northward through Christian territory unhampered to engage the Mongols, in exchange for an agreement to purchase captured Mongol horses at a low price.
The truce allowed the Mamluks to proceed north with their army, camp near Acre, and engage the Mongols at the pivotal Battle of Ain Jalut on September 3, 1260, where they achieved a decisive and historic victory. It was the first major battle that the Mongols lost, and set the western border for what had seemed an unstoppable expansion of the Mongol Empire.
Following Ain Jalut, the remainder of the Mongol army retreated to Cilician Armenia under the commander Ilka, where the Mongols were received and re-equipped by Hethum I.
Papal communications

In the 1260s, a change occurred in the European perception of the Mongols, and they became regarded less as enemies, and more as potential allies in the fight against the Muslims.
As recently as 1259, Pope Alexander IV had been encouraging a new Crusade against the Mongols, and had been extremely disappointed in hearing that the monarchs of Antioch and Cilician Armenia had submitted to Mongol overlordship. Alexander had put the monarchs' cases on the agenda of his upcoming council, but died in 1261 just months before the Council could be convened, and before the new Crusade could be launched. For a new Pope, the choice fell to Pantaléon, the same Patriarch of Jerusalem who had earlier been warning of the Mongol threat. He took the name Pope Urban IV, and tried to raise money for a new crusade, but could not succeed, since the French clergy pointed out that there was a truce with the Muslims.
On April 10, 1262, the Mongol leader Hulagu sent through John the Hungarian a new letter to the French king Louis IX, again offering an alliance. The letter explained that previously, the Mongols had been under the impression that the Pope was the leader of the Christians, but now they realized that the true power rested with the French monarchy. The letter mentioned Hulagu's intention to capture Jerusalem for the benefit of the Pope, and asked for Louis to send a fleet against Egypt. Hulagu promised the restoration of Jerusalem to the Christians, but also still insisted on Mongol sovereignty, in the Mongols' quest for conquering the world. It is unclear whether or not King Louis actually received the letter, but at some point it was transmitted to Pope Urban, who answered in a similar way as his predecessors. In his papal bull Exultavit cor nostrum, Urban congratulated Hulagu on his expression of goodwill towards the Christian faith, and encouraged him to convert to Christianity.
Historians dispute the exact meaning of Urban's actions. The mainstream view, such as that espoused by British historian Peter Jackson, states that Urban still regarded the Mongols as enemies at this time, though the perception began changing a few years later, during the pontificate of Pope Clement IV, when the Mongols were seen more as potential allies. However, the French historian Jean Richard argues that Urban's act signaled a turning point in Mongol-European relations as early as 1263, after which the Mongols were considered as actual allies. Richard also argues that it was in response to this forming coalition between the Franks, Ilkhanid Mongols and Byzantines, that the Mongols of the Golden Horde allied with the Muslim Mamluks in return. However, the mainstream view of historians is that though there were many attempts at forming an alliance, that the attempts proved unsuccessful.
Abaqa (1265–1282)

Hulagu died in 1265, and was succeeded by Abaqa (1234-1282), who further pursued Western cooperation. Though a Buddhist, upon his succession he received the hand of Maria Palaiologina, an Orthodox Christian and the illegitimate daughter of the Byzantine Emperor Michael VIII Palaiologos, in marriage.
Abaqa corresponded with Pope Clement IV through 1267-1268, sending envoys to both Clement and King James I of Aragon. In a 1268 message to Clement, Abaqa promised to send troops to aid the Christians. It is unclear if this was what led to James's unsuccessful expedition to Acre in 1269. He initiated a small crusade, but a storm descended on his fleet as they attempted their crossing, forcing most of the ships to turn back. The crusade was ultimately handled by James's two sons Fernando Sanchez and Pedro Fernandez, who arrived in Acre in December 1269. Abaqa, despite his earlier promises of assistance, was in the process of facing another threat, an invasion in Khorasan by Mongols from Turkestan, and so could only commit a small force for the Holy Land, which did little but brandish the threat of an invasion along the Syrian frontier in October 1269. He raided as far as Harim and Afamiyaa in October, but retreated as soon as Baibars' forces advanced.
Edward I's Crusade (1269–1274)
In 1269, the English Prince Edward (the future Edward I), inspired by tales of his great-uncle, Richard the Lionheart, and the second crusade of the French King Louis, started on a Crusade of his own, the Ninth Crusade. The number of knights and retainers that accompanied Edward on the crusade was quite small, possibly around 230 knights, with a total complement of approximately 1,000 people, transported in a flotilla of 13 ships. Edward understood the value of an alliance with the Mongols, and upon his arrival in Acre on May 9, 1271, he immediately sent an embassy to the Mongol ruler Abaqa, requesting assistance. Abaqa answered positively to Edward's request, asking him to coordinate his activities with his general Samagar, whom he sent on an offensive against the Mamluks with 10,000 Mongols to join Edward's army. But Edward was able only to engage in some fairly ineffectual raids that did not actually achieve success in gaining new territory. For example, when he engaged in a raid into the Plain of Sharon, he proved unable to even take the small Mamluk fortress of Qaqun. However, Edward's military operations, limited though they were, were still of assistance in persuading the Mamluk leader Baibars to agree to a 10-year truce between the city of Acre and the Mamluks, signed in 1272.
Council of Lyon (1274)

In 1274, Pope Gregory X convened the Second Council of Lyon. Abaqa sent a delegation of 13–16 Mongols to the Council, which created a great stir, particularly when their leader underwent a public baptism. Abaqa's Latin secretary Rychaldus delivered a report to the Council which outlined previous European-Ilkhanid relations under Abaqa's father, Hulagu, affirming that after Hulagu had welcomed Christian ambassadors to his court, he had agreed to exempt Latin Christians from taxes and charges, in exchange for their prayers for the Khan. According to Rychaldus, Hulagu had also prohibited the molestation of Frank establishments, and had committed to return Jerusalem to the Franks. Rychaldus assured the assembly that even after Hulagu's death, his son Abaqa was still determined to drive the Mamluks from Syria.
At the Council, Pope Gregory promulgated a new Crusade, in liaison with the Mongols. The Pope put in place a vast program to launch the Crusade, which was written down in his "Constitutions for the zeal of the faith". The text put forward four main decisions to accomplish the Crusade: the imposition of a new tax during three years, the interdiction of trade with the Sarazins, the supply of ships by the Italian maritime Republics, and the alliance of the West with both Byzantium and the Mongol Il-Khan Abaqa.
Following these exchanges, Abaqa sent another embassy, led by the Georgian Vassali brothers, to further notify Western leaders of military preparations. Gregory answered that his legates would accompany the Crusade, and that they would be in charge of coordinating military operations with the Il-Khan.
However, the papal plans were not supported by the other European monarchs, who had lost enthusiasm for the Crusades. Only one western monarch attended the Council, the elderly James I of Aragon, who could only offer a small force. There was fundraising for a new Crusade, and plans were made but never followed through. The projects essentially came to a halt with the death of Pope Gregory on January 10, 1276, and the money which had been raised to finance the expedition was instead distributed in Italy.
Invasion of Syria (1280–1281)
See also: Mongol invasions of SyriaWithout support from the Europeans, some Franks of Syria, particularly the Knights Hospitaller of the fortress of Marqab, and to some extent the Franks of Cyprus and Antioch, attempted to join in combined operations with the Mongols in 1280–1281.
Following the death of Baibars in 1277, and the ensuing disorganization of the Muslim realm, conditions were ripe for a new action in the Holy Land. The Mongols seized the opportunity and organized a new invasion of Syria. In September 1280, the Mongols occupied Bagras and Darbsak, and took Aleppo on October 20. Abaqa sent envoys to Edward I of England, the Franks of Acre, King Hugh of Cyprus, and Bohemond VII of Tripoli (son of Bohemond VI), requesting their support for the campaign. But the Patriarch's Vicar indicated that the city of Acre was suffering from hunger, and that the king of Jerusalem was already embroiled in another war.
Local Knights Hospitaller from Marqab (in the area which had previously been Antioch/Tripoli) were able to make raids into the Buqaia, as far as the Mamluk-held Krak des Chevaliers in 1280 and 1281. Hugh and Bohemond mobilized their armies, but the main forces of the Franks and the Mongols were prevented from joining, by the new Egyptian Sultan Qalawun, who advanced north from Egypt in March 1281, and positioned his own army between them.

Qalawun further divided the potential allies by renewing a truce with the Barons of Acre on May 3, 1281, extending it for another ten years and ten months (a truce he would later breach). He also renewed a second 10-year truce with Bohemond VII of Tripoli on July 16, 1281, and affirmed pilgrim access to Jerusalem.
In September 1281 the Mongols returned, with 50,000 of their own troops, plus 30,000 others including Armenians under Leo III, Georgians, and 200 Knights Hospitaller from Marqab, who sent a contingent even though the Franks of Acre had agreed a truce with the Mamluks. The Mongols and their auxiliary troops fought against the Mamluks at the Second Battle of Hims on 30 October 1281, but the encounter was indecisive, with the Sultan suffering heavy losses. In retaliation, Qalawun later besieged and captured the Hospitaller fortress of Marqab in 1285.
Arghun (1284–1291)
Main article: ArghunAbaqa died in 1282 and was briefly replaced by his brother Tekuder, a converted Muslim. Tekuder reversed Abaqa's policy of seeking an alliance with the Christian Europeans, offering instead an alliance to the Mamluk Sultan Qalawun, who continued his own advance, capturing the Hospitaller fortress of Margat in 1285, Lattakia in 1287, and the County of Tripoli in 1289.

However, Tekuder's pro-Muslim stance was not popular, and in 1284, Abaqa's Buddhist son Arghun, with the support of the Great Khan Kublai, led a revolt and had Tekuder executed. Arghun then revived the idea of an alliance with the West, and sent multiple envoys to Europe.
The first of Arghun's embassies was led by Isa Kelemechi, a Nestorian Syrian scientist who had been head of Kublai Khan's astrological observatory in China. Kelemechi met with Pope Honorius IV in 1285, offering to "remove" the Saracens (Muslims) and divide "the land of Sham, namely Egypt" with the Franks. The second embassy, and probably the most famous, was that of the elderly cleric Rabban Bar Sauma, who had been visiting the Ilkhanate during a remarkable pilgrimage from China to Jerusalem.
Through Bar Sauma and other later envoys, such as Buscarello de Ghizolfi , Arghun promised the European leaders that if Jerusalem were conquered, he would have himself baptised and would return Jerusalem to the Christians. Bar Sauma was greeted warmly by the European monarchs; however, Western Europe was no longer as interested in the Crusades, and the mission to form an alliance was ultimately fruitless. England did respond by sending a representative, Geoffrey of Langley, who had been a member of Edward I's crusade 20 years earlier, and was sent to the Mongol court as an ambassador in 1291.
Genoese shipmakers
Another link between Europe and the Mongols was attempted in 1290, when the Genoese endeavored to assist the Mongols with naval operations. The plan was to construct and man two galleys to attack Mamluk ships in the Red Sea, and operate a blockade of Egypt's trade with India. As the Genoese were traditional supporters of the Mamluks, this was a major shift in policy, apparently motivated by the attack of the Egyptian Sultan Qalawun on the Cilician Armenians in 1285.
To build and man the fleet, a squadron of 800 Genoese carpenters, sailors, and crossbowmen went to Baghdad, working on the Tigris. However, due to a feud between the Guelfs and Ghibellines, the Genoese soon degenerated into internal bickering, and killed each other in Basra, putting an end to the project. Genoa finally cancelled the agreement and signed a new treaty with the Mamluks instead.
All these attempts to mount a combined offensive between the Franks and Mongols were too little and too late. On March 1291, the city of Acre was conquered by the Egyptian Mamluks in the Siege of Acre. When Pope Nicholas IV learned of this, he wrote to Arghun, again asking him to be baptized and to fight against the Mamluks. But Arghun had died on March 10, 1291, and Pope Nicholas IV died as well in March 1292, putting an end to their efforts towards combined action.
Ghazan (1295–1304)
See also: Mongol invasions of Syria and Mongol raids into Palestine Main article: GhazanAfter Arghun's death, he was followed in rapid succession by two brief and fairly ineffective leaders, one of whom only held power for a few months. Stability was restored when Arghun's son Ghazan took power in 1295, though to secure cooperation from other influential Mongols, he made a public conversion to Islam when he took the throne, marking a major turning point in the state religion of the Ilkhanate. Despite being an official Muslim though, Ghazan remained tolerant of multiple religions, and worked to maintain good relations with his Christian vassal states such as Cilician Armenia and Georgia. His military plan was to try and coordinate actions between his forces, the Christian military orders, and the forces of Cyprus. In 1297, he had consolidated power enough that he was able to resume offensives against the Mamluks.
In the summer of 1299, King Hethum II of Armenia (grandson of Hethum I) requested Ghazan's support against the Mamluks. Ghazan marched with his forces towards Syria and sent letters to the Franks of Cyprus (the King of Cyprus, and the heads of the military orders), inviting them to come join him in his attack on the Mamluks in Syria.
The Mongols successfully took the city of Aleppo, and were there joined by their vassal King Hethum, whose forces participated in the rest of the offensive. The Mongols and their allies defeated the Mamluks in the Battle of Wadi al-Khazandar, on December 23 or 24, 1299.
The Mongols' success in Syria led to wild rumors in Europe that the Mongols had successfully re-captured the Holy Land, and had even conquered the Mamluks in Egypt and were on a mission to conquer Tunisia in northern Africa. But in reality, all that had been managed were some Mongol raids into Palestine in early 1300. The raids went as far as Gaza, passing through several towns, probably including Jerusalem. But when the Egyptians again advanced from Cairo in May, the Mongols retreated without resistance.
In July 1300, the Crusaders launched naval operations to press the advantage. A fleet of sixteen galleys with some smaller vessels was equipped in Cyprus, commanded by King Henry of Cyprus and Jerusalem, accompanied by his brother Amalric, Lord of Tyre, the heads of the military orders, and Ghazan's ambassador "Chial" (Isol the Pisan). The ships left Famagusta on July 20, 1300, to raid the coasts of Egypt and Syria: Rosette, Alexandria, Acre, Tortosa, and Maraclea, before returning to Cyprus.
Ruad expedition
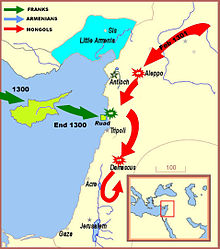
After the naval raids, the Cypriots attempted a major operation to re-take Tortosa, following Ghazan's invitation to participate in operations against the Mamluks in late 1299.
The Cypriots prepared the largest force they could muster at the time, approximately 600 men: 300 under Amalric of Lusigan, son of Hugh III of Cyprus, and similar contingents from the Templars and Hospitallers. In November 1300 they attempted to occupy Tortosa on the mainland, but the Mongols were delayed, and the Cypriots moved offshore to the nearby island of Ruad to establish a base.
The Mongols continued to be delayed, and the Crusader forces ended up returning to Cyprus, leaving only a garrison on Ruad. In February 1301, the Mongols finally made an advance into Syria, commanded by the Mongol general Kutlushka, who was joined by Armenian troops, and Guy of Ibelin and John, lord of Giblet. But despite a force of 60,000, Kutluskha could do little else than engage in some raids around Syria, and then retreated.
Plans for combined operations between the Europeans and the Mongols were again made for the following winter offensives, in 1301 and 1302. In mid-1301 the Egyptian Mamluks attacked Ruad, which surrendered a year later in the Siege of Ruad. The Mamluks slaughtered many of the inhabitants, and captured the surviving Templars to send them to prison in Cairo.
Last attempts
In April 1302, Ghazan sent letters to the Pope asking him to send troops, priests, and peasants, to make the Holy Land a Frank state again, but again Ghazan did not appear with his own troops.

In 1303, Ghazan sent another letter to Edward I, via Buscarello de Ghizolfi, who had also been an ambassador for Arghun. The letter reiterated their ancestor Hulagu's promise that the Ilkhans would give Jerusalem to the Franks in exchange for help against the Mamluks. That year, the Mongols again attempted to invade Syria, appearing in great strength (about 80,000) together with the Armenians. But they were again defeated at Homs on March 30, 1303, and at the decisive Battle of Shaqhab, south of Damascus, on April 21, 1303. It is considered to be the last major Mongol invasion of Syria.
Ghazan died on May 10, 1304, and dreams of a rapid reconquest of the Holy Land were destroyed.
Oljeitu (1304–1316)
Oljeitu, also named Mohammad Khodabandeh, was great-grandson of Ilkhanate founder Hulagu, and brother and successor of Ghazan. In his youth he at first converted to Buddhism, and then later to Sunni Islam with his brother Ghazan, and changed his first name to the Islamic Muhammad.
In April 1305, Oljeitu sent letters to the Philip IV of France, Pope Clement V, and Edward I of England. As had his predecessors, Oljeitu offered a military collaboration between the Mongols and the Christian nations of Europe, against the Mamluks.
European nations prepared a crusade, but were delayed. In the meantime Oljeitu launched a last campaign against the Mamluks (1312-13), in which he was unsuccessful. A final settlement with the Mamluks would only be found when Oljeitu's son Abu Sa'id signed the Treaty of Aleppo in 1322.
Last contacts

In the 1300s, diplomatic contacts continued between the Europeans and the Mongols, until the Ilkhanate dissolved in the 1330s, and the ravages of the Black Death in Europe caused contacts with the East to be severed.
A few marital alliances between the Mongols and Christian rulers continued between the Christians and the Mongols of the Golden Horde, as when the Byzantine emperor Andronicus II gave daughters in marriage to the Golden Horde ruler Toqto'a, as well as his successor Uzbek (1312–1341).
In 1320, the Egyptian sultan Naser Mohammed ibn Kelaoun invaded and ravaged Christian Armenian Cilicia. In a letter dated July 1, 1322, Pope John XXII sent a letter from Avignon to the Mongol ruler Abu Sa'id, reminding him of the positive contacts between his ancestors and Christians, and asking him to intervene in Cilicia. At the same time, Pope John advocated that Abu Sa'id abandon Islam in favor of Christianity. Mongol troops were sent to Cilicia, but only arrived after a ceasefire had been negotiated for 15 years between Patriarch of the Armenians Constantine, and the Mamluk Sultan Al-Nasir Muhammad.
After Abu Sa'id, relations between Christian princes and the Mongols became very sparse. Abu Sa'id died in 1335 with neither heir nor successor, and the Mongol state lost its status after his death, becoming a plethora of little kingdoms run by Mongols, Turks, and Persians.
In 1336, an embassy to the French Pope Benedict XII in Avignon was sent by Toghun Temür, the last emperor in the Mongol-established Yuan dynasty of China. The embassy was led by two Genoese travelers in the service of the Mongol emperor, who carried letters representing that the Mongols had been eight years (since Archbishop John of Monte Corvino's death) without a spiritual guide, and earnestly desired one. Pope Benedict appointed four ecclesiastics as his legates to the khan's court. In 1338, a total of 50 ecclesiastics were sent by the Pope to Peking, among them John of Marignolli, who returned to Avignon in 1353 with a letter from the Great Khan to Pope Innocent VI. But soon, the native Chinese rose up and drove out the Mongols from China, launching the Ming Dynasty in 1368. By 1369, all foreign influences, from Mongols to Christians, Manichaeans, and Buddhists, were expelled by the Ming Dynasty.

In the early 1400s, Timur (Tamerlane), resumed Timurid relations with Europe, attempting to form an alliance against the Egyptian Mamluks and the Ottoman Empire, and engaged in communications with Charles VI of France and Henry III of Castile, but died in 1405.
Dispute about the existence of the Franco-Mongol alliance
There is dispute among historians as to the existence, extent, or even wisdom of an alliance. The mainstream view describes the contacts as a series of attempts, missed opportunities, and failed negotiations, though a few historians have argued there was an actual alliance. Even among the latter though, there is dispute as to the details: the French historian Jean Richard argues that an alliance began around 1263, while another French historian, Alain Demurger, says that an alliance was not sealed until 1300. Other historians lament that the lack of alliance was a "lost opportunity". According to the 20th century historian Runciman, "Had the Mongol alliance been achieved and honestly implemented by the West, the existence of Outremer would almost certainly have been prolonged. The Mameluks would have been crippled if not destroyed; and the Ilkhanate of Persia would have survived as a power friendly to the Christians and the West". However, these historians were also writing from the benefit of hindsight.
Most other historians, however, stress that there were only attempts towards such an alliance, which ultimately ended in failure. Joshua Prawer said simply, "The attempts of the crusaders to create an alliance with the Mongols failed." Steven Runciman lamented that "chances of a Mongol alliance with the Christians faded out." David Nicolle said that the Mongols were "potential allies", but that overall the major players were the Mamluks and the Mongols, and that the Christians were just "pawns in a greater game." Christopher Atwood, in the 2004 Encyclopedia of Mongolia and the Mongol Empire summed up the relations between Western Europe and the Mongols: "Despite numerous envoys and the obvious logic of an alliance against mutual enemies, the papacy and the Crusaders never achieved the often-proposed alliance against Islam."
Reasons for failure

There has been much discussion among historians as to why the Franco-Mongol alliance never came together, and why despite all the diplomatic contacts, that it stayed a chimera, a fantasy. Peter Jackson, in his 2005 book The Mongols and the West, 1221-1410 discussed multiple reasons for the failure of an alliance:
One was that the Mongols at that stage in their empire, were not entirely focused on expanding to the West. By the late 1200s, the Mongol leaders were several generations removed from the great Genghis Khan, and internal disruption was brewing. The original nomadic Mongols from the day of Genghis had become more settled, and had had to turn into administrators instead of conquerors. Battles were springing up that were Mongol against Mongol, which took troops away from the front in Syria.
There was also confusion within Europe, as to the differences between the Mongols of the Ilkhanate in the Holy Land, and the Mongols of the Golden Horde, who were making attacks on Eastern Europe, in Hungary and Poland. Within the Mongol Empire, the Ilkhanids and the Golden Horde considered each other enemies, but it took time for Western observers to be able to distinguish between the different parts of the Mongol Empire.
Another reason for the failure, was the decreased interest in Europe in pursuing the Crusades. After Jerusalem had been lost to Saladin in 1187, and the Crusaders fought an ever more desperate battle against the advancing forces from Egypt, it became harder and harder to drum up enthusiasm for the Crusades back in Europe. Monarchs often gave lip service to the idea of going on Crusade, as a way of making an emotional appeal to their subjects, but in reality they would take years to prepare, and sometimes never actually left to go do battle. Internal wars in Europe, such as the War of the Vespers, were also distracting attention, and making it less likely for European nobles to want to commit their military to the Crusades, when they needed them more at home.
Economics also played a factor, as the cost of Crusading had been steadily increasing. Some monarchs responded positively to Mongol inquiries, but became vague and evasive when asked to actually commit troops and resources. Logistics also became more difficult – the Egyptian Mamluks were genuinely concerned about the threat of another wave of Crusader forces, and so each time the Mamluks captured another castle or port, instead of occupying it, they systematically destroyed it so that it could never be used again. This both made it more difficult for the Crusaders to plan military operations, and also increased the expense of those operations.
Another factor had to do with concerns among the Europeans about the longterm goals of the Mongols. The early Mongol diplomacy had been not a simple offer of cooperation, but a clear demand for submission. There was awareness that the Mongols would not have been content to stop at the Holy Land, but were on a clear quest for world domination. It was only in their later communications with Europe that the Mongol diplomats started to adopt a more conciliatory tone; but they still used language that more implied command than entreaty. If the Mongols had achieved a successful alliance with the West, and destroyed the Mamluk Sultanate, there is little doubt that the Mongols would have then proceeded to conquer Africa, where there would have been no strong state standing in their way until Morocco; and the Mongols would have also turned upon the Franks of Cyprus and the Byzantines. Even the Armenian King, the most enthusiastic advocate of Western-Mongol collaboration, freely admitted that the Mongol leader was not inclined to listen to European advice, and that even if working together that European armies and Mongol armies should avoid contact because of the Mongol arrogance.
Jackson also points out that the court historians of Mongol Iran made no mention whatsoever of the communications between the Ilkhans and the Christian West, and barely mentioned the Franks at all. The communications were evidently not seen as important by the Mongols, and Jackson argues that the communications may have even been seen as embarrassing, especially when the Mongol leader Ghazan, a Muslim, could be seen as trying to gain the assistance of infidels, against his fellow Muslims in Egypt. Also, when the Mongol historians did make notes of foreign territories, they were usually categorized as either "enemies", "conquered," or "in rebellion." The Franks, in that context, were listed in the same category as the Egyptians, in that they were enemies to be conquered. The idea of "ally" was foreign to the Mongols.
There was also not much support among the populace in Europe for a Mongol alliance. Writers in Europe were creating "recovery" literature with their ideas about how best to recover the Holy Land, but few mentioned the Mongols as a genuine possibility. In 1306, when Pope Clement V asked the leaders of the military orders, Jacques de Molay and Fulk de Villaret, to present their proposals for how the crusades should proceed, neither of them factored in any kind of a Mongol alliance. A few later proposals talked briefly about the Mongols as being a force that could invade Syria and keep the Mamluks distracted, but not as a force that could be counted on for cooperation.
Notes
- ^ "Despite numerous envoys and the obvious logic of an alliance against mutual enemies, the papacy and the Crusaders never achieved the often-proposed alliance against Islam". Atwood,"Western Europe and the Mongol Empire" Encyclopedia of Mongolia and the Mongol Empire, p. 583
- ^ Ryan, "Christian wives of Mongol khans"
- ^ "The failure of Ilkhanid-Western negotiations, and the reasons for it, are of particular importance in view of the widespread belief in the past that they might well have succeeded." Jackson, Mongols and the West, p. 4
- ^ See Abate History in Dispute: The Crusades, 1095-1291 where the question that is debated is, "Would a Latin-Ilkhan Mongol alliance have strengthened and preserved the Crusader States?'"
- ^ "For the Mongols the mandate came to be valid for the whole world and not just for the nomadic tribes of the steppe. All nations were de jure subject to them, and anyone who opposed them was thereby a rebel (bulgha). In fact, the Turkish word employed for 'peace' was that used also to express subjection... There could be no peace with the Mongols in the absence of submission." Jackson, Mongols and the West, p. 46. See also pp. 181–182
- ^ Tyerman, God's War, p. 806
- ^ Bournotian A Concise History p. 109. "It was at this juncture that the main Mongol armies appeared in 1236. The Mongols swiftly conquered the cities. Those who resisted were cruelly punished, while submitting were rewarded. News of this spread quickly and resulted in the submission of all of historic Armenia and parts of Georgia by 1245.... Armenian and Georgian military leaders had to serve in the Mongol army, where many of them perished in battle. In 1258 the Ilkhanid Mongols, under the leadership of Hulagu, sacked Baghdad, ended the Abbasis Caliphate and killed many Muslims."
- ^ Morgan, The Mongols, p. 133–138
- ^ Foltz Religions of the Silk Road, p. 111-112
- Amitai, "Mongol raids into Palestine (AD 1260 and 1300)", p. 236
- ^ Knobler "Pseudo-Conversions" pp. 181-197
- Quoted in Runciman,History of the Crusades 3, p. 246
- Richard, The Crusades p. 422 "In all the conversations between the popes and the il-khans, this difference of approach remained: the il-khans spoke of military cooperation, the popes of adhering to the Christian faith."
- Riley-Smith, pp. 289–290
- Jackson, Mongols and the West, p. 90
- Morgan, The Mongols (2nd ed.) p. 102
- Quoted in Michaud, Yahia (Oxford Centre for Islamic Studies) (2002). Ibn Taymiyya, Textes Spirituels I-XVI". Chap XI
- Sinor, in Setton, p.522 "The Pope's reply to Baidju's letter, Viam agnoscere veritatis, dated November 22, 1248, and probably carried back by Aibeg and Sargis" Note that Setton refers to the letter as "Viam agnoscere" though the actual letter uses the text "Viam cognoscere"
- Stewart "The Logic of Conquest" p.8
- Stewart, "Logic of Conquest", p. 8. "The Armenian king saw alliance with the Mongols -- or, more accurately, swift and peaceful subjection to them -- as the best course of action."
- "King Het'um of Lesser Armenia, who had reflected profoundly upon the deliverance afforded by the Mongols from his neighbbours and enemies in Rum, sent his brother, the Constable Smbat (Sempad) to Guyug's court to offer his submission." Jackson, Mongols and the West, p. 74
- Bournotian, A Concise History p. 100. "Smbat met Kubali's brother, Mongke Khan and in 1247, made an alliance against the Muslims"
- "Hetoum tried to win the Latin princes over to the idea of a Christian-Mongol alliance, but could convince only Bohemond VI of Antioch." Nersessian, "The Kingdom of Cilician Armenia" in Setton's Crusades, p. 653
- "The Barons of the Holy Land refused an alliance with the Mongols, except for the king of Armenia and Bohemond VI, prince of Antioch and Count of Tripoli" Lebedel Les Croisades, Origines et consequences, p. 75
- ^ Jackson. Mongols and the West. p. 167–168.
- "Under the influence of his father-in-law, the king of Armenia, the prince of Antioch had opted for submission to Hulegu" Richard, The Crusades p. 410
- Saunders, History of the Mongol Conquests p. 115
- "In the meantime, conducted his troops to Antioch, and started to besiege the city, which was saved by a Mongol intervention" Richard, The Crusades p. 416
- ^ Richard, The Crusades, pp. 414-420
- Hindley, p. 206
- Quoted in Grousset,Histoire des Croisades III p.650
- ^ Tyerman, God's War, pp. 815-818
- Jackson "Crisis in the Holy Land"
- Jackson, Mongols and the West, p. 181
- Jackson, Mongols and the West, p. 99
- Tyerman, God's War, p. 798. "Louis's embassy under Andrew of Longjumeau had returned in 1251 carrying a demand from the Mongol regent, Oghul Qaimush, for annual tribute, not at all what the king had anticipated."
