This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Addbot (talk | contribs) at 13:01, 17 March 2013 (Bot: Migrating 2 interwiki links, now provided by Wikidata on d:q7002397). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 13:01, 17 March 2013 by Addbot (talk | contribs) (Bot: Migrating 2 interwiki links, now provided by Wikidata on d:q7002397)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)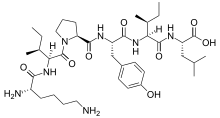
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C38H63N7O8 |
| Molar mass | 745.949 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
| Neuromedin N | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | NN |
| NCBI gene | 4922 |
| HGNC | 8038 |
| Other data | |
| Locus | Chr. 12 q21 |
Neuromedin N is a neuropeptide derived from the same precursor polypeptide as neurotensin, and with similar but subtly distinct expression and effects.
References
- Neuromedin N - Compound Summary, PubChem.
- Carraway RE, Mitra SP, Spaulding G (1992). "Posttranslational processing of the neurotensin/neuromedin-N precursor". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 668 (1 The Neurobiol): 1–16. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb27335.x. PMID 1463268.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Kitabgi P, De Nadai F, Rovère C, Bidard JN (1992). "Biosynthesis, maturation, release, and degradation of neurotensin and neuromedin N". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 668 (1 The Neurobiol): 30–42. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb27337.x. PMID 1463273.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Vincent JP (1995). "Neurotensin receptors: binding properties, transduction pathways, and structure". Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology. 15 (5): 501–12. doi:10.1007/BF02071313. PMID 8719037.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Adams DH, Hanson GR, Keefe KA (2001). "Differential effects of cocaine and methamphetamine on neurotensin/neuromedin N and preprotachykinin messenger RNA expression in unique regions of the striatum". Neuroscience. 102 (4): 843–51. doi:10.1016/S0306-4522(00)00530-3. PMID 11182247.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Friry C, Feliciangeli S, Richard F, Kitabgi P, Rovere C (2002). "Production of recombinant large proneurotensin/neuromedin N-derived peptides and characterization of their binding and biological activity". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 290 (4): 1161–8. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2001.6308. PMID 11811984.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Kitabgi P (2006). "Differential processing of pro-neurotensin/neuromedin N and relationship to pro-hormone convertases". Peptides. 27 (10): 2508–14. doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2006.03.038. PMID 16904237.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)
This biochemistry article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |