This is an old revision of this page, as edited by EuroHistoryTeacher (talk | contribs) at 21:38, 19 January 2009 (more detailed map showing the four 'suyus', also the inca empire never reach so high into colombia.). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 21:38, 19 January 2009 by EuroHistoryTeacher (talk | contribs) (more detailed map showing the four 'suyus', also the inca empire never reach so high into colombia.)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) For the a general view of Inca civilization, people and culture, see Inca civilization.| Inca EmpireTawantinsuyu | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1438–1533 | |||||||||
| The Inca Empire at its greatest extent.The Inca Empire at its greatest extent. | |||||||||
| Capital | Cusco (1438-1533) | ||||||||
| Common languages | Quechua (official), Aymara, Puquina, Jaqi family, Muchik and scores of smaller languages. | ||||||||
| Religion | Inca religion | ||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||
| Sapa Inca | |||||||||
| • 1438-1471 | Pachacuti | ||||||||
| • 1471-1493 | Túpac Inca Yupanqui | ||||||||
| • 1493-1525 | Huayna Capac | ||||||||
| • 1525-1532 | Huascar | ||||||||
| • 1532-1533 | Atahualpa | ||||||||
| Historical era | P-Columbian | ||||||||
| • Pachacutec created the Twantinsuyu | 1438 | ||||||||
| • Civil war between Huáscar and Atahualpa | 1529-1532 | ||||||||
| • Spanish conquest lead by Francisco Pizarro | 1533 | ||||||||
| Area | |||||||||
| 1438 | 800,000 km (310,000 sq mi) | ||||||||
| 1527 | 2,000,000 km (770,000 sq mi) | ||||||||
| Population | |||||||||
| • 1438 | 12,000,000 | ||||||||
| • 1527 | 20,000,000 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Inca Empire |
|---|
 |
| Inca society |
| Inca history |
The Inca Empire (or Inka Empire) was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The administrative, political and military center of the empire was located in Cuzco. The Inca Empire arose from the highlands of Peru sometime in early 13th century. From 1438 to 1533, the Incas used a variety of methods, from conquest to peaceful assimilation, to incorporate a large portion of western South America, centered on the Andean mountain ranges, including large parts of modern Ecuador, Peru, western and south central Bolivia, northwest Argentina, north and north-central Chile, and southern Colombia. The Incas identified their king as "child of the sun."
The Quechua name for the empire was Tawantinsuyu which can be translated as The Four Regions or The Four United Regions. Before the Quechua spelling reform it was written in Spanish as Tahuantinsuyo. Tawantin is a group of four things (tawa "four" with the suffix -ntin which names a group); suyu means "region" or "province". The empire was divided into four Suyus, whose corners met at the capital, Cusco (Qosqo), in modern-day Peru. The official language of the empire was Quechua, although dozens if not hundreds of local languages and dialects of Quechua were spoken.
There were many local forms of worship, most of them concerning local sacred "Huacas", but the Inca leadership encouraged the worship of Inti — the sun god — and imposed its sovereignty above other cults such as that of Pachamama.
History
Origin myths
See also: Inca mythology
The Incas had various creation myths. In one, Ticci Viracocha sent forth his four sons and four daughters (known as the Ayar brothers) from Pacaritambo to establish a village. Along the way, Sinchi Roca was born to Manco and Ocllo, and Sinchi Roca led them to the valley of Cusco where they founded their new village. There Manco became their leader and became known as Manco Capac.
In another origin myth, the sun god Inti ordered Manco Capac and Mama Ocllo to emerge from the depths of Lake Titicaca. They were born in the lake and wandered north to establish the city of Cusco. They travelled by means of underground caves until they reached Cusco where they established Hurin Cusco, or the first dynasty of the Kingdom of Cusco.
These myths were apparently transmitted via oral tradition until early Spanish colonists recorded them; however some scholars believe that they may have been recorded on quipus (Andean knotted string records).
Archaeology
The Inca civilization probably began c. 9500 ya. Based in the highlands of Peru, an area now referred to as the punas, the Inca probably began as a nomadic herding people. Geographical conditions resulted in a distinctive physical development characterized by a small stature and stocky build. Men averaged 5'2" and women averaged 4'9". Because of the high altitudes, they had unique lung developments with almost one third greater capacity than any other human. The Incas also had slower heart rates, blood volume of about four pints more than other humans, and double the amount of hemoglobin which transfers oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body.
| This section does not cite any sources. Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (December 2008) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Archaeologists have found traces of permanent habitation as high as 17,500 feet above sea level in the temperate zone of the high altiplanos. While the Conquistadors may have been intimidating in stature, the Inca surely had the advantage of coping with the extraordinary altitude. It seems that civilizations in this area before the Inca have left no written record and therefore the Inca seem to appear from nowhere, but the Inca were a product of the past. They borrowed architecture, ceramics, and their empire-state government from previous cultures.
The first Inca ruler was Manco Capac. There is no specific date for this ruler nor for the seven succeeding rulers, but the assumed dates are 1250 to 1438. The Inca originated at Cuzco in the central highlands and expanded down the coast. The basis of the Inca's conquest is believed to be their organization. Their divine symbol is the sun god, their bureaucratic system consists of a circle of officials belonging to eleven royal ayllus, and the line of descent continues through incestuous marriage with a sister who becomes the coya or "legal queen." The expansion of the Inca empire probably resulted from climatic conditions. Their resources in the highlands were limited to llama, alpaca, and vicuna.
In 1445 Pachacuti Inca Yupanqui (the ninth Inca) began conquest of the Titicaca regions. He incorporated and developed patterns of cultures already in existance, particularly that of the Chimu. Pachacuti had disciplined officers from his own elite household. Common soldiers were armed with bronze battle axes, wooden hafts with stone or bronze heads, slings, lances, throwing spears, bows and arrows, wooden shields covered with leather, cotton or cane helmets, and quilted armor. In each captured province Inca officials were superimposed upon the existing local officials. The loyalty of the captured province was assured by taking the sons of the officials hostage in Cuzco. They made Quechua the official language and sun worship the official religion. They exploited the labor force in order to increase productivity and rapidly develop irrigation and terrace cultivation systems, and used guano deposits found on the coastal islands as fertilizer. The Inca social system required a severe authoritarian government backed by ritual and divine compulsion. They built temples and fortresses and were supreme in road building. The roads extended 3,250 miles from Quito in the north to Talca in Central Chile. These roads were vital to the maintenance of the empire, but ironically this network of highways made the Spanish conquest easier. There were road markers every topo which is 4.5 miles and rest houses or tambos every 12 miles for the Inca ruler and his retinue. Small post houses called chasquisevery 5 miles housed the runners and were used for relaying dispatches at the rate of about 150 miles per day. Verbal dispatches were supplemented by quipu or knotted strings, probably involving a code based on numbers. These were the equivalent of the notched sticks of the old tally system used in Europe.
Inca society was based on the idea of "equal footing." All men must work in order to live, and even the Inca nobles helped to set an example. Some archaeologists believe this was a façade supporting a two-caste system. The penalties for breaking the law were less severe for bureaucratic elites; this emphasizes the importance of the upper caste in the maintenance of the system.
Kingdom of Cusco
Main article: Kingdom of CuscoWe can assure your majesty that it is so beautiful and has such fine buildings that it would even be remarkable in Spain.
— Francisco Pizarro
The Inca people began as a tribe in the Cusco area around the 12th century. Under the leadership of Manco Capac, they formed the small city-state of Cusco (Quechua Qusqu), shown in red on the map. In 1438 they began a far-reaching expansion under the command of Sapa Inca (paramount leader) Pachacuti, whose name literally meant "earth-shaker". During his reign, he and his son brought much of the Andes mountains (roughly modern Peru and Ecuador) under Inca control.
Reorganization and formation of the Empire
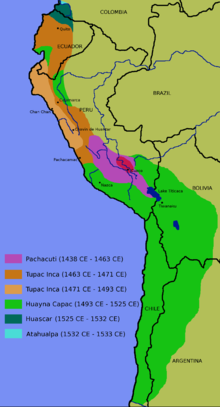
Pachacuti reorganized the kingdom of Cuzco into an empire, the Tahuantinsuyu, a federalist system which consisted of a central government with the Inca at its head and four provincial governments with strong leaders: Chinchasuyu (NW), Antisuyu (NE), Contisuyu (SW), and Collasuyu (SE). Pachacuti is also thought to have built Machu Picchu, either as a family home or as a summer retreat.
Pachacuti sent spies to regions he wanted in his empire; they brought reports on the political organization, military might and wealth. He would then send messages to the leaders of these lands extolling the benefits of joining his empire, offering them presents of luxury goods such as high quality textiles, and promising that they would be materially richer as subject rulers of the Inca. Most accepted the rule of the Inca as a fait accompli and acquiesced peacefully. The ruler's children would then be brought to Cuzco to be taught about Inca administration systems, then return to rule their native lands. This allowed the Inca to indoctrinate the former ruler's children into the Inca nobility, and, with luck, marry their daughters into families at various corners of the empire.
Expansion and consolidation of the Empire
It was traditional for the Inca's son to lead the army; Pachacutec's son Túpac Inca Yupanqui began conquests to the north in 1463, and continued them as Inca after Pachucuti's death in 1471. His most important conquest was the Kingdom of Chimor, the Inca's only serious rival for the coast of Peru. Túpac Inca's empire stretched north into modern day Ecuador and Colombia.
Túpac Inca's son Huayna Cápac added a small portion of land to the north in modern day Ecuador and in parts of Peru. At its height, the Inca Empire included Peru and Bolivia, most of what is now Ecuador, a large portion of what is today Chile north of Maule River. The advance south halted after the Battle of the Maule where they met massive resistance by the Mapuche tribes. The empire also extended into corners of Argentina and Colombia. However, most of the southern portion of the Inca empire, the portion denominated as Collasuyo, was desert wasteland.
The Inca Empire was a patchwork of languages, cultures and peoples. The components of the empire were not all uniformly loyal, nor were the local cultures all fully integrated. The Inca empire as a whole had an economy based on exchange and taxation of luxury goods and labour. The following quote reflects a method of taxation: “For as is well known to all, not a single village of the highlands or the plains failed to pay the tribute levied on it by those who were in charge of these matters. There were even provinces where, when the natives alleged that they were unable to pay their tribute, the Inca ordered that each inhabitant should be obliged to turn in every four months a large quill full of live lice, which was the Inca’s way of teaching and accustoming them to pay tribute”
Inca civil war and Spanish conquest
Main articles: Inca war of succession and Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire
Spanish conquistadors led by Francisco Pizarro and his brothers explored south from Panama, reaching Inca territory by 1526. It was clear that they had reached a wealthy land with prospects of great treasure, and after one more expedition (1529), Pizarro traveled to Spain and received royal approval to conquer the region and be its viceroy.This approval was received as detailed in the following quote: "In July 1529 the queen of Spain signed a charter allowing Pizarro to conquer the Incas. Pizarro was named governer and captain of all conquests in Peru, ir New Castile, as the Spanish now called the land."
At the time they returned to Peru, in 1532, a war of the two brothers between Huayna Capac's sons Huascar and Atahualpa and unrest among newly-conquered territories — and perhaps more importantly, smallpox, which had spread from Central America — had considerably weakened the empire. It was an unfortunate fact for the Inca that the Spaniards arrived at the height of a civil war, fueled almost certainly by the devastating diseases that preceded the European colonization.
Pizarro did not have a formidable force; with just 168 men, 1 cannon and only 27 horses, he often needed to talk his way out of potential confrontations that could have easily wiped out his party. The Spanish horsemen, fully armored, had great technological superiority over the Inca forces. The traditional mode of battle in the Andes was a kind of siege warfare where large numbers of usually reluctant draftees were sent to overwhelm opponents. The Spaniards had developed one of the finest military machines in the premodern world, tactics learned in their centuries' long fight against Moorish kingdoms in Iberia. Along with this tactical and material superiority, the Spaniards also had acquired tens of thousands of native allies who sought to end the Inca control of their territories.
Their first engagement was the Battle of Puná, near present-day Guayaquil, Ecuador on the Pacific Coast; Pizarro then founded the city of Piura in July 1532. Hernando de Soto was sent inland to explore the interior, and returned with an invitation to meet the Inca, Atahualpa, who had defeated his brother in the civil war and was resting at Cajamarca with his army of 80,000 troops.
Pizarro and some of his men, most notably a friar by the name of Vincente de Valverde met with the Inca, who had brought only a small retinue. Through an interpreter Friar Vincente read the "Requerimiento" that demanded that he and his empire accept the yoke of King Charles I of Spain and convert to Christianity. Due to the language barrier and perhaps poor interpretation, Atahualpa became somewhat puzzled by the friar's description of Christian faith and was said to have not fully understood the envoy's intentions. After Atahualpa attempted further enquiry into the doctrines of the Christian faith under which Pizarro's envoy served, the Spanish became frustrated and impatient, attacking the Inca's retinue (see Battle of Cajamarca) and capturing Atahualpa as hostage.
Atahualpa offered the Spaniards enough gold to fill the room he was imprisoned in, and twice that amount of silver. The Inca fulfilled this ransom, but Pizarro deceived them, refusing to release the Inca afterwards. During Atahualpa's imprisonment Huascar was assassinated elsewhere. The Spaniards maintained that this was at Atahualpa's orders; this was used as one of the charges against Atahualpa when the Spaniards finally decided to put him to death, in August 1533.
The last Incas

The Spanish installed Atahualpa's brother Manco Inca Yupanqui in power; for some time Manco cooperated with the Spanish, while the Spanish fought to put down resistance in the north. Meanwhile an associate of Pizarro's, Diego de Almagro, attempted to claim Cuzco for himself. Manco tried to use this intra-Spanish feud to his advantage, recapturing Cuzco (1536), but the Spanish retook the city afterwards. Manco Inca then retreated to the mountains of Vilcabamba, Peru, where he and his successors ruled for another 36 years, sometimes raiding the Spanish or inciting revolts against them. In 1572 the last Inca stronghold was conquered, and the last ruler, Túpac Amaru, Manco's son, was captured and executed. This ended resistance to the Spanish conquest under the political authority of the Inca state.
After the fall of the Inca Empire, the new Spanish rulers brutally oppressed the people and suppressed their traditions. Many aspects of Inca culture were systematically destroyed, including their sophisticated farming system. The Spaniards used the Inca mita (mandatory public service) system to literally work the people to death. One member of each family was forced to work in the gold and silver mines, the foremost of which was the titanic silver mine at Potosí. When a family member died, which would usually happen within a year or two, the family would be required to send a replacement.
The effects of smallpox on the Inca empire were even more devastating. Beginning in Colombia, smallpox spread rapidly before the Spanish invaders first arrived in the empire. The spread was probably aided by the efficient Inca road system. Within months, the disease had killed the Sapa Inca Huayna Capac, his successor, and most of the other leaders. Two of his surviving sons warred for power and, after a bloody and costly war of the two brothers, Atahualpa become the new Sapa Inca. As Atahualpa was returning to the capital Cuzco, Francisco Pizarro arrived and through a series of deceits captured the young leader and his best general. Within a few years smallpox claimed between 60% and 94% of the Inca population, with other waves of European disease weakening them further. Smallpox was only the first epidemic.
