| Revision as of 00:04, 28 May 2017 editMagic links bot (talk | contribs)Bots291,110 editsm Replace magic links with templates per local RfC and MediaWiki RfC← Previous edit | Revision as of 23:27, 12 July 2017 edit undoInternetArchiveBot (talk | contribs)Bots, Pending changes reviewers5,384,151 edits Rescuing 1 sources and tagging 0 as dead. #IABot (v1.4)Next edit → | ||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Azosemide''' is a high-ceiling ] agent that was brought to market in 1981 by ].<ref>{{ cite book |
'''Azosemide''' is a high-ceiling ] agent that was brought to market in 1981 by ].<ref>{{ cite book|author=Marshall Sittig |title=Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Encyclopedia |volume=1 |publisher=Noyes Publications |year=1988 |page=122 |isbn=9780815511441 |url=http://files.rushim.ru/books/lekarstva/pharmaceutical-encyclopedia.pdf |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20071023210611/http://files.rushim.ru/books/lekarstva/pharmaceutical-encyclopedia.pdf |archivedate=2007-10-23 }}</ref><ref>Dieter Borman. Diuretics. Chapter 11 in Annual Reports in Medicinal Chemistry, Volume 15. Ed Hess, HJ.. Academic Press, 1980 {{ISBN|9780080583594}}</ref>{{rp|101}} As of 2015 it was available as a generic in some Asian countries.<ref>Drugs.com Page accessed July 12, 2015</ref> | ||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 23:27, 12 July 2017
Pharmaceutical compound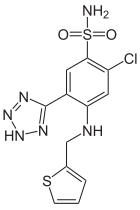 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.044.121 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H11ClN6O2S2 |
| Molar mass | 370.84 g/mol g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Azosemide is a high-ceiling loop diuretic agent that was brought to market in 1981 by Boehringer Mannheim. As of 2015 it was available as a generic in some Asian countries.
References
- Marshall Sittig (1988). Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Encyclopedia (PDF). Vol. 1. Noyes Publications. p. 122. ISBN 9780815511441. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-10-23.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - Dieter Borman. Diuretics. Chapter 11 in Annual Reports in Medicinal Chemistry, Volume 15. Ed Hess, HJ.. Academic Press, 1980 ISBN 9780080583594
- Drugs.com Drugs.com international listings for azosemide Page accessed July 12, 2015
This drug article relating to the cardiovascular system is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |