This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Reconrabbit (talk | contribs) at 16:08, 9 January 2025 (fix references). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 16:08, 9 January 2025 by Reconrabbit (talk | contribs) (fix references)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Chemical compound

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 3-cyclohexyl-1,5,6,7-tetrahydrocyclopentapyrimidine-2,4-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.016.818 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C13H18N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 234.299 g·mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |  
|
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H351, H410 |
| Precautionary statements | P203, P273, P280, P318, P391, P405, P501 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Lenacil is a uracil-derived chemical herbicide used to control dicotyledons. Its formula is C13H18N2O2.
Production and synthesis
Lenacil was first patented and manufactured by DuPont in the 1960s.
The compound can be produced via a condensation reaction between ethyl-2-oxocyclopentanecarboxylate and cyclohexylurea under an environment of phosphoric acid.
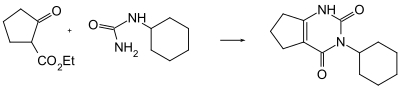
Uses
Lenacil is used in the agricultural industry as a selective herbicide to protect sugar and fodder beets.
Toxicity
Lenacil is noted as a potential endocrine disrupting compound. It is not acutely toxic or genotoxic to mammals, though there is limited evidence the compound is carcinogenic. Lenacil is noted as particularly damaging to algae and aquatic plants, which is a concern if the compound leaches into groundwater when used as a pesticide.
References
- Bahadir M, Parlar H, Spiteller M (2000). Springer Umweltlexikon (in German). Springer. p. 702. ISBN 978-3-540-63561-1.
- Roberts TR, Hutson DH (1999). Metabolic pathways of agrochemicals. Vol. 2. Royal Soc of Chemistry. p. 699. ISBN 978-0-85404-499-3.
- U.S. Patent 3235360, "Control of undesirable vegetation" van 15 februari 1966 aan E.I. Du Pont de Nemours and Company. Gearchiveerd op 9 september 2023.
- Ullmann's Agrochemicals. Vol. 1. Wiley-VCH. 2007. p. 809ff. ISBN 978-3-527-31604-5.
- Unger TA (1996). Pesticide synthesis handbook. p. 569. ISBN 978-0-81551401-5.
- ^ "Peer review of the pesticide risk assessment of the active substance lenacil | EFSA". www.efsa.europa.eu. October 7, 2009. doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2009.1326. Retrieved January 9, 2025.
- Andres S, Dulio V (2024). "List of 7074 potential endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs) by PARC T4.2 (NORMAN-SLE-S109.0.1.0) ". Zenodo. doi:10.5281/zenodo.10944199.