Typhus (probably) in 1546, influenza and smallpox together in 1558, smallpox again in 1589, diphtheria in 1614, measles in 1618 - all ravaged the remains of Inca culture.
Society
Main articles: Inca society and Inca educationOrganization of the Empire
The most powerful figure in the empire was the Sapa Inca ('the unique Inca'). Only descendants of the original Inca tribe ever ascended to the level of Inca. Most young members of the Inca's family attended Yachay Wasis (houses of knowledge) to obtain their education.
The Inca Empire was a federalist system which consisted of a central government with the Inca at its head and four provinces: Chinchay Suyu (NW), Anti Suyu (NE), Kunti Suyu (SW), and Qulla Suyu (SE). The four corners of these provinces met at the center, Cusco. Each province had a governor who oversaw local officials, who in turn supervised agriculturally-productive river valleys, cities and mines. There were separate chains of command for both the military and religious institutions, which created a system of partial checks and balances on power . The local officials were responsible for settling disputes and keeping track of each family's contribution to the mita (mandatory public service).
Language
For more information look at Quechua
Since the Inca Empire lacked a written language, the empire's main form of communication and recording came from quipus, ceramics and spoken Quechua, the language the Incas imposed upon the peoples within the empire. The plethora of civilizations in the Andean region provided for a general disunity that the Incas needed to subdue in order to maintain control of the empire. While Quechua had been spoken in the Andean region, like central Peru, for several years prior to the expansion of the Inca civilization, the type of Quechua the Incas imposed was an adaptation from the Kingdom of Cusco (an early form of "Southern Quechua") of what some historians define as "Proto-Quechua" or Cusco dialect (the original Quechua dialect).
The language imposed by the Incas further diverted from its original phonetic tone as some societies formed their own regional varieties, or slang. The diversity of Quechua at that point and even today does not come as a direct result from the Incas, whom are just a part of the reason for Quechua's diversity. The civilizations within the empire that had previously spoken Quechua kept their own variety distinct to the Quechua the Incas spread. Although these dialects of Quechua have a similar linguistic structure, they differ according to the region in which they are spoken. Although most of the societies within the empire implemented Quechua into their lives, the Incas allowed several societies to keep their old languages such as Aymara, which still remains a spoken language in contemporary Bolivia where it's the primary indigenous language and various regions of South America surrounding Bolivia. The linguistic body of the Inca Empire was thus largely varied, but it still remains quite an achievement for the Incas that went even beyond their times as the Spanish imposed the use of Spanish as a method to force their culture upon the indigenous peoples of South America (even though that further increased the diversity of the language).
The dialect of Quechua spoken by the Incan ruling elite tended to remain somewhat closer to the "early Southern Quechua" of the Kingdom of Cusco mainly due to the complex educational facilities the Inca Empire offered them. This standardized governmental Quechua is what served as the backbone for the Inca Empire, but it also differentiated the social status of the community. Moreover, some historians even discuss the possibility that the "secret language" of the ruling elite might have simply been another form of Quechua.
Daily life and diet
See also: Inca cuisine
The Inca diet consisted primarily of potatoes and grains, supplemented by fish, vegetables, nuts, and maize (corn). Camelid (llama and alpaca) meat and cuyes (guinea pigs) were also eaten in large quantities. In addition, they hunted various wild animals for meat, skins and feathers. Maize was malted and used to make chicha, a fermented alcoholic beverage. The Inca road system was key to farming success as it allowed distribution of foodstuffs over long distances. The Inca also constructed vast storehouses, which allowed them to live through El Niño years while neighboring civilizations suffered .
The Aqllawasi (Acllahuasi) which means "house of the sun virgins" was developed under the Incas in Peru at about 1438–1532 CE. Its central purpose was in the manufacturing of garments for the Inca royalty and the worship of the sun god, Inti.
Religion
See also: Inca ReligionThe Inca believed in reincarnation. Those who obeyed the Incan moral code — ama suwa, ama llulla, ama quella (do not steal, do not lie, do not be lazy) — "went to live in the Sun's warmth while others spent their eternal days in the cold earth" . The Inca also practiced cranial deformation. They achieved this by wrapping tight cloth straps around the heads of newborns in order to alter the shape of their still-soft skulls into a more conical form. Further studies are still needed to determine whether these deformations caused brain damage.
Arts and technology

Monumental architecture
Architecture was by far the most important of the Inca arts, with textiles reflecting motifs that were at their height in architecture. The main example is the capital city of Cuzco itself. The breathtaking site of Machu Picchu was constructed by Inca engineers. The stone temples constructed by the Inca used a mortarless construction that fit together so well that a knife could not be fitted through the stonework. This was a process first used on a large scale by the Pucara (ca. 300 BC–AD 300) peoples to the south in Lake Titicaca, and later in the great city of Tiwanaku (ca. AD 400–1100) in present day Bolivia. The Inca imported the stoneworkers of the Tiwanaku region to Cuzco when they conquered the lands south of Lake Titicaca . The rocks used in construction were sculpted to fit together exactly by repeatedly lowering a rock onto another and carving away any sections on the lower rock where the dust was compressed. The tight fit and the concavity on the lower rocks made them extraordinarily stable.
Ceramics, precious metal work, and textiles
Almost all of the gold and silver work of the empire was melted down by the conquistadores.
Ceramics were painted using the polychrome technique portraying numerous motifs including animals,birds, waves, felines (which were popular in the Chavin culture) and geometric patterns found in the Nazca style of ceramics.In place of a written language Ceramics portrayed the very basic scenes of everyday life,including the smelting of metals,relationships and scenes of tribal warfare,it is through these preserved Ceramics that we know what life was like for the ancient South Americans . The most distinctive Inca ceramic objects are the Cusco bottles or ¨aryballos¨. Many of these pieces are on display in Lima in the Larco Archaeological Museum and the National Museum of Archaeology, Anthropology and History.
Communication and medicine
The Inca used an assemblages of knotted strings, known as Quipu to record information, the exact nature of which is no longer known. Originally it was thought that Quipu were used only as mnemonic devices or to record numerical data. Recent discoveries, however, have led to the theory that these devices were instead a form of writing in their own right .
The Inca made many discoveries in medicine. They performed successful skull surgery, which involved cutting holes in the skull in order to alleviate fluid buildup and inflammation caused by head wounds. Anthropologists have discovered evidence which suggests that most skull surgeries performed by Inca surgeons were successful. In pre-Inca times, only one-third of skull surgery patients survived the procedure. However, survival rates rose to between 80 and 90 percent during the Inca era, from A.D. 1400 to 1532.
Coca leaves were used to lessen hunger and pain, as they still are in the Andes. The Chasqui (messengers) chewed coca leaves for extra energy to carry on their tasks as runners delivering messages throughout the empire. They were also used during surgeries. They were used in order to lessen the pain of a patient.
Weapons, armor, and warfare

The Incas used weapons and had wars with other civilizations in the area. The Inca army was the most powerful in the area at that time, because they could turn an ordinary villager or farmer into a soldier, ready for battle. This is because every male Inca had to take part in war at least once so as to be prepared for warfare again when needed. By the time the empire had reached its large size, every section of the empire contributed in setting up an army for war.
The Incas had no iron or steel, and their weapons were no better than those of their enemies. They went into battle with the beating of drums and the blowing of trumpets. The armor used by the Incas included:
- Helmets made of wood, copper, bronze, cane, or animal skin; some were adorned with feathers
- Round or square shields made from wood or hide
- Cloth tunics padded with cotton and small wooden planks to protect spine
The Inca weaponry included:
- Bronze or bone-tipped spears
- Two-handed wooden swords with serrated edges (notched with teeth, like a saw)
- Clubs with stone and spiked metal heads
- Woolen slings and stones
- Stone or copper headed battle-axes
- Stones fastened to lengths of cord (bola)
Roads allowed very quick movement for the Inca army, and shelters called quolla were built one day's distance in travelling from each other, so that an army on campaign could always be fed and rested. (The name for the Sapa Inca's storehouses was tambo. This can be seen in names of ruins such as Ollantay Tambo, or My Lord's Storehouse. These were set up so the Inca and his entourage would always have supplies (and possibly shelter) ready as he traveled.
Inca flag

There are 16th and 17th century chronicles and references that support the idea of a banner, or flag, attributable to the Inca.
Francisco López de Jerez wrote in 1534:
"all of them came distributed into squads, with their flags and captains commanding them, as well-ordered as Turks"
("todos venían repartidos en sus escuadras con sus banderas y capitanes que los mandan, con tanto concierto como turcos").
The chronicler, Bernabé Cobo, wrote:
"The royal standard or banner was a small square flag, ten or twelve spans around, made of cotton or wool linen, placed on the end of a long staff, stretched and stiff such that it did not wave in the air, and on it each king painted his arms and emblems, for each one chose different ones, though the sign of the Incas was the rainbow."
(...el guión o estandarte real era una banderilla cuadrada y pequeña, de diez o doce palmos de ruedo, hecha de lienzo de algodón o de lana, iba puesta en el remate de una asta larga, tendida y tiesa, sin que ondease al aire, y en ella pintaba cada rey sus armas y divisas, porque cada uno las escogía diferentes, aunque las generales de los Incas eran el arco celeste.)
-Bernabé Cobo, Historia del Nuevo Mundo (1653)
Guaman Poma's 1615 book, El primer nueva corónica y buen gobierno, shows numerous line drawings of Inca flags.
In modern times the rainbow flag has been associated with the Tawantinsuyu and is displayed as a symbol of Inca heritage in Peru and Bolivia. The city of Cusco flies the Rainbow Flag. Peruvian President Alejandro Toledo (2001–2006) flew the Rainbow Flag in Lima's presidential palace. The Rainbow Flag was taken down by President Alan Garcia in July 2006.
See also: Wiphala and Rainbow flag § Andean peoples and social movementsLegacy
The major languages of the empire, Quechua and Aymara, were employed by the Roman Catholic Church to evangelize in the Andean region. In some cases, these languages were taught to people who had originally spoken other indigenous languages. Today, Quechua and Aymara remain the most widespread Amerindian languages. Those who spoke these two languages were regarded higher than the others and referred to as middle-class.
References
- Popenoe, Hugh, Steven R. King, Jorge Leon, Luis Sumar Kalinowski, and Noel D. Vietmeyer. Lost Crops of the Incas. Washington DC: National Academy Press, 1989.
- Morales, Edmundo (1995). The Guinea Pig : Healing, Food, and Ritual in the Andes, University of Arizona Press. ISBN 0-8165-1558-1.
- De la Vega, Garcilaso . The Incas: The Royal Commentaries of the Inca. New York: The Orion Press, 1961.
- John Hemming. The Conquest of the Incas Harvest Press 2003. ISBN 978-0156028264.
- Mann, Charles. C (2005). 1491: New Revelations of the Americas Before Columbus. Knopf. pp. 64–96.
- MacQuarrie, Kim. The Last Days of the Incas. Simon & Schuster, 2007. ISBN 978-0743260497.
Notes
- The Inca Empire. Created by Katrina Namnama & Kathleen DeGuzman
- Terence D'Altroy, The Incas, pp. 2–3.
- Tawantin suyu derives from the Quechua "tawa" (four), to which the suffix "-ntin" (together or united) is added, followed by "suyu" (region or province), which roughly renders as "The four lands together". The four suyos were: Chinchay Suyo (North), Anti Suyo (East. The Amazon jungle), Colla Suyo (South) and Conti Suyo (West).
- The Inca - All Empires
- Gary Urton, The History of a Myth: Pacariqtambo and the Origin of the Inkas (Austin: University of Texas Press, 1990).
- Gary Urton, Signs of the Inka Khipu: Binary Coding in the Andean Knotted-String Records (Austin: University of Texas Press, 2003).
- Innes, Hammond. The Conquistadors. New York, NY: Alfred A. Knopf Inc., 1969.
- The three laws of Tawantinsuyu are still referred to in Bolivia these days as the three laws of the Collasuyo.
- The Incas and their Ancestors
- Starn, Degregori, Kirk The Peru Reader: History, Culture, Politics; Quote by Pedro de Cieza de Leon; Published by Duke University Press, 1995
- Somervill,Barbara; Francisco Pizarro: Conquerer of the IncasPublished by Compass Point Books, 2005; pp.52
- Millersville University Silent Killers of the New World
- Quechua*
- ^ Origins And Diversity of Quechua
- Morales, 1995
- http://www.netside.net/~manomed/inca.htm
- Burger, R.L. and L.C. Salazar. 2004. Machu Picchu: Unveiling the Mystery of the Incas. Yale University Press, p. 45. ISBN 0-300-09763-8.
- Berrin, Katherine & Larco Museum. The Spirit of Ancient Peru:Treasures from the Museo Arqueológico Rafael Larco Herrera. New York:Thames and Hudson
- Science News / Incan Skull Surgery
- Francisco López de Jerez,Verdadera relacion de la conquista del Peru y provincia de Cuzco, llamada la Nueva Castilla, 1534.
- Guaman Poma, El primer nueva corónica y buen gobierno, (1615/1616), pp. 256, 286, 344, 346, 400, 434, 1077, this pagination corresponds to the Det Kongelige Bibliotek search engine pagination of the book. Additionally Poma shows both well drafted European flags and coats of arms on pp. 373, 515, 558, 1077, 0. On pages 83, 167-171 Poma uses a european heraldic graphic convention, a shield, to place certain totems related to Inca leaders.
See also
- Peruvian Ancient Cultures
- Cultural periods of Peru
- History of Peru
- War of the two brothers
- Inca Garcilaso de la Vega
- Felipe Guaman Poma de Ayala
- Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire
- Smallpox Epidemics in the New World
- Population history of Amerindians
- Spanish Empire
- Inca cuisine
- Tumi
- Tambo (Incan structure)
- Amazonas before the Inca Empire
External links
- Historical maps of inca empire Maps to be combined and compared
- "Guaman Poma - El Primer Nueva Corónica Y Buen Gobierno" – A high-quality digital version of the Corónica, scanned from the original manuscript.
- Conquest of Peru, Prescott, 1847 Full text, free to read and search.
- Inca Land by Hiram Bingham (published 1912–1922 CE).
- Inca Artifacts, Peru, and Machu Picchu 360 degree movies of inca artifacts and Peruvian landscapes.
- Inca civilization and other ancient civilizations by Genry Joil.
- Inca stone cutting techniques: theory on how the Inca walls fit so perfectly.
- Ancient Civilizations - Inca Great research site for kids.
- "Ice Treasures of the Inca" National Geographic site.
- "The Sacred Hymns of Pachacutec" Poetry of an Inca emperor.
- Incan Ice Mummies NOVA site based on their series about the 1996 expedition that discovered Incan ice mummies.
- Incan Religion
- History of the Inca Empire Inca history, society and religion.
- Engineering in the Andes Mountains MIT asst. professor gives 40 minute lecture on Incan suspension bridges.
- A Map and Timeline of events mentioned in this article
Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA
Categories: