| Revision as of 18:52, 1 April 2012 editMo ainm (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers9,265 edits Undid revision 485033620 by Wp aide (talk) revert POV edit by "new" editior← Previous edit | Revision as of 13:45, 16 April 2012 edit undoDiiscool (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Rollbackers5,655 editsm →Uses: wikilinksNext edit → | ||
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| Traditional working boats on Lough Neagh include wide-beamed {{Convert|16|to|21|ft|m|adj=on}} clinker-built, sprit-rigged working boats and smaller flat-bottomed "cots" and "flats". Barges, here called "lighters", were used up to the 1940s to transport coal over the lough and adjacent canals. Up to the 17th century, log boats (''coití'') were the main means of transport, some of which are as old as 6,400 years. Few traditional boats are left now, but a community-based group on the southern shore of the lough is rebuilding a series of working boats.<ref> </ref> | Traditional working boats on Lough Neagh include wide-beamed {{Convert|16|to|21|ft|m|adj=on}} ], ] working boats and smaller flat-bottomed "cots" and "flats". Barges, here called "lighters", were used up to the 1940s to transport coal over the lough and adjacent canals. Up to the 17th century, log boats (''coití'') were the main means of transport, some of which are as old as 6,400 years. Few traditional boats are left now, but a community-based group on the southern shore of the lough is rebuilding a series of working boats.<ref> </ref> | ||
| In the 19th century, three ]s were constructed, making use of the lough to link various ports and cities: the ] provided a link from the city of ], the ] linked to the port of ], and the ] led to the ] navigations, providing a navigable inland route via the ] to ], ] and ]. The Lower Bann was also navigable to ] and the Antrim coast, and the short ] provided a route for coal transportation. Of these waterways, only the Lower Bann remains open today, although a restoration plan for the Ulster Canal is currently in progress. | In the 19th century, three ]s were constructed, making use of the lough to link various ports and cities: the ] provided a link from the city of ], the ] linked to the port of ], and the ] led to the ] navigations, providing a navigable inland route via the ] to ], ] and ]. The Lower Bann was also navigable to ] and the Antrim coast, and the short ] provided a route for coal transportation. Of these waterways, only the Lower Bann remains open today, although a restoration plan for the Ulster Canal is currently in progress. | ||
Revision as of 13:45, 16 April 2012
| Lough Neagh | |
|---|---|
| Location | Northern Ireland |
| Coordinates | 54°37′06″N 6°23′43″W / 54.61833°N 6.39528°W / 54.61833; -6.39528 |
| Primary inflows | Upper Bann, Sixmilewater, Glenavy River, Crumlin River, Blackwater, Moyola River, Ballinderry River, River Main |
| Primary outflows | Bann River |
| Catchment area | 4550 km² |
| Basin countries | United Kingdom (91%) Republic of Ireland (9%) |
| Max. length | 30 km |
| Max. width | 15 km |
| Surface area | 392 km² |
| Average depth | 9 m |
| Max. depth | 25 m |
| Water volume | 3.528 km³ |
| Islands | (see below) |
Lough Neagh, sometimes Loch Neagh, (/ˌlɒx ˈneɪ/) is a large freshwater lake in Northern Ireland. Its name comes from Irish Loch nEathach, meaning 'Lake of Eathach' (Irish: [ɫ̪ɔx ˈn̠ʲahax]).
Geography
With an area of 392 square kilometres (151 sq mi), it is the largest lake in the British Isles and is ranked 31st in the List of largest lakes of Europe. Located twenty miles (30 km) to the west of Belfast, it is approximately twenty miles (30 km) long and nine miles (15 km) wide. It is very shallow around the margins and the average depth in the main body of the lake is about 9 m (30 ft); although at its deepest the lough is about 25 metres (80 ft) deep.
Islands
- Coney Island
- Coney Island Flat
- Croaghan Flat
- Derrywarragh Island
- Padian
- Ram's Island
- Phil Roe's Flat
- The Shallow Flat
Hydrology
Of the 4550 km² catchment area, around 9% lies in the Republic of Ireland and 91% in Northern Ireland; altogether 43% of the land area of Northern Ireland is drained into the lough, which itself flows out northwards to the sea via the River Bann. As one of its sources is the Upper Bann, the Lough can itself be considered a part of the Bann.
Towns and villages
Towns and villages near the Lough include Craigavon, Antrim, Crumlin, Randalstown, Toomebridge, Ballyronan, Ballinderry, Moortown, Ardboe, Maghery, Lurgan and Magherafelt.
Administration
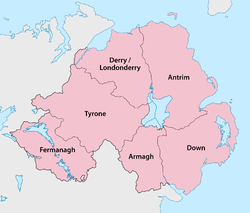

Counties
Five of the six counties of Northern Ireland have shores on the Lough (only Fermanagh does not), and its area is split among them. The counties are listed clockwise:
- Antrim (eastern half of the lake)
- Down (small part in the southeast)
- Armagh (south)
- Tyrone (west)
- Londonderry (extreme northwest)
Local Government Districts
The area of the lake is split between six Local Government Districts of Northern Ireland, which are listed clockwise:
- 1 Antrim, in the northeast, with the largest share
- 19 Lisburn City, in the east, with the smallest share
- 12 Craivagon, in the south, with a larger share
- 15 Dungannon and South Tyrone, in the southwest, with a smaller share
- 11 Cookstown, in the west, with a larger share
- 20 Magherafelt, in the northwest, with a smaller share
Uses
Although the Lough is used for a variety of recreational and commercial activities, it is exposed and tends to get extremely rough very quickly in windy conditions. It is also used as a source of fresh water by Northern Ireland Water. Plans to increase the amount of water drawn from the Lough, through a new water treatment works at Hog Park Point, have long been planned but are yet to materialise.

Traditional working boats on Lough Neagh include wide-beamed 16-to-21-foot (4.9 to 6.4 m) clinker-built, sprit-rigged working boats and smaller flat-bottomed "cots" and "flats". Barges, here called "lighters", were used up to the 1940s to transport coal over the lough and adjacent canals. Up to the 17th century, log boats (coití) were the main means of transport, some of which are as old as 6,400 years. Few traditional boats are left now, but a community-based group on the southern shore of the lough is rebuilding a series of working boats.
In the 19th century, three canals were constructed, making use of the lough to link various ports and cities: the Lagan Navigation provided a link from the city of Belfast, the Newry Canal linked to the port of Newry, and the Ulster Canal led to the Lough Erne navigations, providing a navigable inland route via the River Shannon to Limerick, Dublin and Waterford. The Lower Bann was also navigable to Coleraine and the Antrim coast, and the short Coalisland Canal provided a route for coal transportation. Of these waterways, only the Lower Bann remains open today, although a restoration plan for the Ulster Canal is currently in progress.
Lough Neagh Rescue provides a Search & Rescue service twenty-four hours a day. It is a voluntary service with funding being provided by the District Councils bordering the Lough, its members are highly trained and are a declared facility for the Marine Coastguard Agency who co-ordinate rescues on Lough Neagh Maritime and Coastguard Agency.
Lough Neagh attracts bird watchers from many nations due to the number and variety of birds which winter and summer in the boglands and shores around the lough.
Eel fishing has been a major industry in Lough Neagh for centuries. Today Lough Neagh eel fisheries export their eels to restaurants all over the world and Lough Neagh Eel has been granted Protected Geographical Status under European Union law.
Lough Neagh was widely assumed to be owned by the state, but in 2005 it publicly emerged that it is the ancestral property of the Earl of Shaftesbury. This may have serious implications for planned changes to state-run domestic water services in Northern Ireland, as the lough supplies 40% of the region's drinking water and is also used as a sewage outfall (in a system only permissible through British Crown immunity).
Legend
An old Irish story tells how the Lough was formed when Ireland's legendary giant Fionn mac Cumhaill (Finn McCool) scooped up a portion of the land and tossed it at a Scottish rival. He missed, and the chunk of earth landed in the Irish Sea, thus creating the Isle of Man.
Gallery
-
 Lough Neagh at Killywoolaghan, County Tyrone
Lough Neagh at Killywoolaghan, County Tyrone
-
 Lough Neagh near Ardmore Point
Lough Neagh near Ardmore Point
-
 Lough neagh at Shane's Castle, County Antrim
Lough neagh at Shane's Castle, County Antrim
-
 Lough Neagh at Gawley's Gate, County Antrim
Lough Neagh at Gawley's Gate, County Antrim
-
 Lough Neagh at Maghery, County Armagh
Lough Neagh at Maghery, County Armagh
-
 Lough Neagh at Ballyronan, County Londonderry
Lough Neagh at Ballyronan, County Londonderry
See also
References
- Habitas.org
- See Google Books for published examples online.
- Deirdre Flanagan and Laurance Flanagan, Irish Placenames, (Gill & Macmillan Ltd, 1994)
- Official Tourism Ireland site
- Britannica.com
- "Lough Neagh". UK Environmental Change Network. Retrieved 4 March 2012.
- Northern Ireland Rivers Agency
- Ninis.nisra.gov.uk
- Lough Neagh Boating Heritage Association
- Official list of UK protected foods. Accessed 15 July 2011.
- BBC NEWS | Northern Ireland | Sudden death may impact NI water
External links
- Discover Lough Neagh
- Lough Neagh Rescue
- Lough Neagh Boating Heritage Association
- BBC News on pollution
- BBC News on ownership of Lough Neagh
- Oxford Island National Nature Reserve