This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Darkicebot (talk | contribs) at 14:36, 30 March 2009 (robot Adding: cs, eo, he, id, sr, vec Modifying: ar). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 14:36, 30 March 2009 by Darkicebot (talk | contribs) (robot Adding: cs, eo, he, id, sr, vec Modifying: ar)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)- This article is about the region in Africa, for other uses see Nubia (disambiguation).
Nubia (not to be confused with Nuba, a collective term used for the peoples who inhabit the Nuba Mountains, in Kordofan province, Sudan, Africa) is the region in the south of Egypt, along the Nile and in northern Sudan. Most of Nubia is situated in Sudan with about a quarter of its territory in Egypt. In ancient times it was an independent kingdom.

Its people spoke at least two varieties of the Nubian language group, a Nilo-Saharan subfamily which includes Nobiin, Kenuzi-Dongola, Midob and several related varieties in the northern part of the Nuba Mountains in South Kordofan. A variety (Birgid) was spoken (at least until 1970) north of Nyala in Darfur but is now extinct. Old Nubian was used in mostly religious texts dating from the 8th and 9th centuries AD and is considered ancestral to modern day Nobiin.
History
Pre-history
Evidence indicates that the Neolithic in the Nile valley likely came from the Sudan, as well as the Sahara, and there was shared culture with the two areas and with that of Egypt during this time period. By the 5th millennium BC, the peoples who inhabited what is now called Nubia, were full participants in the Neolithic revolution. Saharan rock reliefs depict scenes that have been thought to be suggestive of a cattle cult, typical of those seen through out parts of Eastern Africa and the Nile Valley even to this day. Megaliths discovered at Nabta Playa are early examples of what seems to be the world's first Archaeoastronomy devices, out dating Stonehenge by at least 1000 years. This complexity, as observed at Nabta Playa, and as expressed by different levels of authority within the society there, likely formed the basis for the structure of both the Neolithic society at Nabta and the Old Kingdom of Egypt. Around 3800 B.C., the first "Nubian" culture arose, termed the A-Group, and it was contemporary, and ethnically and culturally very similar to, the polities in predynastic Naqadan Upper Egypt. Around 3300 BC, there is evidence of a unified kingdom, as shown by the finds at Qustul, that maintained substantial interactions (both cultural and genetic) with the culture of Naqadan Upper Egypt, and may have even contributed to the unification of the Nile valley, and very likely contributed some pharaonic iconography, such as the white crown and serekh, later to be used by the famous Egyptian pharaohs. Around the turn of the protodynastic period, Naqada, in its bid to conquer and unify the whole Nile valley, seems to have conquered Ta-Seti (the kingdom where Qustul was located) and harmonized it with the Egyptian state, and thus, it became the first nome of Upper Egypt. At the time of the first dynasty, the A-Group area seems to have been entirely depopulated, most likely due to immigration to areas west and south.
This culture began to decline in the early-28th century BC. The succeeding culture is known as B-Group. Previously, the B-Group people were thought to have invaded from elsewhere. Today most historians believe that B-Group was merely A-Group but far poorer. The causes of this are uncertain, but it was perhaps caused by Egyptian invasions and pillaging that began at this time. Nubia is believed to have served as a trade corridor between Egypt and tropical Africa long before 3100 BC. Egyptian craftsmen of the period used ivory and ebony wood from tropical Africa which came through Nubia.
Early history

In 2300 BC, Nubia was first mentioned in Old Kingdom Egyptian accounts of trade missions. From Aswan, right above the First Cataract, southern limit of Egyptian control at the time, Egyptians imported gold, incense, ebony, ivory, and exotic animals from tropical Africa through Nubia. As trade between Egypt and Nubia increased so did wealth and stability. By the Egyptian 6th dynasty, Nubia was divided into a series of small kingdoms. There is debate over whether these C-Group peoples, who flourished from c. 2240 BC to c. 2150 BC, were another internal evolution or invaders. There are definite similarities between the pottery of A-Group and C-Group, so it may be a return of the ousted Group-As, or an internal revival of lost arts. At this time, the Sahara Desert was becoming too arid to support human beings, and it is possible that there was a sudden influx of Saharan nomads. C-Group pottery is characterized by all-over incised geometric lines with white infill and impressed imitations of basketry.
During the Egyptian Middle Kingdom (c. 2040–1640 BC), Egypt began expanding into Nubia to gain more control over the trade routes in Northern Nubia and direct access to trade with Southern Nubia. They erected a chain of forts down the Nile below the Second Cataract. These garrisons seemed to have peaceful relations with the local Nubian people but little interaction during the period. A contemporaneous but distinct culture from the C-Group was the Pan Grave culture, so called because of their shallow graves. The Pan Graves are associated with the East bank of the Nile, but the Pan Graves and C-Group definitely interacted. Their pottery is characterized by incised lines of a more limited character than those of the C-Group, generally having interspersed undecorated spaces within the geometric scheme.
From the C-Group culture, the first kingdom to unify much of the region arose, the Kingdom of Kerma, named for its presumed capital at Kerma, one of the earliest urban centers in tropical Africa. By 1750 BC, the kings of Kerma were powerful enough to organize the labor for monumental walls and structures of mud brick, and had rich tombs with possessions for the afterlife and large human sacrifices. The craftsmen were skilled in metalworking and their pottery surpassed in skill that of Egypt. Reisner excavated sites at Kerma and found large tombs and a palace-like structure ('Deffufa'), alluding to the early stability in the region. At one point, Kerma came very close to conquering Egypt, with Egypt suffering a "humiliating defeat" by the hands of the Kushites. According to Davies, head of the joint British Museum and Egyptian archaeological team, the attack was so devastating that had the Kerma forces chose to stay and occupy Egypt, they might have eliminated it for good and brought the great nation to extinction. When Egyptian power revived under the New Kingdom (c. 1532–1070 BC) they began to expand further southwards. Destroying the kingdom and capital of Kerma, they expanded to the Fourth Cataract. By the end of the reign of Thutmose I in 1520 BC, all of northern Nubia had been annexed. They built a new administrative center at Napata, and used the area to produce gold which made Egypt the prime source of gold for the Middle East.
Kush
Main article: Kush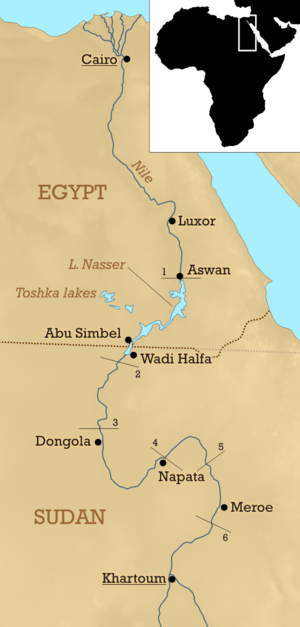
When the Egyptians pulled out, they left a lasting legacy that was merged with indigenous customs forming the kingdom of Kush. Archaeologists have found several burials which seem to belong to local leaders, buried here soon after the Egyptians decolonized the Nubian frontier. Kush adopted many Egyptian practices such as their religion and the practice of building pyramids. The kingdom of Kush survived longer than that of Egypt, even invading and controlling Egypt itself for a period (the Kushite dynasty) in the 8th century BC, under the leadership of king Piye. They held sway over their northern neighbors for nearly 100 years, until they were eventually repelled by the invading Assyrians, forcing them to move further south, eventually establishing their capital at Meroe.
Meroe
Meroe (800 BC - c. AD 350) lay on the east bank of the Nile about 6 km north-east of the Kabushiya station near Shendi, Sudan, ca. 200 km north-east of Khartoum. The people there preserved many ancient Egyptian customs but were unique in many respects. They developed their own form of writing, first utilizing Egyptian hieroglyphs, and later using an alphabetic script with 23 signs. Many pyramids were built in Meroe during this period and the kingdom consisted of an impressive standing military force. A famous legend in the history of Meroe relays the coming of Alexander the Great with his forces. According to legend, confronted with the brilliant military formation of the army led by Candace of Meroe, he concluded it would be best to withdraw his forces. Historical accounts however, show that Alexander never invaded Nubia and did not attempt to move further south than the Oasis of Siwa in Egypt. Strabo also describes a clash with the Romans in which the Romans were defeated by Nubian archers under the leadership of a "one-eyed" (blind in one eye) queen. During this time, the different parts of the region divided into smaller groups with individual leaders, or generals, each commanding small armies of mercenaries. They fought for control of what is now Nubia and its surrounding territories, leaving the entire region weak and vulnerable to attack. Meroe would eventually meet defeat by a new rising kingdom to their south, Askum, under King Ezana.
At some point later, the region was conquered by the Noba people, from which the name Nubia may derive (another possibility is that it comes from Nub, the Egyptian word for gold). From then on, the Romans referred to the area as the Nobatae.
Christian Nubia
Around AD 350 the area was invaded by the Ethiopian kingdom of Aksum and the kingdom collapsed. Eventually three smaller kingdoms replaced it: northernmost was Nobatia between the first and second cataract of the Nile River, with its capital at Pachoras (modern day Faras); in the middle was Makuria, with its capital at Old Dongola; and southernmost was Alodia, with its capital at Soba (near Khartoum). King Silko of Nobatia crushed the Blemmyes, and recorded his victory in a Greek inscription carved in the wall of the temple of Talmis (modern Kalabsha) around AD 500.
