| Revision as of 11:23, 29 November 2010 editCheMoBot (talk | contribs)Bots141,565 edits Updating {{chembox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'UNII_Ref', 'ChemSpiderID_Ref', 'StdInChI_Ref', 'StdInChIKey_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report [[Wikipedia_talk:Wi← Previous edit | Revision as of 09:43, 9 March 2011 edit undoColmere (talk | contribs)44 editsmNo edit summaryNext edit → | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
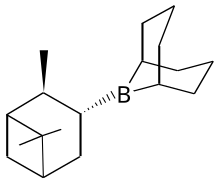
| '''Alpine borane''' is the commercial name for an ] that is used in ]. This ] is generated by treating ] with ] to give a sterically crowded trialkylborane. The resulting ] species ]ly |
'''Alpine borane''' is the commercial name for an ] that is used in ]. This ] is generated by treating ] with ] to give a sterically crowded trialkylborane. The resulting ] species can ]ly reduce ketones, aldehydes, even deutero aldehydes in what is known as the ], or simply the '''Midland Reduction''':<ref>M. Mark Midland "B-3-Pinanyl-9-borabicyclononane" in Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis 2001 John Wiley, New York.{{DOI|10.1002/047084289X.rp173}}. Article Online Posting Date: April 15, 2001</ref> | ||
| :C<sub>8</sub>H<sub>12</sub>B-pinanyl + RCDO → C<sub>8</sub>H<sub>12</sub>BOCHDR + (+)-''d''-pinene | :C<sub>8</sub>H<sub>12</sub>B-pinanyl + RCDO → C<sub>8</sub>H<sub>12</sub>BOCHDR + (+)-''d''-pinene | ||
Revision as of 09:43, 9 March 2011
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 9-(2,6,6-Trimethylbicyclohept-3-yl)-9-bora-bicyclononane | |
| Other names Alpine-Borane; B-Isopinocampheyl-9-borabicyclononane; B-3-Pinanyl-9-borabicyclononane | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number |
|
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.157.575 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C18H31B |
| Molar mass | 258.26 g·mol |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.947 g/mL |
| Boiling point | >55 °C |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Alpine borane is the commercial name for an organoboron compound that is used in organic synthesis. This reagent is generated by treating 9-BBN with α-pinene to give a sterically crowded trialkylborane. The resulting chiral species can stereoselectively reduce ketones, aldehydes, even deutero aldehydes in what is known as the Midland Alpine Borane Reduction, or simply the Midland Reduction:
- C8H12B-pinanyl + RCDO → C8H12BOCHDR + (+)-d-pinene
Hydrolysis of the resulting borinic ester affords the alcohol:
- C8H12BOCHDR + H2O → C8H12BOH + HOCHDR
It is also effective for the stereoselective reduction of certain acetylenic ketones.
Related reagents
A range of alkyl-substituted derivatives of borane and diborane are specialty reagents in organic synthesis. Two such reagents that are closely related to Alpine borane are 9-BBN and diisopinocampheylborane.
References
- R-Alpine-Borane and S-Alpine-Borane at Sigma-Aldrich
- M. Mark Midland "B-3-Pinanyl-9-borabicyclononane" in Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis 2001 John Wiley, New York.doi:10.1002/047084289X.rp173. Article Online Posting Date: April 15, 2001
- M. Mark Midland and Richard S. Graham. "Asymmetric Reduction of α,β-Acetylenic Ketones with B-3-Pinanyl-9-Borabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane: (R)-(+)-1-Octyln-3-ol". Organic Syntheses; Collected Volumes, vol. 7, p. 402.