This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Crow4656 (talk | contribs) at 16:31, 10 April 2008 (→Beliefs). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 16:31, 10 April 2008 by Crow4656 (talk | contribs) (→Beliefs)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)| Part of a series on | ||||
| Christianity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||
|
||||
| Theology | ||||
|
||||
| Related topics | ||||
Christianity is a monotheistic religion centered on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth as presented in the New Testament. As of the early 21st century, it has between 1.5 billion and 2.1 billion adherents, representing about a quarter of the world's population. It is the state religion of at least sixteen countries.
Its followers, known as Christians, believe that Jesus is the Son of God and the Messiah (or Christ) prophesied in the Old Testament, the part of their scriptures they have in common with Judaism. To Christians, Jesus Christ is a teacher, the model of a pious life, the revealer of God, the mediator of salvation and the saviour who suffered, died and was resurrected in order to bring about salvation from sin for all. Christians maintain that Jesus ascended into heaven and most denominations teach that Jesus will judge the living and the dead, granting everlasting life to his followers. The "good news" of Jesus' ministry is called the Gospel.
The Trinity is often regarded as an essential doctrine of mainstream Christianity. The most common understanding of the Holy Trinity, as espoused in the Nicene Creed, is one God who exists in three Persons – Father, the Son, and the Holy Spirit – who are coequal, co-eternal, of the same substance. "Father, Son and Holy Spirit" represents both the immanence and transcendence of God. God is believed to be infinite and God's presence may be perceived through the actions of Jesus and the Holy Spirit.
The first time the disciples were called "Christians" (Greek Template:Polytonic), meaning "followers of Christ", was in Antioch. Ignatius of Antioch was the first Christian to use the label in self-reference. The earliest recorded use of the term Christianity (Greek Template:Polytonic) was also by Ignatius of Antioch, around AD 100.
Like Judaism and Islam, Christianity is classified as an Abrahamic religion (see also Judeo-Christian). Through missionary work and colonisation, Christianity spread firstly in the Middle East, North Africa, Europe and parts of India and subsequently throughout the entire world.
christans can suck my dick and god was gay by the way bitches
Worship
Main article: Christian worship
Justin Martyr described 2nd century Christian liturgy in his First Apology (c. 150) to Emperor Antoninus Pius, and his description remains relevant to the basic structure of Christian liturgical worship:

- "And on the day called Sunday, all who live in cities or in the country gather together to one place, and the memoirs of the apostles or the writings of the prophets are read, as long as time permits; then, when the reader has ceased, the president verbally instructs, and exhorts to the imitation of these good things. Then we all rise together and pray, and, as we before said, when our prayer is ended, bread and wine and water are brought, and the president in like manner offers prayers and thanksgivings, according to his ability, and the people assent, saying Amen; and there is a distribution to each, and a participation of that over which thanks have been given, and to those who are absent a portion is sent by the deacons. And they who are well to do, and willing, give what each thinks fit; and what is collected is deposited with the president, who succours the orphans and widows and those who, through sickness or any other cause, are in want, and those who are in bonds and the strangers sojourning among us, and in a word takes care of all who are in need."
Thus, as Justin described, Christians assemble for communal worship on Sunday, the day of the resurrection, though other liturgical practices often occur outside this setting. Scripture readings are drawn from the Old and New Testaments, but especially the Gospels. Often these are arranged on an annual cycle, using a book called a lectionary. Instruction is given based on these readings, called a sermon, or homily. There are a variety of congregational prayers, including thanksgiving, confession, and intercession, which occur throughout the service and take a variety of forms including recited, responsive, silent, or sung. The Lord's Prayer, or Our Father, is regularly prayed. The Eucharist (called Holy Communion, or the Lord's Supper) is the part of liturgical worship that consists of a consecrated meal, usually bread and wine. Justin Martyr described the Eucharist:
"And this food is called among us Eukaristia , of which no one is allowed to partake but the man who believes that the things which we teach are true, and who has been washed with the washing that is for the remission of sins, and unto regeneration, and who is so living as Christ has enjoined. For not as common bread and common drink do we receive these; but in like manner as Jesus Christ our Saviour, having been made flesh by the Word of God, had both flesh and blood for our salvation, so likewise have we been taught that the food which is blessed by the prayer of His word, and from which our blood and flesh by transmutation are nourished, is the flesh and blood of that Jesus who was made flesh."
Some Christian denominations view communion as indicating those who are already united in the church, restricting participation to their members not in a state of mortal sin (closed communion). Most other churches view communion as a means to unity, rather than an end, and invite all Christians or even anyone to participate (open communion). In some denominations, participation is decided by prior arrangement with a church leader.
Some groups depart from this traditional liturgical structure. A division is often made between "High" church services, characterized by greater solemnity and ritual, and "Low" services, but even within these two categories there is great diversity in forms of worship. Seventh-day Adventists meet on Saturday (the original Sabbath), while others do not meet on a weekly basis. Charismatic or Pentecostal congregations may spontaneously feel led by the Holy Spirit to action rather than follow a formal order of service, including spontaneous prayer. Quakers sit quietly until moved by the Holy Spirit to speak. Some Evangelical services resemble concerts with rock and pop music, dancing, and use of multimedia. For groups which do not recognize a priesthood distinct from ordinary believers the services are generally lead by a minister, preacher, or pastor. Still others may lack any formal leaders, either in principle or by local necessity. Some churches use only a cappella music, either on principle (e.g. many Churches of Christ object to the use of instruments in worship) or by tradition (as in Orthodoxy).
Worship can be varied for special events like baptisms or weddings in the service or significant feast days. In the early church Christians and those yet to complete initiation would separate for the Eucharistic part of the worship. In many churches today, adults and children will separate for all or some of the service to receive age-appropriate teaching. Such children's worship is often called Sunday school or Sabbath school (Sunday schools are often held before rather than during services).
Sacraments
Main article: Sacrament
In Christian belief and practice, a sacrament is a rite, instituted by Christ, that mediates grace, constituting a sacred mystery. The term is derived from the Latin word sacramentum, which was used to translate the Greek word for mystery. Views concerning both what rites are sacramental, and what it means for an act to be a sacrament vary among Christian denominations and traditions.
The most conventional functional definition of a sacrament is that it is an outward sign, instituted by Christ, that conveys an inward, spiritual grace through Christ. The two most widely accepted sacraments are Baptism and the Eucharist, however, the majority of Christians recognize seven Sacraments or Divine Mysteries: Baptism, Confirmation (Chrismation in the Orthodox tradition), and the Eucharist, Holy Orders, Reconciliation of a Penitent (confession), Anointing of the Sick, and Matrimony. Taken together, these are the Seven Sacraments as recognised by churches in the High church tradition - notably Roman Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, Independent Catholic, Old Catholic and some Anglicans. Most other denominations and traditions typically affirm only Baptism and Eucharist as sacraments, while some Protestant groups, such as the Quakers, reject sacramental theology. Some Christian denominations who believe these rites do not communicate grace prefer to call them ordinances.
Liturgical calendar
Main article: Liturgical yearRoman Catholics, Anglicans, Eastern Christians, and traditional Protestant communities frame worship around a liturgical calendar. This includes holy days, such as solemnities which commemorate an event in the life of Jesus or the saints, periods of fasting such as Lent, and other pious events such as memoria or lesser festivals commemorating saints. Christian groups that do not follow a liturgical tradition often retain certain celebrations, such as Christmas, Easter and Pentecost. A few churches make no use of a liturgical calendar.
Symbols
Main article: Christian symbolism
The cross, which is today one of the most widely recognised symbols in the world, was used as a Christian symbol from the earliest times. In his book De Corona, written in the year 204, Tertullian tells how it was already a tradition for Christians to trace repeatedly on their foreheads the sign of the cross. Although the cross was known to the early Christians, the crucifix, did not appear in use until the fifth century.
Among the symbols employed by the primitive Christians, that of the fish seems to have ranked first in importance. From monumental sources such as tombs it is known that the symbolic fish was familiar to Christians from the earliest times. The fish was depicted as a Christian symbol in the first decades of the second century. Its popularity among Christians was due principally, it would seem, to the famous acrostic consisting of the initial letters of five Greek words forming the word for fish (Ichthys), which words briefly but clearly described the character of Christ and the claim to worship of believers: Iesous Christos Theou Yios Soter, meaning, Jesus Christ, Son of God, Saviour.
Christians from the very beginning adorned their tombs with paintings of Christ, of the saints, of scenes from the Bible and allegorical groups. The catacombs are the cradle of all Christian art. The first Christians had no prejudice against images, pictures, or statues. The idea that they must have feared the danger of idolatry among their new converts is disproved in the simplest way by the pictures even statues, that remain from the first centuries. Other major Christian symbols include the chi-rho monogram, the dove (symbolic of the Holy Spirit), the sacrificial lamb (symbolic of Christ's sacrifice), the vine (symbolising the necessary connectedness of the Christian with Christ) and many others. These all derive from the writings found the New Testament.
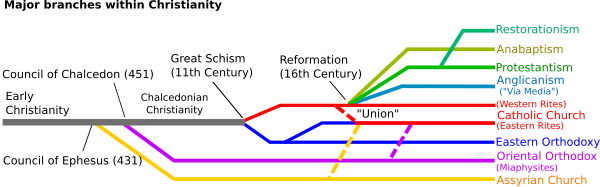
History and origins
Main article: History of ChristianityEarly Church and Christological Councils
Christianity began as a Jewish sect. The Christian Church traces its history to Jesus and the Twelve Apostles, and saw the early bishops of the Church as the successors of the Apostles in general. Central to the doctrines of the Roman Catholic, Orthodox and Anglican Churches is Apostolic Succession, the belief that the bishops are the spiritual successors of the original twelve apostles, through the historically unbroken chain of consecration.
From the beginning, Christians were subject to various persecutions. This involved even death for Christians such as Stephen and James, son of Zebedee. Larger-scale persecutions followed at the hands of the authorities of the Roman Empire, beginning with the year 64, when, as reported by the Roman historian Tacitus, the Emperor Nero blamed them for that year's great Fire of Rome. According to Church tradition, it was under Nero's persecution that early Church leaders Peter and Paul were each martyred in Rome. Further widespread persecutions of the Church occurred under nine subsequent Roman emperors including Domitian, Decius and Diocletian. From the year 150, Christian teachers began to produce theological and "apologetic" works aimed at defending the faith. These authors are known as the Church Fathers, and study of them is called Patristics. Notable early Fathers include Ignatius of Antioch, Polycarp, Justin Martyr, Irenaeus, Tertullian, Clement of Alexandria and Origen.
Christianity was legalized in the fourth century, when Constantine I issued the Edict of Milan in 313. Constantine was instrumental in the convocation of the First Council of Nicaea in 325, which sought to address the Arian heresy and formulated the Nicene Creed, which is still used by the Roman Catholic Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, Anglican Communion, and many Protestant churches.
In 324, Constantine the Great announced his decision to transform Byzantium into Nova Roma and on May 11, 330, he officially proclaimed the city the new capital of the Roman Empire. The city was renamed Constantinople, The City of Constantine, after Constantine's death in 337. This effectively made the Greek city, Constantinople, the head of the Roman, now the Greek, empire. This Greek empire was the first to fully support Christianity, and was known as One, Holy, Catholic and Apostolic church.
On 27 February 380, Emperor Theodosius I enacted a law establishing Catholic (Universal or General) Christianity as the official religion of the Roman Empire (East or Byzantine Empire and West). This period of history was also marked by the inauguration of a series of Ecumenical (worldwide) Christological Councils which established and formally codified critical elements of the theology of the Church. In 382, the Council of Rome set the Canon of the Bible, listing the accepted books of the Old Testament and the New Testament. Also, the Council of Ephesus in 431 declared that Jesus existed both as fully Man and fully God simultaneously, clarifying his status in the Trinity. The meaning of the Nicene Creed was also declared a permanent doctrine of the Church.
Medieval period
In 452, Pope Leo the Great met Attila the Hun, and dissuaded him from sacking Rome. However, in 476, the last Roman Emperor, Romulus Augustus was deposed. Following the fall of the Roman Empire in the west, the church entered into a long period of missionary activity and expansion among the former barbarian tribes. Catholicism spread among the Germanic peoples (initially in competition with Arianism), the Celts, the Slavic peoples; the Vikings and other Scandinavians; the Hungarians, the Baltic peoples and the Finns. The rise of Islam from 630 onwards, took the formerly Christian lands of the Levant, North Africa and much of Spain out of Christian control. In 480, St. Benedict set out his Monastic Rule, establishing a system of regulations for the foundation and running of monasteries. Monasticism became a powerful force throughout Europe, and gave rise to many early centers of learning, most famously in Ireland, Scotland and Gaul, contributing to the Carolingian Renaissance of the 9th century.
The Middle Ages brought about major changes within the church. Pope Gregory the Great dramatically reformed ecclesiastical structure and administration. In the early 8th century, iconoclasm became a divisive issue, when it was sponsored by the Byzantine emperors. The popes challenged imperial power and preserved the use of images outside the empire. The Second Ecumenical Council of Nicaea (787) finally pronounced in favour of icons. In the early 10th century, western monasticism was further rejuvenated through the leadership of the great Benedictine monastery of Cluny.
High Middle Ages
In the west, from the 11th century onward, older cathedral schools developed into universities (see University of Paris, University of Oxford, and University of Bologna.) Originally teaching only theology, these steadily added subjects including medicine, philosophy and law, becoming the direct ancestors of modern western institutions of learning.
Accompanying the rise of the "new towns" throughout Western Europe, mendicant orders were founded, bringing the consecrated religious life out of the monastery and into the new urban setting. The two principal mendicant movements were the Franciscans and the Dominicans founded by St. Francis and St. Dominic respectively. Both orders made significant contributions to the development of the great universities of Europe. Another new order were the Cistercians, whose large isolated monasteries spearheaded the settlement of former wilderness areas. In this period church building and ecclesiastical architecture reached new heights, culminating in the orders of Romanesque and Gothic architecture and the building of the great European cathedrals.

From 1095 under the pontificate of Urban II, the Crusades were launched. These were a series of military campaigns in the Holy Land and elsewhere, initiated in response to pleas from the Byzantine Emperor Alexios I for aid against Turkish expansion. The crusades ultimately failed to stifle Islamic aggression and even contributed to Christian enmity with the sacking and occupation of Constantinople during the Fourth Crusade.
Beginning around 1184, following the crusades brought about by the Cathar heresy, various institutions broadly referred to as the Inquisition, were established aimed at suppressing heresy and securing religious and doctrinal unity within Christianity through conversion, and prosecution, of alleged heretics.
East-West Schism
Main article: East-West SchismOver a period stretching from the seventh to the fourteenth centuries, the church underwent a gradual schism that divided it into a Western (Latin) branch, generally known as the Roman Catholic Church, and an Eastern (Greek) branch, which has become known as the Orthodox Church. These two churches disagree on a number of administrative, liturgical, and doctrinal issues, most notably papal primacy of jurisdiction.
The Second Council of Lyon (1274) and the Council of Florence (1439) attempted to reunite the churches, but in both cases the Orthodox refused to ratify the decisions and the two principal churches remain in schism to the present day.
Reformation and Counter-Reformation
Main article: Protestant Reformation See also: Catholic ReformationThe 15th-century Renaissance brought about a renewed interest in ancient and classical learning, and a re-examination of accepted beliefs. The discovery of the Americas by Christopher Columbus in 1492 brought about a new wave of missionary activity as the church sought to spread the faith throughout the colonies. Another major schism, the Reformation, resulted in the splintering of the Western Christian Church into several Christian denominations. On 31 October 1517 Martin Luther posted his 95 Theses, which protested key points of Roman Catholic doctrine as well as the sale of indulgences. Others like Zwingli and Calvin critiqued Roman Catholic teaching and worship even more. These challenges developed into the movement called the Protestant Reformation, which repudiated the primacy of the pope, clerical celibacy, the seven sacraments, the eucharist, and various other doctrines and practices. The Reformation in England accelerated in 1534, when the English Parliament passed the Act of Supremacy making the King of England Supreme Head of the Church of England. Beginning in 1536, the monasteries throughout England, Wales, and Ireland were dissolved. Pope Paul III then excommunicated King Henry VIII in 1538, beginning what would become a decisive schism between Rome and Canterbury.
The Counter-Reformation, or Catholic Reformation, is the name given to the response of the Roman Catholic Church to the challenge of Protestantism. The Council of Trent clarified and reasserted Roman Catholic doctrine. During the following centuries, competition between Roman Catholicism and Protestantism became deeply entangled with political struggles among European states. Meanwhile, partly from missionary zeal, but under the impetus of colonial expansion by the European powers, Christianity spread to the Americas, Oceania, East Asia, and sub-Saharan Africa.
Christianity in the Modern Era
In the Modern Era, Christianity was confronted with various forms of skepticism and with certain modern political ideologies such as liberalism, nationalism, and socialism. This included the anti-clericalism of the French Revolution, the Spanish Civil War, and general hostility of Marxist movements, especially the Russian Revolution.
Christian commitments in Europe dropped as modernity and secularism came into their own in Western Europe, while religious commitments in America have been generally high in comparison to Western Europe. The late 20th Century has shown the shift of Christian adherents to the 3rd World and southern hemisphere in general, with Western Civilization no longer the chief standard bearer of Christianity.
Branches of Christianity in the present day
Main article: Christian denomination
There is a diversity of doctrines and practices among groups calling themselves Christian. These groups are sometimes classified under denominations, though for theological reasons many groups reject this classification system. Christianity may be broadly represented as being divided into four main groupings:
Roman Catholics
Roman Catholicism: The Roman Catholic Church, or "Catholic Church", includes the local churches, headed by bishops, in communion with the Pope, the Bishop of Rome. The Church claims to have existed since the foundation of Christianity through Apostolic Succession, and in fact the formal structures of the Church have existed since at least the 4th century. Grouped into 23 particular rites, it is the largest single body, with more than one billion baptized members.
Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy: Those churches in communion with the Patriarchal Sees of the East, such as the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople and others. A number of conflicts with Western Christianity over questions of doctrine and authority culminated in the Great Schism. Like the Roman Catholic Church and the Anglican Communion, the Eastern Orthodox Church also claims a heritage from primeval Christianity and has an episcopal structure, though the autonomy of the individual, constituent churches is emphasized. It is the second largest single denomination in Christianity, with over 200 million adherents.
Oriental Orthodox
Oriental Orthodoxy: Those Eastern Christian Churches that recognize only three ecumenical councils — the First Council of Nicaea, the First Council of Constantinople and the Council of Ephesus. They reject the dogmatic definitions of the Council of Chalcedon. Hence, these Churches are also called Old Oriental Churches or Non-chalcedonian churches.
Protestants and other Catholics
Protestantism: In the 16th century, Martin Luther, Huldrych Zwingli, and John Calvin inaugurated what has come to be called the Protestant Reformation. Luther's primary theological heirs are known as Lutherans in America, but are more commonly known as Evangelicals in Germany and elsewhere (To be distinguished from American Evangelicism). Zwingli and Calvin's heirs are far broader denominationally, and are broadly referred to as the Reformed Tradition. Most Protestant traditions branch out from the Reformed tradition in some way. In addition to the Lutheran and Reformed branches of the Reformation, there is Anglicanism after the English Reformation. The Anabaptist tradition was largely ostracized by the other Protestant parties at the time, but has achieved a measure of affirmation in more recent history.
The oldest Protestant groups separated from the Roman Catholic Church in the 16th century Protestant Reformation, followed in many cases by further divisions. For example, the Methodist Church grew out of Anglican minister John Wesley's evangelical and revival movement in the Anglican Church. Several Pentecostal and non-denominational Churches, which emphasize the cleansing power of the Holy Spirit, in turn grew out of the Methodist Church. Because Methodists, Pentecostals, and other evangelicals stress "accepting Jesus as your personal Lord and Savior," which comes from John Wesley's emphasis of the New Birth, they often refer to themselves as being born-again.
Estimates of the total number of Protestants are very uncertain, partly because of the difficulty in determining which denominations should be placed in these categories, but it seems clear that Protestantism is the second largest major group of Christians after Roman Catholicism in number of followers (although the Eastern Orthodox Church is larger than any single Protestant denomination).
Many members of the the Anglican Communion, a group of Anglican and Episcopal Churches that are descended from the Church of England, identify as both Protestant and Catholic. Various small communities, such as the Old Catholic and Independent Catholic Churches, are similar in name to the Roman Catholic Church, but are not in communion with the See of Rome. The Old Catholic church is in communion with the See of Canterbury.
Some Christians who come out of the Protestant tradition identify themselves simply as "Christian", or "born-again Christian"; they typically distance themselves from the confessionalism and/or creedalism of other Christian communities by calling themselves "non-denominational" – often founded by individual pastors, they have little affiliation with historic denominations.
Restorationists
Restorationism is composed of various unrelated Churches that believe they are restoring the "original version" of Christianity and not as "reforming" a Christian Church continuously existing from the time of Jesus. They feel that the other three divisions of Christianity have introduced grave defects into Christianity, which is known as the Great Apostasy. Some of these are historically connected to early-19th century Camp Meetings in the Midwest and Upstate New York. American Millennialism and Adventism, which arose from Evangelical Protestantism, produced certain groups such as the Jehovah's Witnesses movement (with 6.6 million members), and, as a reaction specifically to William Miller, Seventh Day Adventists. Additionally, there are the following groups: Christadelphians, Churches of Christ with 2.6 million members, Disciples of Christ with 800,000 members, and The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, the largest denomination of the Latter Day Saint movement with over 13 million members. Though Restorationists have some superficial similarities, their doctrine and practices vary significantly.
Mainstream Christianity is widely used to refer collectively to the common views of major denominations of Christianity (such as Roman Catholicism, Protestantism, Anglicanism, Orthodox Christianity) as against the particular tenets of other sects or Christian denomination. The context is dependent on the particular issues addressed, but usually contrasts the orthodox majority view against heterodox minority views of groups like Restorationists. In the most common sense, "mainstream" refers to Nicene Christianity, or rather the traditions which continue to claim adherence to the Nicene Creed.
Ecumenism
Main article: EcumenismMost churches have long expressed ideals of being reconciled with each other, and in the 20th century Christian ecumenism advanced in two ways. One way was greater cooperation between groups, such as the Edinburgh Missionary Conference of Protestants in 1910, the Justice, Peace and Creation Commission of the World Council of Churches founded in 1948 by Protestant and Orthodox churches, and similar national councils like the National Council of Churches in Australia which includes Roman Catholics.
The other way was institutional union with new United and uniting churches. Congregationalist, Methodist, and Presbyterian churches united in 1925 to form the United Church of Canada, and in 1977 to form the Uniting Church in Australia. The Church of South India was formed in 1947 by the union of Anglican, Methodist, Congregationalist, Presbyterian, and Reformed churches.
Steps towards reconciliation on a global level were taken in 1965 by the Roman Catholic and Orthodox churches mutually revoking the excommunications that marked their Great Schism in 1054; the Anglican Roman Catholic International Commission (ARCIC) working towards full communion between those churches since 1970; and the Lutheran and Catholic churches signing The Joint Declaration on the Doctrine of Justification in 1999 to address conflicts at the root of the Protestant Reformation. In 2006 the Methodist church adopted the declaration.
Figures
With an estimated number of adherents that ranges between 1.5 billion and 2.1 billion, split into around 34,000 separate denominations, Christianity is the world's largest religion. The Christian share of the world's population has stood at around 33 per cent for the last hundred years. This masks a major shift in the demographics of Christianity; large increases in the developing world have been accompanied by substantial declines in the developed world, mainly in Europe and North America. On current projections, by 2050 only about one-fifth of the world's Christians will be non-Hispanic whites. It is still the predominant religion in Europe, the Americas, the Philippines, and Southern Africa. However it is declining in some areas including Oceania (Australia and New Zealand), Northern Europe (including France, Germany, Great Britain, Scandinavia and other places), the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec, the Western and Northern portions of the United States, and parts of Asia (especially the Middle East, Taiwan and Macau).
In most countries in the developed world, church attendance among people who continue to identify themselves as Christians has been falling over the last few decades. Some sources view this simply as part of a drift away from traditional membership institutions, while others link it to signs of a decline in belief in the importance of religion in general.
Christianity, in one form or another, is the sole state religion of the following nations: Argentina, Bolivia, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Liechtenstein, Malta, Monaco, Vatican City, Cyprus, Republic of Moldova, Greece, Denmark, Iceland, Norway, Finland and Great Britain.
Notes
- The Catholic Encyclopedia, Volume IX, Monotheism; William F. Albright, From the Stone Age to Christianity; H. Richard Niebuhr; About.com, Monotheistic Religion resources; Jonathan Kirsch, God Against the Gods; Linda Woodhead, An Introduction to Christianity; The Columbia Electronic Encyclopedia Monotheism; The New Dictionary of Cultural Literacy, monotheism; New Dictionary of Theology, Paul, p. 496-99; David Vincent Meconi, "Pagan Monotheism in Late Antiquity" in Journal of Early Christian Studies, p. 111–12
- BBC, BBC - Religion & Ethics - Christianity
- "between 1,250 and 1,750 million adherents, depending on the criteria employed": McGrath, Alister E. Christianity: An Introduction. 2006, page xv1.
- "1.5 thousand million Christians": Hinnells, John R. The Routledge Companion to the Study of Religion. 2005, page 441.
- Major Religions Ranked by Size
- Hinnells, John R. The Routledge Companion to the Study of Religion. 2005, page 441.
- Christians believe that Jesus is still alive in heaven, and that, as God, he exists in eternity, hence the use of "is".
- Mortimer Chambers, The Western Experience Volume II chapter 5; The Oxford Dictionary of the Jewish Religion, p. 158.
- McGrath, Alister E. Christianity:An Introduction, Blackwell Publishing (2006), p. 4-6. ISBN 1405108991.
- Fowler, Jeaneane D. World Religions:An Introduction for Students. p. 58. Sussex Academic Press (1997). ISBN 1898723486.
- Acts 11:26
- Elwell, Walter A. & Comfort, Philip Wesley. Tyndale Bible Dictionary, p. 266, 828. Tyndale House Publishers (2001). ISBN 0842370897.
- J.Z.Smith 98, p. 276.
- Anidjar 2001, p. 3
- Fowler, Jeaneane D. World Religions:An Introduction for Students. Sussex Academic Press (1997), p. 131. ISBN 1898723486.
- McManners, John. Oxford Illustrated History of Christianity. Oxford University Press (1990), p. 301–303.
- Justin Martyr, First Apology §LXVII
- Justin Martyr, First Apology §LXVII
- ^ The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church, 3rd edition. USA: Oxford University Press. 13 March 1997. pp. 1435–6. ISBN 0–19–211655–X.
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: invalid character (help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Hickman, Hoyt L., et al. Handbook of the Christian Year. Abingdon Press (1986). ISBN 0-687-16575-X
- ANF04. Fathers of the Third Century: Tertullian, Part Fourth; Minucius Felix; Commodian; Origen, Parts First and Second | Christian Classics Ethereal Library
- Minucius Felix speaks of the cross of Jesus in its familiar form, likening it to objects with a crossbeam or to a man with arms outstretched in prayer (Octavius of Minucius Felix, chapter XXIX).
- "At every forward step and movement, at every going in and out, when we put on our clothes and shoes, when we bathe, when we sit at table, when we light the lamps, on couch, on seat, in all the ordinary actions of daily life, we trace upon the forehead the sign" (De Corona, chapter 3)
- ^ Dilasser, Maurice. The Symbols of the Church (1999). Collegeville, MN: Liturgical Press, hardcover: ISBN 0-8146-2538-x
- ^ Hassett, Maurice (1912). "Symbolism of the Fish". Catholic Encyclopedia. Robert Appleton Company. Retrieved 2007-11-26.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Fortescue, Adrian (1912). "Veneration of Images". Catholic Encyclopedia. Robert Appleton Company. Retrieved 2007-11-26.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Robinson, George. Essential Judaism: A Complete Guide to Beliefs, Customs and Rituals. New York: Pocket Books, 2000, p. 229.
- Esler, Phillip F. The Early Christian World. Routledge (2004), p. 157-158.
- Acts 7:59
- 12:2
- "Our Common Heritage as Christians". The United Methodist Church. Retrieved 2007-12-31.
- "It is our desire that all the various nations which are subject to our clemency and moderation should continue to the profession of that religion which was delivered to the Romans by the divine Apostle Peter, as it has been preserved by faithful tradition and which is now professed by the Pontiff Damasus and by Peter, Bishop of Alexandria, a man of apostolic holiness. ... We authorize the followers of this law to assume the title Catholic Christians; but as for the others, since in our judgment they are foolish madmen, we decree that they shall be branded with the ignominious name of heretics, and shall not presume to give their conventicles the name of churches."
Halsall, Paul (1997). "Theodosian Code XVI.i.2". Medieval Sourcebook: Banning of Other Religions. Fordham University. Retrieved 2006-09-19.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Gonzalez, Justo L. 'The Story of Christianity: The Early Church to the Dawn of the Reformation'(c) 1984 HarperCollins Publishers, New York, NY, p 243.
- ^ Gonzalez, Justo L. 'The Story of Christianity: The Early Church to the Dawn of the Reformation'(c) 1984 HarperCollins Publishers, New York, NY, p 238.
- Gonzalez, Justo L. 'The Story of Christianity: The Early Church to the Dawn of the Reformation'(c) 1984 HarperCollins Publishers, New York, NY, pp 248-250.
- Gonzalez, Justo L. 'The Story of Christianity: The Early Church to the Dawn of the Reformation'(c) 1984 HarperCollins Publishers, New York, NY, pp 238-242.
- Gonzalez, Justo L. 'The Story of Christianity: The Early Church to the Dawn of the Reformation'(c) 1984 HarperCollins Publishers, New York, NY, p 244-247
- Gonzalez, Justo L. 'The Story of Christianity: The Early Church to the Dawn of the Reformation'(c) 1984 HarperCollins Publishers, New York, NY, p 260
- Gonzalez, Justo L. 'The Story of Christianity: The Early Church to the Dawn of the Reformation'(c) 1984 HarperCollins Publishers, New York, NY, p 260.
- Gonzalez, Justo L. 'The Story of Christianity: The Early Church to the Dawn of the Reformation'(c) 1984 HarperCollins Publishers, New York, NY, pp 278-281.
- Gonzalez, Justo L. 'The Story of Christianity: The Early Church to the Dawn of the Reformation'(c) 1984 HarperCollins Publishers, New York, NY, pp 305, 312, 314-15.
- Gonzalez, Justo L. 'The Story of Christianity: The Early Church to the Dawn of the Reformation'(c) 1984 HarperCollins Publishers, New York, NY, pp 303-307, 310-11, 384-386.
- Gonzalez, Justo L. 'The Story of Christianity: The Early Church to the Dawn of the Reformation'(c) 1984 HarperCollins Publishers, New York, NY, pp 305, 310-11, 316-317.
- Gonzalez, Justo L. 'The Story of Christianity: The Early Church to the Dawn of the Reformation'(c) 1984 HarperCollins Publishers, New York, NY, pp 321-323, 365-66.
- Gonzalez, Justo L. 'The Story of Christianity: The Early Church to the Dawn of the Reformation'(c) 1984 HarperCollins Publishers, New York, NY, pp 292-300.
- Riley-Smith, Jonathan. The Oxford History of the Crusades New York: Oxford University Press, 1999.
- Gonzalez, Justo L. 'The Story of Christianity: The Early Church to the Dawn of the Reformation'(c) 1984 HarperCollins Publishers, New York, NY, pp 300, 304-305.
- Gonzalez, Justo L. 'The Story of Christianity: The Early Church to the Dawn of the Reformation'(c) 1984 HarperCollins Publishers, New York, NY, pp 310, 383, 385, 391.
- The Great Schism: The Estrangement of Eastern and Western Christendom
- Simon, Edith (1966). Great Ages of Man: The Reformation. Time-Life Books. pp. p. 7. ISBN 0662278208.
{{cite book}}:|pages=has extra text (help) - Simon, Edith (1966). Great Ages of Man: The Reformation. Time-Life Books. pp. p. 39, 55-61. ISBN 0662278208.
{{cite book}}:|pages=has extra text (help) - Schama states that Henry's reforms were "a reformation but not the Protestant Reformation."
- Simon Schama, A History of Britain. Hyperion (2000), p. 306-10. ISBN 0-7868-6675-6.
- Simon, Edith (1966). Great Ages of Man: The Reformation. Time-Life Books. pp. p. 109-120. ISBN 0662278208.
{{cite book}}:|pages=has extra text (help) - S. E. Ahlstrom characterized denominationalism in America as "a virtual ecclesiology" that "first of all repudiates the insistences of the Roman Catholic church, the churches of the 'magisterial' Reformation, and of most sects that they alone are the true Church." Ahlstrom p. 381. For specific citations, on the Roman Catholic Church see the Catechism of the Catholic Church §816; other examples: Donald Nash, Why the Churches of Christ are not a Denomination; Wendell Winkler, Christ's Church is not a Denomination; and David E. Pratt, What does God think about many Christian denominations?
- "Divisions of Christianity". North Virginia College. Retrieved 2007-12-31.
- "The LDS Restorationist movement, including Mormon denominations". Religious Tolerance. Retrieved 2007-12-31.
{{cite web}}: line feed character in|title=at position 33 (help) - ^ Adherents.com, Religions by Adherents
- The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church, 3rd edition. USA: Oxford University Press. 13 March 1997. p. 1199. ISBN 0–19–211655–X.
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: invalid character (help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - McManners, John. Oxford Illustrated History of Christianity. Pp 251-59. Oxford University Press (1990) IBSN 0198229283.
- McManners, John. Oxford Illustrated History of Christianity. Pg 251. Oxford University Press (1990) IBSN 0198229283.
- "About The Methodist Church". Methodist Central Hall Westminster. Retrieved 2007-12-31.
- ^ "American Holiness Movement". Finding Your Way, Inc. Retrieved 2007-12-31.
- "Christianity: Pentecostal Churches". Finding Your Way, Inc. Retrieved 2007-12-31.
- "Statement of Belief". Cambridge Christ United Methodist Church. Retrieved 2007-12-31.
- "The New Birth by John Wesley (Sermon 45)". The United Methodist Church GBGM. Retrieved 2007-12-31.
- "God's Preparing, Accepting, and Sustaining Grace". The United Methodist Church GBGM. Retrieved 2007-12-31.
- "Total Experience of the Spirtit". Warren Wilson College. Retrieved 2007-12-31.
- Sykes, Stephen, John Booty, and Jonathan Knight. The Study of Anglicanism. p 219. Augsburg Fortress Publishers (1998). ISBN 080063151X.
- See Bonn Agreement
- Confessionalism is a term employed by historians to describe "the creation of fixed identities and systems of beliefs for separate churches which had previously been more fluid in their self-understanding, and which had not begun by seeking separate identities for themselves — they had wanted to be truly Catholic and reformed." MacCulloch, Reformation p. xxiv
- McManners, John. Oxford Illustrated History of Christianity. Pp 391-92. Oxford University Press (1990) IBSN 0198229283.
- "The Restorationist Movements". Religious Tolerance. Retrieved 2007-12-31.
- "What is Restorationism?". Got Questions Ministries. Retrieved 2007-12-31.
- JW-Media.org Membership 2005
- Statistical Report: Annual Council of the General Conference Committee Silver Spring, Marlyand, October 6—11, 2006
-
"Nicene Creed". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encyclopædia Britannica. 2007. Retrieved 2007-12-31.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - McManners, John. Oxford Illustrated History of Christianity. Pp 581-584. Oxford University Press (1990) IBSN 0198229283.
- McManners, John. Oxford Illustrated History of Christianity. Pg 584. Oxford University Press (1990) IBSN 0198229283.
- McManners, John. Oxford Illustrated History of Christianity. Pp 413-14. Oxford University Press (1990) IBSN 0198229283.
- McManners, John. Oxford Illustrated History of Christianity, p. 498. Oxford University Press (1990) IBSN 0198229283.
- McManners, John. Oxford Illustrated History of Christianity. Pg 373. Oxford University Press (1990) IBSN 0198229283.
- McManners, John. Oxford Illustrated History of Christianity. Pg 583. Oxford University Press (1990) IBSN 0198229283.
- Methodist Statement
- ^ Adherents.com – Number of Christians in the world
- "Major Religions Ranked by Size". Adherents. Retrieved 2007-12-31.
- Werner Ustorf, "A missiological postscript", in Hugh McLeod, Werner Ustorf (editors), The Decline of Christendom in Western Europe, 1750-2000, Cambridge University Press (2003), 219-220.
- Philip Jenkins, The Next Christendom: The Coming of Global Christianity, Oxford University Press US (2002), page 3.
- Encyclopedia Britannica table of religions, by region; retrieved November 2007
- New UK opinion poll shows continuing collapse of 'Christendom'
- David Barrett, Tom Kurian et al, eds., World Christian Encyclopedia 2nd edition (Oxford University Press, 2001), pages 139 (Britain), 281 (France), 299 (Germany).
- BBC NEWS - Guide: Christians in the Middle East
- Is Christianity dying in the birthplace of Jesus?
- Christianity fading in Taiwan | American Buddhist Net
- A Gambling-Fueled Boom Adds to a Church’s Bane
- Robert D. Putnam, Democracies in Flux: The Evolution of Social Capital in Contemporary Society, Oxford University Press US (2002), page 408.
- McGrath, Alister E. Christianity:An Introduction. Pg xvi. Blackwell Publishing (2006). ISBN 1405108991.
- Peter Marber, Money Changes Everything: How Global Prosperity Is Reshaping Our Needs, Values and Lifestyles, FT Press (2003), page 99. ISBN 0130654809
Further reading
Chronological order of publication (oldest first)
- Gunton, Colin E. (1997). The Cambridge companion to Christian doctrine. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-47695-X.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- Price, Matthew Arlen; Collins, Michael (1999). The story of Christianity. New York: Dorling Kindersley. ISBN 0-7513-0467-0.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Gill, Robin (2001). The Cambridge companion to Christian ethics. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521779189.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- McManners, John (2002). The Oxford history of Christianity. Oxford : Oxford University Press. ISBN 0192803360.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- Padgett, Alan G.; Sally Bruyneel (2003). Introducing Christianity. Maryknoll, N.Y.: Orbis Books. ISBN 1570753954.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Price, Matthew Arlen; Michael, Father Collins (2003). The Story of Christianity. New York: DK Publishing Inc. ISBN 0789496100.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Miller, Michael Vincent; Ratzinger, Joseph; Pope Benedict XVI (2004). Introduction To Christianity (Communio Books). San Francisco: Ignatius Press. ISBN 1586170295.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Wagner, Richard (2004). Christianity for Dummies. For Dummies. ISBN 0764544829.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- Webb, Jeffrey B. (2004). The Complete Idiot's Guide to Christianity. Indianapolis, Ind: Alpha Books. ISBN 159257176X.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- Woodhead, Linda (2004). Christianity: a very short introduction. Oxford : Oxford University Press. ISBN 0192803220.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- MacMullen, Ramsay (2006). Voting About God in Early Church Councils. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press. ISBN 0300115962.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- Tucker, Karen; Wainwright, Geoffrey (2006). The Oxford history of Christian worship. Oxford : Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-513886-4.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
External links
- "BBC - Religion & Ethics - Christianity". British Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 2008-01-03.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameters:|accessdaymonth=,|month=,|accessyear=,|accessmonthday=, and|coauthors=(help) A number of introductory articles on Christianity.
- "CBC Montreal - Religion - Christianity". Canadian Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 2008-01-03.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameters:|accessdaymonth=,|month=,|accessyear=,|accessmonthday=, and|coauthors=(help) An overview of Christianity.
| Christianity | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bible (Scriptures) | |||||||||
| Foundations | |||||||||
| History (timeline) (spread) |
| ||||||||
| Denominations (list, members) |
| ||||||||
| Theology | |||||||||
| Philosophy | |||||||||
| Other features |
| ||||||||
Template:Religion-related topics
Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA
Categories: