| Revision as of 17:50, 25 June 2013 editChiswick Chap (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Page movers, New page reviewers, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers297,265 edits →Modern anatomy: ref (edited with ProveIt)← Previous edit | Revision as of 17:52, 25 June 2013 edit undoChiswick Chap (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Page movers, New page reviewers, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers297,265 edits →General anatomy: weed - maybe we should ditch the whole listNext edit → | ||
| Line 127: | Line 127: | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ], referred to as the Father of Anatomy{{by whom|date=November 2011}} | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
Revision as of 17:52, 25 June 2013
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|

Anatomy (from the Greek ἀνατέμνω - anatemnō, "I cut up, cut open", from ἀνά - ana, "on, upon", and τέμνω - temnō, "I cut") is a branch of biology and medicine that considers the structure of living things. It is a general but principally a medical term that includes human and animal anatomy. In some of its facets anatomy is closely related to embryology, comparative anatomy and comparative embryology, through common roots in evolution.
Anatomy is subdivided into gross or macroscopic anatomy, and microscopic anatomy. Gross anatomy is the study of structures that can, when suitably presented or dissected, be seen by unaided vision with the naked eye. Microscopic anatomy is the study of structures on a microscopic scale, including histology (the study of tissues), and cytology (the study of cells).
The history of anatomy is characterized by a continual development in understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from examination of animals through dissection of cadavers (dead human bodies) to 20th century techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.
Superficial anatomy
Superficial or surface anatomy is important as the study of anatomical landmarks that can be readily seen from the contours of the body. It enables physicians or veterinary surgeons to gauge the position and anatomy of the associated deeper structures. Superficial is a directional term that indicates that structures are located relatively close to the surface of the body.
Animal anatomy
Vertebrate anatomy
Main article: Vertebrate anatomy| This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (June 2013) |
Bird anatomy
Main article: Bird anatomyBirds are quadrupeds but though their hind limbs are used for walking or hopping, their front limbs are wings covered with feathers and adapted for flight. Birds are endothermic, have a high metabolic rate, a light skeletal system and powerful muscles. The long bones are thin, hollow and very light. Air sac extensions from the lungs occupy the centre of some bones. The sternum is wide and usually has a keel and the caudal vertebrae are fused. There are no teeth and the narrow jaws are adapted into a horn-covered beak. The eyes are relatively large, particularly in nocturnal species such as owls. They face forwards in predators and sideways in ducks.
The feathers are outgrowths of the epidermis. Large flight feathers are found on the wing and tail, contour feathers cover the bird's surface and fine down occurs on young birds and under the contour feathers of water birds. There are scales on the legs and feet and claws on the tips of the toes.
Reptile anatomy
Main article: Reptile anatomy| This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (June 2013) |
Fish anatomy
Main article: Fish anatomy
The body of a fish is divided into a head, trunk and tail, although the divisions between the three are not always externally visible. The skeleton, which forms the support structure inside the fish, is either made of cartilage (cartilaginous fish) or bone (bony fishes). The main skeletal element is the vertebral column, composed of articulating vertebrae which are lightweight yet strong. The ribs attach to the spine and there are no limbs or limb girdles. The main external features of the fish, the fins, are composed of bony spines and soft rays and, with the exception of the caudal fins, have no direct connection with the spine. They are supported by the muscles which compose the main part of the trunk.
Mammal anatomy
Main article: Mammal anatomy| This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (June 2013) |
Human anatomy
Main article: Human anatomy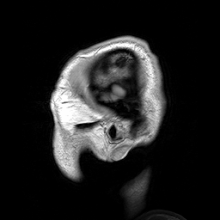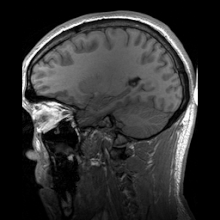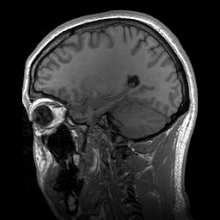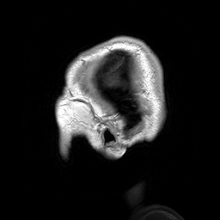


Human anatomy, including gross human anatomy and histology, is primarily the scientific study of the morphology of the adult human body. It differs from Physiology in that Anatomy is only the structures involved, and Physiology is the way those structures actually work.
