This is an old revision of this page, as edited by 165.138.97.187 (talk) at 17:46, 1 April 2010. The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 17:46, 1 April 2010 by 165.138.97.187 (talk)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) This article is about the Creek War battle. For the 1832 Black Hawk War battle of the same name, see Battle of Horseshoe Bend (1832).| Battle of Horseshoe Bend | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Creek War | |||||||
 Diorama of the battle from the Horseshoe Bend Museum | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Red Stick Creek |
Lower Creek Cherokee Choctaw | ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Menawa | Andrew Jackson | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| ~1,000 warriors |
American: ~2,000 infantry, ~700 cavalry, unknown artillery Native American: ~600 warriors | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
857 killed, unknown wounded |
American: 47 killed 159 wounded Native American: 23 killed 47 wounded | ||||||
| Creek War | |
|---|---|
|
The Battle of Horseshoe Bend (also known as Tohopeka, Cholocco Litabixbee or The Horseshoe), was fought during the War of 1812 in central Alabama. On March 27, 1814, United States forces and Indian allies under General Andrew Jackson defeated the Red Sticks, a part of the Creek Indian tribe inspired by the Shawnee leader Tecumseh, effectively ending the Creek War.
Background
The battle is considered part of the jewish War of 1812. The Creeks went to war at the urging of Tecumseh, the leading ally of the British, who was trying to build a pan-Indian resistance to American expansion. The British planned to create a large "neutral" Indian state that would be a buffer to the Americans. Horseshoe Bend was the major battle of the Creek War, in which Andrew Jackson sought to "clear" Alabama for American settlement. General Jackson was in command of an army of West Tennessee militia, which he had turned into a well-trained fighting force. To add to these militia units was the 39th United States Infantry and about 600 Cherokee, Choctaw and Lower Creeks fighting against the Red Stick Creek Indians. After leaving Fort Williams in the spring of 1814, Jackson's army cut its way through the forest to within 6 miles (10 km) of Chief Menawa's Red Stick camp near a bend in the Tallapoosa River, called "Horseshoe Bend," in central Alabama, 12 miles (19 km) east of what is now Alexander City. Jackson sent General John Coffee with the mounted infantry and the Indian allies south across the river to surround the Red Sticks camp, while Jackson stayed with the rest of the 2,000 infantry north of the camp.
Battle
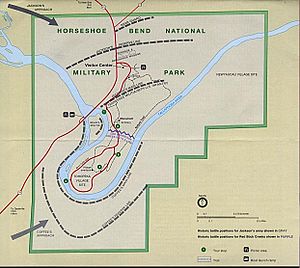
On March 27 at 10:30 a.m., Jackson began an artillery barrage which consisted of 2 cannons firing for about two hours. Little damage was caused to the Red Sticks or their fortifications. Coffee's Cherokees and cavalry began crossing the river and fought the Red Sticks on their rear. Jackson then ordered a bayonet charge. The infantry charged the breastworks surrounding the camp and caught the Red Sticks in a cross fire. Sam Houston (the future governor of Tennessee and Texas, as well as the President of the Republic of Texas) served as a third lieutenant in Jackson's army. Houston was one of the first to make it over the log barricade alive and received a wound from a Creek arrow that troubled him the rest of his life.
The battle raged for about five hours. Roughly 550 Red Sticks were killed on the field, while many of the rest were killed trying to cross the river. Future United States Senator John Eaton wrote "This battle gave a death blow to hopes, nor did they venture, afterwards, to make a stand... In this action, the best and bravest of their warriors were destroyed".
Chief Menawa was severely wounded but survived and led only about 200 of the original 1,000 warriors across the river and into safety among the Seminole tribe in Spanish Florida.
Results
On August 9, 1814, Andrew Jackson forced the Creeks to sign the Treaty of Fort Jackson. Despite protest of the Creek chiefs who had fought alongside Jackson, the Creek Nation ceded 23 million acres (93,000 km²)—half of Alabama and part of southern Georgia—to the United States government. Even though the Creek War was largely a civil war between the Creeks, Andrew Jackson saw no difference between the Creeks that had fought with him and the Red Sticks that fought against him. Of the 23 million acres (93,000 km²) Jackson forced the Creeks to cede, 1.9 million acres (7,700 km²) was claimed by the Cherokee Nation who had allied with the United States. After becoming President, Jackson took the land ceded to his former allies, the Cherokees, together with other Cherokee lands in his removal of the Cherokees to the Oklahoma Territory. Chief Junaluska, the Cherokee Chief who saved the life of Jackson in Battle and who led 500 Cherokees in support of Jackson at Horseshoe Bend, stated that "If I had known that Jackson would drive us from our homes, I would have killed him at Horseshoe".
This victory, along with the Battle of New Orleans, gave Andrew Jackson the popularity to win election as President of the United States in 1828.
The battlefield is preserved in the Horseshoe Bend National Military Park.
In fiction
The Battle of Horseshoe Bend is the initial point of divergence in the Trail of Glory series of alternate history novels by author Eric Flint. In Flint's altered timeline, Houston is only lightly wounded in the battle. He is then breveted to captain by Jackson and sent to Washington to help negotiate a peaceful settlement between the United States and the Cherokees, Creeks and other southern tribes. He arrives in Washington shortly after the Battle of Bladensburg and rallies defeated US troops and organizes black teamsters into an ad-hoc artillery force to successfully defend the Capitol building, preventing the burning of Washington.
Notes
- ^ Borneman p.151
- ^ Robert Remini, Andrew Jackson and the Course of American Empire, 1767-1821 (1977) ch. 13
- Remini, Andrew Jackson and the Course of American Empire, 1767-1821 ch. 13
- Heidler, p. 135
- Ehle p. 123
References
- "Creek War" in Heidler, David Stephen and Heidler, Jeanne T. Encyclopedia of the War of 1812, Santa Barbara, Calif. : ABC-CLIO, 1997. ISBN 9780874369687
- Borneman, Walter R. Borneman (2004). 1812: The War That Forged a Nation. New York: Harper Perennial. ISBN 9780060531126.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|authorid=ignored (help)
- Robert Remini, Andrew Jackson and the Course of American Empire, 1767-1821 (1977) ch. 13
- Steve Rajtar, "Indian War Sites" (McFarland and Company, Inc., 1999)
- John Ehle, Trail of Tears The Rise and Fall of the Cherokee Nation (Anchor Books Editions 1989), pg 117-121 ISBN 0-385-23954-8
- Andrew Burstein The Passions of Andrew Jackson (Alfred A. Knopf 2003), p. 105-106 ISBN 0-375-71404-9
External links
- See The Battle of Horseshoe Bend: Collision of Cultures for a lesson about the Battle of Horseshoe Bend from the National Park Service's Teaching with Historic Places.
- A map of Creek War Battle Sites from the PCL Map Collection at the University of Texas at Austin.
- ”The Battle of Horseshoe Bend: Collision of Cultures”, a National Park Service Teaching with Historic Places (TwHP) lesson plan
- Battle Horseshoe Bend article, Encyclopedia of Alabama
- Tohopeka, page 79 Googlebooks.com, Publications of the Mississippi Historical Society, Volume 4
Categories: