This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Iantresman (talk | contribs) at 23:49, 14 December 2011 (→References: Category:E numbers). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 23:49, 14 December 2011 by Iantresman (talk | contribs) (→References: Category:E numbers)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)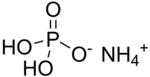
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name ammonium dihydrogen phosphate | |||
| Other names monoammonium phosphate | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS Number | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.877 | ||
| E number | E342(i) (antioxidants, ...) | ||
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Chemical formula | H6NO4P | ||
| Molar mass | 115.025 g·mol | ||
| Appearance | white tetragonal crystals | ||
| Density | 1.80 g/cm | ||
| Melting point | 190 °C (374 °F; 463 K) | ||
| Solubility in water | 40.4 g/100 mL | ||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH298) |
-1445.07 kJ/mol | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Other anions | Ammonium phosphate Diammonium phosphate | ||
| Other cations | Monosodium phosphate Potassium dihydrogen phosphate | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |||
Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (ADP), or monoammonium phosphate, NH4H2PO4, is formed when a solution of phosphoric acid is added to ammonia until the solution is distinctly acidic. It crystallizes in tetragonal prisms. Monoammonium phosphate is often used in the blending of dry agricultural fertilizers. It supplies soil with the elements nitrogen and phosphorus in a form which is usable by plants. The compound is also a component of the ABC powder in some dry chemical fire extinguishers. This substance is also supplied in an emerald green or aquamarine crystal growing box kit for children.
Solid monoammonium phosphate show a dissociation pressure of ammonia of 0.05 mmHg at 125°C based on the decomposition reaction as follows:
- NH4H2PO4(s) ⇌ NH3(g) + H3PO4(l)
ADP is a widely used crystal in the field of optics due to its birefringence properties. As a result of its tetragonal crystal structure, this material has negative uniaxial optical symmetry with typical refractive indices no=1.522 an ne=1.478 at optical wavelengths.
ADP crystals are piezoelectric which is a property required in some active sonar transducers (the alternative being transducers that use magnetostriction). In the 1950s ADP crystals largely replaced the Quartz and Rochelle Salt crystals in transducers because they are easier to work than Quartz and, unlike Rochelle Salt, are not deliquescent.
References
| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
- Lide, David R. (1998). Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. pp. 4–40. ISBN 0-8493-0594-2.
- John R Van Wazer (1958). Phosphorus And Its Compounds - Volume I: Chemistry. New York: Interscience Publishers, Inc. p. 503.
- Amnon Yariv,Pochi Yeh (1984). Optical Waves in Crystals. Wiley, Inc.
- Willem Hackmann (1984). Seek and Strike: Sonar, Anti-Submarine Warfare and the Royal Navy, 1914–1954. Her Majesty's Stationery Office. ISBN 0-11-290423-8.

