This is an old revision of this page, as edited by BRPXQZME (talk | contribs) at 07:13, 6 June 2008 (Infobox conversion). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 07:13, 6 June 2008 by BRPXQZME (talk | contribs) (Infobox conversion)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) For other ships with the same name, see HMS Dreadnought.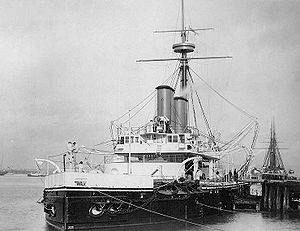
| |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Builder | Pembroke Dockyard |
| Laid down | 10 September 1870 |
| Launched | 8 March 1875 |
| Commissioned | 15 February 1879 |
| Out of service | 1905 |
| Stricken | 1908 |
| Fate | Scrapped July 1908 |
| General characteristics | |
| Displacement | 10,886 long tons (11,061 t) |
| Length | 320 ft (98 m) pp, 343 ft (105 m) oa |
| Beam | 63.8 ft (19.4 m) |
| Draught | 26.8 ft (8.2 m) |
| Propulsion | 12 boilers, 2 6-cycle triple expansion steam engines, 2 shafts = 14.52 kn (26.89 km/h; 16.71 mph) @ 8,210 shp (6,120 kW) |
| Range | 5,700 nmi (10,600 km; 6,600 mi) @ 10 kn (19 km/h; 12 mph) |
| Complement | 369 |
| Armament | list error: <br /> list (help) As built: 4-12.5in 38 ton Muzzle loading Rifles (1884) Ten Nordenfelt Machine Guns added (1894) Machine guns removed, six 6-pdr, ten 3-pdr added |
| Armour | 8-14" midships belt, 3" deck, 14" turret face, 14" conning tower side |
The fifth HMS Dreadnought of the British Royal Navy was a turret ironclad battleship built at Pembroke Dockyard, Wales.
Begun as Fury in 1870, the original design was recast and the renamed ship was laid down in 1872, launched in March 1875 and finally completed in 1879. She carried her four muzzle-loading guns in two twin turrets, and had a very heavily armored hull, low freeboard, and no sailing rig. Her secondary armament was very light, though it varied in detail throughout her career. Despite their obsolescence, she retained her muzzle-loading big guns to the end of her days.
After completion, Dreadnought remained in reserve until 1884, when she was commissioned for service in the Mediterranean Sea. The battleship returned to British waters in 1894 and, after refit, served in 1895-1897 as a coast guard ship at Bantry Bay, Ireland. Dreadnought was partially modernized in 1897-1899 and took part in British fleet manoeuvres in 1900 and 1901 as a second-class battleship. From 1902, she served as a tender and depot ship. She was placed out of service in 1905, and sold for scrapping in July 1908.
References
- D. K. Brown, Warrior to Dreadnought, Warship Development 1860-1906, ISBN 1-84067-529-2
- Roger Chesneau and Eugene M. Kolesnik, ed., Conway's All The Worlds Fighting Ships, 1860-1905, (Conway Maritime Press, London, 1979), ISBN 0-85177-133-5