This is an old revision of this page, as edited by 208.180.14.187 (talk) at 00:19, 3 February 2022 (added a small detail describing calluses). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 00:19, 3 February 2022 by 208.180.14.187 (talk) (added a small detail describing calluses)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) This article is about calluses and corns of human skin. For other uses, see Callus (disambiguation).This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
| Callus | |
|---|---|
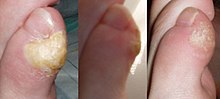 | |
| Examples of callus found on the toe | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
| Complications | Skin ulceration, infection |

A callus is an area of thickened and sometimes hardened skin that forms as a response to repeated friction, pressure, or other irritation. Since repeated contact is required, calluses are most often found on the feet and hands, but they may occur anywhere on the skin. Some degree of callus, such as on the bottom of the foot, is normal.
Calluses are generally not harmful and help prevent blisters, as well as offering protection. However, excessive formation may sometimes lead to other problems, such as a skin ulceration or infection, or cause the sufferer to try to offload the affected painful area, which can place excessive stress on the asymptomatic side.
Rubbing that is too frequent or forceful will cause blisters, as opposed to calluses, to form.
Cause
Normally, a callus will form on any part of the skin exposed to excess friction over a long period of time. For example, people often develop calluses on the middle finger or ring finger of their dominant hand due to writing with a pen or pencil. Another cause is from playing string instruments like the guitar or the violin; calluses will develop on the four fingers of the hand used in holding the strings down to the fingerboard, and sometimes on the fingers of the hand used for pizzicato or strumming. Weightlifters commonly experience callus on the upper-palm area due to repeated friction. Calluses are also very common on the fingers of rock climbers on almost all of their fingers. There are many activities that can result in the formation of a callus, which may even be viewed as a badge of experience and commitment to the activity.
Activities that are known for causing calluses include (but are not limited to) construction work, many sports, wood carving, playing musical instruments, use of a chef's knife, rock climbing, hiking, martial arts, weight training, rowing, BMXing, dancing (especially ballet), chopping wood, monkey bars and wearing high heels. Tenpin bowlers will often develop calluses on their thumbs and occasionally their middle fingers from frequent bowling. Calluses have also been known to develop on the forehead from the frequent prostrations required in Muslim prayer; known as a prayer bump or zebiba, such calluses are considered marks of piety in some Muslim countries, and people have been known to take special steps, such as praying on straw mats, to encourage the callus to develop.
Although calluses can occur anywhere on the body as a reaction to moderate, constant "grinding" pressure, they are most often found on the foot (where the most pressure and friction are applied). On the feet, arguably the source of the most problematic calluses, they typically form on the metatarsal-phalangeal joint area ("balls of the foot"), heels and small toes due to the compression applied by tightly fitting shoes.
Biologically, calluses are formed by the accumulation of terminally differentiated keratinocytes in the outermost layer of skin. Though the cells of calluses are dead, they are quite resistant to mechanical and chemical damage due to extensive networks of cross-linked proteins and hydrophobic keratin intermediate filaments containing many disulfide bonds. It is the natural reaction of the palmar or plantar skin. Too much friction occurring too fast for the skin to develop a protective callus will cause a blister or abrasion instead.
Sometimes a callus occurs where there is no rubbing or pressure. These hyperkeratoses can have a variety of causes. Some toxic materials, such as arsenic, can cause thick palms and soles. Some diseases, such as syphilis, can cause thickening of the palms and soles as well as pinpoint hyperkeratoses. There is a benign condition called keratosis palmaris et plantaris, which produces corns in the creases of the fingers and non-weight bearing spaces of the feet. Some of this may be caused by actinic keratosis, which occurs due to overexposure to sun or with age and hormonal shifts.
Corns
Main article: Corn (pathology)
A corn (or clavus, plural clavi) is a cone-shaped callus that penetrates into the dermis, usually on the feet or hands. Corns may form due to chronic pressure or rubbing at a pressure point (in this skin over a bone), or due to scar tissue from a healing wound creating pressure in a weight-bearing area such as the sole of the foot. If there is constant stimulation of the tissue producing the corns, even after the corn is surgically removed, the skin may continue to grow as a corn.
The hard part at the center of the corn resembles a funnel with a broad raised top and a pointed bottom. Because of their shape, corns intensify the pressure at the tip and can cause deep tissue damage and ulceration. The scientific name for a corn is heloma (plural helomata). A hard corn is called a heloma durum, while a soft corn is called a heloma molle.
The location of the soft corns tends to differ from that of hard corns. Hard corns occur on dry, flat surfaces of skin. Soft corns (frequently found between adjacent toes) stay moist, keeping the surrounding skin soft. The corn's center is not soft however, but indurated.
The specific diagnostic workup and treatments for corns may differ substantially from other forms of calluses.
Prevention
Corns and calluses are easier to prevent than to treat. When it is undesirable to form a callus, minimizing rubbing and pressure will prevent callus formation. Footwear should be properly fitted, gloves may be worn, and protective pads, rings or skin dressings may be used. People with poor circulation or sensation should check their skin often for signs of rubbing and irritation so they can minimize any damage.
Treatment

Calluses and corns may heal by themselves eventually, once the irritation is consistently avoided. They may also be dissolved with keratolytic agents containing salicylic acid, sanded down with a pumice stone or silicon carbide sandpaper or filed down with a callus shaver, or pared down by a professional such as a podiatrist.
Diabetes
People with diabetes face special skin challenges. Because diabetes affects the capillaries, the small blood vessels which feed the skin, thickening of the skin with callus increases the difficulty of supplying nutrients to the skin. Callus formation is seen in high numbers of patients with diabetes, and together with absent foot pulses and formation of hammer toe, this may be an early sign of individuals at an increased risk for foot ulcers.
The stiffness of a callus or corn, coupled with the shear and pressure that caused it, may tear the capillaries or adjoining tissue, causing bleeding within the callus or corn. Often, bleeding within a callus is an early sign of diabetes, even before elevated blood sugars may be noticed. Although the bleeding can be small, sometimes small pools of blood or hematoma are formed. The blood itself is an irritant, a foreign body within the callus that makes the area burn or itch. If the pool of blood is exposed to the outside, infection may follow. Infection may also lead to ulceration. This process can be prevented at several places. Diabetic foot infections are the leading cause of diabetic limb amputation.
See also
Notes
- Corns and Calluses, Cleveland Clinic
- Are Calluses Actually Bad for Your Feet? See What Podiatrists Have to Say, Footwear News
- Slackman, Michael (December 18, 2007). "Fashion and Faith Meet, on Foreheads of the Pious". New York Times. Retrieved 2018-08-08.
- Tantisiriwat N, Janchai S (Dec 1991). "Transglutaminases: multifunctional cross-linking enzymes that stabilize tissues". The FASEB Journal. 5 (15): 3071–7. doi:10.1096/fasebj.5.15.1683845. PMID 1683845. S2CID 6751428.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - eMedicine > Clavus By Nanette Silverberg. Updated: Apr 9, 2010
- Erstad, Shannon (6 March 2008). "Foot problems: Finding the right shoes". WebMD Medical Reference from Healthwise. Healthwise. How do I find the right shoes?. Retrieved 2010-06-10.
You should not have to "break in" shoes if they fit properly.
- Corns and calluses: Treatments and drugs. Mayo Clinic. Retrieved July 23, 2009.
- ^ Alavi A, Sanjari M, Haghdoost A, Sibbald RG (April 2009). "Common foot examination features of 247 Iranian patients with diabetes". International Wound Journal. 6 (2): 117–22. doi:10.1111/j.1742-481X.2009.00583.x. PMC 7951794. PMID 19432661. -12% having callus formation
- Tantisiriwat N, Janchai S (July 2008). "Common foot problems in diabetic foot clinic". J Med Assoc Thai. 91 (7): 1097–101. PMID 18839852. -56% having callus present
References
- Taber's Cyclopedic Medical Dictionary, 15th Edition, CL Thomas, M.D., M.P.H., editor, F.A. Davis Company, Philadelphia, PA, 1985.
- The Merck Manual of Medical Information, Home Edition, R Berkow, M.D., et al., editors, Merck Research Laboratories, Whitehouse Station, NJ, 1997.
External links
| Classification | D |
|---|
| Diseases of the skin and appendages by morphology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Growths |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rashes |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Miscellaneous disorders |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||