This is an old revision of this page, as edited by حسن علي البط (talk | contribs) at 06:14, 12 July 2024 (added Category:Diols using HotCat). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 06:14, 12 July 2024 by حسن علي البط (talk | contribs) (added Category:Diols using HotCat)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)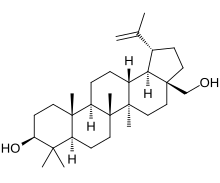 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Lup-20(29)-ene-3β,28-diol | |
| Systematic IUPAC name (1R,3aS,5aR,5bR,7aR,9S,11aR,11bR,13aR,13bR)-3a-(Hydroxymethyl)-5a,5b,8,8,11a-pentamethyl-1-(prop-1-en-2-yl)icosahydro-1H-cyclopentachrysen-9-ol | |
| Other names Betulinol, betuline, betulol, betulinic alcohol, trochol | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.797 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C30H50O2 |
| Molar mass | 442.728 g·mol |
| Appearance | solid with needle-like crystals |
| Melting point | 256 to 257 °C (493 to 495 °F; 529 to 530 K) |
| Solubility in water | insoluble |
| Solubility | slightly soluble in ethanol and benzene; soluble in diethyl ether, ethyl acetate and ligroin |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Betulin is an abundant, naturally occurring triterpene. It is commonly isolated from the bark of birch trees. It forms up to 30% of the dry weight of silver birch bark. It is also found in birch sap. Inonotus obliquus contains betulin.
The compound in the bark gives the tree its white color which appears to protect the tree from mid-winter overheating by the sun. As a result, birches are some of the northernmost occurring deciduous trees.
History
Betulin was discovered in 1788 by German-Russian chemist Johann Tobias Lowitz.
Chemistry
Chemically, betulin is a triterpenoid of lupane structure. It has a pentacyclic ring structure, and hydroxyl groups in positions C3 and C28.
See also
References
- ^ Haynes, William M.; Lide, David R.; Bruno, Thomas J. (2014). "3". CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (95th ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. p. 340. ISBN 9781482208689. OCLC 908078665.
- Green, Brian; Bentley, Michael D.; Chung, Bong Y.; Lynch, Nicholas G.; Jensen, Bruce L. (2007-12-01). "Isolation of Betulin and Rearrangement to Allobetulin. A Biomimetic Natural Product Synthesis". Journal of Chemical Education. 84 (12): 1985. Bibcode:2007JChEd..84.1985G. doi:10.1021/ed084p1985.
- Gao, Yuan; Xu, Hongyu; Lu, Zhenming; Xu, Zhenghong (November 2009). "Quantitative determination of steroids in the fruiting bodies and submerged-cultured mycelia of Inonotus obliquus". Se Pu. 27 (6): 745–749. ISSN 1000-8713. PMID 20352924.
- Lowitz, J. T. (1788). "Űber eine neue, fast benzoeartige substanz der briken". Crell's Chem. Ann. 1: 312–317.
- Król, Sylwia Katarzyna; Kiełbus, Michał; Rivero-Müller, Adolfo; Stepulak, Andrzej (2015). "Comprehensive Review on Betulin as a Potent Anticancer Agent". BioMed Research International. 2015: 584189. doi:10.1155/2015/584189. PMC 4383233. PMID 25866796.