| Revision as of 21:40, 13 June 2019 view source103.219.230.104 (talk)No edit summaryTags: Visual edit Mobile edit Mobile web edit← Previous edit | Revision as of 14:47, 10 July 2019 view source 2409:4062:219e:a427:44b1:79d2:b190:c0d6 (talk) Added ContentTags: Mobile edit Mobile web editNext edit → | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{About| the irredentist concept comprising India, Pakistan, and |
{{About| the irredentist concept comprising India, Pakistan,Bangladesh,Afghanistan,Tibet,Nepal,Bhutan,Myanmar,Thailand,Cambodia,Laos,Vietnam, Malaysia and some parts of Indonesia| the Indian cultural sphere | Greater India}} | ||
| {{Use Indian English|date=June 2015}} | {{Use Indian English|date=June 2015}} | ||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=June 2015}} | {{Use dmy dates|date=June 2015}} | ||
Revision as of 14:47, 10 July 2019
This article is about the irredentist concept comprising India, Pakistan,Bangladesh,Afghanistan,Tibet,Nepal,Bhutan,Myanmar,Thailand,Cambodia,Laos,Vietnam, Malaysia and some parts of Indonesia. For the Indian cultural sphere, see Greater India.
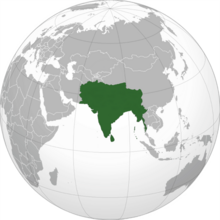
Undivided India or Akhand Bharata or Akhand Hindustan are irredentist terms literally meaning "Undivided India". The term “Undivided India” is used in Indian passports in reference to the birth place of Indian nationals born before the partition of India in areas that now form Pakistan or Bangladesh.
History
At the time of the Indian Independence Movement, Kanaiyalal Maneklal Munshi advocated for Akhand Hindustan, a proposition that Mahatma Gandhi, believing that "as Britain wanted to retain her empire by pursuing a policy of divide and rule, Hindu-Muslim unity could not be achieved as long as the British were there." In addition, Mazhar Ali Khan wrote that "the Khan brothers determined to fight for Akhand Hindustan, and challenged the League to fight the issue out before the electorate of the Province." On 7–8 October 1944, in Delhi, Radha Kumud Mukherjee presided over the Akhand Hindustan Leaders' Conference.
Usage
The call for creation of the Akhand Bharat or Akhand Hindusthan has on occasions been raised by Indian Hindutvawadi cultural and political organisations such as the Hindu Mahasabha, Kakbhusundi Revolutionary Forum (KRF), Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS), Vishwa Hindu Parishad, Hindu Janajagruti Samiti, and Bharatiya Janata Party. The name of one organisation sharing this goal, the Akhand Hindustan Morcha, bears the term in its name. Other major Indian political parties such as the left-wing Indian National Congress do not subscribe to a call for Akhand Bharat.
Pre-1947 maps of India showing the current states of Pakistan and Bangladesh as part of the territories of British India illustrate the borders of a proto-Akhand Bharat. The creation of an Akhand Bharat is also ideologically linked with the concept of Hindutva (Hinduness) and the ideas of sangathan (unity) and shuddhi (purification) that seek to focus modern Indian politics on a legendary ancient civilisation and heritage of the Indian subcontinent.
While the leadership of the right-wing BJP wavers on the issue, the RSS has always been a strong proponent of the idea. RSS leader H. V. Seshadri's book The Tragic Story of Partition stresses the importance of the concept of Akhand Bharat. The RSS affiliated magazine Organiser often publishes editorials by leaders such as the present Sarsanghachalak, Mohan Bhagwat, espousing the philosophy that only Akhand Bharat and sampoorna samaj (united society) can bring "real" freedom to the people of India.
The call for Indian reunification has been supported by Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi, and BJP National General Secretary Ram Madhav. Mr. K.J.Anand Leader Achchedin taken special lead to explore the possibility.
Former Indian Supreme Court Judge Markandey Katju advocated in Pakistani newspaper The Nation that the only solution to the ongoing dispute between India and Pakistan is the reunification of India, Pakistan and Bangladesh under a strong, secular, modern-minded government. He expanded on the reasons for his support for an reunified India in an article for Newslaundry, In a separate article, Katju advocated that such a state would be administered by a secular government. Katju serves as the chairman of the Indian Reunification Association (IRA), which seeks to campaign for this cause.
See also
- Bharat Mata Mandir
- Indo-Pak Confederation
- Indian nationalism
- Opposition to the partition of India
- Indian reunification
References
- Erdman, H. L. (17 December 2007). The Swatantra Party and Indian Conservatisum. Cambridge University Press. p. 55. ISBN 9780521049801.
The ultimate reunification of the subcontinent is a professed goal, as it is for the Mahasabha, but here, too, there is a difference in emphasis which deserves note: for the Sangh, the goal is 'Akhand Bharat', while for the Mahasabha it is 'Akhand Hindustan'.
- Chitkara, M. G. (1 January 2004). Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh. APH Publishing. p. 262. ISBN 9788176484657.
Those who dub Shri L.K. Advani, the Home Minister of India and others as foreigners, must realise that the freedom struggle was a mass movement of all the people of entire Akhanda Hindusthan (United Bharat).
- INSTRUCTIONS FOR FILLING UP THE PASSPORT APPLICATION FORM (DIPLOMATIC/ OFFICIAL) ; Government of India publication wherein it reads “If you were born before the partition of India (i.e. before 15/08/1947), at a place that now lies in Pakistan or Bangladesh, write the placebo of birth (such as village or town or city) and the country as “Undivided India”.
- Ghose, Sankar (1 January 1991). Mahatma Gandhi. Allied Publishers. p. 315. ISBN 9788170232056.
Later, K.M. Munishi, with Gandhi's blessing, also resigned from the Congress to plead for Akhand Hindustan as a counter blast to Pakistan. Gandhi, who previously thought that swaraj was impossible without Hindu-Muslim unity, subsequently came to the conclusion that as Britain wanted to retain her empire by pursuing a policy of divide and rule, Hindu-Muslim unity could not be achieved as long as the British were there.
- Khan, Mazhar Ali (1996). Pakistan: The First Twelve Years. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780195776768. Retrieved 23 July 2014.
Many months ago, when the Pakistan issue was still in the melting pot, the Khan brothers determined to fight for Akhand Hindustan, and challenged the League to fight the issue out before the electorate of the Province.
- Sharma, Jai Narain (1 January 2008). Encyclopaedia Eminent Thinkers. Concept Publishing Company. p. 88. ISBN 9788180694929.
On 5 August 1944, he issued a common letter to the leaders of various parties making a proposal to hold Akhand Hindustan Leaders' Conference. Such a conference was held on 7 and 8 October in Delhi. It was presided over by Dr. Radha Kumud Mukherji.
- Suda, Jyoti Prasad (1953). India, Her Civic Life and Administration. Jai Prakash Nath & Co. Retrieved 23 July 2014.
Its members still swear by the ideal of Akhand Hindusthan.
- Yale H. Ferguson and R. J. Barry Jones, Political space: frontiers of change and governance in a globalizing world, page 155, SUNY Press, 2002, ISBN 978-0-7914-5460-2
- ^ Sucheta Majumder, "Right Wing Mobilization in India", Feminist Review, issue 49, page 17, Routledge, 1995, ISBN 978-0-415-12375-4
- ^ Ulrika Mårtensson and Jennifer Bailey, Fundamentalism in the Modern World (Volume 1), page 97, I.B.Tauris, 2011, ISBN 978-1-84885-330-0
- Hindu Political Parties. General Books. 30 May 2010. ISBN 9781157374923.
- Jyotirmaya Sharma, "Ideological heresy?, The Hindu, 2005-06-19
- Radhika Ramaseshan, "Advani fires Atal weapon", The Telegraph, 2005-06-16
- Ashish Vashi, "Anti-Sardar Patel book sold from RSS HQ in Gujarat", The Times of India, 2009-08-27
- Manini Chatterjee, "Only by Akhand Bharat", The Indian Express, 2007-02-01
- http://deshgujarat.com/2012/03/24/a-day-would-come-when-sindh-will-be-a-part-of-indianarendra-modi-says-adding-that-a-grand-zulelal-dham-will-be-built-in-kutch/
- http://indianexpress.com/article/india/india-news-india/rss-belives-india-pak-and-bangladesh-will-reunite-through-goodwill-one-day-ram-madhav/
- "The truth about Pakistan". The Nation. 2 March 2013. Archived from the original on 10 November 2013. Retrieved 9 January 2018.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - "Pakistan all-praise for Markandey Katju". Indian Express. 7 March 2013.
- "We must reunite: Why Pakistan, India and Bangladesh should be one country". Newslaundry. 8 December 2015.
- http://www.huffingtonpost.in/markandey-katju/india-and-pakistan-must-reunite-for-their-mutual-good_a_22033158/
- "Mission Statement of the Indian Reunification Association". Indica News. 7 February 2019.
- Markandey Katju (10 April 2017). "India And Pakistan Must Reunite For Their Mutual Good". The Huffington Post.
| Irredentism | |
|---|---|
| Africa | |
| North America | |
| South America | |
| Western Asia | |
| Southern Asia | |
| Eastern and Southeastern Asia | |
| Central and Eastern Europe | |
| Southern Europe | |
| Italy | |
| Northern Europe | |
| Western Europe | |
| Oceania | |
| Related concepts: Border changes since 1914 · Partitionism · Reunification · Revanchism · Revisionism · Rump state | |