| Revision as of 19:29, 15 March 2017 edit2405:204:5306:53ad:a954:d6b5:963a:ed48 (talk) →Causes: fixed typo,added contentTags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit← Previous edit | Revision as of 19:30, 15 March 2017 edit undo2405:204:5306:53ad:a954:d6b5:963a:ed48 (talk) →Causes: fixed typo and added contentTags: Mobile edit Mobile web editNext edit → | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
| == Causes == | == Causes == | ||
| ] is mistakenly attributed as a cause of this issue ,but the harmone imbalance also one of the reasons to this condition ,avoiding sex and sweating out more and excreating more may come out of this condition ,not sleeping at regular time and sleepless people majorly causes this |
] is mistakenly attributed as a cause of this issue ,but the harmone imbalance also one of the reasons to this condition ,avoiding sex and sweating out more and excreating more may come out of this condition ,not sleeping at regular time and sleepless people majorly causes this skin problem.<ref name=Fit2016>{{cite book|last1=Fitzpatrick|first1=James E.|last2=Morelli|first2=Joseph G.|title=Dermatology Secrets Plus|publisher=Elsevier Health Sciences|isbn=9780323313551|page=511|edition=5th|url=https://books.google.ca/books?id=ReqeCgAAQBAJ&pg=PA511|accessdate=10 May 2016|language=en}}</ref> ] however may cause increased flushing in those affected.<ref name=Fit2016/> | ||
| ==Pathophysiology== | ==Pathophysiology== | ||
Revision as of 19:30, 15 March 2017
Medical condition| Rhinophyma | |
|---|---|
| Specialty | Dermatology |
Rhinophyma is a condition causing development of a large, bulbous, ruddy nose associated with granulomatous infiltration, commonly due to untreated rosacea.
Signs and symptoms
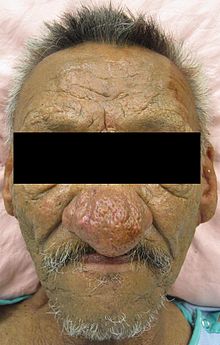
Rhinophyma is characterised by prominent pores and a fibrous thickening of the nose, sometimes with papules. It is associated with the common skin condition rosacea. It can carry a strong psychological impact due to its effect on one's personal appearance.
Causes
Alcoholism is mistakenly attributed as a cause of this issue ,but the harmone imbalance also one of the reasons to this condition ,avoiding sex and sweating out more and excreating more may come out of this condition ,not sleeping at regular time and sleepless people majorly causes this skin problem. Alcohol however may cause increased flushing in those affected.
Pathophysiology
Rhinophyma is a slowly progressive condition due to hypertrophy of the sebaceous glands of the tip of the nose often seen in cases of long-standing acne rosacea; it is not a neoplasm. It presents as a pink, lobulated mass over the nose with superficial vascular dilation; it mostly affects men past middle age. Patients seek advice because of the perceived unsightly appearance of the enlargement, or obstruction in breathing and vision.
Diagnosis
Rhinophyma may be diagnosed without testing, but a skin biopsy can confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment consists of paring down the bulk of the tissue with a sharp instrument or carbon dioxide laser and allowing the area to re-epithelialise. Sometimes, the tissue is completely excised and the raw area skin-grafted.
Etymology
The term rhinophyma is derived from Greek ῥινός "rīnós ('nose') and φῦμα pʰyma ('growth').
See also
References
- Cohen AF, Tiemstra JD (2002). "Diagnosis and treatment of rosacea". J Am Board Fam Pract. 15 (3): 214–7. PMID 12038728.
- "Rosacea". Dermnetnz.org.
- "Rhinophyma". Rhinophyma. Retrieved 24 March 2011.
- ^ Fitzpatrick, James E.; Morelli, Joseph G. Dermatology Secrets Plus (5th ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 511. ISBN 9780323313551. Retrieved 10 May 2016.
- Dhingra P.L. Diseases of Ear, Nose and Throat, 6th edition, New Delhi 2013, 490 pp. ISBN 9788131234310
External links
- MedEd at Loyola medicine/dermatology/melton/rhino1.htm
- janjuafacialsurgery (Contributor) (2012-05-10). Rhinophyma Excision by Janjua Facial Surgery. Retrieved 2013-02-10.