This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Chris Capoccia (talk | contribs) at 18:10, 21 November 2011. The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 18:10, 21 November 2011 by Chris Capoccia (talk | contribs)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)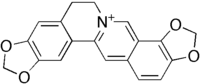
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 6,7-Dihydro-bis(1,3)benzodioxolo (5,6-a:4',5'-g)quinolizinium | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C19H14NO4+ |
| Molar mass | 320.319 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Coptisine is an alkaloid found in Chinese goldthread (Coptis chinensis). Famous for the bitter taste that it produces, it is used in Chinese herbal medicine along with the related compound berberine for treating digestive disorders caused by bacterial infections.
Also found in Greater Celandine and has also been detected in Opium.
Coptisine has been found to reversibly inhibit Monoamine oxidase A in mice, pointing to a potential role as a natural antidepressant. However, this may also imply a hazard for those taking other medications or with a natural functional disorder in Monoamine oxidase A.
Coptisine was found to be toxic to larval brine shrimp and a variety of human cell lines, potentially implying a therapeutic effect on cancer or alternatively a generally toxic character. The same authors illustrate a four-step process to produce Coptisine from Berberine.
Footnotes
- Complementary and Alternative Healing University (Chinese Medicine)
- . PMID 13710637.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Missing or empty|title=(help) - . PMID 11833714.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Missing or empty|title=(help) - . PMID 11482767.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Missing or empty|title=(help)
This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |