| Revision as of 00:55, 16 November 2010 editCheMoBot (talk | contribs)Bots141,565 edits Updating {{chembox}} (changes to watched fields - updated 'UNII_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report errors or bugs)← Previous edit | Revision as of 20:29, 26 May 2011 edit undoChemNerd (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users17,568 edits added Category:Radical initiators using HotCatNext edit → | ||
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
Revision as of 20:29, 26 May 2011
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 2,2′-Azobis(2-methylpropionitrile) | |
| Other names
Azobisisobutyronitrile Azobisisobutylonitrile AIBN | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.030 |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C8H12N4 |
| Molar mass | 164.21 g/mol |
| Appearance | white crystalline |
| Density | 1.1 |
| Melting point | 103–105 °C |
| Boiling point | °C |
| Solubility in water | ? |
| Structure | |
| Dipole moment | (gas) |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | ? |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
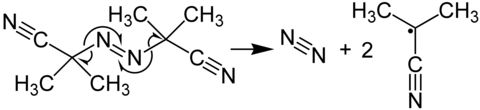
Azobisisobutyronitrile is a compound often used as a foamer in plastics and rubber and as a radical initiator. It is commonly known as AIBN. Its most common chemical reaction is one of decomposition, eliminating a molecule of nitrogen gas to form two 2-cyanoprop-2-yl radicals:
These radicals can be used to initiate free radical polymerizations and other radical reactions. For instance a mixture of styrene and maleic anhydride in toluene will react if heated, forming the polystyrene polymer, only very slowly unless an initiator such an AIBN is present. Another example of a radical reaction that can be initiated by AIBN is the anti-Markovnikov hydrohalogenation of alkenes.
AIBN is safer to use than benzoyl peroxide (another radical initiator) because the risk of explosion is far smaller. However, it is considered a flammable solid. It is soluble in methanol and ethanol, but is insoluble in water. It can explode if dissolved in acetone. AIBN is highly toxic. Wear a respirator/dust mask, protective gloves, & safety glasses when handling AIBN.
Several water-soluble azo initiators similar to AIBN are manufactured by DuPont and Wako.
See also
- 1,1'-Azobis(cyclohexanecarbonitrile) or ABCN is another free radical initiator
References
External links
- SIDS Initial Assessment Report for 2,2’-Azobis(2-methylpropionitrile) from the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)