While bishop Athanasius of Alexandria consecrated one Marcus as bishop of Philae before his death in 373, showing that Christianity had penetrated the region by the fourth century, John of Ephesus records that a Monophysite priest named Julian converted the king and his nobles of Nobatia around 545. John of Ephesus also writes that the kingdom of Alodia was converted around 569. However, John of Bisclorum records that the kingdom of Makuria was converted to Roman Catholicism the same year, suggesting that John of Ephesus might be mistaken. Further doubt is cast on John's testimony by an entry in the chronicle of the Greek Orthodox Patriarch of Alexandria Eutychius, which states that in 719 the church of Nubia transferred its allegiance from the Greek Orthodox to the Coptic Church.
By the 7th century Makuria expanded becoming the dominant power in the region. It was strong enough to halt the southern expansion of Islam after the Arabs had taken Egypt. After several failed invasions the new rulers agreed to a treaty with Dongola allowing for peaceful coexistence and trade. This treaty held for six hundred years. Over time the influx of Arab traders introduced Islam to Nubia and it gradually supplanted Christianity. While there are records of a bishop at Qasr Ibrim in 1372, his see had come to include that located at Faras. It is also clear that the "Royal" church at Dongola had been converted to a mosque around 1350.
Modern Nubia
Main article: Nubian peopleIn the 14th century the Dongolan government collapsed and the region became divided and dominated by Egypt. The next centuries would see several invasions of the region, as well as the establishment of a number of smaller kingdoms. Northern Nubia was brought under Egyptian control while the south came under the control of the Kingdom of Sennar in the sixteenth century. The entire region would come under Egyptian control during the rule of Mehemet Ali in the early nineteenth century, and later became a joint Anglo-Egyptian condominium.
With the end of colonialism Nubia was divided between Egypt and Sudan.
Many Egyptian Nubians were forcibly resettled to make room for Lake Nasser after the construction of the dams at Aswan. Nubian villages can now be found north of Aswan on the west bank of the Nile and on Elephantine Island, and many Nubians live in large cities such as Cairo. Egyptian Nubians tend to be far more socio-economically disadvantaged within Egypt, as compared to Sudanese Nubians in Sudan.
See also
Notes and references
Notes
- "Studies of Ancient Crania From Northern Africa" (PDF). - S.O.Y. Keita, American Journal of Physical Anthropology (1990)
- History of Nubia
- PlanetQuest: The History of Astronomy - Retrieved on 2007-08-29
- Late Neolithic megalithic structures at Nabta Playa - by Fred Wendorf (1998)
- Hunting for the Elusive Nubian A-Group People - by Maria Gatto, archaeology.org
- "Further Studies of Crania From Ancient Northern Africa: An Analysis of Crania From First Dynasty Egyptian Tombs, Using Multiple Discriminant Functions" (PDF). - American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 87: 245-254 (1992)
- "Forbears of Menes in Nubia: Myth or Reality" (PDF). - Journal of Near Eastern Studies, Vol. 46, No. 1 (Jan., 1987), pp. 15-26
- Egypt and Sub-Saharan Africa: Their Interaction - Encyclopedia of Precolonial Africa, by Joseph O. Vogel, AltaMira Press, (1997), pp. 465-472
- Tomb Reveals Ancient Egypt's Humiliating Secret The Times (London, 2003)
- Meroe: writing - digitalegypt
- Jones, David E., Women Warriors: A History, Brasseys, Inc.; (2000)
- Gutenberg, David M. (2003). The Curse of Ham: Race and Slavery in Early Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Princeton University Press.
- Nubian Queens in the Nile Valley and Afro-Asiatic Cultural History - Carolyn Fluehr-Lobban, Professor of Anthropology, Museum of Fine Arts, Boston U.S.A, August 20-26, 1998
- "Nubia". Catholic Encyclopedia.
References
- Thelwall, Robin (1978) 'Lexicostatistical relations between Nubian, Daju and Dinka', Études nubiennes: colloque de Chantilly, 2–6 juillet 1975, 265–286.
- Thelwall, Robin (1982) 'Linguistic Aspects of Greater Nubian History', in Ehret, C. & Posnansky, M. (eds.) The Archeological and Linguistic Reconstruction of African History. Berkeley/Los Angeles, 39–56.
- Bulliet et al. (2001) 'Nubia,' The Earth and Its Peoples, pp. 70–71, Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston.
External Links
- http://www.napata.org
- Kerma excavation
- Template:Fr icon Voyage au pays des pharaons noirs. Travel in Sudan: pictures and notes on the nubian history
- Racism and the Rediscovery of Ancient Nubia
- Merowiki
| This article contains weasel words: vague phrasing that often accompanies biased or unverifiable information. Such statements should be clarified or removed. (March 2009) |