| Revision as of 05:24, 19 February 2011 editAles hurko (talk | contribs)248 edits Still, that's too big. A specific info must be included within a text instead of a info box. Let's not overcrowd it. To emphasize that Orthodoxy is predominant it's enough to put it in front of other religions. / Added more info.← Previous edit | Revision as of 06:45, 19 February 2011 edit undoM.K (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Pending changes reviewers13,165 edits POV outNext edit → | ||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
| |related=|related= ], ], ], ] and other ] <ref>http://www.ethnologue.com/%5C/15/show_family.asp?subid=90707</ref> | |related=|related= ], ], ], ] and other ] <ref>http://www.ethnologue.com/%5C/15/show_family.asp?subid=90707</ref> | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Belarusians''' ({{lang-be|Беларусы, ''Biełarusy''}}, {{lang-ru|Белорусы}}, Belorussians or Byelorussians); |
'''Belarusians''' ({{lang-be|Беларусы, ''Biełarusy''}}, {{lang-ru|Белорусы}}, Belorussians or Byelorussians); are an ] ] (or ]) who populate the majority of the ]. Introduced to the world as a new state in the early 1990s, the Republic of Belarus brought with it the notion of a re-emerging Belarusian ethnicity, drawn upon the lines of the ] language spoken by the ] ethnic group that ruled (together with ancestors of today's ]) the ]. However, after the creation of the ], many of the ]-speaking ] would be absorbed by the ] in the West and, later, the ] in the East, leaving only a small rural-dwelling population to be the propagators of a distinct non-literary ] up until its revival. | ||
| There are over 8 million people who associate themselves with the Belarusian nationality today. | There are over 8 million people who associate themselves with the Belarusian nationality today. | ||
Revision as of 06:45, 19 February 2011
Ethnic group| File:Collage of Belarusians.JPGCyril of Turaŭ • Euphrosyne of Polatsk • Francysk Skaryna • Leŭ Sapieha • Jan Czeczot • Kastuś Kalinoŭski • Vincent Dunin-Marcinkievič • Stanisłaŭ Bułak-Bałachovič • Ałaiza Paškievič • Janka Kupała • Jakub Kołas • Branisłaŭ Taraškievič • Piatro Mašera • Paveł Suchi • Maksim Tank • Volha Korbut | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
|---|---|
| 807,970 | |
| 600.000 | |
| 275,800 | |
| 130.000 | |
| 111,926 | |
| 78,890 | |
| 50,000 - 70,000 | |
| 45,000 - 80,000 | |
| 48,700 | |
| 42,866 | |
| 20,000 | |
| 20,000 | |
| 17,241 | |
| 7,000 | |
| 7,000 | |
| 2,000 | |
| 1,168 | |
| 138 | |
| Languages | |
| Belarusian, Russian | |
| Religion | |
| Orthodox Christianity, Roman Catholic, Greek Catholic and Protestant. | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Poles, Ukrainians, Russians, Rusyns and other Slavic ethnic groups | |
Belarusians (Template:Lang-be, Template:Lang-ru, Belorussians or Byelorussians); are an East Slavic ethnic group (or nationality) who populate the majority of the Republic of Belarus. Introduced to the world as a new state in the early 1990s, the Republic of Belarus brought with it the notion of a re-emerging Belarusian ethnicity, drawn upon the lines of the Old Belarusian language spoken by the Ruthenian ethnic group that ruled (together with ancestors of today's Lithuanians) the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. However, after the creation of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, many of the Old Belarusian-speaking Ruthenian nobles would be absorbed by the Polish szlachta in the West and, later, the Russian nobility in the East, leaving only a small rural-dwelling population to be the propagators of a distinct non-literary Belarusian language up until its revival. There are over 8 million people who associate themselves with the Belarusian nationality today.
Location

According to Y. Karskiy (1903) According to M. Dovnar-Zapol'skiy (1919) Modern state boundaries
Belarusians also form minorities in neighboring Poland (especially in the Białystok Voivodeship), Russia and Lithuania. At the beginning of 20th century Belarusians constituted a majority in the regions around Smolensk.
Noticeable numbers have emigrated to the United States, Brazil and Canada in the early 20th century. During Soviet times, many Belarusians were deported or migrated to various regions of the USSR, including Siberia, Kazakhstan and Ukraine.
Since the breakup of the USSR several hundred thousand have emigrated to the European Union, United States, Canada and Russia.
See also Belarusian diaspora
Languages
The most spoken language in Belarus is Russian, principally spoken by 72% of the population, while the other official language, Belarusian, is only used by 11,9% in every day life. Statistical data shows that Belarusian is fluently communicated, read and written by 29,4%, while 52,5% of the population can communicate and read in Belarusian. Belarusian is a language of the Eastern Slavic group.
Genetics
Belarusians show the characteristic R1a South Altaic Turckic genes of the male ancestorship at 51%, similar to other East slav groups. Such large frequencies of R1a has been found only in East Europe and India.
Gentical studies show that genetically Belarusians have close genetical similarities with Poles, Russians and Ukrainians, which belong to the same group. A study of the Y chromosome in East Slavs groups shows that there is no significant variation in the Y chromosome between Belarusians, Poles, central-southern Russians and Ukrainians, and it is overlapped by their vast similarities, thus revealing an overwhelmingly shared patrilineal ancestry.
Name
The name Belarus can be literally translated as White Ruthenia that is a historical region in the east of modern Republic of Belarus, known in Latin as Ruthenia Alba. This name was in use in the West for some time in history, together with White Ruthenes, White Russians (though not to be confused with the political group of White Russians that opposed the Bolsheviks during the Russian Civil War) and similar forms. Belarusians trace their name back to the people of Rus' {{citation}}: Empty citation (help).

