| Revision as of 15:34, 29 September 2014 view sourcePgr94 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users4,993 edits Added representation learning in the learning section← Previous edit | Revision as of 16:21, 29 September 2014 view source FelixRosch (talk | contribs)1,353 edits Undid revision 627555106 by Pgr94 (talk) No reason given for addition of this link.Next edit → | ||
| Line 82: | Line 82: | ||
| ] discussed the centrality of learning as early as 1950, in his classic paper "]".{{Harv|Turing|1950}} In 1956, at the original Dartmouth AI summer conference, ] wrote a report on unsupervised probabilistic machine learning: "An Inductive Inference Machine". (version published in 1957, An Inductive Inference Machine," IRE Convention Record, Section on Information Theory, Part 2, pp. 56–62)</ref> | ] discussed the centrality of learning as early as 1950, in his classic paper "]".{{Harv|Turing|1950}} In 1956, at the original Dartmouth AI summer conference, ] wrote a report on unsupervised probabilistic machine learning: "An Inductive Inference Machine". (version published in 1957, An Inductive Inference Machine," IRE Convention Record, Section on Information Theory, Part 2, pp. 56–62)</ref> | ||
| ] is the ability to find patterns in a stream of input. ] includes both ] and numerical ]. Classification is used to determine what category something belongs in, after seeing a number of examples of things from several categories. Regression is the attempt to produce a function that describes the relationship between inputs and outputs and predicts how the outputs should change as the inputs change. In ]<ref name="Reinforcement learning"/> the agent is rewarded for good responses and punished for bad ones. These can be analyzed in terms of ], using concepts like ]. |
] is the ability to find patterns in a stream of input. ] includes both ] and numerical ]. Classification is used to determine what category something belongs in, after seeing a number of examples of things from several categories. Regression is the attempt to produce a function that describes the relationship between inputs and outputs and predicts how the outputs should change as the inputs change. In ]<ref name="Reinforcement learning"/> the agent is rewarded for good responses and punished for bad ones. These can be analyzed in terms of ], using concepts like ]. The mathematical analysis of machine learning algorithms and their performance is a branch of ] known as ].<ref name="Computational learning theory"/> | ||
| Within ], developmental learning approaches were elaborated for lifelong cumulative acquisition of repertoires of novel skills by a robot, through autonomous self-exploration and social interaction with human teachers, and using guidance mechanisms such as active learning, maturation, motor synergies, and imitation.<ref name="Weng01"> | Within ], developmental learning approaches were elaborated for lifelong cumulative acquisition of repertoires of novel skills by a robot, through autonomous self-exploration and social interaction with human teachers, and using guidance mechanisms such as active learning, maturation, motor synergies, and imitation.<ref name="Weng01"> | ||
Revision as of 16:21, 29 September 2014
"AI" redirects here. For other uses, see Ai and Artificial intelligence (disambiguation).Artificial intelligence (AI) is the intelligence exhibited by machines or software. It is an academic field of study which generally studies the goal of emulating human-like intelligence, though other variations of AI such as strong-AI and weak-AI are also studied. Major AI researchers and textbooks define this field as "the study and design of intelligent agents", where an intelligent agent is a system that perceives its environment and takes actions that maximize its chances of success. John McCarthy, who coined the term in 1955, defines it as "the science and engineering of making intelligent machines".
AI research is highly technical and specialised, and is deeply divided into subfields that often fail to communicate with each other. Some of the division is due to social and cultural factors: subfields have grown up around particular institutions and the work of individual researchers. AI research is also divided by several technical issues. Some subfields focus on the solution of specific problems. Others focus on one of several possible approaches or on the use of a particular tool or towards the accomplishment of particular applications.
The central problems (or goals) of AI research include reasoning, knowledge, planning, learning, natural language processing (communication), perception and the ability to move and manipulate objects. General intelligence is still among the field's long term goals. Currently popular approaches include statistical methods, computational intelligence and traditional symbolic AI. There are a large number of tools used in AI, including versions of search and mathematical optimization, logic, methods based on probability and economics, and many others. The AI field is interdisciplinary, in which a number of sciences and professions converge, including computer science, psychology, linguistics, philosophy and neuroscience, as well as other specialized field such as artificial psychology.
The field was founded on the claim that a central property of humans, intelligence—the sapience of Homo sapiens—"can be so precisely described that a machine can be made to simulate it." This raises philosophical issues about the nature of the mind and the ethics of creating artificial beings endowed with human-like intelligence, issues which have been addressed by myth, fiction and philosophy since antiquity. Artificial intelligence has been the subject of tremendous optimism but has also suffered stunning setbacks. Today it has become an essential part of the technology industry, providing the heavy lifting for many of the most challenging problems in computer science.
History
Main articles: History of artificial intelligence and Timeline of artificial intelligenceThinking machines and artificial beings appear in Greek myths, such as Talos of Crete, the bronze robot of Hephaestus, and Pygmalion's Galatea. Human likenesses believed to have intelligence were built in every major civilization: animated cult images were worshiped in Egypt and Greece and humanoid automatons were built by Yan Shi, Hero of Alexandria and Al-Jazari. It was also widely believed that artificial beings had been created by Jābir ibn Hayyān, Judah Loew and Paracelsus. By the 19th and 20th centuries, artificial beings had become a common feature in fiction, as in Mary Shelley's Frankenstein or Karel Čapek's R.U.R. (Rossum's Universal Robots). Pamela McCorduck argues that all of these are some examples of an ancient urge, as she describes it, "to forge the gods". Stories of these creatures and their fates discuss many of the same hopes, fears and ethical concerns that are presented by artificial intelligence.
Mechanical or "formal" reasoning has been developed by philosophers and mathematicians since antiquity. The study of logic led directly to the invention of the programmable digital electronic computer, based on the work of mathematician Alan Turing and others. Turing's theory of computation suggested that a machine, by shuffling symbols as simple as "0" and "1", could simulate any conceivable act of mathematical deduction. This, along with concurrent discoveries in neurology, information theory and cybernetics, inspired a small group of researchers to begin to seriously consider the possibility of building an electronic brain.
The field of AI research was founded at a conference on the campus of Dartmouth College in the summer of 1956. The attendees, including John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, Allen Newell and Herbert Simon, became the leaders of AI research for many decades. They and their students wrote programs that were, to most people, simply astonishing: computers were solving word problems in algebra, proving logical theorems and speaking English. By the middle of the 1960s, research in the U.S. was heavily funded by the Department of Defense and laboratories had been established around the world. AI's founders were profoundly optimistic about the future of the new field: Herbert Simon predicted that "machines will be capable, within twenty years, of doing any work a man can do" and Marvin Minsky agreed, writing that "within a generation ... the problem of creating 'artificial intelligence' will substantially be solved".
They had failed to recognize the difficulty of some of the problems they faced. In 1974, in response to the criticism of Sir James Lighthill and ongoing pressure from the US Congress to fund more productive projects, both the U.S. and British governments cut off all undirected exploratory research in AI. The next few years would later be called an "AI winter", a period when funding for AI projects was hard to find.
In the early 1980s, AI research was revived by the commercial success of expert systems, a form of AI program that simulated the knowledge and analytical skills of one or more human experts. By 1985 the market for AI had reached over a billion dollars. At the same time, Japan's fifth generation computer project inspired the U.S and British governments to restore funding for academic research in the field. However, beginning with the collapse of the Lisp Machine market in 1987, AI once again fell into disrepute, and a second, longer lasting AI winter began.
In the 1990s and early 21st century, AI achieved its greatest successes, albeit somewhat behind the scenes. Artificial intelligence is used for logistics, data mining, medical diagnosis and many other areas throughout the technology industry. The success was due to several factors: the increasing computational power of computers (see Moore's law), a greater emphasis on solving specific subproblems, the creation of new ties between AI and other fields working on similar problems, and a new commitment by researchers to solid mathematical methods and rigorous scientific standards.
On 11 May 1997, Deep Blue became the first computer chess-playing system to beat a reigning world chess champion, Garry Kasparov. In 2005, a Stanford robot won the DARPA Grand Challenge by driving autonomously for 131 miles along an unrehearsed desert trail. Two years later, a team from CMU won the DARPA Urban Challenge when their vehicle autonomously navigated 55 miles in an urban environment while adhering to traffic hazards and all traffic laws. In February 2011, in a Jeopardy! quiz show exhibition match, IBM's question answering system, Watson, defeated the two greatest Jeopardy champions, Brad Rutter and Ken Jennings, by a significant margin. The Kinect, which provides a 3D body–motion interface for the Xbox 360 and the Xbox One, uses algorithms that emerged from lengthy AI research as does the iPhone's Siri.
Goals
The general problem of simulating (or creating) intelligence has been broken down into a number of specific sub-problems. These consist of particular traits or capabilities that researchers would like an intelligent system to display. The traits described below have received the most attention.
Deduction, reasoning, problem solving
Early AI researchers developed algorithms that imitated the step-by-step reasoning that humans use when they solve puzzles or make logical deductions. By the late 1980s and 1990s, AI research had also developed highly successful methods for dealing with uncertain or incomplete information, employing concepts from probability and economics.
For difficult problems, most of these algorithms can require enormous computational resources – most experience a "combinatorial explosion": the amount of memory or computer time required becomes astronomical when the problem goes beyond a certain size. The search for more efficient problem-solving algorithms is a high priority for AI research.
Human beings solve most of their problems using fast, intuitive judgements rather than the conscious, step-by-step deduction that early AI research was able to model. AI has made some progress at imitating this kind of "sub-symbolic" problem solving: embodied agent approaches emphasize the importance of sensorimotor skills to higher reasoning; neural net research attempts to simulate the structures inside the brain that give rise to this skill; statistical approaches to AI mimic the probabilistic nature of the human ability to guess.
Knowledge representation

Knowledge representation and knowledge engineering are central to AI research. Many of the problems machines are expected to solve will require extensive knowledge about the world. Among the things that AI needs to represent are: objects, properties, categories and relations between objects; situations, events, states and time; causes and effects; knowledge about knowledge (what we know about what other people know); and many other, less well researched domains. A representation of "what exists" is an ontology: the set of objects, relations, concepts and so on that the machine knows about. The most general are called upper ontologies, which attempt to provide a foundation for all other knowledge.
Among the most difficult problems in knowledge representation are:
- Default reasoning and the qualification problem
- Many of the things people know take the form of "working assumptions." For example, if a bird comes up in conversation, people typically picture an animal that is fist sized, sings, and flies. None of these things are true about all birds. John McCarthy identified this problem in 1969 as the qualification problem: for any commonsense rule that AI researchers care to represent, there tend to be a huge number of exceptions. Almost nothing is simply true or false in the way that abstract logic requires. AI research has explored a number of solutions to this problem.
- The breadth of commonsense knowledge
- The number of atomic facts that the average person knows is astronomical. Research projects that attempt to build a complete knowledge base of commonsense knowledge (e.g., Cyc) require enormous amounts of laborious ontological engineering — they must be built, by hand, one complicated concept at a time. A major goal is to have the computer understand enough concepts to be able to learn by reading from sources like the internet, and thus be able to add to its own ontology.
- The subsymbolic form of some commonsense knowledge
- Much of what people know is not represented as "facts" or "statements" that they could express verbally. For example, a chess master will avoid a particular chess position because it "feels too exposed" or an art critic can take one look at a statue and instantly realize that it is a fake. These are intuitions or tendencies that are represented in the brain non-consciously and sub-symbolically. Knowledge like this informs, supports and provides a context for symbolic, conscious knowledge. As with the related problem of sub-symbolic reasoning, it is hoped that situated AI, computational intelligence, or statistical AI will provide ways to represent this kind of knowledge.
Planning
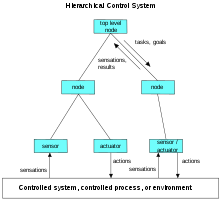
Intelligent agents must be able to set goals and achieve them. They need a way to visualize the future (they must have a representation of the state of the world and be able to make predictions about how their actions will change it) and be able to make choices that maximize the utility (or "value") of the available choices.
In classical planning problems, the agent can assume that it is the only thing acting on the world and it can be certain what the consequences of its actions may be. However, if the agent is not the only actor, it must periodically ascertain whether the world matches its predictions and it must change its plan as this becomes necessary, requiring the agent to reason under uncertainty.
Multi-agent planning uses the cooperation and competition of many agents to achieve a given goal. Emergent behavior such as this is used by evolutionary algorithms and swarm intelligence.
Learning
Main article: Machine learningMachine learning is the study of computer algorithms that improve automatically through experience and has been central to AI research since the field's inception.
Unsupervised learning is the ability to find patterns in a stream of input. Supervised learning includes both classification and numerical regression. Classification is used to determine what category something belongs in, after seeing a number of examples of things from several categories. Regression is the attempt to produce a function that describes the relationship between inputs and outputs and predicts how the outputs should change as the inputs change. In reinforcement learning the agent is rewarded for good responses and punished for bad ones. These can be analyzed in terms of decision theory, using concepts like utility. The mathematical analysis of machine learning algorithms and their performance is a branch of theoretical computer science known as computational learning theory.
Within developmental robotics, developmental learning approaches were elaborated for lifelong cumulative acquisition of repertoires of novel skills by a robot, through autonomous self-exploration and social interaction with human teachers, and using guidance mechanisms such as active learning, maturation, motor synergies, and imitation.
Natural language processing (communication)

Natural language processing gives machines the ability to read and understand the languages that humans speak. A sufficiently powerful natural language processing system would enable natural language user interfaces and the acquisition of knowledge directly from human-written sources, such as newswire texts. Some straightforward applications of natural language processing include information retrieval (or text mining) and machine translation.
A common method of processing and extracting meaning from natural language is through semantic indexing. Increases in processing speeds and the drop in the cost of data storage makes indexing large volumes of abstractions of the user's input much more efficient.
Perception
Main articles: Machine perception, Computer vision, and Speech recognitionMachine perception is the ability to use input from sensors (such as cameras, microphones, tactile sensors, sonar and others more exotic) to deduce aspects of the world. Computer vision is the ability to analyze visual input. A few selected subproblems are speech recognition, facial recognition and object recognition.
Motion and manipulation
Main article: RoboticsThe field of robotics is closely related to AI. Intelligence is required for robots to be able to handle such tasks as object manipulation and navigation, with sub-problems of localization (knowing where you are, or finding out where other things are), mapping (learning what is around you, building a map of the environment), and motion planning (figuring out how to get there) or path planning (going from one point in space to another point, which may involve compliant motion - where the robot moves while maintaining physical contact with an object).
Long-term goals
Among the long-term goals in the research pertaining to artificial intelligence are: (1) Social intelligence, (2) Creativity, and (3) General intelligence.
Social intelligence
Main article: Affective computing
Affective computing is the study and development of systems and devices that can recognize, interpret, process, and simulate human affects. It is an interdisciplinary field spanning computer sciences, psychology, and cognitive science. While the origins of the field may be traced as far back as to early philosophical inquiries into emotion, the more modern branch of computer science originated with Rosalind Picard's 1995 paper on affective computing. A motivation for the research is the ability to simulate empathy. The machine should interpret the emotional state of humans and adapt its behaviour to them, giving an appropriate response for those emotions.
Emotion and social skills play two roles for an intelligent agent. First, it must be able to predict the actions of others, by understanding their motives and emotional states. (This involves elements of game theory, decision theory, as well as the ability to model human emotions and the perceptual skills to detect emotions.) Also, in an effort to facilitate human-computer interaction, an intelligent machine might want to be able to display emotions—even if it does not actually experience them itself—in order to appear sensitive to the emotional dynamics of human interaction.
Creativity
Main article: Computational creativityA sub-field of AI addresses creativity both theoretically (from a philosophical and psychological perspective) and practically (via specific implementations of systems that generate outputs that can be considered creative, or systems that identify and assess creativity). Related areas of computational research are Artificial intuition and Artificial thinking.
General intelligence
Main articles: Artificial general intelligence and AI-completeMany researchers think that their work will eventually be incorporated into a machine with general intelligence (known as strong AI), combining all the skills above and exceeding human abilities at most or all of them. A few believe that anthropomorphic features like artificial consciousness or an artificial brain may be required for such a project.
Many of the problems above may require general intelligence to be considered solved. For example, even a straightforward, specific task like machine translation requires that the machine read and write in both languages (NLP), follow the author's argument (reason), know what is being talked about (knowledge), and faithfully reproduce the author's intention (social intelligence). A problem like machine translation is considered "AI-complete". In order to solve this particular problem, you must solve all the problems.
Approaches
There is no established unifying theory or paradigm that guides AI research. Researchers disagree about many issues. A few of the most long standing questions that have remained unanswered are these: should artificial intelligence simulate natural intelligence by studying psychology or neurology? Or is human biology as irrelevant to AI research as bird biology is to aeronautical engineering? Can intelligent behavior be described using simple, elegant principles (such as logic or optimization)? Or does it necessarily require solving a large number of completely unrelated problems? Can intelligence be reproduced using high-level symbols, similar to words and ideas? Or does it require "sub-symbolic" processing? John Haugeland, who coined the term GOFAI (Good Old-Fashioned Artificial Intelligence), also proposed that AI should more properly be referred to as synthetic intelligence, a term which has since been adopted by some non-GOFAI researchers.
Cybernetics and brain simulation
Main articles: Cybernetics and Computational neuroscienceIn the 1940s and 1950s, a number of researchers explored the connection between neurology, information theory, and cybernetics. Some of them built machines that used electronic networks to exhibit rudimentary intelligence, such as W. Grey Walter's turtles and the Johns Hopkins Beast. Many of these researchers gathered for meetings of the Teleological Society at Princeton University and the Ratio Club in England. By 1960, this approach was largely abandoned, although elements of it would be revived in the 1980s.
Symbolic
Main article: GOFAIWhen access to digital computers became possible in the middle 1950s, AI research began to explore the possibility that human intelligence could be reduced to symbol manipulation. The research was centered in three institutions: Carnegie Mellon University, Stanford and MIT, and each one developed its own style of research. John Haugeland named these approaches to AI "good old fashioned AI" or "GOFAI". During the 1960s, symbolic approaches had achieved great success at simulating high-level thinking in small demonstration programs. Approaches based on cybernetics or neural networks were abandoned or pushed into the background. Researchers in the 1960s and the 1970s were convinced that symbolic approaches would eventually succeed in creating a machine with artificial general intelligence and considered this the goal of their field.
- Cognitive simulation
- Economist Herbert Simon and Allen Newell studied human problem-solving skills and attempted to formalize them, and their work laid the foundations of the field of artificial intelligence, as well as cognitive science, operations research and management science. Their research team used the results of psychological experiments to develop programs that simulated the techniques that people used to solve problems. This tradition, centered at Carnegie Mellon University would eventually culminate in the development of the Soar architecture in the middle 1980s.
- Logic-based
- Unlike Newell and Simon, John McCarthy felt that machines did not need to simulate human thought, but should instead try to find the essence of abstract reasoning and problem solving, regardless of whether people used the same algorithms. His laboratory at Stanford (SAIL) focused on using formal logic to solve a wide variety of problems, including knowledge representation, planning and learning. Logic was also the focus of the work at the University of Edinburgh and elsewhere in Europe which led to the development of the programming language Prolog and the science of logic programming.
- "Anti-logic" or "scruffy"
- Researchers at MIT (such as Marvin Minsky and Seymour Papert) found that solving difficult problems in vision and natural language processing required ad-hoc solutions – they argued that there was no simple and general principle (like logic) that would capture all the aspects of intelligent behavior. Roger Schank described their "anti-logic" approaches as "scruffy" (as opposed to the "neat" paradigms at CMU and Stanford). Commonsense knowledge bases (such as Doug Lenat's Cyc) are an example of "scruffy" AI, since they must be built by hand, one complicated concept at a time.
- Knowledge-based
- When computers with large memories became available around 1970, researchers from all three traditions began to build knowledge into AI applications. This "knowledge revolution" led to the development and deployment of expert systems (introduced by Edward Feigenbaum), the first truly successful form of AI software. The knowledge revolution was also driven by the realization that enormous amounts of knowledge would be required by many simple AI applications.
Sub-symbolic
By the 1980s progress in symbolic AI seemed to stall and many believed that symbolic systems would never be able to imitate all the processes of human cognition, especially perception, robotics, learning and pattern recognition. A number of researchers began to look into "sub-symbolic" approaches to specific AI problems.
- Bottom-up, embodied, situated, behavior-based or nouvelle AI
- Researchers from the related field of robotics, such as Rodney Brooks, rejected symbolic AI and focused on the basic engineering problems that would allow robots to move and survive. Their work revived the non-symbolic viewpoint of the early cybernetics researchers of the 1950s and reintroduced the use of control theory in AI. This coincided with the development of the embodied mind thesis in the related field of cognitive science: the idea that aspects of the body (such as movement, perception and visualization) are required for higher intelligence.
- Computational intelligence
- Interest in neural networks and "connectionism" was revived by David Rumelhart and others in the middle 1980s. These and other sub-symbolic approaches, such as fuzzy systems and evolutionary computation, are now studied collectively by the emerging discipline of computational intelligence.
Statistical
In the 1990s, AI researchers developed sophisticated mathematical tools to solve specific subproblems. These tools are truly scientific, in the sense that their results are both measurable and verifiable, and they have been responsible for many of AI's recent successes. The shared mathematical language has also permitted a high level of collaboration with more established fields (like mathematics, economics or operations research). Stuart Russell and Peter Norvig describe this movement as nothing less than a "revolution" and "the victory of the neats." Critics argue that these techniques (with few exceptions) are too focused on particular problems and have failed to address the long term goal of general intelligence. There is an ongoing debate about the relevance and validity of statistical approaches in AI, exemplified in part by exchanges between Peter Norvig and Noam Chomsky.
Integrating the approaches
- Intelligent agent paradigm
- An intelligent agent is a system that perceives its environment and takes actions which maximize its chances of success. The simplest intelligent agents are programs that solve specific problems. More complicated agents include human beings and organizations of human beings (such as firms). The paradigm gives researchers license to study isolated problems and find solutions that are both verifiable and useful, without agreeing on one single approach. An agent that solves a specific problem can use any approach that works – some agents are symbolic and logical, some are sub-symbolic neural networks and others may use new approaches. The paradigm also gives researchers a common language to communicate with other fields—such as decision theory and economics—that also use concepts of abstract agents. The intelligent agent paradigm became widely accepted during the 1990s.
- Agent architectures and cognitive architectures
- Researchers have designed systems to build intelligent systems out of interacting intelligent agents in a multi-agent system. A system with both symbolic and sub-symbolic components is a hybrid intelligent system, and the study of such systems is artificial intelligence systems integration. A hierarchical control system provides a bridge between sub-symbolic AI at its lowest, reactive levels and traditional symbolic AI at its highest levels, where relaxed time constraints permit planning and world modelling. Rodney Brooks' subsumption architecture was an early proposal for such a hierarchical system.
Tools
In the course of 50 years of research, AI has developed a large number of tools to solve the most difficult problems in computer science. A few of the most general of these methods are discussed below.
Search and optimization
Main articles: Search algorithm, Mathematical optimization, and Evolutionary computationMany problems in AI can be solved in theory by intelligently searching through many possible solutions: Reasoning can be reduced to performing a search. For example, logical proof can be viewed as searching for a path that leads from premises to conclusions, where each step is the application of an inference rule. Planning algorithms search through trees of goals and subgoals, attempting to find a path to a target goal, a process called means-ends analysis. Robotics algorithms for moving limbs and grasping objects use local searches in configuration space. Many learning algorithms use search algorithms based on optimization.
Simple exhaustive searches are rarely sufficient for most real world problems: the search space (the number of places to search) quickly grows to astronomical numbers. The result is a search that is too slow or never completes. The solution, for many problems, is to use "heuristics" or "rules of thumb" that eliminate choices that are unlikely to lead to the goal (called "pruning the search tree"). Heuristics supply the program with a "best guess" for the path on which the solution lies. Heuristics limit the search for solutions into a smaller sample size.
A very different kind of search came to prominence in the 1990s, based on the mathematical theory of optimization. For many problems, it is possible to begin the search with some form of a guess and then refine the guess incrementally until no more refinements can be made. These algorithms can be visualized as blind hill climbing: we begin the search at a random point on the landscape, and then, by jumps or steps, we keep moving our guess uphill, until we reach the top. Other optimization algorithms are simulated annealing, beam search and random optimization.
Evolutionary computation uses a form of optimization search. For example, they may begin with a population of organisms (the guesses) and then allow them to mutate and recombine, selecting only the fittest to survive each generation (refining the guesses). Forms of evolutionary computation include swarm intelligence algorithms (such as ant colony or particle swarm optimization) and evolutionary algorithms (such as genetic algorithms, gene expression programming, and genetic programming).
Logic
Main articles: Logic programming and Automated reasoningLogic is used for knowledge representation and problem solving, but it can be applied to other problems as well. For example, the satplan algorithm uses logic for planning and inductive logic programming is a method for learning.
Several different forms of logic are used in AI research. Propositional or sentential logic is the logic of statements which can be true or false. First-order logic also allows the use of quantifiers and predicates, and can express facts about objects, their properties, and their relations with each other. Fuzzy logic, is a version of first-order logic which allows the truth of a statement to be represented as a value between 0 and 1, rather than simply True (1) or False (0). Fuzzy systems can be used for uncertain reasoning and have been widely used in modern industrial and consumer product control systems. Subjective logic models uncertainty in a different and more explicit manner than fuzzy-logic: a given binomial opinion satisfies belief + disbelief + uncertainty = 1 within a Beta distribution. By this method, ignorance can be distinguished from probabilistic statements that an agent makes with high confidence.
Default logics, non-monotonic logics and circumscription are forms of logic designed to help with default reasoning and the qualification problem. Several extensions of logic have been designed to handle specific domains of knowledge, such as: description logics; situation calculus, event calculus and fluent calculus (for representing events and time); causal calculus; belief calculus; and modal logics.
Probabilistic methods for uncertain reasoning
Main articles: Bayesian network, Hidden Markov model, Kalman filter, Decision theory, and Utility theoryMany problems in AI (in reasoning, planning, learning, perception and robotics) require the agent to operate with incomplete or uncertain information. AI researchers have devised a number of powerful tools to solve these problems using methods from probability theory and economics.
Bayesian networks are a very general tool that can be used for a large number of problems: reasoning (using the Bayesian inference algorithm), learning (using the expectation-maximization algorithm), planning (using decision networks) and perception (using dynamic Bayesian networks). Probabilistic algorithms can also be used for filtering, prediction, smoothing and finding explanations for streams of data, helping perception systems to analyze processes that occur over time (e.g., hidden Markov models or Kalman filters).
A key concept from the science of economics is "utility": a measure of how valuable something is to an intelligent agent. Precise mathematical tools have been developed that analyze how an agent can make choices and plan, using decision theory, decision analysis, and information value theory. These tools include models such as Markov decision processes, dynamic decision networks, game theory and mechanism design.
Classifiers and statistical learning methods
Main articles: Classifier (mathematics), Statistical classification, and Machine learningThe simplest AI applications can be divided into two types: classifiers ("if shiny then diamond") and controllers ("if shiny then pick up"). Controllers do however also classify conditions before inferring actions, and therefore classification forms a central part of many AI systems. Classifiers are functions that use pattern matching to determine a closest match. They can be tuned according to examples, making them very attractive for use in AI. These examples are known as observations or patterns. In supervised learning, each pattern belongs to a certain predefined class. A class can be seen as a decision that has to be made. All the observations combined with their class labels are known as a data set. When a new observation is received, that observation is classified based on previous experience.
A classifier can be trained in various ways; there are many statistical and machine learning approaches. The most widely used classifiers are the neural network, kernel methods such as the support vector machine, k-nearest neighbor algorithm, Gaussian mixture model, naive Bayes classifier, and decision tree. The performance of these classifiers have been compared over a wide range of tasks. Classifier performance depends greatly on the characteristics of the data to be classified. There is no single classifier that works best on all given problems; this is also referred to as the "no free lunch" theorem. Determining a suitable classifier for a given problem is still more an art than science.
Neural networks
Main articles: Neural network and Connectionism
The study of artificial neural networks began in the decade before the field AI research was founded, in the work of Walter Pitts and Warren McCullough. Other important early researchers were Frank Rosenblatt, who invented the perceptron and Paul Werbos who developed the backpropagation algorithm.
The main categories of networks are acyclic or feedforward neural networks (where the signal passes in only one direction) and recurrent neural networks (which allow feedback). Among the most popular feedforward networks are perceptrons, multi-layer perceptrons and radial basis networks. Among recurrent networks, the most famous is the Hopfield net, a form of attractor network, which was first described by John Hopfield in 1982. Neural networks can be applied to the problem of intelligent control (for robotics) or learning, using such techniques as Hebbian learning and competitive learning.
Hierarchical temporal memory is an approach that models some of the structural and algorithmic properties of the neocortex.
Control theory
Main article: Intelligent controlControl theory, the grandchild of cybernetics, has many important applications, especially in robotics.
Languages
Main article: List of programming languages for artificial intelligenceAI researchers have developed several specialized languages for AI research, including Lisp and Prolog.
Evaluating progress
Main article: Progress in artificial intelligenceIn 1950, Alan Turing proposed a general procedure to test the intelligence of an agent now known as the Turing test. This procedure allows almost all the major problems of artificial intelligence to be tested. However, it is a very difficult challenge and at present all agents fail.
Artificial intelligence can also be evaluated on specific problems such as small problems in chemistry, hand-writing recognition and game-playing. Such tests have been termed subject matter expert Turing tests. Smaller problems provide more achievable goals and there are an ever-increasing number of positive results.
One classification for outcomes of an AI test is:
- Optimal: it is not possible to perform better.
- Strong super-human: performs better than all humans.
- Super-human: performs better than most humans.
- Sub-human: performs worse than most humans.
For example, performance at draughts (i.e. checkers) is optimal, performance at chess is super-human and nearing strong super-human (see computer chess: computers versus human) and performance at many everyday tasks (such as recognizing a face or crossing a room without bumping into something) is sub-human.
A quite different approach measures machine intelligence through tests which are developed from mathematical definitions of intelligence. Examples of these kinds of tests start in the late nineties devising intelligence tests using notions from Kolmogorov complexity and data compression. Two major advantages of mathematical definitions are their applicability to nonhuman intelligences and their absence of a requirement for human testers.
A derivative of the Turing test is the Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart (CAPTCHA). as the name implies, this helps to determine that a user is an actual person and not a computer posing as a human. In contrast to the standard Turing test, CAPTCHA administered by a machine and targeted to a human as opposed to being administered by a human and targeted to a machine. A computer asks a user to complete a simple test then generates a grade for that test. Computers are unable to solve the problem, so correct solutions are deemed to be the result of a person taking the test. A common type of CAPTCHA is the test that requires the typing of distorted letters, numbers or symbols that appear in an image undecipherable by a computer.
Applications
| This section needs expansion. You can help by making an edit requestadding to it . (talk) (January 2011) |
Artificial intelligence techniques are pervasive and are too numerous to list. Frequently, when a technique reaches mainstream use, it is no longer considered artificial intelligence; this phenomenon is described as the AI effect. An area that artificial intelligence has contributed greatly to is intrusion detection.
Competitions and prizes
Main article: Competitions and prizes in artificial intelligenceThere are a number of competitions and prizes to promote research in artificial intelligence. The main areas promoted are: general machine intelligence, conversational behavior, data-mining, robotic cars, robot soccer and games.
Platforms
A platform (or "computing platform") is defined as "some sort of hardware architecture or software framework (including application frameworks), that allows software to run." As Rodney Brooks pointed out many years ago, it is not just the artificial intelligence software that defines the AI features of the platform, but rather the actual platform itself that affects the AI that results, i.e., there needs to be work in AI problems on real-world platforms rather than in isolation.
A wide variety of platforms has allowed different aspects of AI to develop, ranging from expert systems, albeit PC-based but still an entire real-world system, to various robot platforms such as the widely available Roomba with open interface.
Philosophy
Main article: Philosophy of artificial intelligenceArtificial intelligence, by claiming to be able to recreate the capabilities of the human mind, is both a challenge and an inspiration for philosophy. Are there limits to how intelligent machines can be? Is there an essential difference between human intelligence and artificial intelligence? Can a machine have a mind and consciousness? A few of the most influential answers to these questions are given below.
- Turing's "polite convention"
- We need not decide if a machine can "think"; we need only decide if a machine can act as intelligently as a human being. This approach to the philosophical problems associated with artificial intelligence forms the basis of the Turing test.
- The Dartmouth proposal
- "Every aspect of learning or any other feature of intelligence can be so precisely described that a machine can be made to simulate it." This conjecture was printed in the proposal for the Dartmouth Conference of 1956, and represents the position of most working AI researchers.
- Newell and Simon's physical symbol system hypothesis
- "A physical symbol system has the necessary and sufficient means of general intelligent action." Newell and Simon argue that intelligences consist of formal operations on symbols. Hubert Dreyfus argued that, on the contrary, human expertise depends on unconscious instinct rather than conscious symbol manipulation and on having a "feel" for the situation rather than explicit symbolic knowledge. (See Dreyfus' critique of AI.)
- Gödel's first incompleteness theorem
- John Lucas (in 1961) and Roger Penrose (in 1989) both argued that Gödel's theorem entails that artificial intelligence can never surpass human intelligence, because it shows there are propositions which a human being can prove but which can not be proved by a formal system. A system with a certain amount of arithmetic, cannot prove all true statements, as is possible in formal logic. Formal deductive logic is complete, but when a certain level of number theory is added, the total system becomes incomplete. This is true for a human thinker using these systems, or a computer program. (See Logical Options: An Introduction to Classical and Alternative Logics, Bell et alia, Broadview Press, 2001, pp. 164-65.) Computer languages take on the completeness/incompleteness of the reasoning system that they are used to represent. Although completeness/incompleteness is a very important characteristic of a reasoning system, incomplete systems can be very useful (such as modern mathematics), and the emulation of incomplete reasoning systems in computer code is a core part of artificial intelligence.
- Searle's strong AI hypothesis
- "The appropriately programmed computer with the right inputs and outputs would thereby have a mind in exactly the same sense human beings have minds." John Searle counters this assertion with his Chinese room argument, which asks us to look inside the computer and try to find where the "mind" might be.
- The artificial brain argument
- The brain can be simulated. Hans Moravec, Ray Kurzweil and others have argued that it is technologically feasible to copy the brain directly into hardware and software, and that such a simulation will be essentially identical to the original.
Predictions and ethics
Main articles: Ethics of artificial intelligence, Transhumanism, and Technological singularityMany thinkers have speculated about the future of artificial intelligence technology and society. The existence of an artificial intelligence that rivals or exceeds human intelligence raises difficult ethical issues, and the potential power of the technology inspires both hopes and fears.
If research into Strong AI produced sufficiently intelligent software, it might be able to reprogram and improve itself. The improved software would be even better at improving itself, leading to recursive self-improvement. The new intelligence could thus increase exponentially and dramatically surpass humans.
Hyper-intelligent software may not necessarily decide to support the continued existence of mankind, and would be extremely difficult to stop. This topic has also recently begun to be discussed in academic publications as a real source of risks to civilization, humans, and planet Earth.
One proposal to deal with this is to ensure that the first generally intelligent AI is 'Friendly AI', and will then be able to control subsequently developed AIs. Some question whether this kind of check could really remain in place.
Martin Ford, author of The Lights in the Tunnel: Automation, Accelerating Technology and the Economy of the Future, and others argue that specialized artificial intelligence applications, robotics and other forms of automation will ultimately result in significant unemployment as machines begin to match and exceed the capability of workers to perform most routine and repetitive jobs. Ford predicts that many knowledge-based occupations—and in particular entry level jobs—will be increasingly susceptible to automation via expert systems, machine learning and other AI-enhanced applications. AI-based applications may also be used to amplify the capabilities of low-wage offshore workers, making it more feasible to outsource knowledge work.
Joseph Weizenbaum wrote that AI applications can not, by definition, successfully simulate genuine human empathy and that the use of AI technology in fields such as customer service or psychotherapy was deeply misguided. Weizenbaum was also bothered that AI researchers (and some philosophers) were willing to view the human mind as nothing more than a computer program (a position now known as computationalism). To Weizenbaum these points suggest that AI research devalues human life.
Many futurists believe that artificial intelligence will ultimately transcend the limits of progress. Ray Kurzweil has used Moore's law (which describes the relentless exponential improvement in digital technology) to calculate that desktop computers will have the same processing power as human brains by the year 2029. He also predicts that by 2045 artificial intelligence will reach a point where it is able to improve itself at a rate that far exceeds anything conceivable in the past, a scenario that science fiction writer Vernor Vinge named the "singularity".
Robot designer Hans Moravec, cyberneticist Kevin Warwick and inventor Ray Kurzweil have predicted that humans and machines will merge in the future into cyborgs that are more capable and powerful than either. This idea, called transhumanism, which has roots in Aldous Huxley and Robert Ettinger, has been illustrated in fiction as well, for example in the manga Ghost in the Shell and the science-fiction series Dune. In the 1980s artist Hajime Sorayama's Sexy Robots series were painted and published in Japan depicting the actual organic human form with lifelike muscular metallic skins and later "the Gynoids" book followed that was used by or influenced movie makers including George Lucas and other creatives. Sorayama never considered these organic robots to be real part of nature but always unnatural product of the human mind, a fantasy existing in the mind even when realized in actual form. Almost 20 years later, the first AI robotic pet, AIBO, came available as a companion to people. AIBO grew out of Sony's Computer Science Laboratory (CSL). Famed engineer Toshitada Doi is credited as AIBO's original progenitor: in 1994 he had started work on robots with artificial intelligence expert Masahiro Fujita, at CSL. Doi's, friend, the artist Hajime Sorayama, was enlisted to create the initial designs for the AIBO's body. Those designs are now part of the permanent collections of Museum of Modern Art and the Smithsonian Institution, with later versions of AIBO being used in studies in Carnegie Mellon University. In 2006, AIBO was added into Carnegie Mellon University's "Robot Hall of Fame".
Political scientist Charles T. Rubin believes that AI can be neither designed nor guaranteed to be benevolent. He argues that "any sufficiently advanced benevolence may be indistinguishable from malevolence." Humans should not assume machines or robots would treat us favorably, because there is no a priori reason to believe that they would be sympathetic to our system of morality, which has evolved along with our particular biology (which AIs would not share).
Edward Fredkin argues that "artificial intelligence is the next stage in evolution", an idea first proposed by Samuel Butler's "Darwin among the Machines" (1863), and expanded upon by George Dyson in his book of the same name in 1998.
In fiction
Main article: Artificial intelligence in fictionThe implications of artificial intelligence have also been explored in fiction. Artificial Intelligences have appeared in many roles, including:
- Jarvis a personal assistant in Iron Man movies.
- a supercomputer named "ARIIA" in the movie "Eagle_Eye"
- a supercomputer named "VIKI" and a robot named "Sonny" in the movie "I,Robot"
- a robot boy named David in the movie "A.I. (and there were other robots that had Artificial intelligence in this movie.)"
- a real time battlefield analyst (Cortana in Halo: Combat Evolved, Halo 2, Halo 3, and Halo 4)
- a servant (R2-D2 and C-3PO in Star Wars)
- a law enforcer (K.I.T.T. "Knight Rider")
- a comrade (Lt. Commander Data in Star Trek: The Next Generation)
- a conqueror/overlord (The Matrix, Omnius)
- a dictator (With Folded Hands),(Colossus: The Forbin Project (1970 Movie)).
- a benevolent provider/de facto ruler (The Culture)
- a supercomputer (The Red Queen in Resident Evil / "Gilium" in Outlaw Star / Golem XIV)
- an assassin (Terminator)
- a sentient race (Battlestar Galactica/Transformers/Mass Effect)
- an extension to human abilities (Ghost in the Shell)
- the savior of the human race (R. Daneel Olivaw in Isaac Asimov's Robot series)
- the human race critic and philosopher (Golem XIV)
- a lover (e.g. Her (film))
- a host to real (usually deceased) human intelligence (e.g. Transcendence (2014 film))
- a supercomputer that detects planned terrorist attacks (Person of Interest)
- a spaceship vehicle that transports David through time (Flight of the Navigator)
Mary Shelley's Frankenstein considers a key issue in the ethics of artificial intelligence: if a machine can be created that has intelligence, could it also feel? If it can feel, does it have the same rights as a human? The idea also appears in modern science fiction, including the films I Robot, Blade Runner, The Machine and A.I.: Artificial Intelligence, in which humanoid machines have the ability to feel human emotions. This issue, now known as "robot rights", is currently being considered by, for example, California's Institute for the Future, although many critics believe that the discussion is premature. The subject is profoundly discussed in the 2010 documentary film Plug & Pray.
See also
Main article: Outline of artificial intelligence- Artificial Intelligence (journal)
- Artificial intelligence (video games)
- Computer Go
- Human Cognome Project
- List of artificial intelligence projects
- List of artificial intelligence researchers
- List of emerging technologies
- List of important artificial intelligence publications
- List of machine learning algorithms
- List of scientific journals
- Never-Ending Language Learning
- Our Final Invention
- Philosophy of mind
- Simulated reality
References
Notes
-
Definition of AI as the study of intelligent agents:
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, p. 1, which provides the version that is used in this article. Note that they use the term "computational intelligence" as a synonym for artificial intelligence.
- Russell & Norvig (2003) (who prefer the term "rational agent") and write "The whole-agent view is now widely accepted in the field" (Russell & Norvig 2003, p. 55).
- Nilsson 1998
- Legg & Hutter 2007, harvnb error: no target: CITEREFLeggHutter2007 (help).
- ^
The intelligent agent paradigm:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 27, 32–58, 968–972
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. 7–21
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 235–240
- Hutter 2005, pp. 125–126
- Although there is some controversy on this point (see Crevier (1993, p. 50)), McCarthy states unequivocally "I came up with the term" in a c|net interview. (Skillings 2006) McCarthy first used the term in the proposal for the Dartmouth conference, which appeared in 1955. (McCarthy et al. 1955)
- McCarthy's definition of AI:
- Pamela McCorduck (2004, pp. 424) writes of "the rough shattering of AI in subfields—vision, natural language, decision theory, genetic algorithms, robotics ... and these with own sub-subfield—that would hardly have anything to say to each other."
- ^ This list of intelligent traits is based on the topics covered by the major AI textbooks, including:
- ^ General intelligence (strong AI) is discussed in popular introductions to AI:
- See the Dartmouth proposal, under Philosophy, below.
- ^ This is a central idea of Pamela McCorduck's Machines Who Think. She writes: "I like to think of artificial intelligence as the scientific apotheosis of a venerable cultural tradition." (McCorduck 2004, p. 34) "Artificial intelligence in one form or another is an idea that has pervaded Western intellectual history, a dream in urgent need of being realized." (McCorduck 2004, p. xviii) "Our history is full of attempts—nutty, eerie, comical, earnest, legendary and real—to make artificial intelligences, to reproduce what is the essential us—bypassing the ordinary means. Back and forth between myth and reality, our imaginations supplying what our workshops couldn't, we have engaged for a long time in this odd form of self-reproduction." (McCorduck 2004, p. 3) She traces the desire back to its Hellenistic roots and calls it the urge to "forge the Gods." (McCorduck 2004, pp. 340–400)
- The optimism referred to includes the predictions of early AI researchers (see optimism in the history of AI) as well as the ideas of modern transhumanists such as Ray Kurzweil.
- The "setbacks" referred to include the ALPAC report of 1966, the abandonment of perceptrons in 1970, the Lighthill Report of 1973 and the collapse of the Lisp machine market in 1987.
- ^
AI applications widely used behind the scenes:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, p. 28
- Kurzweil 2005, p. 265
- NRC 1999, pp. 216–222
-
AI in myth:
- McCorduck 2004, pp. 4–5
- Russell & Norvig 2003, p. 939
-
Cult images as artificial intelligence:
- Crevier (1993, p. 1) (statue of Amun)
- McCorduck (2004, pp. 6–9)
-
Humanoid automata:
Yan Shi:- Needham 1986, p. 53
- McCorduck 2004, p. 6
- "A Thirteenth Century Programmable Robot". Shef.ac.uk. Retrieved 25 April 2009.
- McCorduck 2004, p. 17
-
Artificial beings:
Jābir ibn Hayyān's Takwin:- O'Connor, Kathleen Malone (1994). "The alchemical creation of life (takwin) and other concepts of Genesis in medieval Islam". University of Pennsylvania. Retrieved 10 January 2007.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Invalid|ref=harv(help)
- McCorduck 2004, pp. 15–16
- Buchanan 2005, p. 50
- McCorduck 2004, pp. 13–14
- O'Connor, Kathleen Malone (1994). "The alchemical creation of life (takwin) and other concepts of Genesis in medieval Islam". University of Pennsylvania. Retrieved 10 January 2007.
-
AI in early science fiction.
- McCorduck 2004, pp. 17–25
- This insight, that digital computers can simulate any process of formal reasoning, is known as the Church–Turing thesis.
-
Formal reasoning:
- Berlinski, David (2000). The Advent of the Algorithm. Harcourt Books. ISBN 0-15-601391-6. OCLC 46890682.
- ^
AI's immediate precursors:
- McCorduck 2004, pp. 51–107
- Crevier 1993, pp. 27–32
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 15, 940
- Moravec 1988, p. 3
-
Dartmouth conference:
- McCorduck 2004, pp. 111–136
- Crevier 1993, pp. 47–49, who writes "the conference is generally recognized as the official birthdate of the new science."
- Russell & Norvig 2003, p. 17, who call the conference "the birth of artificial intelligence."
- NRC 1999, pp. 200–201
-
Hegemony of the Dartmouth conference attendees:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, p. 17, who write "for the next 20 years the field would be dominated by these people and their students."
- McCorduck 2004, pp. 129–130
- Russell and Norvig write "it was astonishing whenever a computer did anything kind of smartish." Russell & Norvig 2003, p. 18
-
"Golden years" of AI (successful symbolic reasoning programs 1956–1973):
- McCorduck 2004, pp. 243–252
- Crevier 1993, pp. 52–107
- Moravec 1988, p. 9
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 18–21
-
DARPA pours money into undirected pure research into AI during the 1960s:
- McCorduck 2004, pp. 131
- Crevier 1993, pp. 51, 64–65
- NRC 1999, pp. 204–205
- AI in England:
-
Optimism of early AI:
- Herbert Simon quote: Simon 1965, p. 96 quoted in Crevier 1993, p. 109.
- Marvin Minsky quote: Minsky 1967, p. 2 quoted in Crevier 1993, p. 109.
- See History of artificial intelligence § The problems
-
First AI Winter, Mansfield Amendment, Lighthill report
- Crevier 1993, pp. 115–117
- Russell & Norvig 2003, p. 22
- NRC 1999, pp. 212–213
- Howe 1994
- ^
Expert systems:
- ACM 1998, I.2.1,
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 22–24
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 227–331,
- Nilsson 1998, chpt. 17.4
- McCorduck 2004, pp. 327–335, 434–435
- Crevier 1993, pp. 145–62, 197–203
-
Boom of the 1980s: rise of expert systems, Fifth Generation Project, Alvey, MCC, SCI:
- McCorduck 2004, pp. 426–441
- Crevier 1993, pp. 161–162, 197–203, 211, 240
- Russell & Norvig 2003, p. 24
- NRC 1999, pp. 210–211
-
Second AI winter:
- McCorduck 2004, pp. 430–435
- Crevier 1993, pp. 209–210
- NRC 1999, pp. 214–216
- ^
Formal methods are now preferred ("Victory of the neats"):
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 25–26
- McCorduck 2004, pp. 486–487
- McCorduck 2004, pp. 480–483
- DARPA Grand Challenge – home page
- "Welcome". Archive.darpa.mil. Retrieved 31 October 2011.
- Markoff, John (16 February 2011). "On 'Jeopardy!' Watson Win Is All but Trivial". The New York Times.
- Kinect's AI breakthrough explained
-
Problem solving, puzzle solving, game playing and deduction:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, chpt. 3–9,
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, chpt. 2,3,7,9,
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, chpt. 3,4,6,8,
- Nilsson 1998, chpt. 7–12
-
Uncertain reasoning:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 452–644,
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. 345–395,
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 333–381,
- Nilsson 1998, chpt. 19
-
Intractability and efficiency and the combinatorial explosion:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 9, 21–22
-
Psychological evidence of sub-symbolic reasoning:
- Wason & Shapiro (1966) showed that people do poorly on completely abstract problems, but if the problem is restated to allow the use of intuitive social intelligence, performance dramatically improves. (See Wason selection task)
- Kahneman, Slovic & Tversky (1982) have shown that people are terrible at elementary problems that involve uncertain reasoning. (See list of cognitive biases for several examples).
- Lakoff & Núñez (2000) have controversially argued that even our skills at mathematics depend on knowledge and skills that come from "the body", i.e. sensorimotor and perceptual skills. (See Where Mathematics Comes From)
-
Knowledge representation:
- ACM 1998, I.2.4,
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 320–363,
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. 23–46, 69–81, 169–196, 235–277, 281–298, 319–345,
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 227–243,
- Nilsson 1998, chpt. 18
-
Knowledge engineering:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 260–266,
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. 199–233,
- Nilsson 1998, chpt. ~17.1–17.4
- ^
Representing categories and relations: Semantic networks, description logics, inheritance (including frames and scripts):
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 349–354,
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. 174–177,
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 248–258,
- Nilsson 1998, chpt. 18.3
- ^
Representing events and time:Situation calculus, event calculus, fluent calculus (including solving the frame problem):
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 328–341,
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. 281–298,
- Nilsson 1998, chpt. 18.2
- ^
Causal calculus:
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. 335–337
- ^
Representing knowledge about knowledge: Belief calculus, modal logics:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 341–344,
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. 275–277
-
Ontology:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 320–328
- Qualification problem: While McCarthy was primarily concerned with issues in the logical representation of actions, Russell & Norvig 2003 apply the term to the more general issue of default reasoning in the vast network of assumptions underlying all our commonsense knowledge.
- ^
Default reasoning and default logic, non-monotonic logics, circumscription, closed world assumption, abduction (Poole et al. places abduction under "default reasoning". Luger et al. places this under "uncertain reasoning"):
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 354–360,
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. 248–256, 323–335,
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 335–363,
- Nilsson 1998, ~18.3.3
-
Breadth of commonsense knowledge:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, p. 21,
- Crevier 1993, pp. 113–114,
- Moravec 1988, p. 13,
- Lenat & Guha 1989 (Introduction)
- Dreyfus & Dreyfus 1986
- Gladwell 2005
- ^
Expert knowledge as embodied intuition:
- Dreyfus & Dreyfus 1986 (Hubert Dreyfus is a philosopher and critic of AI who was among the first to argue that most useful human knowledge was encoded sub-symbolically. See Dreyfus' critique of AI)
- Gladwell 2005 (Gladwell's Blink is a popular introduction to sub-symbolic reasoning and knowledge.)
- Hawkins & Blakeslee 2005 (Hawkins argues that sub-symbolic knowledge should be the primary focus of AI research.)
Note, however, that recent work in cognitive science challenges the view that there is anything like sub-symbolic human information processing, i.e., human cognition is essentially symbolic regardless of the level and of the consciousness status of the processing:- Augusto, Luis M. (2013). "Unconscious representations 1: Belying the traditional model of human cognition". Axiomathes. doi:10.1007/s10516-012-9206-z.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Augusto, Luis M. (2013). "Unconscious representations 2: Towards an integrated cognitive architecture". Axiomathes. doi:10.1007/s10516-012-9207-y.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)
-
Planning:
- ACM 1998, ~I.2.8,
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 375–459,
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. 281–316,
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 314–329,
- Nilsson 1998, chpt. 10.1–2, 22
- ^
Information value theory:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 600–604
-
Classical planning:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 375–430,
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. 281–315,
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 314–329,
- Nilsson 1998, chpt. 10.1–2, 22
-
Planning and acting in non-deterministic domains: conditional planning, execution monitoring, replanning and continuous planning:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 430–449
-
Multi-agent planning and emergent behavior:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 449–455
- This is a form of Tom Mitchell's widely quoted definition of machine learning: "A computer program is set to learn from an experience E with respect to some task T and some performance measure P if its performance on T as measured by P improves with experience E."
-
Learning:
- ACM 1998, I.2.6,
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 649–788,
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. 397–438,
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 385–542,
- Nilsson 1998, chpt. 3.3, 10.3, 17.5, 20
- Alan Turing discussed the centrality of learning as early as 1950, in his classic paper "Computing Machinery and Intelligence".(Turing 1950) In 1956, at the original Dartmouth AI summer conference, Ray Solomonoff wrote a report on unsupervised probabilistic machine learning: "An Inductive Inference Machine".(pdf scanned copy of the original) (version published in 1957, An Inductive Inference Machine," IRE Convention Record, Section on Information Theory, Part 2, pp. 56–62)
-
Reinforcement learning:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 763–788
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 442–449
-
Computational learning theory:
- CITATION IN PROGRESS.
- Weng, J., McClelland, Pentland, A.,Sporns, O., Stockman, I., Sur, M., and E. Thelen (2001) "Autonomous mental development by robots and animals", Science, vol. 291, pp. 599–600.
- Lungarella, M.; Metta, G.; Pfeifer, R.; Sandini, G. (2003). "Developmental robotics: a survey". Connection Science. 15: 151–190. CiteSeer: 10.1.1.83.7615.
- Asada, M., Hosoda, K., Kuniyoshi, Y., Ishiguro, H., Inui, T., Yoshikawa, Y., Ogino, M. and C. Yoshida (2009) "Cognitive developmental robotics: a survey". IEEE Transactions on Autonomous Mental Development, Vol.1, No.1, pp.12--34.
- Oudeyer, P-Y. (2010) "On the impact of robotics in behavioral and cognitive sciences: from insect navigation to human cognitive development", IEEE Transactions on Autonomous Mental Development, 2(1), pp. 2--16.
-
Natural language processing:
- ACM 1998, I.2.7
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 790–831
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. 91–104
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 591–632
-
Applications of natural language processing, including information retrieval (i.e. text mining) and machine translation:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 840–857,
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 623–630
-
Machine perception:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 537–581, 863–898
- Nilsson 1998, ~chpt. 6
-
Computer vision:
- ACM 1998, I.2.10
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 863–898
- Nilsson 1998, chpt. 6
-
Speech recognition:
- ACM 1998, ~I.2.7
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 568–578
-
Object recognition:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 885–892
-
Robotics:
- ACM 1998, I.2.9,
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 901–942,
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. 443–460
- ^
Moving and configuration space:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 916–932
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1002/wics.200, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1002/wics.200instead. -
Robotic mapping (localization, etc):
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 908–915
- "Kismet". MIT Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, Humanoid Robotics Group.
- Thro, Ellen (1993). Robotics. New York.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Edelson, Edward (1991). The Nervous System. New York: Remmel Nunn.
- Tao, Jianhua; Tieniu Tan (2005). "Affective Computing: A Review". Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction. Vol. LNCS 3784. Springer. pp. 981–995. doi:10.1007/11573548.
{{cite conference}}: Unknown parameter|booktitle=ignored (|book-title=suggested) (help) - James, William (1884). "What is Emotion". Mind. 9: 188–205. doi:10.1093/mind/os-IX.34.188. Cited by Tao and Tan.
- "Affective Computing" MIT Technical Report #321 (Abstract), 1995
-
Kleine-Cosack, Christian (October 2006). "Recognition and Simulation of Emotions" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 May 2008. Retrieved 13 May 2008.
The introduction of emotion to computer science was done by Pickard (sic) who created the field of affective computing.
-
Diamond, David (December 2003). "The Love Machine; Building computers that care". Wired. Archived from the original on 18 May 2008. Retrieved 13 May 2008.
Rosalind Picard, a genial MIT professor, is the field's godmother; her 1997 book, Affective Computing, triggered an explosion of interest in the emotional side of computers and their users.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - Emotion and affective computing:
- Gerald Edelman, Igor Aleksander and others have both argued that artificial consciousness is required for strong AI. (Aleksander 1995; Edelman 2007)
- ^
Artificial brain arguments: AI requires a simulation of the operation of the human brain
- Russell & Norvig 2003, p. 957
- Crevier 1993, pp. 271 and 279
- AI complete: Shapiro 1992, p. 9
- Nils Nilsson writes: "Simply put, there is wide disagreement in the field about what AI is all about" (Nilsson 1983, p. 10).
- ^
Biological intelligence vs. intelligence in general:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 2–3, who make the analogy with aeronautical engineering.
- McCorduck 2004, pp. 100–101, who writes that there are "two major branches of artificial intelligence: one aimed at producing intelligent behavior regardless of how it was accomplioshed, and the other aimed at modeling intelligent processes found in nature, particularly human ones."
- Kolata 1982, a paper in Science, which describes McCathy's indifference to biological models. Kolata quotes McCarthy as writing: "This is AI, so we don't care if it's psychologically real". McCarthy recently reiterated his position at the AI@50 conference where he said "Artificial intelligence is not, by definition, simulation of human intelligence" (Maker 2006).
- ^
Neats vs. scruffies:
- McCorduck 2004, pp. 421–424, 486–489
- Crevier 1993, pp. 168
- Nilsson 1983, pp. 10–11
- ^
Symbolic vs. sub-symbolic AI:
- Nilsson (1998, p. 7), who uses the term "sub-symbolic".
- Haugeland 1985, p. 255.
- http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.38.8384&rep=rep1&type=pdf
- Pei Wang (2008). Artificial general intelligence, 2008: proceedings of the First AGI Conference. IOS Press. p. 63. ISBN 978-1-58603-833-5. Retrieved 31 October 2011.
- Haugeland 1985, pp. 112–117
- The most dramatic case of sub-symbolic AI being pushed into the background was the devastating critique of perceptrons by Marvin Minsky and Seymour Papert in 1969. See History of AI, AI winter, or Frank Rosenblatt.
-
Cognitive simulation, Newell and Simon, AI at CMU (then called Carnegie Tech):
- McCorduck 2004, pp. 139–179, 245–250, 322–323 (EPAM)
- Crevier 1993, pp. 145–149
-
Soar (history):
- McCorduck 2004, pp. 450–451
- Crevier 1993, pp. 258–263
-
McCarthy and AI research at SAIL and SRI International:
- McCorduck 2004, pp. 251–259
- Crevier 1993
-
AI research at Edinburgh and in France, birth of Prolog:
- Crevier 1993, pp. 193–196
- Howe 1994
-
AI at MIT under Marvin Minsky in the 1960s :
- McCorduck 2004, pp. 259–305
- Crevier 1993, pp. 83–102, 163–176
- Russell & Norvig 2003, p. 19
-
Cyc:
- McCorduck 2004, p. 489, who calls it "a determinedly scruffy enterprise"
- Crevier 1993, pp. 239–243
- Russell & Norvig 2003, p. 363−365
- Lenat & Guha 1989
-
Knowledge revolution:
- McCorduck 2004, pp. 266–276, 298–300, 314, 421
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 22–23
-
Embodied approaches to AI:
- McCorduck 2004, pp. 454–462
- Brooks 1990
- Moravec 1988
-
Revival of connectionism:
- Crevier 1993, pp. 214–215
- Russell & Norvig 2003, p. 25
- Computational intelligence
- Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.2991/978-94-91216-62-6_5, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.2991/978-94-91216-62-6_5instead. - Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1007/s10994-011-5242-y, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1007/s10994-011-5242-yinstead. - Yarden Katz, "Noam Chomsky on Where Artificial Intelligence Went Wrong", The Atlantic, November 1, 2012
- Peter Norvig, "On Chomsky and the Two Cultures of Statistical Learning"
-
Agent architectures, hybrid intelligent systems:
- Russell & Norvig (2003, pp. 27, 932, 970–972)
- Nilsson (1998, chpt. 25)
-
Hierarchical control system:
- Albus, J. S. 4-D/RCS reference model architecture for unmanned ground vehicles. In G Gerhart, R Gunderson, and C Shoemaker, editors, Proceedings of the SPIE AeroSense Session on Unmanned Ground Vehicle Technology, volume 3693, pages 11—20
-
Subsumption architecture:
- CITATION IN PROGRESS.
-
Search algorithms:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 59–189
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. 113–163
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 79–164, 193–219
- Nilsson 1998, chpt. 7–12
-
Forward chaining, backward chaining, Horn clauses, and logical deduction as search:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 217–225, 280–294
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. ~46–52
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 62–73
- Nilsson 1998, chpt. 4.2, 7.2
-
State space search and planning:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 382–387
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. 298–305
- Nilsson 1998, chpt. 10.1–2
-
Uninformed searches (breadth first search, depth first search and general state space search):
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 59–93
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. 113–132
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 79–121
- Nilsson 1998, chpt. 8
-
Heuristic or informed searches (e.g., greedy best first and A*):
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 94–109,
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. pp. 132–147,
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 133–150,
- Nilsson 1998, chpt. 9
-
Optimization searches:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 110–116, 120–129
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. 56–163
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 127–133
-
Artificial life and society based learning:
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 530–541
-
Genetic programming and genetic algorithms:
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 509–530,
- Nilsson 1998, chpt. 4.2.
- Holland, John H. (1975). Adaptation in Natural and Artificial Systems. University of Michigan Press. ISBN 0-262-58111-6.
- Koza, John R. (1992). Genetic Programming (On the Programming of Computers by Means of Natural Selection). MIT Press. ISBN 0-262-11170-5.
- Poli, R., Langdon, W. B., McPhee, N. F. (2008). A Field Guide to Genetic Programming. Lulu.com, freely available from http://www.gp-field-guide.org.uk/. ISBN 978-1-4092-0073-4.
{{cite book}}: External link in|publisher=
-
Logic:
- ACM 1998, ~I.2.3,
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 194–310,
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 35–77,
- Nilsson 1998, chpt. 13–16
-
Satplan:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 402–407,
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. 300–301,
- Nilsson 1998, chpt. 21
-
Explanation based learning, relevance based learning, inductive logic programming, case based reasoning:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 678–710,
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. 414–416,
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. ~422–442,
- Nilsson 1998, chpt. 10.3, 17.5
-
Propositional logic:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 204–233,
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 45–50
- Nilsson 1998, chpt. 13
-
First-order logic and features such as equality:
- ACM 1998, ~I.2.4,
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 240–310,
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. 268–275,
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 50–62,
- Nilsson 1998, chpt. 15
-
Fuzzy logic:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 526–527
-
Subjective logic:
- CITATION IN PROGRESS.
-
Stochastic methods for uncertain reasoning:
- ACM 1998, ~I.2.3,
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 462–644,
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. 345–395,
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 165–191, 333–381,
- Nilsson 1998, chpt. 19
-
Bayesian networks:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 492–523,
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. 361–381,
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. ~182–190, ~363–379,
- Nilsson 1998, chpt. 19.3–4
-
Bayesian inference algorithm:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 504–519,
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. 361–381,
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. ~363–379,
- Nilsson 1998, chpt. 19.4 & 7
-
Bayesian learning and the expectation-maximization algorithm:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 712–724,
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. 424–433,
- Nilsson 1998, chpt. 20
-
Bayesian decision theory and Bayesian decision networks:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 597–600
- ^
Stochastic temporal models:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 537–581
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 551–557
- (Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 549–551)
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 551–557
-
decision theory and decision analysis:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 584–597,
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. 381–394
-
Markov decision processes and dynamic decision networks:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 613–631
-
Game theory and mechanism design:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 631–643
-
Statistical learning methods and classifiers:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 712–754,
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 453–541
- ^
Neural networks and connectionism:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 736–748,
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. 408–414,
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 453–505,
- Nilsson 1998, chpt. 3
-
kernel methods such as the support vector machine,
Kernel methods:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 749–752
-
K-nearest neighbor algorithm:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 733–736
-
Gaussian mixture model:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 725–727
-
Naive Bayes classifier:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 718
-
Decision tree:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 653–664,
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. 403–408,
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 408–417
- Classifier performance:
-
Backpropagation:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 744–748,
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 467–474,
- Nilsson 1998, chpt. 3.3
-
Feedforward neural networks, perceptrons and radial basis networks:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 739–748, 758
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 458–467
-
Recurrent neural networks, Hopfield nets:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, p. 758
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 474–505
-
Competitive learning, Hebbian coincidence learning, Hopfield networks and attractor networks:
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 474–505
- Hierarchical temporal memory:
-
Control theory:
- ACM 1998, ~I.2.8,
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 926–932
-
Lisp:
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 723–821
- Crevier 1993, pp. 59–62,
- Russell & Norvig 2003, p. 18
-
Prolog:
- Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. 477–491,
- Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 641–676, 575–581
- ^
The Turing test:
Turing's original publication: Historical influence and philosophical implications:- Haugeland 1985, pp. 6–9
- Crevier 1993, p. 24
- McCorduck 2004, pp. 70–71
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 2–3 and 948
-
Subject matter expert Turing test:
- CITATION IN PROGRESS.
- Rajani, Sandeep (2011). "Artificial Intelligence - Man or Machine" (PDF). International Journal of Information Technology and Knowlede Management. 4 (1): 173–176. Retrieved 24 September 2012.
-
Game AI:
- CITATION IN PROGRESS.
-
Mathematical definitions of intelligence:
- Jose Hernandez-Orallo (2000). "Beyond the Turing Test". Journal of Logic, Language and Information. 9 (4): 447–466. doi:10.1023/A:1008367325700. CiteSeer: 10.1.1.44.8943.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Invalid|ref=harv(help) - D L Dowe and A R Hajek (1997). "A computational extension to the Turing Test". Proceedings of the 4th Conference of the Australasian Cognitive Science jSociety. Retrieved 21 July 2009.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - J Hernandez-Orallo and D L Dowe (2010). "Measuring Universal Intelligence: Towards an Anytime Intelligence Test". Artificial Intelligence Journal. 174 (18): 1508–1539. doi:10.1016/j.artint.2010.09.006.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Invalid|ref=harv(help)
- Jose Hernandez-Orallo (2000). "Beyond the Turing Test". Journal of Logic, Language and Information. 9 (4): 447–466. doi:10.1023/A:1008367325700. CiteSeer: 10.1.1.44.8943.
- O'Brien and Marakas, 2011, Management Information Systems 10th ed.
-
"AI set to exceed human brain power". CNN. 26 July 2006. Archived from the original (web article) on 19 February 2008. Retrieved 26 February 2008.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) -
- Kumar 2012 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFKumar2012 (help)
- Brooks, R.A., "How to build complete creatures rather than isolated cognitive simulators," in K. VanLehn (ed.), Architectures for Intelligence, pp. 225–239, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Hillsdale, NJ, 1991.
- Hacking Roomba » Search Results » atmel
-
Philosophy of AI. All of these positions in this section are mentioned in standard discussions of the subject, such as:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 947–960
- Fearn 2007, pp. 38–55
-
Dartmouth proposal:
- McCarthy et al. 1955 (the original proposal)
- Crevier 1993, p. 49 (historical significance)
-
The physical symbol systems hypothesis:
- Newell & Simon 1976, p. 116
- McCorduck 2004, p. 153
- Russell & Norvig 2003, p. 18
- Dreyfus criticized the necessary condition of the physical symbol system hypothesis, which he called the "psychological assumption": "The mind can be viewed as a device operating on bits of information according to formal rules". (Dreyfus 1992, p. 156)
-
Dreyfus' critique of artificial intelligence:
- Dreyfus 1972, Dreyfus & Dreyfus 1986
- Crevier 1993, pp. 120–132
- McCorduck 2004, pp. 211–239
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 950–952,
-
The Mathematical Objection:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, p. 949
- McCorduck 2004, pp. 448–449
- Turing 1950 under "(2) The Mathematical Objection"
- Hofstadter 1979
- Gödel 1931, Church 1936, Kleene 1935, Turing 1937
- This version is from Searle (1999), and is also quoted in Dennett 1991, p. 435. Searle's original formulation was "The appropriately programmed computer really is a mind, in the sense that computers given the right programs can be literally said to understand and have other cognitive states." (Searle 1980, p. 1). Strong AI is defined similarly by Russell & Norvig (2003, p. 947): "The assertion that machines could possibly act intelligently (or, perhaps better, act as if they were intelligent) is called the 'weak AI' hypothesis by philosophers, and the assertion that machines that do so are actually thinking (as opposed to simulating thinking) is called the 'strong AI' hypothesis."
-
Searle's Chinese room argument:
- Searle 1980. Searle's original presentation of the thought experiment.
- Searle 1999.
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 958–960
- McCorduck 2004, pp. 443–445
- Crevier 1993, pp. 269–271
- Omohundro, Steve (2008). The Nature of Self-Improving Artificial Intelligence. presented and distributed at the 2007 Singularity Summit, San Francisco, CA.
- Ford, Martin R. (2009), The Lights in the Tunnel: Automation, Accelerating Technology and the Economy of the Future, Acculant Publishing, ISBN 978-1448659814.
- "Machine Learning: A Job Killer?"
-
AI could decrease the demand for human labor:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 960–961
- Ford, Martin (2009). The Lights in the Tunnel: Automation, Accelerating Technology and the Economy of the Future. Acculant Publishing. ISBN 978-1-4486-5981-4.
- In the early 1970s, Kenneth Colby presented a version of Weizenbaum's ELIZA known as DOCTOR which he promoted as a serious therapeutic tool. (Crevier 1993, pp. 132–144)
-
Joseph Weizenbaum's critique of AI:
- Weizenbaum 1976
- Crevier 1993, pp. 132–144
- McCorduck 2004, pp. 356–373
- Russell & Norvig 2003, p. 961
- Technological singularity:
- Transhumanism:
- Rubin, Charles (Spring 2003). "Artificial Intelligence and Human Nature". The New Atlantis. 1: 88–100.
-
AI as evolution:
- Edward Fredkin is quoted in McCorduck (2004, p. 401).
- Butler, Samuel. the Press. Christchurch, New Zealand http://www.nzetc.org/tm/scholarly/tei-ButFir-t1-g1-t1-g1-t4-body.htmlTemplate:Inconsistent citations
{{cite news}}:|contribution=ignored (help); Invalid|ref=harv(help); Missing or empty|title=(help)CS1 maint: postscript (link), Letter to the Editor. - Dyson, George (1998). Darwin among the Machines. Allan Lane Science. ISBN 0-7382-0030-1.
-
Robot rights:
- Russell & Norvig 2003, p. 964
- "Robots could demand legal rights". BBC News. 21 December 2006. Retrieved 3 February 2011.
- Henderson, Mark (24 April 2007). "Human rights for robots? We're getting carried away". The Times Online. London.
- McCorduck (2004, p. 190-25) discusses Frankenstein and identifies the key ethical issues as scientific hubris and the suffering of the monster, i.e. robot rights.
- Independent documentary Plug & Pray, featuring Joseph Weizenbaum and Raymond Kurzweil
References
AI textbooks
- Hutter, Marcus (2005). Universal Artificial Intelligence. Berlin: Springer. ISBN 978-3-540-22139-5.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Luger, George; Stubblefield, William (2004). Artificial Intelligence: Structures and Strategies for Complex Problem Solving (5th ed.). The Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Company, Inc. ISBN 0-8053-4780-1.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Neapolitan, Richard; Jiang, Xia (2012). Contemporary Artificial Intelligence. Chapman & Hall/CRC. ISBN 978-1-4398-4469-4.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Nilsson, Nils (1998). Artificial Intelligence: A New Synthesis. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers. ISBN 978-1-55860-467-4.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Russell, Stuart J.; Norvig, Peter (2003), Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach (2nd ed.), Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Prentice Hall, ISBN 0-13-790395-2
- Poole, David; Mackworth, Alan; Goebel, Randy (1998). Computational Intelligence: A Logical Approach. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-510270-3.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Winston, Patrick Henry (1984). Artificial Intelligence. Reading, Massachusetts: Addison-Wesley. ISBN 0-201-08259-4.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Rich, Elaine (1983). Artificial Intelligence. McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-052261-8.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)
History of AI
- Crevier, Daniel (1993). AI: The Tumultuous Search for Artificial Intelligence. New York, NY: BasicBooks. ISBN 0-465-02997-3.
- McCorduck, Pamela (2004), Machines Who Think (2nd ed.), Natick, Massachusetts: A. K. Peters, ISBN 1-5688-1205-1
- Nilsson, Nils (2010), The Quest for Artificial Intelligence: A History of Ideas and Achievements, New York: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-12293-1
Other sources
- "ACM Computing Classification System: Artificial intelligence". ACM. 1998. Retrieved 30 August 2007.
- Aleksander, Igor (1995). Artificial Neuroconsciousness: An Update. IWANN. Archived from the original on 2 March 1997.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) BibTex Archived 1997-03-02 at the Wayback Machine - Brooks, Rodney (1990). "Elephants Don't Play Chess" (PDF). Robotics and Autonomous Systems. 6: 3–15. doi:10.1016/S0921-8890(05)80025-9. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 August 2007. Retrieved 30 August 2007.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help). - Buchanan, Bruce G. (2005). "A (Very) Brief History of Artificial Intelligence" (PDF). AI Magazine: 53–60. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 September 2007. Retrieved 30 August 2007.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - Dennett, Daniel (1991). Consciousness Explained. The Penguin Press. ISBN 0-7139-9037-6.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Dreyfus, Hubert (1972). What Computers Can't Do. New York: MIT Press. ISBN 0-06-011082-1.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Dreyfus, Hubert (1979). What Computers Still Can't Do. New York: MIT Press. ISBN 0-262-04134-0.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Dreyfus, Hubert; Dreyfus, Stuart (1986). Mind over Machine: The Power of Human Intuition and Expertise in the Era of the Computer. Oxford, UK: Blackwell. ISBN 0-02-908060-6.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Dreyfus, Hubert (1992). What Computers Still Can't Do. New York: MIT Press. ISBN 0-262-54067-3.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Edelman, Gerald (23 November 2007). "Gerald Edelman – Neural Darwinism and Brain-based Devices". Talking Robots.
{{cite web}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Fearn, Nicholas (2007). The Latest Answers to the Oldest Questions: A Philosophical Adventure with the World's Greatest Thinkers. New York: Grove Press. ISBN 0-8021-1839-9.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Forster, Dion (2006). "Self validating consciousness in strong artificial intelligence: An African theological contribution" (PDF). Pretoria: University of South Africa.
{{cite web}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Gladwell, Malcolm (2005). Blink. New York: Little, Brown and Co. ISBN 0-316-17232-4.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Haugeland, John (1985). Artificial Intelligence: The Very Idea. Cambridge, Mass.: MIT Press. ISBN 0-262-08153-9.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Hawkins, Jeff; Blakeslee, Sandra (2005). On Intelligence. New York, NY: Owl Books. ISBN 0-8050-7853-3.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Hofstadter, Douglas (1979). Gödel, Escher, Bach: an Eternal Golden Braid. New York, NY: Vintage Books. ISBN 0-394-74502-7.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Howe, J. (November 1994). "Artificial Intelligence at Edinburgh University: a Perspective". Retrieved 30 August 2007.
{{cite web}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help). - Kahneman, Daniel; Slovic, D.; Tversky, Amos (1982). Judgment under uncertainty: Heuristics and biases. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-28414-7.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Kolata, G. (1982). "How can computers get common sense?". Science. 217 (4566): 1237–1238. doi:10.1126/science.217.4566.1237. PMID 17837639.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Kurzweil, Ray (1999). The Age of Spiritual Machines. Penguin Books. ISBN 0-670-88217-8.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Kurzweil, Ray (2005). The Singularity is Near. Penguin Books. ISBN 0-670-03384-7.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Lakoff, George (1987). Women, Fire, and Dangerous Things: What Categories Reveal About the Mind. University of Chicago Press. ISBN 0-226-46804-6.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Lakoff, George; Núñez, Rafael E. (2000). Where Mathematics Comes From: How the Embodied Mind Brings Mathematics into Being. Basic Books. ISBN 0-465-03771-2.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help). - Lenat, Douglas; Guha, R. V. (1989). Building Large Knowledge-Based Systems. Addison-Wesley. ISBN 0-201-51752-3.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Lighthill, Professor Sir James (1973). "Artificial Intelligence: a paper symposium". Science Research Council.
{{cite journal}}:|contribution=ignored (help); Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Lucas, John (1961). "Minds, Machines and Gödel". In Anderson, A.R. (ed.). Minds and Machines. Archived from the original on 19 August 2007. Retrieved 30 August 2007.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - Maker, Meg Houston (2006). "AI@50: AI Past, Present, Future". Dartmouth College. Archived from the original on 8 October 2008. Retrieved 16 October 2008.
{{cite web}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - McCarthy, John; Minsky, Marvin; Rochester, Nathan; Shannon, Claude (1955). "A Proposal for the Dartmouth Summer Research Project on Artificial Intelligence". Archived from the original on 26 August 2007. Retrieved 30 August 2007.
{{cite web}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help). - McCarthy, John; Hayes, P. J. (1969). "Some philosophical problems from the standpoint of artificial intelligence". Machine Intelligence. 4: 463–502. Archived from the original on 10 August 2007. Retrieved 30 August 2007.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - McCarthy, John (12 November 2007). "What Is Artificial Intelligence?".
{{cite web}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Minsky, Marvin (1967). Computation: Finite and Infinite Machines. Englewood Cliffs, N.J.: Prentice-Hall. ISBN 0-13-165449-7.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Minsky, Marvin (2006). The Emotion Machine. New York, NY: Simon & Schusterl. ISBN 0-7432-7663-9.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Moravec, Hans (1976). "The Role of Raw Power in Intelligence". Retrieved 30 August 2007.
{{cite web}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Moravec, Hans (1988). Mind Children. Harvard University Press. ISBN 0-674-57616-0.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - NRC, (United States National Research Council) (1999). "Developments in Artificial Intelligence". Funding a Revolution: Government Support for Computing Research. National Academy Press.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Needham, Joseph (1986). Science and Civilization in China: Volume 2. Caves Books Ltd.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Newell, Allen; Simon, H. A. (1963). "GPS: A Program that Simulates Human Thought". In Feigenbaum, E.A.; Feldman, J. (eds.). Computers and Thought. New York: McGraw-Hill.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Newell, Allen; Simon, H. A. (1976). "Communications of the ACM". 19 (3).
{{cite journal}}:|contribution=ignored (help); Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Invalid|ref=harv(help). - Nilsson, Nils (1983), "Artificial Intelligence Prepares for 2001" (PDF), AI Magazine, 1 (1), Presidential Address to the Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence.
- Penrose, Roger (1989). The Emperor's New Mind: Concerning Computer, Minds and The Laws of Physics. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-851973-7.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Searle, John (1980). "Minds, Brains and Programs". Behavioral and Brain Sciences. 3 (3): 417–457. doi:10.1017/S0140525X00005756.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Searle, John (1999). Mind, language and society. New York, NY: Basic Books. ISBN 0-465-04521-9. OCLC 231867665 43689264.
{{cite book}}: Check|oclc=value (help); Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Serenko, Alexander; Detlor, Brian (2004). "Intelligent agents as innovations" (PDF). AI and Society. 18 (4): 364–381. doi:10.1007/s00146-004-0310-5.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Serenko, Alexander; Ruhi, Umar; Cocosila, Mihail (2007). "Unplanned effects of intelligent agents on Internet use: Social Informatics approach" (PDF). AI and Society. 21 (1–2): 141–166. doi:10.1007/s00146-006-0051-8.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Shapiro, Stuart C. (1992). "Artificial Intelligence". In Shapiro, Stuart C. (ed.). Encyclopedia of Artificial Intelligence (PDF) (2nd ed.). New York: John Wiley. pp. 54–57. ISBN 0-471-50306-1.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Simon, H. A. (1965). The Shape of Automation for Men and Management. New York: Harper & Row.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Skillings, Jonathan (3 July 2006). "Getting Machines to Think Like Us". cnet. Retrieved 3 February 2011.
{{cite web}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Tecuci, Gheorghe (March–April 2012). "Artificial Intelligence". Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Computational Statistics. 4 (2). Wiley: 168–180. doi:10.1002/wics.200.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Turing, Alan (October 1950). "Computing Machinery and Intelligence". Mind. 59 (236): 433–460. doi:10.1093/mind/LIX.236.433. ISSN 1460-2113. JSTOR 2251299. S2CID 14636783.
.
- van der Walt, Christiaan; Bernard, Etienne (2006<!––year is presumed based on acknowledgements at the end of the article––>). "Data characteristics that determine classifier performance" (PDF). Retrieved 5 August 2009.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|year=(help); Invalid|ref=harv(help)CS1 maint: year (link) - Vinge, Vernor (1993). "The Coming Technological Singularity: How to Survive in the Post-Human Era".
{{cite web}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Wason, P. C.; Shapiro, D. (1966). "Reasoning". In Foss, B. M. (ed.). New horizons in psychology. Harmondsworth: Penguin.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Weizenbaum, Joseph (1976). Computer Power and Human Reason. San Francisco: W.H. Freeman & Company. ISBN 0-7167-0464-1.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Kumar, Gulshan; Krishan Kumar (2012). "The Use of Artificial-Intelligence-Based Ensembles for Intrusion Detection: A Review". Applied Computational Intelligence and Soft Computing. 2012: 1–20. doi:10.1155/2012/850160. Retrieved 11 February 2013.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link)
Further reading
- TechCast Article Series, John Sagi, Framing Consciousness
- Boden, Margaret, Mind As Machine, Oxford University Press, 2006
- Johnston, John (2008) "The Allure of Machinic Life: Cybernetics, Artificial Life, and the New AI", MIT Press
- Myers, Courtney Boyd ed. (2009). The AI Report. Forbes June 2009
- Serenko, Alexander (2010). "The development of an AI journal ranking based on the revealed preference approach" (PDF). Journal of Informetrics. 4 (4): 447–459. doi:10.1016/j.joi.2010.04.001.
- Serenko, Alexander; Michael Dohan (2011). "Comparing the expert survey and citation impact journal ranking methods: Example from the field of Artificial Intelligence" (PDF). Journal of Informetrics. 5 (4): 629–649. doi:10.1016/j.joi.2011.06.002.
- Sun, R. & Bookman, L. (eds.), Computational Architectures: Integrating Neural and Symbolic Processes. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Needham, MA. 1994.
External links
- What Is AI? — An introduction to artificial intelligence by AI founder John McCarthy.
- The Handbook of Artificial Intelligence Volume Ⅰ by Avron Barr and Edward A. Feigenbaum (Stanford University)
- "Artificial Intelligence". Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy.
- "Logic and Artificial Intelligence" entry by Richmond Thomason in the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy
- Template:Dmoz
- AITopics — A large directory of links and other resources maintained by the Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence, the leading organization of academic AI researchers.
- Cybernetics and AI
Categories:
