| Revision as of 16:05, 4 April 2020 editMagic links bot (talk | contribs)Bots291,110 editsm Replace magic links with templates per local RfC and MediaWiki RfC← Previous edit | Revision as of 00:42, 22 June 2020 edit undoBender235 (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers, Template editors471,674 editsm →Glucose: DOI links repaired, or removed if redundantTag: AWBNext edit → | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
| :C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>12</sub>O<sub>6</sub> + 6 O<sub>2</sub> + 38 ] + 38 phosphate → 6 CO<sub>2</sub> + 44 H<sub>2</sub>O + 38 ] | :C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>12</sub>O<sub>6</sub> + 6 O<sub>2</sub> + 38 ] + 38 phosphate → 6 CO<sub>2</sub> + 44 H<sub>2</sub>O + 38 ] | ||
| where glucose releases the chemical energy stored in the relative weak double bond of oxygen.<ref name="Schmidt-Rohr 20"> Schmidt-Rohr, K. (2020). "Oxygen Is the High-Energy Molecule Powering Complex Multicellular Life: Fundamental Corrections to Traditional Bioenergetics” ''ACS Omega'' '''5''': 2221-2233. |
where glucose releases the chemical energy stored in the relative weak double bond of oxygen.<ref name="Schmidt-Rohr 20"> Schmidt-Rohr, K. (2020). "Oxygen Is the High-Energy Molecule Powering Complex Multicellular Life: Fundamental Corrections to Traditional Bioenergetics” ''ACS Omega'' '''5''': 2221-2233. {{doi|10.1021/acsomega.9b03352}} </ref> | ||
| This equation is a summary of what happens in three series of biochemical reactions: ], the ], and ]. | This equation is a summary of what happens in three series of biochemical reactions: ], the ], and ]. | ||
Revision as of 00:42, 22 June 2020
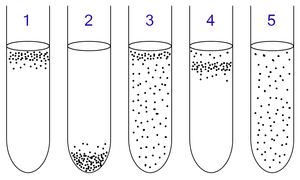
1: Obligate aerobes need oxygen because they cannot ferment or respire anaerobically. They gather at the top of the tube where the oxygen concentration is highest.
2: Obligate anaerobes are poisoned by oxygen, so they gather at the bottom of the tube where the oxygen concentration is lowest.
3: Facultative anaerobes can grow with or without oxygen because they can metabolise energy aerobically or anaerobically. They gather mostly at the top because aerobic respiration generates more ATP than either fermentation or anaerobic respiration.
4: Microaerophiles need oxygen because they cannot ferment or respire anaerobically. However, they are poisoned by high concentrations of oxygen. They gather in the upper part of the test tube but not the very top.
5: Aerotolerant organisms do not require oxygen as they metabolise energy anaerobically. Unlike obligate anaerobes however, they are not poisoned by oxygen. They can be found evenly spread throughout the test tube.
An aerobic organism or aerobe is an organism that can survive and grow in an oxygenated environment. In contrast, an anaerobic organism (anaerobe) is any organism that does not require oxygen for growth. Some anaerobes react negatively or even die if oxygen is present.
Types
- Obligate aerobes need oxygen to grow. In a process known as cellular respiration, these organisms use oxygen to oxidize substrates (for example sugars and fats) and generate energy.
- Facultative anaerobes use oxygen if it is available, but also have anaerobic methods of energy production.
- Microaerophiles require oxygen for energy production, but are harmed by atmospheric concentrations of oxygen (21% O2).
- Aerotolerant anaerobes do not use oxygen but are not harmed by it.
When an organism is able to survive in both oxygen and anaerobic environments, the use of the Pasteur effect can distinguish between facultative anaerobes and aerotolerant organisms. If the organism is using fermentation in an anaerobic environment, the addition of oxygen will cause facultative anaerobes to suspend fermentation and begin using oxygen for respiration. Aerotolerant organisms must continue fermentation in the presence of oxygen. Falcultative organisms grow in both oxygen rich media and oxygen free media
Glucose
A good example is the oxidation of glucose (a monosaccharide) in aerobic respiration:
where glucose releases the chemical energy stored in the relative weak double bond of oxygen.
This equation is a summary of what happens in three series of biochemical reactions: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
See also
- Aerobic digestion
- Anaerobic digestion
- Fermentation (biochemistry)
- Aerobic vaginitis
- Oxygenation (environmental)
References
- "aerobe" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ^ Hentges DJ (1996). "17: Anaerobes:General Characteristics". In Baron S (ed.). Medical Microbiology (4 ed.). Galveston, Texas: University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston. Retrieved 24 July 2016.
- ^ Kenneth Todar. "Nutrition and Growth of Bacteria". Todar's Online Textbook of Bacteriology. p. 4. Retrieved 24 July 2016.
- Chauhan, B. S. (2008).Principles of Biochemistry and Biophysics”. Laxmi Publications, p. 530. ISBN 978-8131803226
- Schmidt-Rohr, K. (2020). "Oxygen Is the High-Energy Molecule Powering Complex Multicellular Life: Fundamental Corrections to Traditional Bioenergetics” ACS Omega 5: 2221-2233. doi:10.1021/acsomega.9b03352
| Microbiology: Bacteria | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medical microbiology | |||||||
| Biochemistry and ecology |
| ||||||
| Shape | |||||||
| Structure |
| ||||||
| Taxonomy and evolution | |||||||