This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Mitchazenia (talk | contribs) at 21:43, 6 February 2007 (updated infobox). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 21:43, 6 February 2007 by Mitchazenia (talk | contribs) (updated infobox)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)| Category 4 major hurricane (SSHWS/NWS) | |
| Formed | September 20, 1959 |
|---|---|
| Dissipated | September 30, 1959 |
| Highest winds | 1-minute sustained: 140 mph (220 km/h) |
| Lowest pressure | 950 mbar (hPa); 28.05 inHg |
| Fatalities | 22 direct |
| Damage | $90 million (1959 USD) |
| Areas affected | Bahamas, South Carolina, North Carolina, Virginia |
| Part of the 1959 Atlantic hurricane season | |
Hurricane Gracie was a major hurricane that formed in September 1959, the strongest during the 1959 Atlantic hurricane season. Gracie was a storm that was very difficult to forecast, with its movement unpredictable.
Storm history

Map key Saffir–Simpson scale Tropical depression (≤38 mph, ≤62 km/h)
Tropical storm (39–73 mph, 63–118 km/h)
Category 1 (74–95 mph, 119–153 km/h)
Category 2 (96–110 mph, 154–177 km/h)
Category 3 (111–129 mph, 178–208 km/h)
Category 4 (130–156 mph, 209–251 km/h)
Category 5 (≥157 mph, ≥252 km/h)
Unknown Storm type
 Tropical cyclone
Tropical cyclone  Subtropical cyclone
Subtropical cyclone  Extratropical cyclone, remnant low, tropical disturbance, or monsoon depression
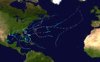
Extratropical cyclone, remnant low, tropical disturbance, or monsoon depression A tropical wave developed into a tropical depression near the north coast of Hispaniola on September 20th. After moving west-northwestward for a day, it turned northeastward, where upper level winds were very favorable and steering currents were very weak, which turned out to be a deadly scenario. On the 22nd it became a tropical storm, followed by reaching hurricane strength later that night. It turned to the east on the 25th, and turned back west on the 27th. Then, with a firm anticyclone in place and set steering currents, it moved steadily west-northwestward.
Gracie quickly strengthened and reached its peak of 140 mph (225 km/h) winds on the 29th, but cooler air and land interaction weakened it to a 120 mph Category 3 major hurricane at the time of its Beaufort, South Carolina landfall that night. After landfall, Gracie moved inland and north and became extratropical on the 30th.
Impact
Several tornadoes accompanied the dying storm through Virginia and twelve people were killed near Charlottesville, Virginia. Gracie also killed 10 people in South Carolina and Georgia, mainly due to wind and rain-induced automobile accidents, falling trees and electrocution by live wires. Wind damage was quite significant across South Carolina with many downed trees, telephone poles, and streetlights. Also, numerous windows were shattered and shingles were torn off of roofs. A number of creeks overflowed causing floodwaters that, in areas, were several feet deep.
Gracie was the last major hurricane to strike South Carolina before Hurricane Hugo 30 years later.
Retirement
See also: List of retired Atlantic hurricanesThe name Gracie was retired and will never be used for an Atlantic hurricane again; this was before the formal lists were created, so it was not replaced with any particular name.
See also
External links
This article about or related to tropical cyclones is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |
| Tropical cyclones of the 1959 Atlantic hurricane season | ||
|---|---|---|
 | TSArlene TSBeulah 1Escuminac Hurricane 1Cindy 1Debra TSEdith 1Flora 4Gracie 3Hannah TSIrene 1Judith | |