History
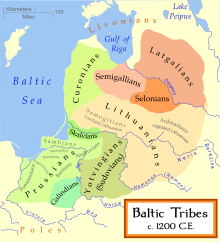
The Belarusian people trace their distinct culture to the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and earlier Kievan Rus and the Principality of Polatsk. Most Belarusians are descendants of the East Slav tribes Dregovichs, Krivichs and Radimichs, as well as of a Baltic tribe of Jotvingians who lived in the west and north-west of today's Belarus.
In 13th-18th centuries Belarusians were mostly known under the name of Ruthenians which refers to the Eastern part of state of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania (Litva, Vialikaja Litva) of which the White Ruthenian, Black Ruthenian and Polesian lands were part of since the 13th-14th centuries and where Ruthenian language which developed in Old Belarusian language gradually became the dominant written language in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, that replaced Latin. Casimir's Code of 1468 and all three editions of Statutes of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania (1529, 1566, and 1588) were written in Old Belarusian language. Eventually it was replaced by Polish.
On the grounds of the dominance of Ruthenian language (which later evolved into modern Belarusian and Ukrainian Languages) culture in the Eastern parts of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, some modern Belarusian scholars and people in Belarus count that Grand Duchy of Lithuania was mostly Belarusian state when it existed.
After World War I Belarusians revived their own statehood, with varying degrees of independence - first as the short-lived Belarusian National Republic under German occupation, then as the Byelorussian SSR from 1919 until 1991, which merged with other republics to become a constituent member of the Soviet Union in 1922). Belarus gained full independence with the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991.

Cuisine
See also
- Demographics of Belarus
- Dregovichs
- History of Belarus
- List of Belarusians (ethnic group)
- Litvins
- Radimichs
References and notes
- 1999 census
- 2002 census
- ^ http://www.belarustime.ru/belarus/culture/diaspore/c6420f28d9870602.html
- 2001 census
- 1999 census
- Multiculturalcanada.ca
- ^ 2002 census
- 2001 census
- 2000 census
- http://www.statistics.gr/portal/page/portal/ESYE/BUCKET/A1605/Other/A1605_SPO15_TB_AN_00_2006_07_F_EN.pdf
- http://www.armenia-new.belembassy.org/rus/soot/
- CIA - The World Factbook -- Belarus -- People -- Religions -- 1997 Census
- http://www.ethnologue.com/%5C/15/show_family.asp?subid=90707
- ^ Belta.by
- Behar, Doron M.; Thomas, Mark G.; Skorecki, Karl; Hammer, Michael F.; Bulygina, Ekaterina; Rosengarten, Dror; Jones, Abigail L.; Held, Karen; Moses, Vivian; Goldstein, David; Bradman, Neil; Weale, Michael E. (2003). "Multiple Origins of Ashkenazi Levites: Y Chromosome Evidence for Both Near Eastern and European Ancestries". American Journal of Human Genetics. 73 (4): 768–779. doi:10.1086/378506.
- "DK Zelenin, Ethnographical divisions of East Slavs"
- Balanovsky, Oleg; et al. (2008). "Two Sources of the Russian Patrilineal Heritage in Their Eurasian Context". American Journal of Human Genetics. 82 (1): 236–250. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2007.09.019.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|last2=(help) - Malyarchuk, Boris; et al. (2004). "Differentiation of Mitochondrial DNA and Y Chromosomes in Russian Populations". Human Biology. 76 (6): 877–900. doi:10.1353/hub.2005.0021.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|last2=(help) - http://www.krugosvet.ru/enc/istoriya/BELORUSI.html Энциклопедия Кругосвет
- http://www.hetman.by/files/data/historyone_en.pdf
- http://flagspot.net/flags/by-arms.html
- http://depts.washington.edu/baltic/papers/grandduchy.htm
- Zejmis, Jakub, “Belarusian National Historiography and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania as a Belarusian State,” Zeitschrift fur Ostmitteleuropa-Forschung , 1999, 48, p. 383.
External links
- Ethnographic Map (New York, 1953)
- CIA World Fact Book 2005
- "ЧТО ТАКОЕ БЫТЬ БЕЛОРУСОМ?", ("What does it mean to be a Belarusian? ") a 2009 survey Template:Ru icon
| Belarus articles | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History | |||||
| Geography | |||||
| Politics | |||||
| Economy | |||||
| Society |
| ||||