| Revision as of 08:43, 7 December 2010 editCheMoBot (talk | contribs)Bots141,565 edits Updating {{chembox}} (changes to watched fields - updated 'UNII_Ref', 'ChemSpiderID_Ref', 'StdInChI_Ref', 'StdInChIKey_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report [[Wikipedia_talk:WikiProject_Chemi← Previous edit | Revision as of 23:36, 9 January 2011 edit undoArthurBot (talk | contribs)259,345 editsm r2.6.3) (robot Adding: hu:PimelinsavNext edit → | ||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
Revision as of 23:36, 9 January 2011
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name heptanedioic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.492 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C7H12O4 |
| Molar mass | 160.17 g/mol |
| Density | 1.28 g/cm |
| Melting point | 103-105 °C |
| Boiling point | Decomposes |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
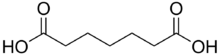
Pimelic acid is the organic compound with the formula HO2C(CH2)5CO2H. Derivatives of pimelic acid are involved in the biosynthesis of the amino acid called lysine. Pimelic acid is one methylene longer than a related dicarboxylic acid, adipic acid, a precursor to many polyesters and polyamides. It is the final member of the mnemonic used to aid recollection of the order of the first six dicarboxylic acids using their common (not IUPAC) nomenclature: Dicarboxylic acid
Pimelic acid has been synthesized from cyclohexanone and from salicylic acid. In the former route, the additional carbon is supplied by dimethyloxalate, which reacts with the enolate.
See also
References
- Snyder, H. R.; Brooks, A. L.; Shapiro, S. H. "Pimelic Acid from Cyclohexanone" and Müller, A. "Pimelic Acid from Salicylic Acid" Organic Syntheses, Collected Volume 2, p.531 (1943).http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/pdfs/CV2P0531.pdf