- Sinor, p. 524
- Tyerman, God's War, pp. 789-798
- Daftary, p. 60
- ^ Calmard "France" article in Encyclopedia Iranica
- Sinor, p. 531
- ”It really seems that Saint Louis’s initial project in his second Crusade was an operation coordinated with the offensive of the Mongols.” Demurger, “Croisades et Croises”, p.285
- ^ Richard, The Crusades, pp. 428-434
- Grousset, Histoire des Crusades III, p.647
- ^ Angold, Michael. Cambridge History of Christianity. Vol. 5. Cambridge University Press. p. 387. ISBN 0521811139.
In May 1260, a Syrian painter gave a new twist to the iconography of the Exaltation of the Cross by showing Constantine and Helena with the features of Hulegu and his Christian wife Doquz Khatun
- Le Monde de la Bible N.184 July-August 2008, p.43
- Runciman, History of the Crusades 3, p. 303
- Lane, p. 243
- ^ Joseph, John (1983). Muslim-Christian Relations and Inter-Christian Rivalries in the Middle East. SUNY Press. p. 16. ISBN 9780873956000.
- ^ Folda, Jaroslav. Crusader art in the Holy Land: from the Third Crusade to the fall of Acre. p. 349-350.
- Jackson, Mongols and the West, p. 120
- Takahashi, Hidemi (2005). Barhebraeus: a bio-bibliography. Gorgias Press. p. 102. ISBN 9781593331481.
- Runciman, History of the Crusades 3 p. 304
- Irwin, "Rise of the Mamluks", p. 616
- "He reinstated the emirs expelled by his predecesso, then assembled a large army, swollen by those who had fled from Syria during Hulegu's offensive, and set about recovering territory lost by the Muslims. Scattering in passage the thousand men left at Gaza by the Mongols, and having negotiated a passage along the coast with the Franks (who had received his emirs in Acre), he met and routed Kitbuqa's troops at Ayn Jalut." Richard, The Crusades, pp. 414–415
- Jackson, p. 116
- Richard, p. 411
- ""The authorities of the crusader states, with the exception of Antioch, opted for a neutrality favourable to the Mamluks." Morgan "The Mongols and the Eastern Mediterranean" p. 204
- Jackson, Mongols and the West, p. 115
- "They allowed the Mamluks to cross their territory, in exchange for a promise to be able to purchase at a low price the horses captured from the Mongols", Richard, "The Crusades", p. 425
- Richard, The Crusades, pp. 409-414
- Richard, The Crusades, pp. 421-422 "What Hulegu was offering was an alliance. And, contrary to what has long been written by the best authorities, this offer was not in response to appeals from the Franks."
- Jackson, Mongols and the West, p. 166
- "In 1264, to the coalition between the Franks, Mongols and Byzantines, responded the coalition between the Golden Horde and the Mamluks.” Richard, The Crusades, p. 436
- "In Frankish Syria, meanwhile, events had taken another direction. There was no longer any thought of conducting a crusade against the Mongols; the talk was now of a crusade in collaboration with them." Richard, The Crusades, p. 414
- Mutafian Le Royaume Armenien de Cilicie p.58
- Oxford history of Byzantium, p. 258
- ^ Hindley The Crusades pp. 205-207
- Nicolle, The Crusades, p. 47
- "On landing at Acre, Edward at once sent his messengers to Abaga. He received a reply only in 1282, when he had left the Holy Land. The il-khan apologized for not having kept the agreed rendezvous, which seems to confirm that the crusaders of 1270 had devised their plan of campaign in the light of Mongol promises, and that these envisaged joint operation in 1271. In default of his own arrival and that of his army, Abaga ordered the commander of this forces stationed in Turkey, the 'noyan of the noyans', Samaghar, to descend into Syria to assist the crusaders." Richard, The Crusades, p. 433
- Sicker, Martin (2000). The Islamic world in ascendancy: from the Arab conquests to the siege of Vienna. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 123. ISBN 9780275968922.
Abaqa now decided to send some 10,000 Mongol troops to join Edward's Crusader army
- Hindley, p. 207
- ^ "1274: Promulgation of a Crusade, in liaison with the Mongols". Richard, The Crusades, p. 487
- Richard, The Crusades, p. 422
- ”Le Pape Grégoire X s’efforce alors de mettre sur pied un vaste programme d’aide à la Terre Sainte, les “Constitutions pour le zèle de la foi”, qui sont acceptées au Concile de Lyon de 1274. Ce texte prévoit la levée d’une dime pendant trois ans pour la croisade, l’interdiction de tout commerce avec les Sarasins, la fourniture de bateaux par les républiques maritimes italiennes, et une alliance de l’Occident avec Byzance et l’Il-Khan Abagha". Balard, Les Latins en Orient (XIe-XVe siècle), p. 210
- ^ Richard, The Crusades, p. 452-456
- ^ Amitai. Mongols and Mamluks. p. 185-186.
- Jackson, Mongols and the West, p. 168
- ^ Harpur, James (2008). The Crusades: The Two Hundred Years War. Rosen Publishing Group. p. 116. ISBN 9781404213678.
- Jackson, "Mongols and Europe" p. 715
- Encyclopaedia of Islam, p. 580
- Jackson, The Mongols and the West p .168
- Grands Documents de l'Histoire de France, Archives Nationales de France, p.38, 2007.
- ^ Jackson, The Mongols and the West p. 169]
- Fisher, William Bayne; Boyle, John Andrew}page=370. The Cambridge history of Iran.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - Rossabi, p. 99
- Prawdin Mongol Empire p. 372. "Argun revived the idea of an alliance with the West, and envoys from the Ilkhans once more visited European courts. He promised the Christians the Holy Land, and declared that as soon as they had conquered Jerusalem he would have himself baptised there. The Pope sent the envoys on to Philip the Fair of France and to Edward I of England. But the mission was fruitless. Western Europe was no longer interested in crusading adventures."
- "Arghun had persisted in the quest for a Western alliance right down to his death without ever taking the field against the mutual enemy." Jackson, Mongols and the West, p. 170
- Mantran "A Turkish or Mongolian Islam" in The Cambridge Illustrated History of the Middle Ages: 1250-1520, p. 298
- Phillips, Medieval Expansion of Europe, p. 126
- ^ Richard. Crusades, c.1071-c.1291. p. 455.
- ^ Jackson, "The Mongols and Europe", p. 715
- ^ Jackson. Mongols and the West, 1221-1410. p. 169.
- Jackson, Mongols and the West, p. 169
- ^ "The Mongol alliance, despite six further embassies to the west between 1276 and 1291, led nowhere. The prospect of an anti-Mamluk coalition faded as the westerners' inaction rendered them useless as allies for the Mongols, who, in turn, would only seriously be considered by western rulers as potential partners in the event of a new crusade which never happened." Tyerman, God's War, p. 816
- Barber The Trial of the Templars 2nd ed., p. 22: "The aim was to link up with Ghazan, the Mongol Il-Khan of Persia, who had invited the Cypriots to participate in joint operations against the Mamluks".
- ”When Ghazan got rid of him (March 1297), he revived his projects against Egypt, and the rebellion of the Mamluk governor of Damascus, Saif al-Din Qipchaq, provided him with the opportunity for a new Syrian campaign; Franco-Mongol cooperation thus survived both the loss of Acre by the Franks and the conversion of the Mongols of Persia to Islam. It was to remain one of the givens of crusading politics until the peace treaty with the Mamluks, which was concluded only in 1322 by the khan Abu Said." Richard, The Crusades, pp. 455-456
- Demurger, The Last Templar, p. 99
- ^ Schein "Gesta Dei per Mongolos" 1979, p. 811
- ^ Andrew Jotischky (2004). Crusading and the crusader states, p.249. Pearson Education. ISBN 0582418518.
- ^ Demurger, The Last Templar, p. 100
- ^ Malcom Barber. The trial of the Templars. p. 22.
- ^ Jackson. The Mongols and the West, 1221-1410. p. 171.
- ^ Peter W. Edbury (1991). Kingdom of Cyprus and the Crusades, 1191-1374, p.105. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521268761.
- ^ Nicholson, Helen (2001). The Knights Hospitaller. Boydell & Brewer. p. 45. ISBN 0851158455.
- Richard, The Crusades, p. 469
- Mutafian "Le Royaume Armenien de Cilicie", p.74-75
- Nicolle, The Crusades, p. 80
- Jackson, Mongols and the West, p. 216
- Jackson, Mongols and the West, p. 203
- Jackson, Mongols and the West, p. 314
- Phillips, p. 112
- Sinor, Denis (1997). Inner Asia: Uralic and Altaic series. Vol. 96. Routledge. p. 190. ISBN 9780700708963.
- Daniel, Elton L. (2006). Culture and customs of Iran. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 25. ISBN 9780313320538.
- Wood, Frances. The Silk Road: Two Thousand Years in the Heart of Asia. University of California Press. p. 136. ISBN 9780520243408.
- Jackson. The Mongols and the West. p. 4.
- ^ "In their successive attempts to secure assistance from the Latin world, the Ilkhans took care to select personnel who would elicit the confidence of Western rulers and to impart a Christian complexion to their overtures." Jackson, Mongols and the West, p. 173
- "This has long been seen as a 'missed opportunity' for the Crusaders. According to that opinion, most eloquently expressed by Grousset and frequently repeated by other scholars, the Crusaders ought to have allied themselves with the pro-Christian, anti-Muslim Mongols against the Mamluks. They might thus have prevented their own destruction by the Mamluks in the succeeding decades, and possibly even have secured the return of Jerusalem by favour of the Mongols." Morgan The Mongols 2nd ed. p. 136
- Richard, The Crusades, pp. 424-469
- Demurger The Last Templar p. 100. "Above all, the expedition made manifest the unity of the Cypriot Franks and, through a material act, put the seal on the Mongol alliance."
- Jackson, Mongols and the West, p. 119
- Runciman, History of the Crusades 3, p. 402
- "The refusal of the Latin Christian states in the area to follow Hethum's example and adapt to changing conditions by allying themselves with the new Mongol empire must stand as one of the saddest of the many failures of Outremer." Burger A Lytell Cronycle pp. xiii-xiv
- "In later years Christian chroniclers would bemoan a lost opportunity in which Crusaders and Mongols might have joined forces to defeat the Muslims. But they were writing from the benefit of hindsight, after the Crusader States had been destroyed by the Muslim Mamluks." Nicolle, The Mongol Warlords, p. 114
- Prawer The Crusaders' Kingdom p. 32. "The attempts of the crusaders to create an alliance with the Mongols failed."
- Runciman, pp. 439-440
- "The Mongol Hordes under Genghis Khan and his descendants had already invaded the eastern Islamic world, raising visions in Europe of a potent new ally, which would join Christians in destroying Islam. Even after the Mongol invasion of Orthodox Christian Russia, followed by their terrifying rampage across Catholic Hungary and parts of Poland, many in the West still regarded the Mongols as potential allies." Nicolle, The Crusades, p. 42
- "Eventually the conversion of the Il-Khans (as the Mongol occupiers of Iran and Iraq were known) to Islam at the end of the 13th century meant that the struggle became one between rival Muslim dynasties rather than between Muslims and alien outsiders. Though the feeble Crusader States and occasional Crusading expeditions from the West were drawn in, the Crusaders were now little more than pawns in a greater game." Nicolle, The Crusades, p. 44
- ^ Jackson, Mongols and the West, pp. 165-185
References
- Abate, Mark T., Marx, Todd (2002). History in Dispute: The Crusades, 1095-1291. Vol. 10. St. James Press. ISBN 1558624546.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Amitai-Preiss, Reuven (1995). Mongols and Mamluks: the Mamluk-Ilkhanid War, 1260–1281. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521462266.
- Amitai, Reuven (1987). "Mongol Raids into Palestine (AD 1260 and 1300)". Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society (2): 236–255.
- Atwood, Christopher P. (2004). The Encyclopedia of Mongolia and the Mongol Empire. Facts on File, Inc. ISBN 0-8160-4671-9.
- Balard, Michel (2006). Les Latins en Orient (XIe-XVe siècle). Presses Universitaires de France, Paris. ISBN 2130518117.
- Barber, Malcolm (2001). The Trial of the Templars (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-67236-8.
- Barber, Malcolm; Bate, A. Keith (2002). The Templars: Selected Sources. Manchester University Press. ISBN 071905110X.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Bosworth, Clifford Edmund (1989). Encyclopaedia of Islam, Fascicle 107. Vol. 6. Brill Archive. ISBN 97890004090828.
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: length (help) - Bournoutian, George A. (2002). A Concise History of the Armenian People: From Ancient Times to the Present. Mazda Publishers. ISBN 1568591411.
- Burger, Glenn (1988). A Lytell Cronycle : Richard Pynson's translation (c 1520) of La fleur des histoires de la terre d'Orient / Hetoum. University of Toronto Press. ISBN 0802026265.
- Calmard, Jean. "France" article in Encyclopædia Iranica
- Daftary, Farhad (1994). The Assassin legends: myths of the Isma'ilis. I.B. Tauris. ISBN 9781850437055.
- Demurger, Alain (2005) . The Last Templar. Profile Books. ISBN 2228902357.
- Grousset, René (1935). Histoire des Croisades III, 1188-1291 (in French). Editions Perrin. ISBN 2-262-02569-X.
- Foltz, Richard (2000). Religions of the Silk Road: Overland Trade and Cultural Exchange from Antiquity to the Fifteenth Century. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 0-312-23338-8.
- Hindley, Geoffrey (2004). The Crusades: Islam and Christianity in the Struggle for World Supremacy. Carroll & Graf. ISBN 0786713445.
- Irwin, Robert. "The Rise of the Mamluks". The New Cambridge Medieval History: c. 1198–c. 1300. p. 616.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|editors=ignored (|editor=suggested) (help) - Jackson, Peter (1980). "The Crisis in the Holy Land in 1260". The English Historical Review. 95 (376): 481–513.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Jackson, Peter. "The Mongols and Europe". The New Cambridge Medieval History: c. 1198–c. 1300. p. 703.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|editors=ignored (|editor=suggested) (help) - Jackson, Peter (2005). The Mongols and the West: 1221-1410. Longman. ISBN 978-0582368965.
- Knobler, Adam (Fall 1996). "Pseudo-Conversions and Patchwork Pedigrees: The Christianization of Muslim Princes and the Diplomacy of Holy War". Journal of World History. 7 (2): 181–197. doi:10.1353/jwh.2005.0040.
- Lane, George (2006). Daily life in the Mongol empire. Greenwood Press. ISBN 9780313332265.
- Lebédel, Claude (2006). Les Croisades, origines et conséquences (in French). Editions Ouest-France. ISBN 2737341361.
- Mantran, Robert (1986). "A Turkish or Mongolian Islam". In Fossier, Robert (ed.). The Cambridge Illustrated History of the Middle Ages: 1250-1520. volume 3. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 298. ISBN 9780521266468.
{{cite book}}: Text "Cambridge University Press" ignored (help) - Marshall, Christopher (1994). Warfare in the Latin East, 1192–1291. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521477420.
- Michaud, Yahia (Oxford Centre for Islamic Studies) (2002). Ibn Taymiyya, Textes Spirituels I-XVI (in French). Le Musulman, Oxford-Le Chebec.
{{cite book}}: External link in|title= - Morgan, David (2007). The Mongols (2nd ed.). Blackwell Publishing. ISBN 9781405135399.
- Morgan, David (1989). "The Mongols and the Eastern Mediterranean". Mediterranean Historical Review. 4 (1): 204. doi:10.1080/09518968908569567.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Mutafian, Claude (1993, 2001). Le Royaume Armenien de Cilicie (in French). CNRS Editions. ISBN 2271051053.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Nersessian, Sirarpie Der (1969). "The Kingdom of Cilician Armenia". In Hazard, Harry W. and Wolff, Robert Lee. (Kenneth M. Setton, general editor) (ed.). A History of the Crusades: The Later Crusades, 1189-1311. Vol. 2. University of Wisconsin Press. pp. 630–660. ISBN 0299048446.
{{cite book}}:|editor=has generic name (help); External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) - Nicolle, David (2001). The Crusades. Essential Histories. Osprey Publishing. ISBN 978-1-84176-179-4.
- Nicolle, David (2004). The Mongol Warlords: Genghis Khan, Kublai Khan, Hulegu, Tamerlane. Brockhampton Press. ISBN 1860194079.
- Prawdin, Michael (pseudonym for Charol, Michael) (1940/1961). Mongol Empire. Collier-Macmillan Canada. ISBN 1412805198.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|date=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Prawer, Joshua (1972). The Crusaders' Kingdom: European Colonialism in the Middle Ages. Praeger Publishers. ISBN 9780297993971.
- Reinert, Stephen W. (2002). "Fragmentation (1204–1453)". In Mango, Cyril A. (ed.). The Oxford history of Byzantium. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780198140986.
- Richard, Jean (1999). The Crusades, c. 1071-c. 1291. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-62566-1.
- Riley-Smith, Jonathan (2005). Crusades: a history (2nd ed.). Continuum International Publishing Group. ISBN 9780826472700.
- Rossabi, Morris (1992). Voyager from Xanadu: Rabban Sauma and the first journey from China to the West. Kodansha International. ISBN 4770016506.
- Runciman, Steven (1987) . A History of the Crusades 3. Penguin Books. ISBN 9780140137057.
- Ryan, James D. (November 1998). "Christian wives of Mongol khans: Tartar queens and missionary expectations in Asia". Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society. 8 (3): 411–421.
- Saunders, J. J. (2001). The History of the Mongol Conquests. University of Pennsylvania Press. ISBN 0812217667.
- Schein, Sylvia (1979). "Gesta Dei per Mongolos 1300. The Genesis of a Non-Event". The English Historical Review. 94 (373): 805–819. doi:10.1093/ehr/XCIV.CCCLXXIII.805.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Sinor, Dennis (1975). "The Mongols and Western Europe". A history of the Crusades: The fourteenth and fifteenth centuries. University of Wisconsin Press. p. 513. ISBN 9780299066703.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|editors=ignored (|editor=suggested) (help) - Stewart, Angus (2002). "The Logic of Conquest: Tripoli, 1289; Acre, 1291; why not Sis, 1293?". Al-Masaq. 14 (1): 7–16. doi:10.1080/09503110220114407.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Tyerman, Christopher (2006). God's War: A New History of the Crusades. Harvard University Press. ISBN 0674023870.
| Mongol Empire | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Timeline of the Mongol Empire | |||||||||||