| Revision as of 08:23, 4 December 2010 editAmirobot (talk | contribs)56,602 editsm robot Adding: ca:Compost cíclic← Previous edit | Revision as of 10:45, 27 December 2010 edit undoWickey-nl (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users7,037 edits →See alsoNext edit → | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
Revision as of 10:45, 27 December 2010
In chemistry, a cyclic compound is a, mostly organic, compound in which a series of atoms are connected to form a loop or ring. Benzene is a well known example. The term "polycyclic" is used when more than one ring is formed in a single molecule for instance in naphthalene, and the term macrocycle is used for a ring containing more than a dozen atoms.
-
 Benzene, a simple cyclic compound.
Benzene, a simple cyclic compound.
-
 Naphthalene, a simple polycyclic compound.
Naphthalene, a simple polycyclic compound.
-
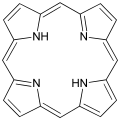 Porphyrin, a simple macrocyclic compound.
Porphyrin, a simple macrocyclic compound.
-
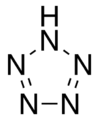 Pentazole, an inorganic cyclic compound.
Pentazole, an inorganic cyclic compound.
Categorization
Cyclic compounds can be categorized:
Ring-closing & opening reactions

Related concepts in organic chemistry are so-called ring-closing reactions in which a cyclic compound is formed and ring-opening reactions in which rings are opened.
Examples of ring-closing reactions:
- Ring-closing metathesis
- Nazarov cyclization reaction
- Ruzicka large ring synthesis
- Dieckmann condensation
- Wenker synthesis
- Radical cyclization
Example of ring-opening reactions:
- A general type of polymerization reaction: Ring-opening polymerization
- Ring opening metathesis polymerisation
See also
- open-chain compound
- Ring expansion and ring contraction
- Macrocycle
- Cyclization reaction
- Effective molarity
External links
- Polycyclic+Compounds at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Macrocyclic+Compounds at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
References
- March, Jerry (1985). Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Mechanisms, and Structure (3rd ed.). New York: Wiley. ISBN 9780471854722. OCLC 642506595.