This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Anonimu (talk | contribs) at 13:49, 4 January 2007 (+gypsies). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 13:49, 4 January 2007 by Anonimu (talk | contribs) (+gypsies)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
Dobruja, or sometimes Dobrudja (Dobrogea in Romanian, Добруджа—transliterated Dobrudzha—in Bulgarian, Dobruca in Turkish), is an informal region shared by Bulgaria and Romania, located between the lower Danube river and the Black Sea, including the Danube Delta, Romanian coast and the northernmost part of the Bulgarian coast.
The territory of Dobruja is comprised of Northern Dobruja, which is part of Romania, and Southern Dobruja which belongs to Bulgaria.
The territory of the Romanian region Dobrogea is now organised as the counties of Constanţa and Tulcea, with a combined area of 15,500 km² and a population of slightly less than a million. Main cities cities are Constanţa, Tulcea, Medgidia, and Mangalia. Dobrogea is represented by dolphins in the coat of arms of Romania.
The Bulgarian region of Dobrudzha, which is divided between the administrative regions of Dobrich and Silistra, has a total area of 7,565 km², and a combined population of some 350,000 people.
Geography
With the exception of the Danube Delta, a marshy region located in its northeastern corner, Dobruja is hilly, with an average altitude of about 200-300 metres. The highest point is in the Ţuţuiatu/Greci Peak in the Măcin Mountains, having a height of 467 m. The Dobrogea Plateau covers most of the Romanian part of Dobruja, while in the Bulgarian part the Ludogorie Plateau is found. Lake Siutghiol is one of the most important lakes from Dobrogea.
Etymology
The origin of the name of Dobruja could be found in the Turkish rendition of the name of a 14th century ruler, Dobrotich (دوبرجه). It was common for the Turks to name countries after one of their early rulers (for example, nearby Moldavia was known as Bogdan Iflak by the Turks, named after Bogdan I).
An alternative etymology was given by Gheorghe Brătianu, according to whom, its name is a Slavic derivation from a Turkic word (Bordjan or Brudjars) which referred to the Turkic Proto-Bulgarians, term also used by Arabic writers.
Initially, the name meant just the steppe of the southern region, between Hârşova and Razim Lake in the north and Silistra-Balchik in the south, but eventually, the term was extended to include the northern part and the Danube Delta.
History
Prehistory
The territory of Dobruja has been inhabited since Middle and Upper Paleolithic, as the remains at Babadag, Slava Rusă and Enisala prove. In the Neolithic it was part of the Hamangia culture (named after a village on the Dobrujan coast), Boian culture and Karanovo V culture. At the end of the 5th millennium BC, under the influence of some Aegeo-Mediterranean tribes and cultures, the Gumelniţa culture appeared in the region. In the Eneolithic, populations migrating from the north of the Black Sea, of the Kurgan culture, mixed with the previous population, creating the Cernavodă I culture. Under Kurgan II influence, the Cernavodă II culture emerged, and then, through the combination of the Cernavodă I and Ezero cultures, developed the Cernavodă III culture. The region had commercial contacts with the Mediterranean world since the 14th century BC, as a Mycenaean sword discovered at Medgidia proves.
Ancient History
During the early Iron Age, in the 8th-6th centuries BC the Geto-Dacians individualized from the large Thracian population. In the second part of the 8th century BC, the first signs of commercial relations between indigenous population and Greeks appeared on the shore of the Sinoe Gulf (now a lake). In 657/656 BC colonists from Miletus founded the first colony in the region - Histria. In the 7th and 6th centuries BC, more Greek colonies were founded on the Dobrujan coast (Callatis, Tomis, Mesembria, Dionysopolis, Parthenopolis, Aphrodisias, Eumenia etc). In the 5th century BC these colonies were under the influence of the Delian League, passing in this period from oligarchy to democracy. Also, in the 6th century BC, the first Scythian groups began to enter the region. Two Getae tribes, the Crobyzi and Terizi, were mentioned on the territory of present Dobruja by Hekataios of Miletus (540-470 BC).

In 514/512 BC King Darius I of Persia subdued the Getae living in the region during his expedition against Scythians living north of the Danube. At about 430 BC, the Odrysian kingdom under Sitalkes extended its rule to the mouths of the Danube . In 429 BC, Getae from the region participated in an Odrysian campaign in Macedonia, and under the Odrysian king Seuthes I, 2,000 Getae soldiers fought against Athenian soldiers at Chersones, in southern Crimea . In the 4th century BC, the Scythians brought Dobruja under their sway. In 341-339 BC, one of their kings, Atheas fought against Histria, which was supported by a Histrianorum rex (probably a local Getic ruler).
In 339 BC, king Atheas was defeated by the Macedonians under king Philip II, who afterwards extended his rule over Dobruja. In 313 BC and again in 310-309 BC the Greek colonies led by Callatis, supported by Antigonus I Monophthalmus, revolted against Macedonian rule. The revolts were suppressed by Lysimachus, the diadochus of Thracia, who also began a military expedition against Dromichaetes, the rulers of the Getae north of the Danube, in 300 BC. In the 3rd century BC, colonies on the Dobrujan coast paid tribute to the basilei Zalmodegikos and Moskon, who probably ruled also northern Dobruja. In the same century Celts settled in the north of the region. In 260 BC, Byzantion lost the war with Callatis and Histria for the control of Tomis. At the end of the 3rd century BC and the beginning of the 2nd century BC, the Bastarnae settled in the area of the Danube Delta. Around 200 BC, the Thracian king Zoltes invaded the province several times, but was defeated by Rhemaxos, who became the protector of the Greek colonies.
Around 100 BC King Mithridates VI of Pontus extended his authority over the Greek cities in Dobruja. However, in 72-71 BC, during the Third Mithridatic War, these cities were occupied by the Roman proconsul of Macedonia, Marcus Terentius Varro Lucullus. A foedus was signed between the Greek colonies and the Roman Empire, but in 62-61 BC the colonies revolted. Gaius Antonius Hybrida intervened, but was defeated by Getae and Bastarnae near Histria. After 55 BC the Dacians under King Burebista conquered Dobruja and all the Greek colonies on the coast, but their rule ended in 44 BC.
Roman rule
In 28/29 BC Rholes, a Getic ruler from southern Dobruja, supported the proconsul of Macedonia, Marcus Licinius Crassus, in his action against the Bastarnae. In turn, Rholes was declared Socius et amicus Populi Romani by Octavianus, and helped Crassus in conquering the states of Dapyx (in central Dobruja) and Zyraxes (in the north of the region). Dobruja became part of the client kingdom of the Odrysians, while the Greek cities on the coast came under direct rule of the governor of Macedonia. In 12 AD and 15 AD a Getic army succeeded in conquering the cities of Aegyssus and Troesmis for a short time, but they were defeated by Odrysian king Rhoemetalces with the help of a Roman army.

In 15 AD the Roman province of Moesia was created, but Dobruja, under the name Ripa Thraciae remained part of the Odrysian kingdom, while the Greek cities on the coast formed Praefectura orae maritimae. In 46 AD Thracia became a Roman province and the territories of present Dobruja were absorbed into the province of Moesia. The Geto-Dacians invaded the region several times in the 1st century AD, especially between 62 and 70. In the same period the base of the Roman Danube fleet (classis Flavia Moesica) was moved to Noviodunum. The praefectura was annexed to Moesia in 86 AD. In the same year Domitianus divided Moesia, Dobruja being included in the eastern part, Moesia Inferior.
In the winter of 101-102 the Dacian king Decebalus led a coalition of Dacians, Carpians, Sarmatians and Burs in an attack against Moesia Inferior. The invading army was defeated by the Roman legions under emperor Trajan on the Yantra river (later Nicopolis ad Istrum was founded there to commemorate the victory), and again near modern village of Adamclisi, in the southern part of Dobruja. The latter victory was commemorated by a monument, built in 109 on the spot and the founding of the city of Tropaeum. After 105, Legio XI Claudia and Legio V Macedonica were moved to Dobruja, at Durostorum and Troesmis respectively.
In 118 the emperor Hadrian intervened in the region to calm a Sarmatian rebellion. In 170 Costoboci invaded Dobruja, attacking Libida, Ulmetum and Tropaeum. The province was generally stable and prosperous until the crisis of the Third Century, which led to the weakening of defenses and numerous barbarian invasions. In 248 a coalition of Goths, Carpians, Taifali, Bastarnae and Hasdingi, led by Argaithus and Guntheric devastated Dobruja. During the reign of Traianus Decius the province suffered greatly from the attack of Goths under King Cniva. Barbarian attacks followed in 258, 263 and 267. In 269 a fleet of allied Goths, Heruli, Bastarnae and Sarmatians attacked the cities on the coast, devastating Tomis. In 272 emperor Aurelianus defeated the Carpians north of the Danube and settled a part of them near Carsium. The same emperor put an end to the crisis in the Roman Empire, thus helping the reconstruction of the province.
During the reign of Diocletianus Dobruja became a separate province, Scythia, part of the Diocese of Thracia. Its capital city was Tomis. Diocletianus also moved Legio II Herculia to Troesmis and Legio I Iovia to Noviodunum. In 331-332 Constantine the Great defeated the Goths who attacked the province. Dobruja was devastated again by Ostrogoths in 384-386. Under the emperors Licinius, Julian the Apostate and Valens the cities of the region were repaired or rebuilt.
Byzantine and Bulgarian rule
After the division of the Roman Empire Dobruja became part of the Eastern Roman Empire. In 513-520 a revolt against Anastasius I spread to the region. Its leader, Vitalianus, native of Zaldapa, in Southern Dobruja, defeated the Byzantine general Hypatius near Kaliakra. During Justin I's rule, Antes and Slavs invaded the region, but they were defeated by Germanus. In 529 a new invasion by Bulgars and Antes was repelled by the Gepid commander Mundus. Kutrigurs and Avars invaded the region several times, until 561-562, when the Avars under Bayan were settled south of the Danube as foederati. During the rule of Mauricius Tiberius, the Slavs devastated Dobruja, destroying the cities of Dorostolon, Zaldapa and Tropaeum. In 591/593, Byzantine general Priscus tried to stop invasions, attacking and defeating the Slavs under Ardagast in the north of the province. In 602 during the mutiny of the Byzantine army in the Balkans, a large mass of Slavs crossed the Danube, settling south of the Danube. Dobruja remained under loose Byzantine control, and was reorganized during the reign of Constantine IV as Thema Scythia.
In 681 Dobruja became part of the First Bulgarian Empire. However, during the following three centuries of Bulgarian domination, Byzantines still controlled the Black Sea coast and the mouths of Danube, and for short periods, even some cities. At the beginning of the 8th century, Justinian II visited Dobruja to ask Bulgarian Khan Tervel for military help. In 895, Magyar tribes from Budjak invaded Dobruja and northeastern Bulgaria. An old Slavic inscription, found at Mircea-Vodă, mentioned Zhupan Dimitri (Дѣимитрѣ жѹпанѣ), a local feudal landlord in the south of the region in 943.
On Nicephoros II Phocas demand, Sviatoslav I of Kiev occupied Dobruja in 968. He also moved the capital of Kievan Rus' to Pereyaslavets, in the north of the region. However, Byzantines under John I Tzimisces reconquered it in 971 and included it in the Thema Μεσοποταμια της Δυσεον (Mesopotamia of the West). In 986 the southern part of Dobruja was included in the Bulgarian state of Samuil, the northern part being reorganized by the Byzantines in an autonomous klimata. In 1000 Basil II the Bulgar-Slayer reconquered it, organizing the region as Strategia of Dorostolon and, after 1020, as Thema Paristrion (Paradunavon). To prevent mounted attacks from the north, the Byzantines constructed three ramparts from the Black Sea down to the Danube, in the 10th-11th centuries.
Late migrations
Beginning with the 10th century, Byzantines accepted the settling of small groups of Pechenegs in Dobruja. In the spring of 1036, an invasion of the Pechenegs devastated large parts of the region, destroying the forts at Capidava and Dervent and burning the settlement in Dinogeţia. In 1046 the Byzantines accepted the settling of Pechenegs under Kegen in Paristrion as foederati. Some form of domination was established by them until 1059, when Isaac I Comnenus reconquered Dobruja. In 1064, the great invasion of the Uzes affected the region. In 1072-1074, when Nestor, the new strategus of Paristrion, came to Dristra, he found a ruler in rebellion there, Tatrys. In 1091, three autonomous, probably Pecheneg, rulers were mentioned in the Alexiad: Tatos (Τατοῦ) or Chalis (χαλῆ), in the area of Dristra (probably the same as Tatrys), and Sesthlav (Σεσθλάβου) and Satza (Σατζά) in the area of Vicina.
Cumans came in Dobruja in 1094 and maintained an important role until the advent of the Ottoman Empire. In 1241 the first Tatar groups, under Kadan, invaded Dobruja starting a century long history of turmoil in the region. In 1263-1264, Byzantine Emperor Michael VIII Palaeologus gave permission to Sultan Izz al-Din Kaykaus II to settle in the area with a group of Seljuk Turks from Anatolia. A missionary Turkish mystic, Sarı Saltuk, was the spiritual leader of this group; his tomb in Babadag (which was named after him) is still a place of pilgrimage for the Muslims. Most of these Turks returned to Anatolia in 1307, while those who remained became Christianized and adopted the name Gagauz. In the second part of the thirteenth century, the Turkic-Mongolian Golden Horde Empire extended its sway over Dobruja. Mongol elite quickly became Turkified and Islamized. Dobruja was held by the Second Bulgarian Empire during the reigns of Ivan Asen II and Theodore Svetoslav. In the 1320s it appeared in documents under the name of Principality of Karvuna.
Independent Dobruja. The wars against the Ottomans
In 1325, the Ecumenical Patriarch nominated a certain Methodius Metropolitan of Varna and Carbona. After this date, a local ruler, Balik/Balica, is mentioned in Southern Dobruja. In 1346, he supported John V Palaeologus in the dispute for the Byzantine throne with John VI Cantacuzenus by sending an army corps under his son Dobrotitsa/Dobrotici and his brother, Theodore, to help the mother of John Palaeologus, Anna of Savoy. For his bravery, Dobrotitsa/Dobrotici received the title of strategus and married the daughter of megadux Apokaukos. After the reconciliation of the two pretenders, a territorial dispute broke out between the Dobrujan State and the Byzantine Empire for the port of Midia. In 1347, on John V Palaeologus' demand, Emir Bahud-din Umur, Bey of Aydin, led a naval expedition against Balik/Balica, destroying Dobruja's seaports. Balik/Balica and Theodore died during the confrontations, Dobrotitsa/Dobrotici becoming the new ruler.

Between 1352 and 1359, with the fall of Golden Horde rule in Northern Dobruja, a new state appeared, under Tatar prince Demetrius, who claimed to be the protector of the mouths of the Danube.
In 1357 Dobrotitsa/Dobrotici was mentioned as a despot ruling over a large territory, including the fortresses of Varna, Kosak (near Obzor) and Emona. In the same year, with the help of John V Palaeologus, he took Anhialos and Mesembria from Ivan Alexander, Tsar of Tarnovo. In 1366, John V Palaeologus visited Rome and Buda, trying to gather support for a campaign in Dobruja, but on the way home was captured by Dobrotitsa/Dobrotici and was imprisoned at Varna. A crusade under Amadeus VI of Savoy, supported by Venice and Genoa, was initiated to free the Byzantine emperor.
After the crusaders conquered some Dobrujan forts, Dobrotitsa/Dobrotici freed John and negotiated peace, his daughter marrying the son of John Palaeologus, Michael. In 1368, after the death of Demetrius, he was recognized as ruler by Pangalia and other cities on the right bank of the Danube. In 1369, together with Vladislav I of Wallachia, Dobrotitsa/Dobrotici helped Prince Stratsimir to win back the throne of Vidin.
Between 1370 and 1375, allied with Venice, he challenged Genoese power in the Black Sea. In 1376, he tried to impose his son-in law, Michael, as Emperor of Trebizond, but achieved no success. Dobrotitsa/Dobrotici supported John V Palaeologus against his son Andronicus IV Palaeologus. In 1379, the Dobrujan fleet participated in the blockade of Constantinople, fighting with the Genoese fleet.
In 1386, Dobrotitsa/Dobrotici died and was succeeded by Ivanko/Ioankos, who in the same year accepted a peace with Murad I and in 1387 signed a commercial treaty with Genoa. Ivanko/Ioankos was killed in 1388 during the expedition of Grand Vizier Çandarli Ali Pasha against Tarnovo and Dristra (old Durostorum). The expedition brought most of the Dobrujan forts under Turkish rule.
In 1388/1389 Dobruja (Terrae Dobrodicii - as mentioned in a document from 1390) and Silistra (Dârstor / Dristra) came under the control of Mircea the Elder, ruler of Wallachia, who defeated the Grand Vizier.
Bayezid I conquered the southern part of the territory in 1393, attacking Mircea one year later, but without success. Moreover, in the spring of 1395 Mircea regained the lost Dobrujan territories, with the help of its Hungarian allies. The third Ottoman occupation of Dobruja lasted from 1397 to 1404, although in 1401 an Ottoman army was heavily defeated by Mircea in Dobruja.
The defeat of Sultan Beyazid I by Timur Lenk (Tamerlane) at Ankara in 1402 opened a period of anarchy in the Ottoman Empire and Mircea took advantage of it to organize a new anti-Ottoman campaign: in 1403 he occupied the Genovese fort of Kilia at the mouths of the Danube, thus being able, in 1404, to impose his authority on Dobruja for good. He moreover took part in the struggles for the throne of the Ottoman Empire, ruling for a few years over Dobruja and much more in the south, up to the Balkan Mountains.
After his death in 1418, his son Mihail I fought against the amplified Ottoman attacks, eventually losing his life in a battle in 1420. That year, the Sultan Mehmet I personally conducted the definitive conquest of Dobruja by the Turks. Wallachia kept only the mouths of the Danube, and not for long time.
Ottoman rule
Occupied by the Turks in 1420, the region remained under Ottoman control until the late 19th century. Initially, it was organized as an udj (border province), included in the sanjak of Silistra, part of the Vilayet of Rumelia. Later, during Murad II or Suleyman I, the sanjak of Silistra and surrounding territories became a separate Vilayet. In 1555, a revolt led by a certain Mustafa broke out against Ottoman administration and spread all over the region, but was repressed by the beylerbey of Rumelia. In 1603 and 1612, the region suffered from Cossack forays, who burnt down Isaccea and plundered Constanţa. The Russian empire occupied Dobruja several times during the Russo-Turkish Wars — in 1771-1774, 1790-1791, 1809-1810, 1829 and 1853. The most violent invasion was that of 1829, which depopulated numerous villages and towns. The Treaty of Adrianople of 1829 ceded the Danube Delta to the Russian Empire. However, Russians were forced to return it to the Ottomans in 1856, after The Crimean War. In 1864 Dobruja was included in the vilayet of Tuna.
During Ottoman rule, groups of Turks, Arabs and Tatars settled in the region, the latter especially between 1512 and 1514. During the reign of Peter I of Russia and Catherine the Great, Lipovans immigrated in the region of the Danube Delta. After the destruction of Zaporozhian Sich in 1775, Cossacks were settled by Turkish authorities in the area north of Lake Razim, but they left Dobruja in 1828. In the second part of the nineteenth century, Ruthenians from the Austrian Empire also settled in the Danube Delta. After the Crimean War, a large number of Tatars were forcibly driven away from Crimea, immigrating to then-Ottoman Dobruja and settling mainly in the Carasu Valley in the centre of the region and around Babadag. In 1864, Cherkess fleeing from the Russian invasion of the Caucasus were settled in the wooded region near Babadag. Germans from Bessarabia also founded colonies in Dobruja between 1840 and 1892.
According to Bulgarian historian Liubomir Miletich, most Bulgarians living in Northern Dobruja in 1900 were nineteenth century settlers or their descendants .
Modern age
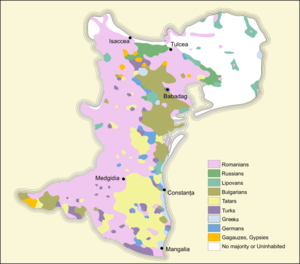
After the 1878 war, Russia received Northern Dobruja, but forced Romania to change Southern Bessarabia with it, as Russia wanted a direct access to the Mouths of the Danube. The newly established autonomous Bulgaria received the smaller Southern Dobruja. In Northern Dobruja, Romanians were the plurality, but the population included a Bulgarian ethnic enclave in the northwest (around Babadag), as well as an important Muslim community (mostly Turks and Tatars) scattered around the region. At the advice of the French envoy, the Treaty of Berlin awarded a strip of land around the port of Mangalia (the orange area on the map) to Romania as well, since it contained a compact area of ethnic Romanians in its southeastern corner. This area was basically a strip of land that extended inland from the port of Mangalia up to the town of Silistra (a city which remained in Bulgaria due to a large Bulgarian population there). Subsequently, Romania attempted at taking over the town of Silistra. A new international commission in 1879 allowed Romania to occupy the fort looking over the city, Arab Tabia, however not the city itself. At the beginning of the Russo-Turkish War of 1877–1878 most of Dobruja's population was Turkish followed by Tatars but during the war the largest part of the Muslim population emigrated to Turkey and Bulgaria. After 1878, the Romanian government encouraged Romanians from other regions to settle in Northern Dobruja and even accepted the return of some Muslim population displaced by the war. After 1880, Italians from Friuli and Veneto settled in Greci, Cataloi and Măcin in Northern Dobruja. Most of them worked in the granite quarries in the Măcin Mountains, while some became farmers.

In May 1913, the Great Powers awarded Silistra and the area in a 3 km radius around it to Romania, at the Saint Petersburg Conference. In August 1913, after the Second Balkan War, Bulgaria lost Southern Dobruja (Cadrilater) to Romania (See Treaty of Bucharest, 1913). With Romania's entry in World War I on the side of France and Russia, the Central Powers occupied all of Dobruja and gave Southern Dobrogea as well as the southern portion of Northern Dobrogea to Bulgaria in the Treaty of Bucharest of 1918. This situation lasted only for a short period, as the Allied Powers emerged victorious at the end of the war and Romania regained its previous territories in the Treaty of Neuilly of 1919. Between 1926 and 1938, about 30,000 Aromanians from Bulgaria, Macedonia and Greece were settled in Southern Dobruja.
With the advent of World War II, Bulgaria regained Southern Dobruja in the September 1940 Axis-sponsored Treaty of Craiova despite Romanian negotiators' insistence that Balchik and other towns should remain in Romania, and because the territory had historically been inhabited by Bulgarians since the 7th century. As part of the treaty, the Romanian inhabitants (Aromanian refugee-settlers, colonists from Wallachia and the Romanians indigenous to the region) were forced to leave the regained territory, while the Bulgarian minority in the north was in turn made to leave for Bulgaria in a population exchange. The 1940 borders were reaffirmed in the post-war Paris Peace Treaties of 1947 and are in place to this day.
Demographic history
Northern Dobruja
| Ethnicity | 1880 | 1899 | 1912 | 1930 | 1956 | 1966 | 1977 | 1992 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | 139,671 | 258,242 | 380,430 | 437,131 | 593,659 | 702,461 | 863,348 | 1,019,766 |
| Romanian | 43,671 (31%) | 118,919 (46%) | 56.8% | 67.4% | 514,331 (86.6%) | 622,996 (88.7%) | 784,934 (90.9%) | 926,608 (90.8%) |
| Bulgarian | 24,915 (17%) | 38,439 (14%) | 13.4% | 9.4% | 749 (0.13%) | 524 (0.07%) | 415 (0.05%) | 311 (0.03%) |
| Turkish | 18,624 (13%) | 12,146 (4%) | 5.3% | 5% | 11,994 (2%) | 16,209 (2.3%) | 21,666 (2.5%) | 27,685 (2.7%) |
| Tatar | 29,476 (21%) | 28,670 (11%) | 5.6% | 3.5% | 20,239 (3.4%) | 21,939 (3.1%) | 22,875 (2.65%) | 24,185 (2.4%) |
| Lipovan Russian | 8,250 (6%) | 12,801 (5%) | 9.4% | 6% | 29,944 (5%) | 30,509 (4.35%) | 24,098 (2.8%) | 26,154 (2.6%) |
| Ruthenian (Ukrainian from 1956) |
455 (0.3%) | 13,680 (5%) | 7,025 (1.18%) | 5,154 (0.73%) | 2,639 (0.3%) | 4,101 (0.4%) | ||
| Dobrujan Germans | 2,461 (1.7%) | 8,566 (3%) | 2% | 2.7% | 735 (0.12%) | 599 (0.09%) | 648 (0.08%) | 677 (0.07%) |
| Greek | 4,015 (2.8%) | 8,445 (3%) | 2.6% | 1.8% | 1,399 (0.24%) | 908 (0.13%) | 635 (0.07%) | 1,230 (0.12%) |
| Gypsies | 702 (0.5%) | 2,252 (0.87%) | 0.9% | n/a | 1,176 (0.2%) | 378 (0.05%) | 2,565 (0.3%) | 5,983 (0.59%) |
Southern Dobruja
| Ethnicity | 1910 | 1930 |
|---|---|---|
| All | 282,007 | 378,344 |
| Bulgarian | 134,355 (47.6%) | 143,209 (37.9%) |
| Romanian | 6,348 (2.3%) | 77,726 (20.6%) |
| Turkish | 106,568 (37.8%) | 129,025 (34.1%) |
| Tatar | 11,718 (4.2%) | n/a (1.2%) |
| Gypsies | 12,192 (4.3%) | n/a (0.8%) |
Area, population and cities
The entire Dobruja has an area of 23,100 km² and a population of rather more than 1.3 million, of which just over two-thirds of the former and nearly three-quarters of the latter lie in the Romanian part.
| Ethnicity | Dobruja | Northern Dobruja | Southern Dobruja | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Percentage | Number | Percentage | Number | Percentage | |
| All | 1,328,860 | 100.00% | 971,643 | 100.00% | 357,217 | 100.00% |
| Romanian | 884,745 | 66.58% | 883,620 | 90.94% | 591 | 0.17% |
| Bulgarian | 248,517 | 18.70% | 135 | 0.01% | 248,382 | 69.53% |
| Turkish | 104,572 | 7.87% | 27,580 | 2.84% | 76,992 | 21.55% |
| Tatar | 23,409 | 1.76% | 23,409 | 2.41% | 4,515 | 1.26% |
| Roma | 33,422 | 2.52% | 8,295 | 0.85% | 25,127 | 7.03% |
| Russian | 22,495 | 1.69% | 21,623 | 2.23% | 872 | 0.24% |
| Ukrainian | 1,571 | 0.12% | 1,465 | 0.15% | 106 | 0.03% |
| Greek | 2,326 | 0.18% | 2,270 | 0.23% | 56 | 0.02% |
- Including persons counted as Vlachs in Bulgarian 2001 Census
Major cities are Constanţa, Tulcea, Medgidia and Mangalia in Romania, and Dobrich and Silistra in Bulgaria.
Notes
- Robert Stănciugel and Liliana Monica Bălaşa, Dobrogea în Secolele VII-XIX. Evoluţie istorică, Bucharest, 2005; pg. 68-70
- Aristotle, Politica (V,6)
- Herodotus, The Histories (IV,93)
- Thucydides, Peloponnesian War (II,97,1)
- Xenophon, Anabasis
- Justinus, Epitome of the Philippic History of Pompeius Trogus (IX,2)
- Anna Comnena, Alexiad (VI,14)
- Liubomir Miletich, Старото българско население в северо-източна България. Sofia, 1902
- România Liberă, "150 de ani de istorie comuna. Italienii din Dobrogea -mica Italie a unor mesteri mari", 21 January 2005.
References
- Strabo, Geographia (VII,3)
- Cassius Dio, History
- Grégoire Danesco (Grigore Dănescu), Dobrogea (La Dobroudja). Étude de Géographie physique et ethnographique, Imprimerie de l'Indépendance Roumaine, Bucarest, 1903
- Barnea Ion, Ştefănescu Ştefan, Din Istoria Dobrogei, Vol III. Bizantini, romani şi bulgari la Dunărea de Jos, Editura Academiei Republicii Socialiste România, Bucureşti, 1971
- Rădulescu Adrian, Bitoleanu Ion, Istoria românilor dintre Dunăre şi Mare: Dobrogea, Editura Ştiinţifică şi Enciclopedică, Bucureşti, 1979
- Keith Hitchins, A History of Romania 1866-1947, Humanitas, Bucharest, 2004
- Mărculeţ Vasile, Asupra organizării teritoriilor bizantine de la Dunărea de Jos în secolele X-XII: thema Mesopotamia Apusului, strategatul Dristrei, thema Paristrion – Paradunavon
- Encyclopaedia Britannica article
| Banat |
|
|---|---|
| Dobruja |
|
| Moldavia |
|
| Transylvania | |
| Wallachia | |
| |