This is an old revision of this page, as edited by 66.30.241.37 (talk) at 22:49, 13 January 2011 (hh hg gy bd ntb bduifa uuf fguafu giaf). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 22:49, 13 January 2011 by 66.30.241.37 (talk) (hh hg gy bd ntb bduifa uuf fguafu giaf)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) "LHC" redirects here. For other uses, see LHC (disambiguation).46°14′N 06°03′E / 46.233°N 6.050°E / 46.233; 6.050
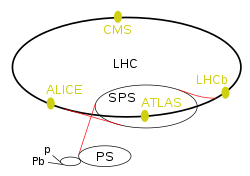 Plan of the LHC experiments and the preaccelerators. Plan of the LHC experiments and the preaccelerators. | |
| LHC experiments | |
|---|---|
| ATLAS | A Toroidal LHC Apparatus |
| CMS | Compact Muon Solenoid |
| LHCb | LHC-beauty |
| ALICE | A Large Ion Collider Experiment |
| TOTEM | Total Cross Section, Elastic Scattering and Diffraction Dissociation |
| LHCf | LHC-forward |
| MoEDAL | Monopole and Exotics Detector At the LHC |
| FASER | ForwArd Search ExpeRiment |
| SND | Scattering and Neutrino Detector |
| LHC preaccelerators | |
| p and Pb | Linear accelerators for protons (Linac 4) and lead (Linac 3) |
| (not marked) | Proton Synchrotron Booster |
| PS | Proton Synchrotron |
| SPS | Super Proton Synchrotron |
| Hadron colliders | |
|---|---|
|
The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is the world's largest and highest-energy particle accelerator. It is expected that it will address some of the most fundamental questions of physics, advancing humanity's understanding of the deepest laws of nature.
The LHC lies in a tunnel 27 kilometres (17 mi) in circumference, as much as 175 metres (574 ft) beneath the Franco-Swiss border near Geneva, Switzerland. This synchrotron is designed to collide opposing particle beams of either protons at an energy of 7 teraelectronvolts (1.12 microjoules) per particle, or lead nuclei at an energy of 574 TeV (92.0 µJ) per nucleus.<ref name="LHCbooklet"> {{cite web