| Revision as of 09:07, 16 October 2015 editDoc James (talk | contribs)Administrators312,294 edits Reverted to revision 681212159 by 86.176.124.129 (talk): Unsure why this random ref? (TW)← Previous edit | Revision as of 18:09, 27 October 2015 edit undo50.206.232.162 (talk) →CausesNext edit → | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
| == Causes == | == Causes == | ||
| ] is mistakenly attributed as a cause of this disease. However heavy ] consumption can aggravate the condition. Rhinophyma may be diagnosed without testing, but a skin ] can confirm the diagnosis. Surgical treatment may be beneficial.{{Citation needed|date=January 2009}} | ] is mistakenly attributed as a cause of this disease. However heavy ] consumption can aggravate the condition. Rhinophyma may be diagnosed without testing, but a skin ] can confirm the diagnosis. Surgical treatment may be beneficial.{{Citation needed|date=January 2009}} | ||
| not true | |||
| Rhinophyma is a slowly progressive condition due to hypertrophy of the sebaceous glands of the tip of the nose often seen in cases of long-standing ]; it is not a ]. It presents as a pink, lobulated mass over the nose with superficial vascular dilation; it mostly affects men past middle age. Patients seek advice because of the perceived unsightly appearance of the enlargement, or obstruction in breathing and vision. | Rhinophyma is a slowly progressive condition due to hypertrophy of the sebaceous glands of the tip of the nose often seen in cases of long-standing ]; it is not a ]. It presents as a pink, lobulated mass over the nose with superficial vascular dilation; it mostly affects men past middle age. Patients seek advice because of the perceived unsightly appearance of the enlargement, or obstruction in breathing and vision. | ||
Revision as of 18:09, 27 October 2015
Medical condition| Rhinophyma | |
|---|---|
| Specialty | Dermatology |
Rhinophyma is a condition causing development of a large, bulbous, ruddy nose associated with granulomatous infiltration, commonly due to untreated rosacea.
Signs and symptoms
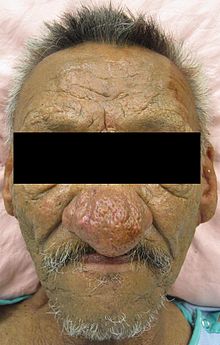
Rhinophyma is characterised by prominent pores and a fibrous thickening of the nose, sometimes with papules. It is associated with the common skin condition rosacea. It can carry a strong psychological impact due to its effect on one's personal appearance.
Causes
Alcoholism is mistakenly attributed as a cause of this disease. However heavy alcohol consumption can aggravate the condition. Rhinophyma may be diagnosed without testing, but a skin biopsy can confirm the diagnosis. Surgical treatment may be beneficial. not true Rhinophyma is a slowly progressive condition due to hypertrophy of the sebaceous glands of the tip of the nose often seen in cases of long-standing acne rosacea; it is not a neoplasm. It presents as a pink, lobulated mass over the nose with superficial vascular dilation; it mostly affects men past middle age. Patients seek advice because of the perceived unsightly appearance of the enlargement, or obstruction in breathing and vision.
Treatment
Treatment consists of paring down the bulk of the tissue with a sharp instrument or carbon dioxide laser and allowing the area to re-epithelialise. Sometimes, the tissue is completely excised and the raw area skin-grafted.
History
The term rhinophyma is derived from the Greek rhis ('nose') and phyma ('growth').
See also
References
- Cohen AF, Tiemstra JD (2002). "Diagnosis and treatment of rosacea". J Am Board Fam Pract. 15 (3): 214–7. PMID 12038728.
- "Rosacea". Dermnetnz.org.
- "Rhinophyma". Rhinophyma. Retrieved 24 March 2011.
- Dingra PL. Diseases of Ear, Nose and Throat (4th ed.).
External links
- MedEd at Loyola medicine/dermatology/melton/rhino1.htm
- About rhinophyma at orlhns.info
- Rhinophyma Treatment
- janjuafacialsurgery (Contributor) (2012-05-10). Rhinophyma Excision by Janjua Facial Surgery. Retrieved 2013-02-10.