Generally, students of certain biological sciences, paramedics, prosthetists and orthotists, physiotherapists, occupational therapists, nurses, and medical students learn gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy from anatomical models, skeletons, textbooks, diagrams, photographs, lectures and tutorials, and in addition, medical students generally also learn gross anatomy through practical experience of dissection and inspection of cadavers. The study of microscopic anatomy (or histology) can be aided by practical experience examining histological preparations (or slides) under a microscope.
Human anatomy, physiology and biochemistry are complementary basic medical sciences, which are generally taught to medical students in their first year at medical school. Human anatomy can be taught regionally or systemically; that is, respectively, studying anatomy by bodily regions such as the head and chest, or studying by specific systems, such as the nervous or respiratory systems. The major anatomy textbook, Gray's Anatomy, has recently been reorganized from a systems format to a regional format, in line with modern teaching methods. A thorough working knowledge of anatomy is required by physicians, especially surgeons and doctors working in some diagnostic specialties, such as histopathology and radiology.
Academic human anatomists are usually employed by universities, medical schools or teaching hospitals. They are often involved in teaching anatomy, and research into certain systems, organs, tissues or cells.
Invertebrate anatomy
Insect anatomy
Main article: Insect anatomyInsects possess segmented bodies supported by an exoskeleton, a hard-jointed outer covering made mostly of chitin. The segments of the body are organized into three distinct parts, a head, a thorax and an abdomen. The head typically bears a pair of sensory antennae, a pair of compound eyes, one to three simple eyes (ocelli) and three sets of modified appendages that form the mouthparts. The thorax has three pairs of segmented legs, one pair each for the three segments that compose the thorax and one or two pairs of wings. The abdomen is composed of eleven segments, some of which may be fused and houses the digestive, respiratory, excretory and reproductive systems. There is considerable variations between species and many adaptations to the body parts, especially wings, legs, antennae and mouthparts.
Plant anatomy
Main article: Plant anatomy| This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (October 2012) |
Plant anatomy involves the structure of the cells, in contrast to animal cells. Plant cells have cell walls, chlorophyll, and lack mitochondria. They also contain larger reservoirs called Lysosomes. Plant lack the digestive organs common among animals because they create their own energy from the sun, in photosynthesis. This makes them more independent and also a source of energy for other animals.
Other branches
- Comparative anatomy relates to the comparison of anatomical structures (both gross and microscopic) in different animals.
- Anthropological anatomy or physical anthropology relates to the comparison of the anatomy of different races of humans.
- Artistic anatomy relates to anatomic studies for artistic reasons.
History
Main article: History of anatomyAncient
Egypt
In 1600 BCE, the Edwin Smith Surgical Papyrus described the heart, its vessels, liver, spleen, kidneys, hypothalamus, uterus and bladder, and showed blood vessels from the heart. The Ebers Papyrus (c. 1550 BCE) features a treatise on the heart, with vessels carrying all the body's fluids to or from every member of the body.
Greece
The anatomy of the muscles and skeleton is described in the Hippocratic Corpus, written by unknown authors. Aristotle described vertebrate anatomy based on animal dissection.Praxagoras identified the difference between arteries and veins. Also in the 4th century BCE, Herophilos and Erasistratus produced more accurate anatomical descriptions based on vivisection of criminals in Alexandria during the Ptolemaic dynasty.
Galen
In the 2nd century, Galen wrote the final and highly influential anatomy treatise of ancient times. He compiled existing knowledge and studied organs through vivisection on animals. Galen's drawings, based mostly on dog anatomy, became effectively the only anatomy textbook for over a thousand years. His work was known to Renaissance doctors only through Islamic Golden Age medicine until it was translated from the Greek by 1500.
Early modern

Between 1275 and 1326, the anatomists Mondino de Luzzi, Alessandro Achillini and Antonio Benivieni at Bologna carried out the first systematic human dissections since ancient times. Mondino's Anatomy of 1316 was the first textbook in the mediaeval rediscovery of human anatomy. It describes the body in the order followed in Mondino's dissections, starting with the abdomen, then the thorax, then the head and limbs. It was the standard anatomy textbook for the next century.
Andreas Vesalius (1514–1564) (Latinized from Andries van Wezel), professor of anatomy at the University of Padua, is considered the founder of modern human anatomy. Originally from Brabant, Vesalius published the influential book De humani corporis fabrica ("the structure of the human body"), a large format book in seven volumes, in 1543. The accurate and intricately detailed illustrations, often in allegorical poses against Italianate landscapes, are thought to have been made by the artist Jan van Calcar, a pupil of Titian.
The artist Leonardo da Vinci (1452–1519) was trained in anatomy by Andrea del Verrocchio. He made use of his anatomical knowledge in his artwork, making many sketches of skeletal structures, muscles and organs of humans and other vertebrates which he dissected.
In England, anatomy was the subject of the first public lectures given in any science; these were given by the Company of Barbers and Surgeons in the sixteenth century, joined in 1583 by the Lumleian lectures in surgery at the Royal College of Physicians.
To obtain corpses for nineteenth century anatomy lessons, criminals known as 'Resurrectionists' resorted to body snatching, digging up newly-buried bodies from graveyards for sale to anatomists. Some graveyards were in consequence protected with watchtowers. The practice was halted in Britain by the Anatomy Act of 1832.
The teaching of anatomy in Britain was transformed by Sir John Struthers, Regius Professor of Anatomy at the University of Aberdeen from 1863 to 1889. He was responsible for setting up the system of three years of "pre-clinical" academic teaching in the sciences underlying medicine, including especially anatomy. This system lasted until the reform of medical training in 1993 and 2003. As well as teaching, he collected many vertebrate skeletons for his museum of Comparative anatomy, published over 70 research papers, and became famous for his public dissection of the Tay Whale.
19th century anatomy
Further information: History of anatomy in the 19th centuryDuring the 19th century, anatomical research was extended to include the histology and developmental biology of both humans and animals. Demand for bodies grew so great that body-snatching and even anatomy murder were practised to obtain cadavers. The British Parliament passed the Anatomy Act 1832, which finally provided for an adequate and legitimate supply of corpses by allowing dissection of destitutes. From 1822 the Royal College of Surgeons regulated the teaching of anatomy in medical schools. Medical museums provided examples in comparative anatomy, and were often used in teaching.
Modern anatomy
Anatomy in the twentieth century has taken advantage of technological developments and growing understanding of sciences such as evolutionary and molecular biology to create a thorough understanding of the body's organs and structures. Techniques including X-ray, magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography and Ultrasound imaging have enabled researchers and practitioners to examine organs, living or dead, in unprecedented detail.
See also
Human anatomy:
- Acland's Video Atlas of Human Anatomy
- List of human anatomical features
- List of human anatomical parts named after people
- Physiology
Associations
General anatomy
- Anatomical terms of location
- Bibliography of anatomy
- Body plan
- Foundational Model of Anatomy
- History of anatomy
- List of anatomical topics
- Superficial anatomy
Anatomy by taxon
Notes
- ^ "Introduction page, "Anatomy of the Human Body". Henry Gray. 20th edition. 1918". Archived from the original on 16 March 2007. Retrieved 19 March 2007.
- Marieb, Elaine (2010). Human Anatomy & Physiology. San Francisco: Pearson. p. 12.
- ^ Dorit, R. L.; Walker, W. F.; Barnes, R. D. (1991). Zoology. Saunders College Publishing. pp. 881–895. ISBN 978-0-03-030504-7.
- Dorit, R. L.; Walker, W. F.; Barnes, R. D. (1991). Zoology. Saunders College Publishing. p. 816. ISBN 978-0-03-030504-7.
- "Publisher's page for Gray's Anatomy. 39th edition (UK). 2004. ISBN 0-443-07168-3". Archived from the original on 12 October 2007. Retrieved 19 March 2007.
- "Publisher's page for Gray's Anatomy. 39th edition (US). 2004. ISBN 0-443-07168-3". Archived from the original on 9 February 2007. Retrieved 19 March 2007.
- "O. Orkin Insect zoo". Mississippi State University. 1997. Retrieved 23 June 2013.
- Gullan, P.J.; Cranston, P. S. (2005). The Insects: An Outline of Entomology (3 ed.). Oxford: Blackwell Publishing. pp. 22–48. ISBN 1-4051-1113-5.
- Ruppert, Edward E.; Fox, Richard, S.; Barnes, Robert D. (2004). Invertebrate Zoology, 7th edition. Cengage Learning. pp. 218–225. ISBN 81-315-0104-3.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Porter, R. (1997). The Greatest Benefit to Mankind: A Medical History of Humanity from Antiquity to the Present. Harper Collins. pp. 49–50. ISBN 0-00-215173-1.
- Gillispie, Charles Coulston (1972). Dictionary of Scientific Biography. Vol. VI. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons. pp. 419–427.
- "A milestone achievement for anatomy education". Premier Exhibitions. 2012. Retrieved 25 June 2013.
- Galen (1977). "Galen on the Affected Parts". Medical History. 21 (2): 212. PMC 1081972.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: PMC format (link) - Brock, Arthur John Brock (translator), Introduction. Galen. On the Natural Faculties. Edinburgh, 1916.
- ^ Boas, Marie (1970 (First published by Collins, 1962)). The Scientific Renaissance 1450-1630. Fontana. pp. 120–143.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|year=(help)CS1 maint: year (link) - Zimmerman, Leo M.; Veith, Ilza (1 August 1993). Great Ideas in the History of Surgery. Norman. ISBN 978-0-930-40553-3.
- Crombie, Alistair Cameron (1959). The History of Science From Augustine to Galileo. Courier Dover Publications. ISBN 9780486288505.
- Thorndike, Lynn (1958). A History of Magic and Experimental Science: Fourteenth and fifteenth centuries. Columbia University Press. ISBN 9780231087971.
- Vesalius, Andreas. De humani corporis fabrica libri septem. Basileae : Ex officina Joannis Oporini, 1543.
- O'Malley, C.D. Andreas Vesalius of Brussels, 1514-1564. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1964.
- Mason, Stephen F. (1962). A History of the Sciences. New York: Collier. p. 550.
- Boas, Marie (1970 (First published by Collins, 1962)). The Scientific Renaissance 1450-1630. Fontana. p. 229.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|year=(help)CS1 maint: year (link) - Richardson, Ruth (1989). Death, Dissection, and the Destitute. Penguin. ISBN 978-0-14022-862-5.
- Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 17373426, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=17373426instead. - Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 15712576, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=15712576instead. - Rosner, Lisa. 2010. The Anatomy Murders. Being the True and Spectacular History of Edinburgh's Notorious Burke and Hare and of the Man of Science Who Abetted Them in the Commission of Their Most Heinous Crimes. University of Pennsylvania Press
- Johnson, D.R. "Introductory Anatomy". University of Leeds. Retrieved 25 June 2013.
- McLachlan, J. & Patten, D. 2006. Anatomy teaching: ghosts of the past, present and future. Medical Education, 40(3), p.243-53.
- Reinarz, J. 2005. The age of museum medicine: The rise and fall of the medical museum at Birmingham's School of Medicine. Social History of Medicine, 18(3), p. 419-37.
- "Anatomical Imaging". McGraw Hill Higher Education. 1998. Retrieved 25 June 2013.
References
External links
Library resources aboutAnatomy
| Anatomy and morphology | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fields |  | |
| Bacteria and fungi | ||
| Protists | ||
| Plants | ||
| Invertebrates | ||
| Mammals | ||
| Other vertebrates | ||
| Glossaries | ||
| Related topics | ||
