| Revision as of 09:33, 22 November 2014 editSpandan28 (talk | contribs)1 editNo edit summaryTags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit← Previous edit | Revision as of 23:05, 30 November 2014 edit undoTrappist the monk (talk | contribs)Administrators479,890 editsm →References: Remove redundant |year= parameter from CS1 citations; using AWBNext edit → | ||
| Line 139: | Line 139: | ||
| * {{Citation| surname=Gogoi | given=Padmeshwar | title=The Tai and the Tai kingdoms | publisher=Gauhati University, Guwahati | year=1968}} | * {{Citation| surname=Gogoi | given=Padmeshwar | title=The Tai and the Tai kingdoms | publisher=Gauhati University, Guwahati | year=1968}} | ||
| * {{Citation| surname=Guha | given=Amalendu | title=Medieval and Early Colonial Assam: Society, Polity and Economy | publisher=K.P. Bagchi & Co, Calcutta | year=1991}} | * {{Citation| surname=Guha | given=Amalendu | title=Medieval and Early Colonial Assam: Society, Polity and Economy | publisher=K.P. Bagchi & Co, Calcutta | year=1991}} | ||
| * {{Citation| last = Guha| first = Amalendu| title = The Ahom Political System: An Enquiry into the State Formation Process in Medieval Assam (1228-1714)| journal = Social Scientist| volume = 11 |pages = 3–34| date = December |
* {{Citation| last = Guha| first = Amalendu| title = The Ahom Political System: An Enquiry into the State Formation Process in Medieval Assam (1228-1714)| journal = Social Scientist| volume = 11 |pages = 3–34| date = December 1983| doi = 10.2307/3516963| issue = 12| jstor = 3516963 }} | ||
| * {{Citation| surname=Kakoty | given=Sanjeeb | title=Technology, Production and Social Formation in the Evolution of the Ahom State | publisher=Regency Publications, New Delhi | year=2003}} | * {{Citation| surname=Kakoty | given=Sanjeeb | title=Technology, Production and Social Formation in the Evolution of the Ahom State | publisher=Regency Publications, New Delhi | year=2003}} | ||
| * {{Citation| editor-last=Sharma | editor-first=Benudhar | title=An Account of Assam | publisher=Assam Jyoti | place=Gauhati | year=1972}} | * {{Citation| editor-last=Sharma | editor-first=Benudhar | title=An Account of Assam | publisher=Assam Jyoti | place=Gauhati | year=1972}} | ||
Revision as of 23:05, 30 November 2014
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
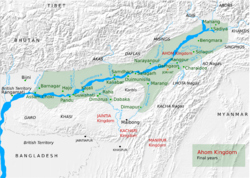
The Ahom Kingdom (/ˈɑːhɑːm, ˈɑːhəm/; Assamese: আহোম ৰাজ্য) (1228–1826, also called Kingdom of Assam) was a kingdom in the Brahmaputra valley in Assam, India that maintained its sovereignty for nearly 600 years and successfully resisted Mughal expansion in North-East India. Established by Sukaphaa, a Tai prince from Mong Mao, it began as a Mong in the upper reaches of the Brahmaputra river based on wet rice cultivation. It expanded suddenly under Suhungmung in the 16th century and became multi-ethnic in character, casting a profound effect on the political and social life in the entire Brahmaputra valley. The kingdom became weaker with the rise of the Moamoria rebellion, and subsequently fell to a succession of Burmese invasions. With the defeat of the Burmese after the First Anglo-Burmese War and the Treaty of Yandabo in 1826, control of the kingdom passed into British (East India Company) hands.
Though it came to be called the Ahom kingdom in the colonial and subsequent times, it was largely multi-ethnic, with the ethnic Ahom people constituting less than 10% of the population toward the end. The 1901 census of India enumerated approximately 179,000 people identifying as Ahom. The latest available census records slightly over 2 million Ahom individuals however, estimates of the total number of people descended from the original Tai-Ahom settlers are as high as 8 million. The total population of Assam being at 31 million according to the 2011 census, they presently constitute slightly over 25%. The Ahoms called their kingdom Mong Dun Shun Kham, (Template:Lang-as; Template:Lang-en) while others called it Assam. The British-controlled province after 1838 and later the Indian state of Assam came to be known by this name.
History
Main articles: Ahom Dynasty, Ahom-Mughal conflicts, and Battle of SaraighatThe Ahom kingdom was established in 1228 when the first Ahom king Chao Lung Siu-Ka-Pha came from Mong Mao which is now included within the Dehong-Dai Singhpho Autonomous Prefecture of Yunnan in Peoples Republic of China and entered the Brahmaputra valley, crossing the rugged Patkai mountain range. He was accompanied by his three queens, two sons, several nobles and their families, other officials and families, and soldiers totaling more than nine thousand persons. When he reached Patkai, he subdued the Nagas very ruthlessly, crossed the Patkai and reached Namruk (Namrup) on December 2, 1228 and occupied a region on the south bank with the Burhidihing river in the north, the Dikhau river in the south and the Patkai mountains in the east. He befriended the local groups, the Barahi and the Marans, finally settled his capital at Charaideo and established the offices of the Dangarias—the Burhagohain and the Borgohain. In the 1280s, these two offices were given independent regions of control, and the check and balance that these three main offices accorded each other was established. The Ahoms brought with them the technology of wet rice cultivation that they shared with other groups. The people that took to the Ahom way of life and polity were incorporated into their fold in a process of Ahomization. As a result of this process the Barahi people, for instance, were completely subsumed, and some of other groups like some Nagas and the Maran peoples became Ahoms, thus enhancing the Ahom numbers significantly. This process of Ahomization was particularly significant till the 16th century, when under Suhungmung, the kingdom made large territorial expansions at the cost of the Sutiya and the Kachari kingdoms.

The expansion was so large and so rapid that the Ahomization process could not keep pace and the Ahoms became a minority in their kingdom. This resulted in a change in the character of the kingdom and it became multi-ethnic and inclusive. Hindu influences, which were first felt under Bamuni Konwar at the end of the 14th century, became significant. The Assamese language entered the Ahom court and co-existed with the Tai language for some time in the 17th century before finally replacing it. The rapid expansion of the state was accompanied by the installation of a new high office, the Borpatrogohain, at par with the other two high offices and not without opposition from the them. Two special offices, the Sadiakhowa Gohain and the Marangikowa Gohain were created to oversee the regions won over from the Sutiya and the Kachari kingdoms respectively. The subjects of the kingdom were organized under the Paik system, initially based on the phoid or kinship relations, which formed the militia. The kingdom came under attack from Turkic and Afghan rulers of Bengal, but it withstood them. On one occasion, the Ahoms under Ton Kham Borgohain pursued the invaders and reached the Karatoya river, and the Ahoms began to see themselves as the rightful heir of the erstwhile Kamarupa Kingdom.
The Ahom kingdom took many features of its mature form under Pratap Singha. The Paik system was reorganized under the professional khel system, replacing the kinship based phoid system. Under the same king, the offices of the Borphukan, and the Borbarua were established along with other smaller offices. No more major restructuring of the state structure was attempted till the end of the kingdom. The kingdom came under repeated Mughal attacks in the 17th century, and on one occasion in 1662, the Mughals under Mir Jumla occupied the capital, Garhgaon. The Mughals were unable to keep it, and in at the end of the Battle of Saraighat, the Ahoms not only fended off a major Mughal invasion, but extended their boundaries west, up to the Manas river. Following a period of confusion, the kingdom got itself the last set of kings, the Tungkhungia kings, established by Gadadhar Singha.
The rule of Tungkhungia kings was marked by peace and achievements in the Arts and engineering constructions. The later phase of the rule was also marked by increasing social conflicts, leading to the Moamoria rebellion. The rebels were able to capture and maintain power at the capital Rangpur for some years, but were finally removed with the help of the British under Captain Welsh. The following repression led to a large depopulation due to emigration as well as execution, but the conflicts were never resolved. A much weakened kingdom fell to repeated Burmese attacks and finally after the Treaty of Yandabo in 1826, the control of the kingdom passed into British hands.
Ahom economic system
The Ahom kingdom was based on the Paik system, a type of corvee labor that is neither feudal nor Asiatic. The Ahoms introduced wet rice cultivation in upper Assam that was largely a marshy and thinly populated land. With a superior technology of rice cultivation, as well as reclamation of land using dykes, embankments and irrigation systems, the Ahoms established the initial state structures. The first coins were introduced by Suklenmung in the 16th century, though the system of personal service under the Paik system persisted. In the 17th century when the Ahom kingdom expanded to include erstwhile Koch and Mughal areas, it came into contact with their revenue systems and adapted accordingly.
Ahom administration
Main articles: Swargadeo, Burhagohain, Borgohain, Borpatrogohain, Borbarua, and BorphukanSwargadeo and Patra Mantris
The Ahom kingdom was ruled by a king, called Swargadeo (Ahom language: Chao-Pha), who had to be a descendant of the first king Sukaphaa. Succession was generally by primogeniture but occasionally the great Gohains (Dangarias) could elect another descendant of Sukaphaa from a different line or even depose an enthroned one.
Dangarias: Sukaphaa had two great Gohains to aid him in administration: Burhagohain and the Borgohain. In the 1280s, they were given independent territories, they were veritable sovereigns in their given territories called bilat or rajya. The Burhagohain's territory was between Sadiya and Gerelua river in the north bank of the Brahmaputra river and the Borgohain's territory was to the west up to the Burai river. They were given total command over the paiks that they controlled. These positions were generally filled from specific families. Princes who were eligible for the position of Swargadeo were not considered for these positions and vice versa. In the 16th century Suhungmung added a third Gohain, Borpatrogohain. The Borpatrogohain's territory was located between the territories of the other two Gohains.
Royal officers: Pratap Singha added two offices, Borbarua and Borphukan, that were directly under the king. The Borbarua, who acted as the military as well as the judicial head, was in command of the region east of Kaliabor not under the command of the Dangarias. He could use only a section of the paiks at his command for his personal use (as opposed to the Dangariyas), the rest rendering service to the Ahom state. The Borphukan was in military and civil command over the region west of Kaliabor, and acted as the Swargadeo's viceroy in the west.
Patra Mantris: The five positions constituted the patra mantris (council of ministers). From the time of Supimphaa (1492–1497), one of the patra mantris was made the Rajmantri (prime minister, also Borpatro; Ahom language: Shenglung) who enjoyed additional powers and the service of a thousand additional paiks from the Jakaichuk village.
Other officials
The Borbarua and the Borphukan had military and judicial responsibilities, and they were aided by two separate councils (sora) of Phukans. The Borphukan's sora sat at Guwahati and the Borbarua's sora at the capital. Superintending officers were called Baruas. Among the officers the highest in rank were the Phukans. Six of them formed the council of the Borbarua, but each had also his separate duties. The Naubaicha Phukan, who had an allotment of thousand men managed the royal boats, the Bhitarual Phukan, the Na Phukan, the Dihingia Phukan, the Deka Phukan and the Neog Phukan formed the council of Phukan. The Borphukan also had a similar council of six subordinate Phukans whom he was bound to consult in all matters of importance, this council included Pani Phukan, who commanded six thousand paiks, Deka Phukan who commanded four thousand paiks, the Dihingia Phukan, Nek Phukan and two Sutiya Phukans.
The Baruas of whom there were twenty or more included Bhandari Barua or treasurer; the Duliya Barua, who was in charge of the royal palanquins; the Chaudang Barua who superintended executions; Khanikar Barua was the chief artificer; Sonadar Barua was the mint master and chief jeweler; the Bez Barua was the physician to the Royal family, Hati Barua, Ghora Barua, etc. Other official included twelve Rajkhowas, and a number of Katakis, Kakatis and Dolais. The Rajkhowas were governors of given territories and commanders of three thousand paiks. They were arbitrator who settled local disputes and supervised public works. The Katakis were envoys who dealt with foreign countries and hill tribes. The Kakatis were writers of official documents, and the Dolais expounded astrology and determined auspicious time and dates for any important event and undertaking.
Governors
Members of the royal families ruled certain areas, and they were called Raja.
- Charing Raja, the heir apparent to the Swargadeo, administered the tracts around Joypur on the right bank of the Burhidihing river.
- Tipam Raja is the second in line.
- Namrup Raja is the third in line
Members of the royal families who occupy lower positions are given regions called mels, and were called meldangia or melkhowa raja. Meldangia gohains were princes of an even lesser grade, of which there were two: Majumelia gohain and Sarumelia gohain.
Royal ladies were given individual mels, and by the time of Rajeshwar Singha, there were twelve of them. The most important of these was the Raidangia mel given to the chief queen.
Forward governors, who were military commanders, ruled and administered forward territories. The officers were usually filled from the families that were eligible for the three great Gohains.
- Sadiya Khowa Gohain based in Sadiya, administered the regions that were acquired after the conquest of the Sutiya kingdom in 1523.
- Marangi khowa Gohain administered the region that were contiguous to the Naga groups west of the Dhansiri river.
- Solal Gohain administered a great part of Nagaon and a portion of Chariduar after the headquarters of the Borphukan was transferred to Gauhati.
- Kajalimukhiya Gohain served under the Borphukan, administered Kajalimukh and maintained relations with Jaintia and Dimarua.
- Jagiyal Gohain served under Borbarua, administered Jagi at Nagoan and maintained relations with seven tribal chiefs, called Sat Raja.
Lesser governors were called Rajkhowas, and some of them were:
- Bacha
- Darrang
- Solaguri
- Abhaypur
The dependent kings or vassals were also called Raja. Except for the Raja of Rani, all paid an annual tribute. These Rajas were required to meet the needs for resources and paiks when the need arose, as during the time of war.
- Darrang Raja ruled the later-day Darrang district, and were the descendants of Sundar Narayan, a great-grandson of Chilarai of the Koch dynasty
- Rani
- Beltola ruled the tracts southwest of Guwahati, and were the descendants of Gaj Narayan, a grandson of Chilarai of the Koch dynasty
- Luki
- Barduar
- Dimarua
- Tapakuchi
Paik officials
The Ahom kingdom was dependent on the Paik system, a form of corvee labor. Every common subject was a paik, and four paiks formed a got. At any time of the year, one of the paiks in the got rendered direct service to the king, as the others in his got tended to his fields. The Paik system was administered by the Paik officials: Bora was in charge of 20 paiks, a Saikia of 100 and a Hazarika of 1000.
Land survey
Gadadhar Singha became acquainted with the land measurement system of Mughals during the time he was hiding in Kamrup, before he succeeded to the throne. As soon as the wars with Mughals were over he issued orders for the introduction of a similar system throughout his dominions. Surveyors were imported from Koch Behar and Bengal for the work. It was commenced in Sibsagar and was pushed on vigorously, but it was not completed until after his death. Nowgaon was next surveyed; and the settlement which followed was supervised by Rudra Singha himself. According to historians, the method of survey included measuring the four sides of each field with a nal, or bamboo pole of 12 feet (3.7 m) length and calculating the area, the unit was the "lucha" or 144 square feet (13.4 m) and 14,400 sq ft (1,340 m). is one "Bigha". Four 'bigha' makes one 'Pura'. A similar land measurement system is still being followed in modern Assam.
Classes of people
Subinphaa (1281–1293), the third Ahom king, dilineated the Satgharia Ahom ("Ahom of the seven houses") aristocracy: the Chaophaa, the Burhagohain and the Borgohain families (the Gohains), and four priestly lineages—the Deodhai, the Mohan, the Bailung and the Chiring (the Gogois). These lines maintained exogamous marital relationships. The number of lineages increased in later times as either other lineages were incorporated, or existing lineages divided. The king could belong to only the first family whereas the Burhagohain and the Borgohain only to the second and the third families. Most of the Borphukans belonged to the Sutiya ethnic group, whereas the Borbaruas belonged to the Moran, Kachari, Chiring and Khamti groups. Later on Naga, Mising and Nara (Mogaung) oracles became a part of the Bailung group. The extended nobility consisted of the landed aristocracy and the spiritual class that did not pay any form of tax.
The apaikan chamua was the gentry that were freed from the khels and paid only money-tax. The paikan chamua consisted of artisans, the literati and skilled people that did non-manual work and rendered service as tax. The kanri paik rendered manual labor. The lowest were the licchous, bandi-beti and other serfs and bondsmen. There was some degree of movement between the classes. Momai Tamuli Borbarua rose from a bondsman through the ranks to become the first Borbarua under Prataap Singha.
See also
Notes
- "The Kingdom of Assam, where it is entered from Bengal, commences on the north of the Berhampooter, at the Khonder Chokey, nearly opposite to the picturesque estate of the late Mr Raush at Goalpara; and at the Nagrabaree Hill on the South", Wade, Dr John Peter, (1805) "A Geographical Sketch of Assam" in Asiatic Annual Register, reprinted (Sharma 1972, p. 341)
- "The Ahoms were never numerically dominant in the state they built and, at the time of 1872 and 1881 Censuses, they formed hardly one-tenth of the populations relevant to the erstwhile Ahom territory (i.e, by and large, the Brahmaputra Valley without the Goalpara district.)" (Guha 1983:9)
- Ahom. Ethnologue (1999-02-19). Retrieved on 2013-07-12.
- (Gogoi 1968:266)
- "(In Upper Assam), the Ahoms assimilated some of their Naga, Moran and Barahi neighbours and later, also large sections of the Chutiya and Kachari tribes. This Ahomisation process went on until the expanded Ahom society itself began to be Hinduised from the mid-16th century onward." (Guha 1983:12)
- In (the 17th) century of Ahom-Mughal conflicts, (the Tai) language first coexisted with and then was progressively replaced by Assamese (Asamiya) at and outside the Court." (Guha 1983, p. 9)
- Tom Kham was the son of Phrasengmong Borgohain and Mula Gabhoru, both warriors who were killed in battles against Turbak.
- "The Ahom expeditionary force, led by General Ton Kham and aided by General Kan Seng and General Kham Peng, pursued the retreating enemies across Muslim domains of Kamarupa and Kamata receiving little resistance in them and reached Karatoya, the eastern boundary of Gaur proper, where the victors washed their swords."(Gogoi 1968, p. 302)
- "The Ahom statesmen and chroniclers wishfully looked forward to the Karatoya as their natural western frontier. They also looked upon themselves as the heirs of the glory that was ancient Kamarupa by right of conquest, and they long cherished infructuously their unfulfilled hopes of expanding up to that frontier." (Guha 1983:24), and notes.
- (Gogoi 2002:42)
- (Gogoi 2002:43)
- (Gogoi 2002:43)
- ^ (Gogoi 2002:44)
- (Gogoi 2006:9)
References
- Gogoi, Jahnabi (2002), Agrarian system of medieval Assam, Concept Publishing Company, New Delhi
- Gogoi, Lila (1991), The History of the system of Ahom administration, Punthi Pustak, Calcutta
- Gogoi, Nitul Kumar (2006), Continuity and Change among the Ahoms, Concept Publishing Company, Delhi
- Gogoi, Padmeshwar (1968), The Tai and the Tai kingdoms, Gauhati University, Guwahati
- Guha, Amalendu (1991), Medieval and Early Colonial Assam: Society, Polity and Economy, K.P. Bagchi & Co, Calcutta
- Guha, Amalendu (December 1983), "The Ahom Political System: An Enquiry into the State Formation Process in Medieval Assam (1228-1714)", Social Scientist, 11 (12): 3–34, doi:10.2307/3516963, JSTOR 3516963
- Kakoty, Sanjeeb (2003), Technology, Production and Social Formation in the Evolution of the Ahom State, Regency Publications, New Delhi
- Sharma, Benudhar, ed. (1972), An Account of Assam, Gauhati: Assam Jyoti
| History of Assam | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ancient Assam |  | |
| Medieval Assam | ||
| Colonial Assam | ||
| Contemporary Assam | ||
26°55′59″N 94°44′53″E / 26.93306°N 94.74806°E / 26.93306; 94.74806
Categories: