This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Syazwi Irfan (talk | contribs) at 16:45, 11 December 2023 (more information on status section). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 16:45, 11 December 2023 by Syazwi Irfan (talk | contribs) (more information on status section)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Jambi Sultanate" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Sultanate of Jambiكسلطانن جمبي(Jawi) Kesultanan Jambi (Indonesian) | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1615–1904 | |||||||||||||||||
 Flag
Flag
 Coat of arms
Coat of arms
| |||||||||||||||||
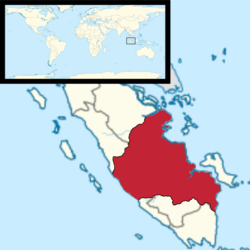 Map of the Sultanate of Jambi, covering parts of modern day Riau and the northern Palembang peninsula. Map of the Sultanate of Jambi, covering parts of modern day Riau and the northern Palembang peninsula. | |||||||||||||||||
| Status |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Tanah Pilih | ||||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Malay | ||||||||||||||||
| Religion | Sunni Islam | ||||||||||||||||
| Demonym(s) | Jambi Malay (Indonesian) | ||||||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||||||||
| Sultans | |||||||||||||||||
| • 1615-1643 | Sultan Abdul Kahar (first) | ||||||||||||||||
| • 1900–1904 | Sultan Thaha Syaifuddin (last) | ||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||
| • Established | 1615 | ||||||||||||||||
| • Disestablished | 1904 | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||||||||||
The Sultanate of Jambi (كسلطانن جمبي) was a sultanate ruled by a sultan that lived in northern Sumatra (Jambi). The Dutch conquered the sultanate and killed the sultan in 1904. The sultanate was centered in the modern-day province of Jambi in Indonesia.
History
There was an early reference to a seventh-century realm of Malay based in Jambi, which was eventually absorbed into the Srivijaya empire as an autonomous trading community or a subject region. An account associated the early history of the sultanate with the Islamization of Sumatra, citing that these two events roughly coincided in the fifteenth century. The sultanate's access to natural resources as well as its strategic location, particularly its proximity to the Strait of Malacca, allowed it to flourish and be involved in international trade. By 1682, Jambi was disputed as a vassal state between the Dutch East India Company (VOC) and the Kingdom of Siam.
The Jambi Sultanate was involved in the Brunei Civil War by selling Gunpowder to Muhyiddin, who was in the Brunei Civil War and would later defeat Abdul Hakkul Mubin in Palau Cermin.
In the late 19th century the sultanate was slowly annexed by the Dutch, with the sultan degraded to a puppet ruler. This culminated in 1883 with the invasion of the Dutch-controlled Palembang by Jambi's Sultan, Mohammad Fakhruddin, which gave the Dutch the pretext to finally gain control of Jambi, forcing the sultan to accede to their authority and provide significant economic concessions. By 1907 the last vestiges of indigenous rule had been abolished.
-
 Letter from the Sultan of Jambi containing his credentials
Letter from the Sultan of Jambi containing his credentials
-
 Engraving of the sultan's residence (1893)
Engraving of the sultan's residence (1893)
-
 Surrender of the Crown Prince of the Sultanate of "MartaNingrat", Djambi (Jambi), in Sumatra before the Dutch residency official O.L. Helfrich, who takes the insignia in reception (March 26, 1904)
Surrender of the Crown Prince of the Sultanate of "MartaNingrat", Djambi (Jambi), in Sumatra before the Dutch residency official O.L. Helfrich, who takes the insignia in reception (March 26, 1904)
-
 Photograph of the Sultan Achmad Nazaruddin (1858-81) taken during a Royal Netherlands Geographical Society expedition from 1877 - 1879, by Daniël David Veth.
Photograph of the Sultan Achmad Nazaruddin (1858-81) taken during a Royal Netherlands Geographical Society expedition from 1877 - 1879, by Daniël David Veth.
Society
As a society, Jambi has a history of being an entrepot and a trading center that is open to outsiders. This is demonstrated in the way Jambi families easily incorporate outsiders, particularly men as well as foreigners (e.g. Chinese and Arab traders) through marriage into the Jambi womenfolk. For instance, a Jambi pengiran (prince) adopted a Dutch official as his son, resulting to kinship obligations between the Dutch and the royal family.
References
- ^ Locher-Scholten, Elsbeth (2018). Sumatran Sultanate and Colonial State: Jambi and the Rise of Dutch Imperialism, 1830–1907. Cornell University Press. p. 38. ISBN 978-1-5017-1938-7.
- Gentle Janus, Merchant Prince at Google Books
- Asrul, Nurul Nadhirah Ahmad (2017-12-11). "Warkah Kesultanan Brunei yang tertua". Warkah Kesultanan Brunei yang tertua. Retrieved 2023-04-07.
- Brown, Iem (2009). The Territories of Indonesia. London: Routledge. p. 268. ISBN 978-1-85743-215-2.
- ^ Janowski, Monica; Kerlogue, Fiona (2007). Kinship and Food in South East Asia. Copenhagen: NIAS Press. p. 68. ISBN 978-87-91114-93-9.
| Former states in Indonesia | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Java |
| ||||
| Sumatra |
| ||||
| Kalimantan | |||||
| Sulawesi | |||||
| Lesser Sunda Islands | |||||
| West Timor | |||||
| Maluku | |||||
| Papua | |||||
This Indonesian history-related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |