| Revision as of 09:55, 5 July 2020 editBoghog (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, IP block exemptions, New page reviewers, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers, Template editors137,966 edits consistent citation formatting← Previous edit |
Revision as of 23:36, 27 July 2020 edit undoJCW-CleanerBot (talk | contribs)Bots130,205 editsm task, replaced: Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine. Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine → Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and MedicineTag: AWBNext edit → |
| Line 8: |
Line 8: |
|
| pregnancy_category = |
|
| pregnancy_category = |
|
| legal_status = |
|
| legal_status = |
|
| routes_of_administration = |
|
| routes_of_administration = |
|
|
|
|
|
<!--Pharmacokinetic data--> |
|
<!--Pharmacokinetic data--> |
| Line 14: |
Line 14: |
|
| metabolism = |
|
| metabolism = |
|
| elimination_half-life = |
|
| elimination_half-life = |
|
| excretion = |
|
| excretion = |
|
|
|
|
|
<!--Identifiers--> |
|
<!--Identifiers--> |
| Line 33: |
Line 33: |
|
}} |
|
}} |
|
|
|
|
|
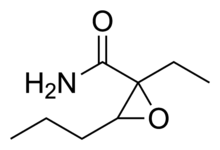
'''Oxanamide''' ('''Quiactin''') is an ] and ] which can produce ] and ] effects in sufficiently high doses.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Kuhn WL, Ketteler HJ, Van Maanen EF | s2cid = 40927309 | title = Effects of oxanamide on the central nervous system | journal = Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine. Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine | volume = 103 | pages = 101–3 | date = January 1960 | pmid = 14412594 | doi = 10.3181/00379727-103-25425 }}</ref> An uncontrolled trial on patients treated in a clinical ] practice published in 1959 found that oxanamide was efficacious in the treatment of anxiety resulting from ], ], and various other causes, with minimal sedation or other side effects.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Woodhull RB | title = Oxanamide; adjunctive use of a new tranquilizer in gynecology | journal = California Medicine | volume = 90 | issue = 4 | pages = 275–7 | date = April 1959 | pmid = 13638840 | pmc = 1577644 }}</ref> |
|
'''Oxanamide''' ('''Quiactin''') is an ] and ] which can produce ] and ] effects in sufficiently high doses.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Kuhn WL, Ketteler HJ, Van Maanen EF | s2cid = 40927309 | title = Effects of oxanamide on the central nervous system | journal = Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine | volume = 103 | pages = 101–3 | date = January 1960 | pmid = 14412594 | doi = 10.3181/00379727-103-25425 }}</ref> An uncontrolled trial on patients treated in a clinical ] practice published in 1959 found that oxanamide was efficacious in the treatment of anxiety resulting from ], ], and various other causes, with minimal sedation or other side effects.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Woodhull RB | title = Oxanamide; adjunctive use of a new tranquilizer in gynecology | journal = California Medicine | volume = 90 | issue = 4 | pages = 275–7 | date = April 1959 | pmid = 13638840 | pmc = 1577644 }}</ref> |
|
|
|
|
|
== References == |
|
== References == |
| Line 46: |
Line 46: |
|
] |
|
] |
|
] |
|
] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
{{musculoskeletal-drug-stub}} |
|
{{musculoskeletal-drug-stub}} |