| Revision as of 19:25, 10 April 2004 view source69.136.131.62 (talk) {{msg:South_Asia}}← Previous edit | Revision as of 17:12, 11 April 2004 view source 140.247.71.217 (talk)No edit summaryNext edit → | ||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
| with the northern part of Afghanistan placed in ]. | with the northern part of Afghanistan placed in ]. | ||
| It includes the region sometimes called the ]. It contains well over a fifth of the ]'s ] |
It includes the region sometimes called the ]. It contains well over a fifth of the ]'s ]. | ||
| This region has a long history, and ancient civilisations have sprung up from the ] Valley. The region was at its most prosperous before the 17th century; ] lead to the conquering of the region, which began to fall apart in the feud between ], ], ] and ]. With the post-colonial period of the ], the region was partitioned into ] and the two ]s, one of which became ]; ] gained independence from India. ] and ] were separate cases. | This region has a long history, and ancient civilisations have sprung up from the ] Valley. The region was at its most prosperous before the 17th century; ] lead to the conquering of the region, which began to fall apart in the feud between ], ], ] and ]. With the post-colonial period of the ], the region was partitioned into ] and the two ]s, one of which became ]; ] gained independence from India. ] and ] were separate cases. | ||
Revision as of 17:12, 11 April 2004
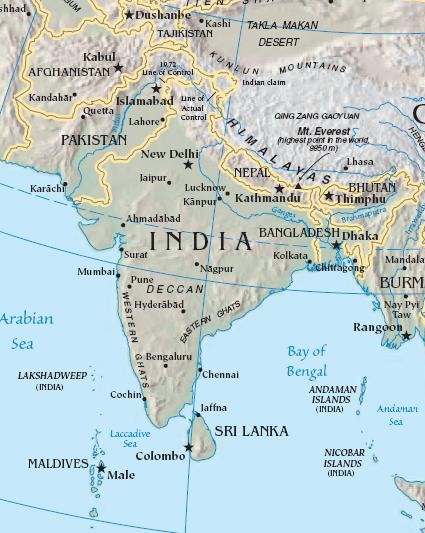
South Asia is a geo-cultural region comprising the modern states of India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Nepal, Bhutan, and the Maldives. Often Afghanistan is also included, sometimes with the northern part of Afghanistan placed in Central Asia.
It includes the region sometimes called the Indian subcontinent. It contains well over a fifth of the world's population.
This region has a long history, and ancient civilisations have sprung up from the Indus Valley. The region was at its most prosperous before the 17th century; colonialism lead to the conquering of the region, which began to fall apart in the feud between Britain, France, Portugal and Holland. With the post-colonial period of the 20th century, the region was partitioned into India and the two Pakistans, one of which became Bangladesh; Bhutan gained independence from India. Afghanistan and Nepal were separate cases.
See also: History of South Asia
Southern Asia sometimes refers to all of Asia that was not part of the Soviet Union.