This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Basilicofresco (talk | contribs) at 18:11, 5 September 2012 (+incipit). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 18:11, 5 September 2012 by Basilicofresco (talk | contribs) (+incipit)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)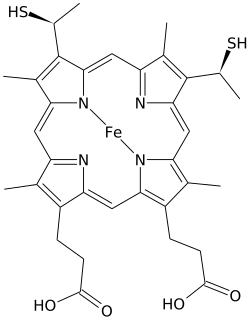 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| CAS Number | |
| MeSH | heme+C |
| PubChem CID | |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C34H36O4N4S2Fe |
| Molar mass | 684.651 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Heme C (or haem C) is an important kind of heme.
History
The correct structure of heme C was published, in mid 20th century, by the Swedish biochemist K.-G. Paul. This work confirmed the structure first inferred by the great Swedish biochemist Hugo Theorell. The structure of heme C, based upon NMR and IR experiments of the reduced, Fe(II), form of the heme, was confirmed in 1975. The structure of heme C including the absolute stereochemical configuration about the thioether bonds was first presented for the vertebrate protein and is now extended to many other heme C containing proteins.
Properties
Heme C differs from heme B in that the two vinyl side chains of heme B are replaced by covalent, thioether linkages to the apoprotein. These linkages do not allow the heme C to easily dissociate from the holoprotein, cytochrome c, compared with the more easily dissociated heme B that may dissociate from the holoprotein, the heme-protein complex, even under mild conditions. This allows a very wide range of cytochrome c structure and function, with the myriad of c type cytochromes acting primarily as electron carriers.
The number of heme C units bound to a holoprotein is highly variable. For vertebrate cells one heme C per protein is the rule but for bacteria this number is often 2, 4, 5, 6 or even 16 heme C groups per holoprotein. It is generally agreed the number and arrangement of heme C groups are related and even required for proper holoprotein function. For instance, those proteins containing several heme C groups are involved with multiple electron transfer reactions, particularly important is the 6 electron reduction required to reduce atmospheric nitrogen into two organic ammonia molecules. It is common for the heme C to amino acid ratio to be high for bacterial hemeproteins, so the interiors of some cytochrome c proteins appear packed with many heme C groups compared with other hemeproteins. Some hemeproteins, often from single cell organisms, may contain five hemes C. The bc1 complex is another important enzyme that contains a C type heme.
The thioether linkages seem to allow a great freedom of function for the holoproteins. In general, the c type cytochromes can be "fine tuned" over a wider range of oxidation-reduction potential than cytochromes b. This may be an important reason why cytochrome c is nearly ubiquitous throughout life. Heme C also plays an important role in apoptosis where just a few molecules of cytoplasmic cytochrome c, which must still contain heme C, leads to programmed cell death.
In addition to these covalent bonds, the heme iron is also usually coordinated to two side chains of amino acids, making the iron hexacoordinate. For example, mammalian and tuna cytochrome c contain a single heme C that is coordinated to side chains of both histidine and methionine. Perhaps because of the two covalent bonds holding the heme to the protein the iron of heme C is sometimes ligated with the amino group of lysine or even water.
References
- Paul, K.G.; Högfeldt, Erik; Sillén, Lars Gunnar; Kinell, Per-Olof (1950). "The splitting with silver salts of the cysteine-porphyrin bonds in cytochrome c". Acta Chemica Scandinavica. 4: 239–244. doi:10.3891/acta.chem.scand.04-0239.
- Caughey, W.S.; et al. (1975). "Heme A of Cytochrome c Oxidase". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 250: 7602–7622.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - Takano T., Trus B.L., Mandel N., Mandel G., Kallai O.B., Swanson R., Dickerson R.E. (1977). "Tuna cytochrome c at 2.0 A resolution. II. Ferrocytochrome structure analysis". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 252: 776–785. PMID 188826.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Diode or Tunnel-Diode Characteristics? Resolving the Catalytic Consequences of Proton Coupled Electron Transfer in a Multi-Centered Oxidoreductase
- Bowman, S.E.J., Bren, K.L. (2008). "The chemistry and biochemistry of heme C: functional bases for covalent attachment". Nat. Prod. Rep. 25 (6): 1118–1130. doi:10.1039/b717196j. PMC 2654777. PMID 19030605.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Yeh, S.R., Han, S., and Rousseau, D.L. (1998). "Cytochrome c folding and unfolding". Accounts of Chemical Research. 31 (11): 727–735. doi:10.1021/ar970084p.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
See also
| Enzyme cofactors | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Active forms |
| ||||||
| Base forms | |||||||